Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jiangang Zhu | -- | 2362 | 2023-12-21 03:47:27 | | | |
| 2 | Sirius Huang | Meta information modification | 2362 | 2023-12-21 09:59:09 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Qi, Q. Recyclable Design of Wooden Furniture. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/53001 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Zhang Z, Zhu J, Qi Q. Recyclable Design of Wooden Furniture. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/53001. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Zhang, Zhuoyu, Jiangang Zhu, Qian Qi. "Recyclable Design of Wooden Furniture" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/53001 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Zhang, Z., Zhu, J., & Qi, Q. (2023, December 21). Recyclable Design of Wooden Furniture. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/53001
Zhang, Zhuoyu, et al. "Recyclable Design of Wooden Furniture." Encyclopedia. Web. 21 December, 2023.
Copy Citation
With the rapid development of the economy and the change in people’s aesthetic concepts, the renewal of furniture has become more and more frequent. Among the huge amount of used furniture, solid wood and wood-based panel furniture account for the vast majority, but the imperfective recycling system and insufficient recycling efforts result in serious waste, which is contrary to the low-carbon transition and sustainable development means.
wooden furniture
recyclable design
recyclable evaluation
1. Introduction
With the development of the economy accompanied by the upgrading of people’s consumption level and concept, the consumption mode of furniture has undergone profound changes. The frequent replacement or accelerating upgrade of furniture can create so much discarded furniture, among which the discarded wooden furniture accounts for a large proportion. According to relevant statistics, China alone produces about 60 million tons (85 million cubic meters) of discarded wood products, mainly used furniture, every year [1]. As an important part of the global manufacturing industry and also one of the leading producers, consumers, and exporters of furniture in the world, the cumulative revenue of China’s furniture industry reached nearly $124.08 billion in 2021 according to the report by the China National Furniture Association (CNFA). With the further expansion of the furniture market, the environmental impact is increasing, and the consumption of natural resources is also growing.
Under the increasing awareness of environmental protection and sustainability, various types of waste wooden furniture recycling institutions have been gradually established all over China. In addition, relevant rules and regulations have been formulated to guide the reuse of waste wooden furniture. Although it is likely to spot successful cases and policy support, in general, furniture recycling has always been a kind of difficult problem [2]. First of all, the conventional appearance-oriented or performance-oriented materials selection of furniture products will inevitably result in unrecyclable furniture parts. Secondly, the low standardization level of furniture parts will lead to the difficulty of reusing after disassembly. Third, various degrees of the properties’ losses will usually happen to furniture after use, making it difficult to reuse. Finally, the unreachable cost of dismantling, sorting, and recycling waste furniture when recycling wooden furniture will bring negligible economic benefit. As a result, public recycling of waste wooden furniture has several options in general: refurbish it when sold at flea markets, use it as fuel, or send it to landfill for burning. These practices not only affect the price mechanism of furniture but also cause certain pollution to the environment [3].
On the one hand, industrialization has brought convenience to people’s lives; on the other hand, industrial production has caused damage to the ecological environment to a certain extent and brought excessive energy consumption. Therefore, ecological design, green design, and sustainable design have become important issues that we should consider. The furniture industry should combine the concept of sustainable design with green ecological design to reduce waste of resources to a certain extent and achieve harmonious coexistence between man and nature [4]. China’s “Manufacturing 2025 Report” pointed out that it is necessary to fully implement green manufacturing, improve the efficient recycling of resources, and increase the recycling rate of waste products. Strengthening the recycling of waste wooden furniture can reduce the environmental pollution caused by waste wood resources, expand the source of raw materials for the wood-based panel industry, and ease the tight supply and demand of wood resources [5].
