
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ellen Ngarande | -- | 2303 | 2022-08-31 14:27:39 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 2303 | 2022-09-01 03:14:59 | | |
Video Upload Options
While mortality in patients with hypertensive emergency has significantly improved over the past decades, the incidence and complications associated with acute hypertension-mediated organ damage have not followed a similar trend. Hypertensive emergency is characterized by an abrupt surge in blood pressure, mostly occurring in people with pre-existing hypertension to result in acute hypertension-mediated organ damage. Acute hypertension-mediated organ damage commonly affects the cardiovascular system, and present as acute heart failure, myocardial infarction, and less commonly, acute aortic syndrome. Elevated cardiac troponin with or without myocardial infarction is one of the major determinants of outcome in hypertensive emergency.
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
|
Author, Year, Country |
Design |
AHF (%) |
AMI (%) |
AAS (%) |
Cumulative (%) |
NIMI (%) |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fragoulis [6], 2021, Greece |
Prospective |
58 |
22.6 |
2 |
82.6 |
NR |
National cardiac referral centre registry data. Potential for bias towards cardiac complications. |
|
Rubin [18], 2019, France |
Prospective |
31 |
NR |
NR |
31% |
63 |
Excluded myocardial infarction from their cohorts and 63% had elevated troponin while 83% had left ventricular hypertrophy. |
|
Zampaglione [15], 1996, Italy |
Prospective |
36.8 |
12 |
2 |
50.8 |
NR |
Cerebral infarction was the most common acute hypertension-mediated organ damage. However, composite of cardiac complications occurred in 50.8%. |
|
Kim [12], 2022, Korea |
CS |
NR |
40.5 |
NR |
40.5 |
60.4 |
Focused on prognostic role of cardiac troponin in acute severe hypertension. Elevated (occurred in 41.6%) and detectable (occurred in 36.5%) cardiac troponin associated with higher mortality at 3 years. |
|
Guiga [20], 2017, France |
CS |
37.4 |
13.8 |
1.8 |
53 |
NR |
Reported higher mortality in hypertensive emergency than hypertensive urgency (12.5 vs. 1.8%). |
|
Salvetti [8], 2021, Italy 2008 data 2015 data |
Prospective |
34 37.5 |
25 25 |
1 0.5 |
60 63 |
NR NR |
Excluded resuscitated cardiac arrest and patients requiring urgent cardiac catheterization. |
|
Pacheco [7], 2103, Mexico |
Prospective |
25.2 |
59.5 |
6.3 |
91 |
NR |
Their cohorts composed of a high-risk group admitted into coronary care unit. Reported high rate of acute coronary syndrome and acute aortic syndrome. |
|
Martin [17], 2004, Brazil |
Retrospective |
25 |
13 |
0 |
33 |
NR |
Reported unstable angina (5%) separately from myocardial infarction (8%). |
|
Vilela-Martin [21], 2011, Brazil |
CS |
30.7 |
25.1 |
3.5 |
47.2 |
NR |
Reported unstable angina (12.1%) separately from myocardial infarction (13%). |
|
Nkoke [19], 2020, Cameroon |
CS |
44.6 |
3.6 |
0 |
48.2 |
NR |
Myocardial infarction occurred in 3.6% of their cohorts. Low rate of detection of myocardial infarction may be related to lack of facilities including low rates of ECG and cardiac troponin assay. |
|
Acosta [22], 2020, USA |
Retrospective |
NR |
1 |
0 |
1 |
15 |
Assessed acute myocardial injury using serial cardiac troponin assay. Excluded acute coronary syndrome from their cohorts. |
|
Pattanshetty [23], 2012, USA |
Retrospective |
20.5 |
11.7 |
2.3 |
34.5 |
NR |
Obstructive coronary artery disease present in 76.5% of their cohorts with elevated cardiac troponin that had angiogram. |
AAS, acute aortic syndrome; AHF, acute heart failure; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; CS, cross-sectional; NIMI, non-ischemic myocardial injury; NR, not reported; USA, United State of America.
