Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Encyclopedia Insights: Where Knowledge Meets the World
Type:
Hot Topic
Blog 09 Mar 2026
Hot Topic
Blog 02 Mar 2026
Community Content
Blog 24 Feb 2026
Hot Topic
Blog 14 Feb 2026
Ongoing
Announcement 09 Feb 2026
Ongoing
Announcement 03 Feb 2026
Ongoing
Announcement 02 Feb 2026
Hot Topic
Blog 19 Jan 2026
Community Content
Blog 12 Jan 2026
Hot Topic
Blog 06 Jan 2026
Community Content
Blog 29 Dec 2025
Hot Topic
Blog 23 Dec 2025
Platform Feature
Blog 16 Dec 2025
Ongoing
Announcement 10 Dec 2025
Hot Topic
Blog 05 Dec 2025
Hot Topic
Blog 01 Dec 2025
Hot Topic
Blog 25 Nov 2025
Hot Topic
Blog 17 Nov 2025
Ongoing
Announcement 10 Nov 2025
Hot Topic
Blog 05 Nov 2025

 >
>
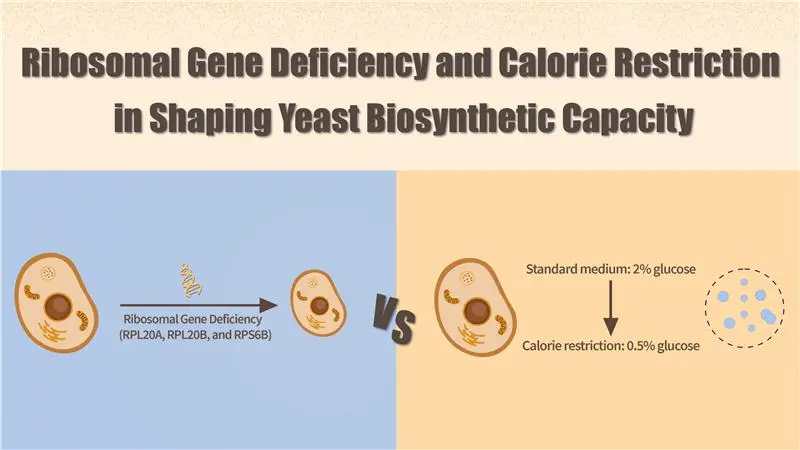 >
>
 >
>
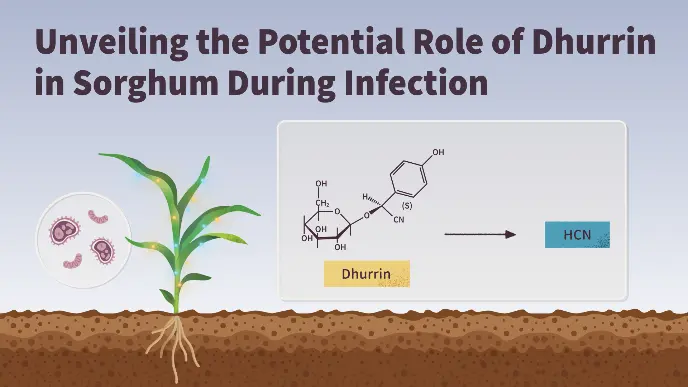 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>
 >
>