2. Recycling and Utilization of Waste Furniture
In the 1990s, developed countries built and formed a recycling system for wood waste. Developed countries such as the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom mainly carry out research on the recycling of waste wooden furniture and the manufacture of wood-based panels from waste wood. Japan is a country with limited resources. As early as 1995, resource recycling was listed as an important national policy, achieving an ultra-high recovery rate of 82% of waste wood, which is mainly used for papermaking, wood-based panel production, power, and heat supply [6]. In Australia, recycled wood is used for a variety of purposes, although these markets are fairly limited. The main uses of recovered wood are for mulch, fuel, animal bedding, and recycling into particleboard [7]. Germany has enacted a waste wood recycling ordinance called the Ordinance on the Management of Waste Wood. This decree prohibits the arbitrary disposal of discarded wooden furniture [8] and classifies recycled wood into five categories. Depending on the species, there are different methods of treating and reusing waste wood. Taiwan has been promoting relevant recycling projects to encourage the recycling and reuse of waste furniture and has excellent waste furniture restoration technology. However, its current demand for remanufacturing furniture remains low. And due to the difference in living habits between urban and rural areas in Taiwan, discarded furniture collected from urban and rural areas is in different states [2].
On 1 June 2009, China implemented GB/T 22529-2008 [9] “Management Specification for Recycling and Utilization of Waste Wood Materials” to encourage the reuse, recycling, and energy utilization of waste wood, among which old wooden furniture is the focus of classification and recycling, and encourage waste solid wood household product materials reprocessing into furniture materials. In the practical application of recycling old wooden furniture, the Shanghai Wanxiang Wood Company (Shanghai, China) is the earliest enterprise in China to recycle Shanghai waste wood to make artificial boards, and old wooden furniture is its main recycling object [10]. In 2011, when Changsha City was creating a hygienic and civilized city, residents disassembled and assembled some old wooden furniture with relatively good quality and transformed them into rest furniture in public places [11]. In 2018, at the request of the government, Beijing piloted the whole process of waste furniture delivery, recycling, transportation, and processing in Haidian District and granted subsidies to enterprises to use the recycled waste wood and sponge as fuel for power generation. In July 2021, Shenzhen drafted the local standard “Specifications for Recycling and Comprehensive Utilization of Waste Furniture”, which stipulates the definition, collection, temporary storage, transportation, and comprehensive utilization requirements of waste furniture and improves the recovery rate of domestic waste in Shenzhen [12].
Mao et al. [13] divided the recycling methods of old wooden furniture into five aspects, namely reuse, recycling, regeneration, energy utilization, and special utilization (as shown in Figure 1).
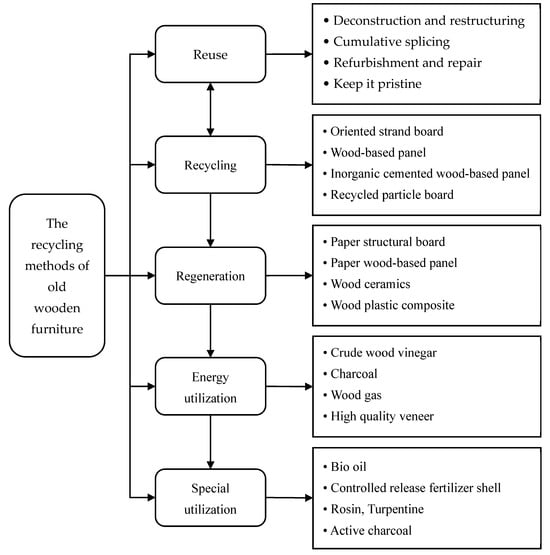
Figure 1. The recycling methods of old wooden furniture.
Reuse refers to the restoration, renovation, or use of a part of recycled old wooden furniture, which belongs to direct utilization and does not change the original attributes. Wang and Li [14] also made a detailed discussion on the reasons for the waste of rural furniture and the methods of recycling: one is directly used for combustion, the second is the renovation of furniture, and the third is the recycling of furniture, disassembly, and recombination.
