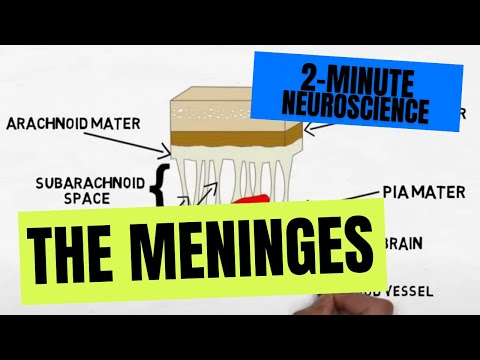
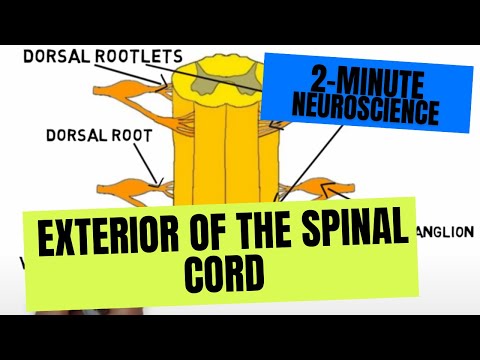
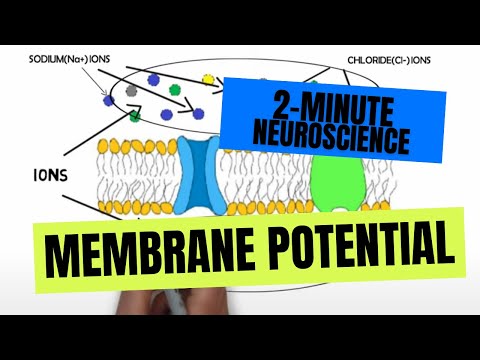
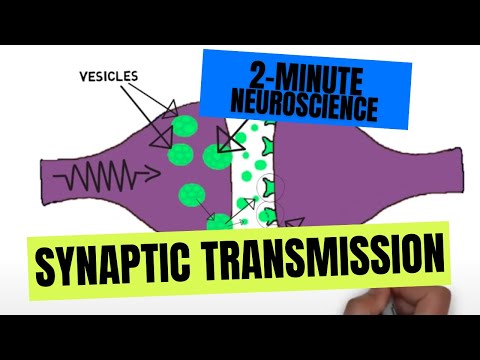
- Subjects: Neurosciences
- |
- Contributor:
- Neuroscientifically Challenged
- hypothalamus
- brain
- hormones
- hormone release
This video is adapted from: https://youtu.be/TVhm2rBGhB0
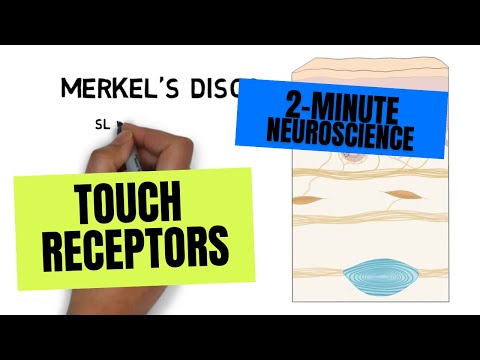
The hypothalamus is a small region situated directly above the brainstem. It is made up of a collection of nuclei with a variety of functions, but in general the hypothalamus is involved in controlling the two H’s: homeostasis and hormones. Homeostasis is a term used to describe the maintenance of balance or stability in a biological system. The hypothalamus can maintain homeostasis either by exerting direct influence over the autonomic nervous system, or by causing the release of hormones. The hypothalamus manipulates hormone release primarily by controlling the pituitary gland.
The pituitary gland is a hormone-secreting gland that sits just below the hypothalamus. It is sometimes called the “master gland” because it not only secretes many extremely important hormones but it also regulates the activity of other hormone-secreting glands throughout the body. The pituitary consists of two lobes, called the anterior and the posterior pituitary. The anterior pituitary is responsible for the release of a number of hormones that have widespread effects throughout the body. They include growth hormone, which is involved with growth, follicle-stimulating hormone, which plays a role in development and reproduction, luteinizing hormone, which is essential to testosterone production and reproduction, adrenocorticotropic hormone, which is involved with the stress/fear response, thyroid sTimulating hormone, which is important to healthy metabolism, and prolactin, which promotes milk production in females. The release of these hormones is controlled by the hypothalamus, which sends signals in the form of releasing hormones to tell the anterior pituitary when to secrete its hormones.
The posterior pituitary also secretes two hormones, but does not synthesize them. Instead, they are synthesized by the hypothalamus and then sent to the posterior pituitary for release into the bloodstream. The names of these hormones are: oxytocin and vasopressin. Oxytocin has important roles in facilitating childbirth and lactation, but is also thought to have a role in compassion and social bonding. Vasopressin's main functions are to control urine output and regulate blood pressure. [1]
- Purves D, Augustine GJ, Fitzpatrick D, Hall WC, Lamantia AS, McNamara JO, White LE. Neuroscience. 4th ed. Sunderland, MA. Sinauer Associates; 2008.