- Subjects: Neurosciences
- |
- Contributor:
- Neuroscientifically Challenged
- insomnia
- medication
- Z-drugs
- side effects
- neurotransmitter
- GABA
This video is adapted from: https://youtu.be/CTWyhpvgOfg
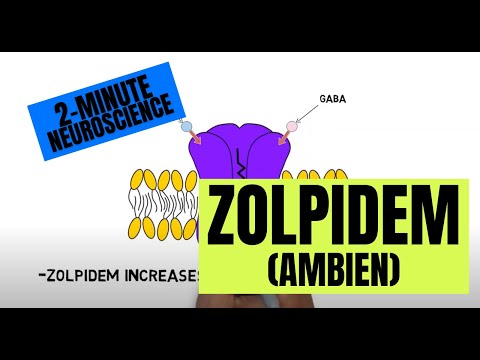
Zolpidem, better known by the brand name Ambien, is a medication primarily used to treat insomnia and other sleep-related problems. Studies have found zolpidem to be effective in reducing sleep latency, or the amount of time it takes someone to fall asleep, as well as in increasing total sleep time. Zolpidem belongs to a class of medications known as non-benzodiazepine hypnotics, sometimes called Z-drugs because many of the first of these drugs to be sold had names that started with the letter Z.
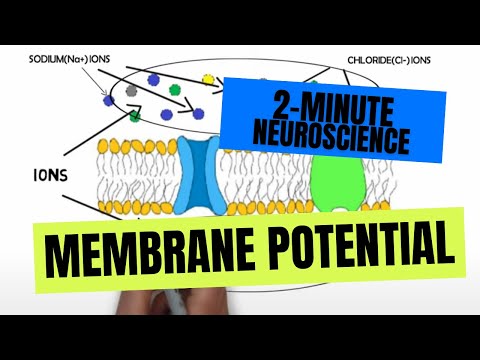
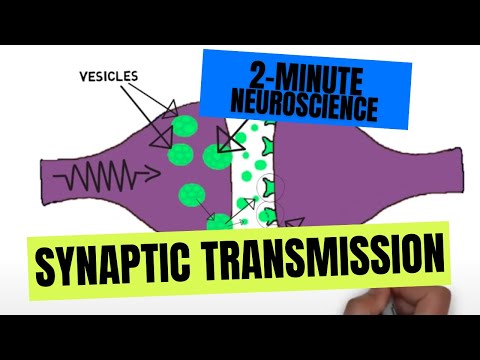
Similar to the benzodiazepines, zolpidem exerts its effects by increasing activity at receptors for the neurotransmitter GABA. GABA is primarily an inhibitory neurotransmitter, and increasing GABA activity can promote sleep as GABA can decrease activity in parts of the brain that promote wakefulness. Unlike benzodiazepines, however, zolpidem is thought to selectively bind to specific GABA receptor subtypes that are especially involved in sleep-inducing effects.
While zolpidem has been found to be effective and safe in the short-term management of sleep problems, the drug can also cause tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms when someone stops taking it, even when taken as prescribed at typical doses. Additionally, while most of the side effects of zolpidem, such as next day drowsiness, are common side effects of sleep medications, some zolpidem users have reported sleepwalking, sleep eating (which involves getting up and eating without waking), and even more dangerous activities like sleep driving, while under the influence of the drug. And due to various concerns, such as potentially impaired metabolism of the drug, an increased risk of falls, and an increased risk of cognitive impairment, zolpidem may pose more problems for older populations. Thus, despite its effectiveness, zolpidem should be prescribed cautiously and used only for as long as is absolutely necessary. [1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8]
- Edinoff AN, Wu N, Ghaffar YT, Prejean R, Gremillion R, Cogburn M, Chami AA, Kaye AM, Kaye AD. Zolpidem: Efficacy and Side Effects for Insomnia. Health Psychol Res. 2021 Jun 18;9(1):24927. doi: 10.52965/001c.24927. PMID: 34746488; PMCID: PMC8567759.
- Fitzgerald AC, Wright BT, Heldt SA. The behavioral pharmacology of zolpidem: evidence for the functional significance of α1-containing GABA(A) receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 May;231(9):1865-96. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3457-x. Epub 2014 Feb 22. PMID: 24563183.
- Gunja N. In the Zzz zone: the effects of Z-drugs on human performance and driving. J Med Toxicol. 2013 Jun;9(2):163-71. doi: 10.1007/s13181-013-0294-y. PMID: 23456542; PMCID: PMC3657033.
- Huedo-Medina TB, Kirsch I, Middlemass J, Klonizakis M, Siriwardena AN. Effectiveness of non-benzodiazepine hypnotics in treatment of adult insomnia: meta-analysis of data submitted to the Food and Drug Administration. BMJ. 2012 Dec 17;345:e8343. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e8343. PMID: 23248080; PMCID: PMC3544552.
- Matheson E, Hainer BL. Insomnia: Pharmacologic Therapy. Am Fam Physician. 2017 Jul 1;96(1):29-35. PMID: 28671376.
- Salvà P, Costa J. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of zolpidem. Therapeutic implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1995 Sep;29(3):142-53. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199529030-00002. PMID: 8521677.
- Wong E, Nguyen TV. Zolpidem Use in the Elderly and Recent Safety Data. Prescription Pad. 2014 Feb;10(2):140-141.
- Xiang T, Cai Y, Hong Z, Pan J. Efficacy and safety of Zolpidem in the treatment of insomnia disorder for one month: a meta-analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Sleep Med. 2021 Nov;87:250-256. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2021.09.005. Epub 2021 Sep 20. PMID: 34688027.