Recycling refers to the classification, separation, and crushing of old wooden furniture, chipping into sawdust, wood granulates, wood fiber, etc., and then further processing and utilization [15]. In 2000, in the project (FPS) supported by the Fifth European Commission, countries such as Germany, Greece, France, and Portugal mixed the discarded wood materials into wood-based panels with high added value in a certain proportion and developed the process technology with reference significance for this purpose [16]. The Mauro Saviola Group in Italy has carried out the actual production of waste wooden furniture and achieved good results; the recycled waste wooden furniture is processed into various particleboards through a series of classification processes [17]. Wang [18] studied the method of hot water treatment of waste wood materials and found out the best process parameters for the hydrothermal treatment of waste wood materials to recycle and regenerate particleboard, the best ratio, and the most ideal process conditions in the whole recycling process.
Regeneration refers to making products that are completely different from old wooden furniture by changing the material properties. For example, wood ceramics can be made of old furniture wood as raw materials, by resin impregnation, high-temperature carbonization formation of new carbon material, a porous structure with high strength, high wear resistance [19]. Li et al. [20] mentioned a series of methods for recycling waste wood-based panels and the resulting new products in the article, such as wood–plastic composite materials, regenerated particleboard, and chemicals. Researchers at the Mining Research Institute in New Mexico, USA, used waste wood materials and plastics to effectively combine a certain proportion and then made wood–plastic composite materials through heating and pressure processing. Wood chips are often considered waste in the wood industry, and these materials can be converted into value-added thermoplastics through benzylation. The chemical properties of lignocellulosic materials make them suitable for a large number of products, and the use of lignocellulosic materials in the production of plastics and composites is becoming more and more attractive [21].
Energy utilization refers to the processing of old wood for furniture into fuel. Oh and Okabe [22] mentioned in the article the research on pyrolysis and gasification of wood materials by using waste wood materials as raw materials. He and Mu [23] used a mechanical furnace and other equipment for high-temperature pyrolysis to produce wood gas, charcoal, and crude wood vinegar with higher usable value, thereby realizing the recycling and reuse of waste wood-based panel resources. Cao and Wang [24] also mentioned in the article that crude wood vinegar is a liquid produced by condensation and separation of the gas mixture in the dry distillation process of carbon materials such as wood or wood waste.
Special utilization refers to the use of breeding, planting, sideline, and so on. Wiltcher et al. [25] believe that mixing recycled plywood with chicken manure, cow manure, and inorganic fertilizers can effectively reduce the toxicity of fertilizers and can be used as soil conditioners. Fu et al. [26] proposed the use of wood residues to make slow/controlled-release fertilizer shells. The shell has the advantages of low cost, simple manufacture, easy degradation, and no pollution, which made a certain contribution to the recovery of wood residues.
3. Recyclable Design of Wooden Furniture
It is now widely believed that design can play a key role in society’s transition to sustainability. In the process of wooden furniture recycling, design can act as a catalyst to trigger and support innovation, and proper recyclable design can help us recycle discarded furniture better on different levels. Building on this, Ceschin and Gaziulusoy [27] present design as the foremost approach to sustainability challenges, proposing an innovative framework that coherently integrates multiple Design for Sustainability (DfS) elements developed to date and is of great help in the recyclable design of furniture. Hebrok [28] proposed to carry out Design for Sustainable Behavior (DfSB) from a practical point of view, which can help prolong the life of furniture and make furniture a more durable commodity. Wang [29] conducted research on sustainability in furniture design and manufacturing, and points out sustainable strategies in wooden furniture manufacturing, namely reducing material usage, reducing scrap, reducing packaging, reducing energy consumption, reducing the choice of toxic resources, using renewable resources, extending the life cycle, etc., to provide design direction for sustainable design. Yang and Sun [30] explored the combination of “new materials” and innovative design methods with practical examples and proposed the methods of sustainable design using new materials, such as the combination innovation method, the alternative creation method, and the transplantation creation method.
In the research of systematic design, Zhu [31] briefly mentioned in his article that he designed more than 80 standard panels, which can be combined flexibly and can be used as a way to replace a certain part of the damaged panel in furniture recycling, which is an excellent case of having strong reference value. Wang and Wang [32] analyzed the design of furniture from the aspects of modular design and group technology design, which provided a good reference for reorganization and replacement of parts in furniture recycling. For IKEA, an internationally renowned furniture manufacturer, most of their products are typical products of modular design and detachable design, which is a good combination of design concept and product design for a model to facilitate recycling household products [33].
