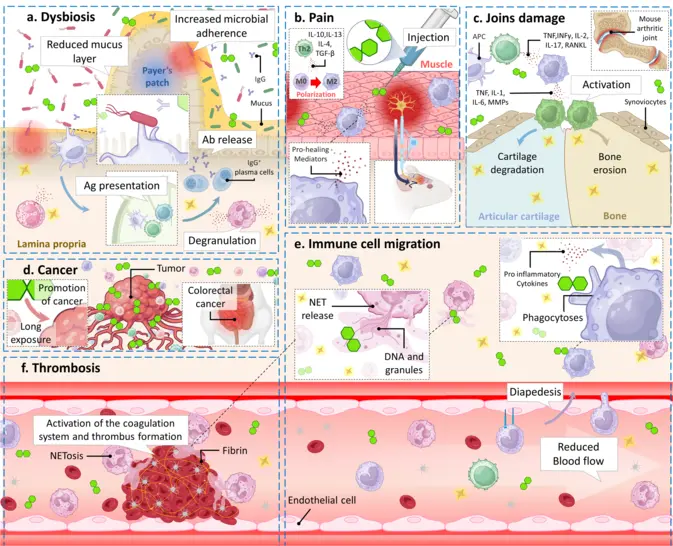
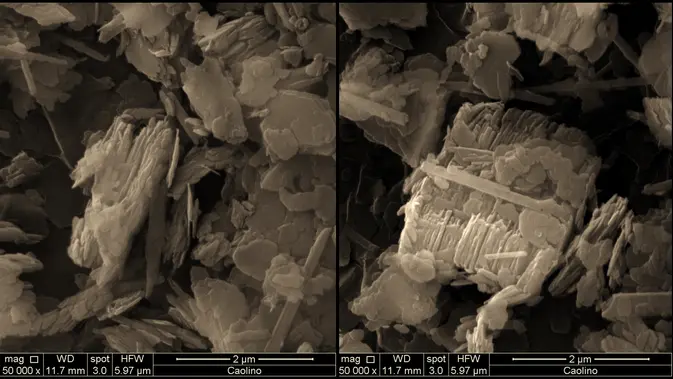
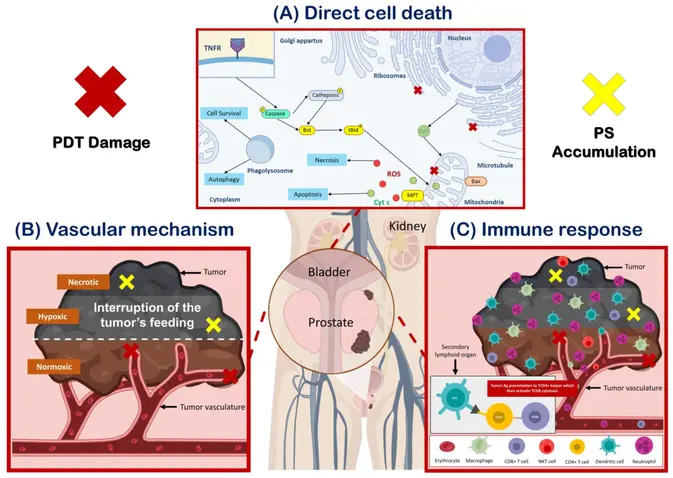
Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Image Gallery: An Exhibition of Scientific Fascination
Showcase Your Research with Scientific Infographics
Calling all researchers and innovators! With our completely free program, you can transform your data, discoveries, and groundbreaking ideas into visually compelling infographics that spark curiosity and deepen understanding. Our experts can help you bring your science to life through powerful visuals that are both informative and captivating, all while sharing your work with a wider audience.
Apply
Encyclopedia Images
All Research Fields
Explore our image collection with extensive coverage across a wide range of topics. From business and art to nature, science, and technology, our diverse image materials provide rich visual content for all your needs.
Academic Image Repository
Link your papers to our comprehensive Academic Image Repository. Access high-quality visuals across diverse fields, to enhance your presentations, publications, and projects.
Free for Everyone
It is a free open-access knowledge-sharing project, that aims to provide convenient access to visual resources, encouraging collaboration and learning across diverse communities worldwide.
Personal Image Gallery
Create your own personalized image collection for free and share your stunning photos with the world. Showcase your creativity, preserve your memories, and connect with others through beautiful visuals.
Featured Galleries