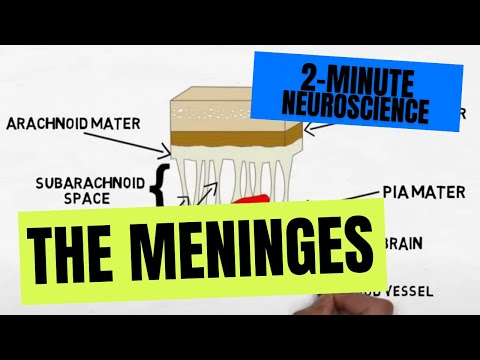
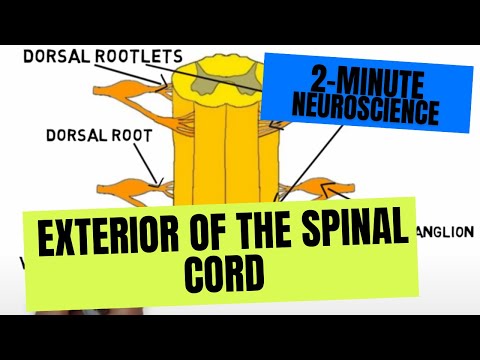
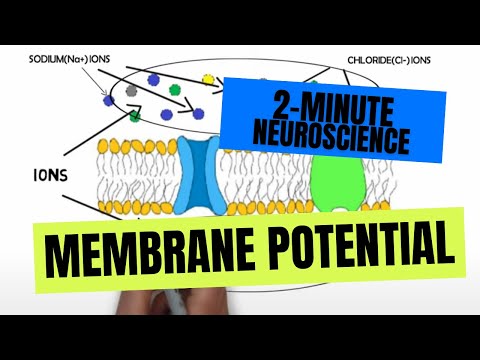
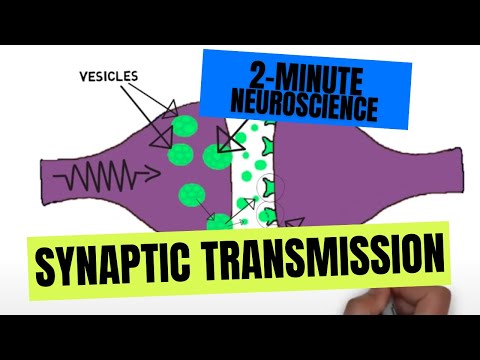
- Subjects: Neurosciences
- |
- Contributor:
- Neuroscientifically Challenged
- DMT
- potent psychoactive drug
- intense
This video is adapted from: https://youtu.be/z4UMjpw5a4Y?si=Ra5RDOvxniJROVl7
DMT is naturally produced in a variety of plants and animals (including humans) and is also a potent psychoactive drug known for its ability to cause intense hallucinations and psychedelic experiences. In this video, I discuss how DMT might act in the brain to produce its unique effects. [1][2]
TRANSCRIPT:
DMT is a substance that’s produced naturally in a variety of plants and animals, including humans. The functions of naturally-produced DMT are unclear, but DMT is also a potent psychoactive drug known for its ability to produce intense but relatively short-lived hallucinations and psychedelic experiences. When used recreationally, DMT is typically smoked, but it’s also the main psychoactive ingredient in ayahuasca, a brewed drink that produces longer-lasting psychedelic effects. Although orally administered DMT is rapidly degraded by an enzyme called monoamine oxidase, ayahuasca is brewed with plants that contain inhibitors of this enzyme, enabling the DMT in ayahuasca to remain active even though it’s administered orally.
The pharmacology of DMT is not well understood. The drug has actions at a variety of receptors in the nervous system, but its best characterized effects are its ability to stimulate a wide range of serotonin receptor subtypes. Studies suggest that DMT’s action at the 5-HT2A serotonin receptor is especially important for producing its characteristically intense visual hallucinations. At the same time, stimulation of the 5-HT2A receptor alone does not seem to be sufficient to cause the hallucinations experienced by DMT users. Thus, it’s thought that other serotonin receptor subtypes might be involved in these effects, and some evidence suggests that receptors for the neurotransmitter glutamate may play a role as well. It’s also possible that DMT’s actions at other receptors, such as sigma-1 receptors and trace amine-associated receptors, may contribute to the drug’s effects, but more research is needed to elucidate DMT’s full mechanism of action.
DMT, like many other psychedelic drugs, is now gaining attention for its therapeutic potential. Studies with ayahuasca have found the drink to have beneficial effects in the treatment of depression, anxiety, and addiction, and studies are currently underway to investigate the possibility of DMT alone offering some of the same benefits.
CREDITS:
The image of ayahuasca is a CC image courtesy of Terpsichore. The work can be seen here: File:Ayahuasca prep.JPG - Wikimedia Commons
The background kaleidoscope image is courtesy of Merlin Lightpainting. The work can be seen here: Merlin Lightpainting - Photography (pexels.com)
- Cameron LP, Olson DE. Dark Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: N, N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT). ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Oct 17;9(10):2344-2357. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00101. Epub 2018 Jul 23. PMID: 30036036.
- Carbonaro TM, Gatch MB. Neuropharmacology of N,N-dimethyltryptamine. Brain Res Bull. 2016 Sep;126(Pt 1):74-88. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.04.016. Epub 2016 Apr 25. PMID: 27126737; PMCID: PMC5048497.