In order to improve the recycling efficiency, in addition to the design of the furniture itself, people have also carried out corresponding explorations on the design of the furniture recycling system. Fujii et al. [34] discussed the demand for recycled products, economic conditions, weight reduction, product reuse, the number and types of recycled products that are competitive, and developed a social system for the convenience of customers. From the perspective of design, relying on the modern e-commerce business model and based on the concept of “customer-centric”, Li et al. [35] focused on the basic methods and applications of the furniture recycling design system, described the design process of furniture recycling based on the network platform, analyzed and summarized the strengthening service content, and provided theoretical guidance for the system innovation construction. Lin, Chen, Tseng, Chiu, and Ali [2] established a cradle-to-cradle production planning model for recycled furniture, remanufacturing the furniture through recycling centers, including cleaning teams responsible for removing and transporting the waste furniture, and the processing center for recycling and remanufacturing the waste furniture.
A series of specific recyclable furniture designs have also been carried out by domestic and foreign design teams: Armchair of the Architecture Department is the work of the team of Boțoroga Ion et al., using cardboard cylinders and 100% recyclable OSB boards, this design work is preserved in the museum as an example of green furniture; Loom chair is the work of the Alexandrov Artem team, made from wood and twine reused in the building, this furniture has a special shape and a comfortable sitting feeling, inspired by the looms in the homes of Romanian farmers; Zig zag chair is inspired by the concept designed by Gerrit Rietveld in 1934, it adopts the sustainable method of plywood reuse and presents a stripe pattern decoration with storage performance and an elegant shape [36]. Taiwan designer Zeng [37] designed an assembled furniture called PLAYER. With the characteristics of assembled furniture and circular design, when some components are damaged, a single component can be simply replaced to reduce the generation of waste, and the recycled parts can be returned to the cycle more accurately and quickly, so that the recycling can be optimized. While developing new products, Zeng considered the subsequent treatment methods of the whole product life cycle (manufacturing, using, waste disposal, etc.), so that the raw materials can be recycled continuously and resources can not be exhausted.
References
- Zhu, J.; Wu, Z. Technology System for Green Manufacturing in Furniture Industry 6th: Green Packaging and Recycling Technology. Furniture 2013, 34, 73–77.
- Lin, C.-W.R.; Chen, M.-T.; Tseng, M.-L.; Chiu, A.S.F.; Ali, M.H. Profit Maximization for Waste Furniture Recycled in Taiwan Using Cradle-to-Cradle Production Programming. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2948049.
- Xiong, X.; Ma, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, M. Current situation and key manufacturing considerations of green furniture in China: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121957.
- Kang, H.; Cao, G.; Zhao, C. Multifunctional furniture design based on product life cycle. Packag. Eng. 2018, 39, 39–43.
- Hu, S.; Tao, T. Recycling of abandoned wooden furniture. Furnit. Inter. Des. 2006, 13, 18–19.
- Huang, R.; Bao, F.; Huang, X. Current situation of wood resource recycling in Japan. World For. Res. 2006, 19, 69–75.
- Daian, G.; Ozarska, B. Wood waste management practices and strategies to increase sustainability standards in the Australian wooden furniture manufacturing sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 1594–1602.
- Tapia, J.F.D.; Promentilla, M.A.B.; Tseng, M.-L.; Tan, R.R. Screening of carbon dioxide utilization options using hybrid Analytic Hierarchy Process-Data Envelopment Analysis method. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1361–1370.
- GB/T 22529-2008; Management Code for Discarded Wooden Recycling and Utilization. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Liu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y. Recycling utilization and treatment technology for the city abandons wood. Guangdong For. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 55–59.
- Huang, B.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Recycle and Reuse of Discarded Wooden Furniture:Taking Changsha City as An Example. Furnit. Inter. Des. 2012, 19, 88–89.
- Xiong, X.; Yue, X.; Dong, W.; Xu, Z. Current status and system construction of used-furniture recycling in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 82729–82739.