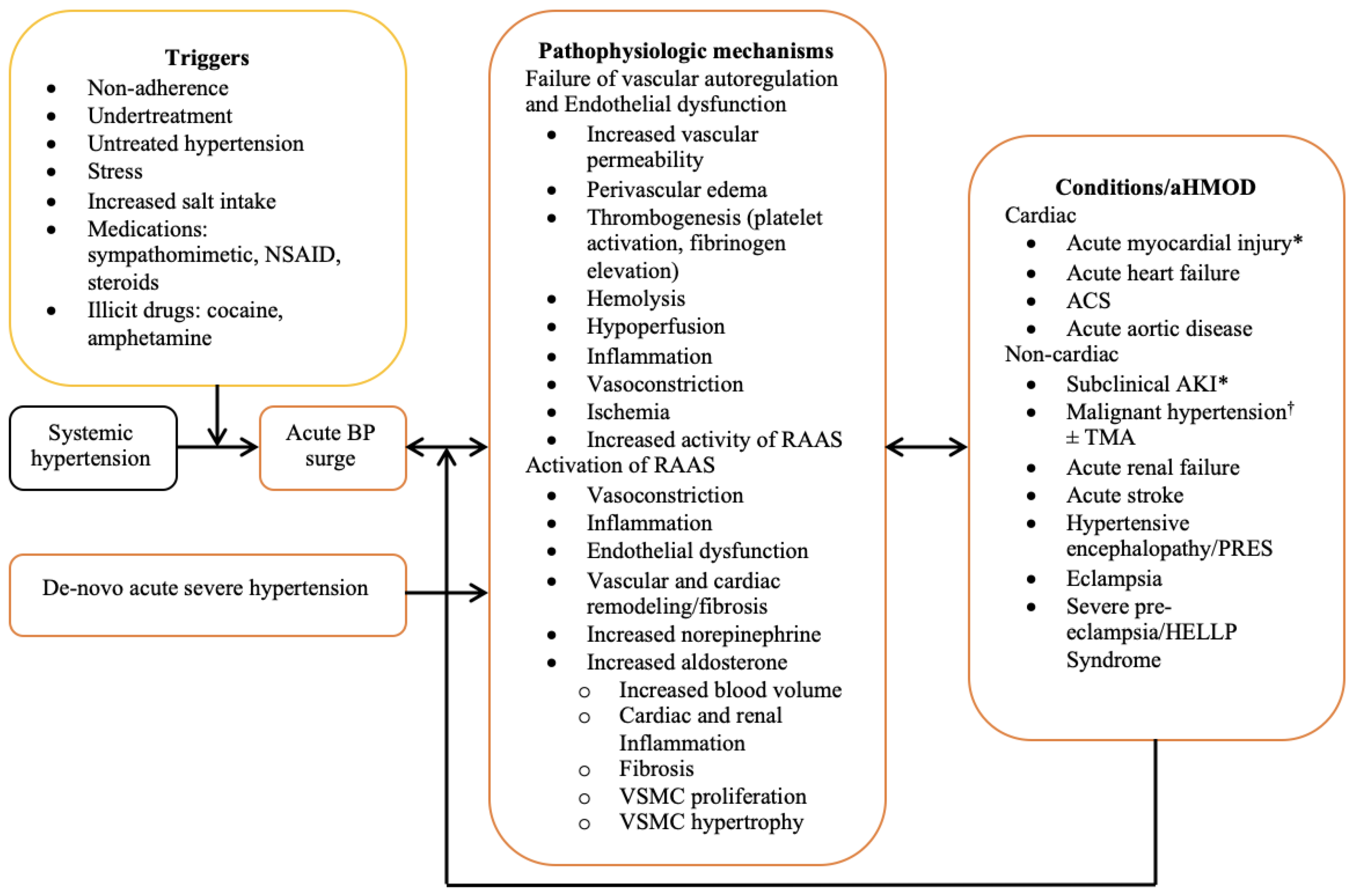
3. Pathophysiology
4. Specific Cardiac Complications of Hypertensive Emergency
|
Acute hypertension mediated-organ damage |
|
Acute heart failure/acute pulmonary edema * |
|
Acute coronary syndrome * |
|
ST-elevation myocardial infarction |
|
Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction |
|
Unstable angina |
|
Acute aortic syndrome |
|
Acute aortic dissection * |
|
Intramural hemorrhage/hematoma |
|
Penetrating atherosclerotic aortic ulcer |
|
Aortic aneurysm |
|
Aortic rupture |
|
Sub-clinical cardiac target organ injury § |
|
Acute myocardial injury |
* Commonly reported cardiac complications; § Not included as a complication in guidelines.