- Mao, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, Z. Recycling and Value-added Design of Old Wooden Furniture. Packag. Eng. 2015, 36, 14–17.
- Wang, H.; Li, C. Discuss the recycling and useage of rural used furniture. Furnit. Inter. Des. 2011, 18, 52–53.
- Lee, B.; McDonald, A. Wood fibre-plastic composite materials for injection moulding. In Proceedings of the 5th Pacific Rim Biobased Composites Symposium, Canberra, Australia, 10–13 December 2000; pp. 10–13.
- Zhang, J. Wood recycling is booming in Europe. China For. Ind. 2005, 2, 30–32+38.
- Tansey, P. Valentins way. Wood Based Panels Int. 1994, 5, 30–33.
- Wang, X. Research on Manufacturing Technology of Recycled Particleboard. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2008.
- Chen, L. Technology status and development prospect of wood ceramics. J. Bijie Univ. 2014, 32, 90–94.
- Li, J.; Hou, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Gao, Z. Research progress on recycling of waste artificial board. For. Sci. Technol. 2019, 44, 55–58.
- Üner, B.; Köse, G.; Yürümez, Y.; Ümit Yalçın, Ö.; Akgül, M. Wood Waste Turned Into Value Added Products: Thermal Plasticization by Benzylation Process. Drv. Ind. 2017, 67, 315–322.
- Oh, S.W.; Okabe, T. Manufacture of woodceramics chip tiles from waste wood. For. Prod. J. 2003, 53, 50. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/214629388?pq-origsite=gscholar&fromopenview=true (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- He, X.; Mu, Y. Discussion on recycling and utilization of wasting wood-based panels. Wood Process. Mach. 2008, 1, 50–53.
- Cao, H.; Wang, H. Research progress of preparation and refining of wood vinegar. Guangdong Chem. Ind. 2014, 41, 37–38.
- Wiltcher, D.; Borazjani, H.; Diehl, S.V.; Stewart, H.A. Composting of phenolic-bonded softwood plywood waste. For. Prod. J. 2000, 50, 82. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/214643199?pq-origsite=gscholar&fromopenview=true (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- Fu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Tang, L. Design of slow/controlled release fertilizer shell prepared from wood residues. Pract. For. Technol. 2010, 53, 50–52.
- Ceschin, F.; Gaziulusoy, İ. Design for Sustainability: A Multi-Level Framework from Products to Socio-Technical Systems; Routledge: London, UK, 2019.
- Hebrok, M. Where Furniture Goes to Die. Designing for Sustainable Behaviour in a Practice Perspective. Tech. Cult. Rev. Semest. D’anthropologie Tech. 2016.
- Wang, S. Research on Sustainable Design of Typical Furniture. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China, 2014.
- Yang, C.; Sun, W. Sustainable design combining “new materials” and innovative design methods. Light Ind. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 114–116.
- Zhu, X. The Application of Opal System Furniture in Interior Design. Furniture 2001, 22, 38–39.
- Wang, D.; Wang, F. Study on Design Methods for Furniture Mass Customization. Furnit. Inter. Des. 2005, 26–29.
- Deng, J. The Research of Modularized Design of Furniture Based on PLM. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2013.
- Fujii, M.; Fujita, T.; Ohnishi, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Yong, G.; Park, H.-S. Regional and temporal simulation of a smart recycling system for municipal organic solid wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 78, 208–215.
- Li, S.; Chen, M.; Lyu, J. User-based Furniture Recycling System Innovation and Its Implementation. In Proceedings of the 2016 5th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environment Engineering (ICSEEE 2016), Zhuhai, China, 12–13 November 2016; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 830–836.
- Munteanu, A. Eco-design. Furniture made of recycling materials-a new concept for the contemporan design. J. Soc. Sci. 2021, 3, 60–70.
- Zeng, Y.-P. Products Design Based on the Circular Design-Assembly Furniture Design. Master’s Thesis, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei City, Taiwan, 2020.
More
Information
Subjects:
Green & Sustainable Science & Technology
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.4K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
21 Dec 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