5. Challenges in Evaluation, Classifications, and Treatment of Cardiac Complications of Hypertensive Emergencies
5.1. Sub-Clinical Acute Target Organ Damage
5.2. Nomenclature and Classification
5.3. Treatment
5.4. Biomarkers of Subclinical Myocardial Injury
References
- Arima, H.; Barzi, F.; Chalmers, J. Mortality patterns in hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, S3–S7.
- Mills, K.T.; Bundy, J.D.; Kelly, T.N.; Reed, J.E.; Kearney, P.M.; Reynolds, K.; Chen, J.; He, J. Global Disparities of Hypertension Prevalence and Control. Circulation 2016, 134, 441–450.
- Berry, K.M.; Parker, W.A.; Mchiza, Z.J.; Sewpaul, R.; Labadarios, D.; Rosen, S.; Stokes, A. Quantifying unmet need for hypertension care in South Africa through a care cascade: Evidence from the SANHANES, 2011–2012. BMJ Glob. Health 2017, 2, e000348.
- van den Born, B.-J.H.; Lip, G.Y.; Brguljan-Hitij, J.; Cremer, A.; Segura, J.; Morales, E.; Mahfoud, F.; Amraoui, F.; Persu, A.; Kahan, T.; et al. ESC Council on hypertension position document on the management of hypertensive emergencies. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2019, 5, 37–46.
- Mishima, E.; Funayama, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Mishima, F.; Nitta, F.; Toyohara, T.; Kikuchi, K.; Kunikata, H.; Hashimoto, J.; Miyazaki, M.; et al. Concurrent analogous organ damage in the brain, eyes, and kidneys in malignant hypertension: Reversible encephalopathy, serous retinal detachment, and proteinuria. Hypertens. Res. 2021, 44, 88–97.
- Fragoulis, C.; Dimitriadis, K.; Siafi, E.; Iliakis, P.; Kasiakogias, A.; Kalos, T.; Leontsinis, I.; Andrikou, I.; Konstantinidis, D.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.; et al. Profile and management of hypertensive urgencies and emergencies in the emergency cardiology department of a tertiary hospital: A 12-month registry. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 194–201.
- Pacheco, H.G.; Victorino, N.M.; Urquiza, J.P.N.; Castillo, A.A.; Herrera, U.J.; Mendoza, A.A.; Manzur, F.A.; de la Cruz, J.L.B.; Sánchez, C.M. Patients with hypertensive crises who are admitted to a coronary care unit: Clinical characteristics and outcomes. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2013, 15, 210–214.
- Salvetti, M.; Paini, A.; Colonetti, E.; Tarozzi, L.; Bertacchini, F.; Aggiusti, C.; Stassaldi, D.; Rosei, C.A.; Rosei, E.A.; Muiesan, M.L. Hypertensive emergencies and urgencies: A single-centre experience in Northern Italy 2008–2015. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 52–58.
- Astarita, A.; Covella, M.; Vallelonga, F.; Cesareo, M.; Totaro, S.; Ventre, L.; Apra, F.; Veglio, F.; Milan, A. Hypertensive emergencies and urgencies in emergency departments: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1203–1210.
- Gonzalez, R.; Morales, E.; Segura, J.; Ruilope, L.M.; Praga, M. Long-term renal survival in malignant hypertension. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 3266–3272.
- Cremer, A.; Amraoui, F.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Morales, E.; Rubin, S.; Segura, J.; Van den Born, B.J.; Gosse, P. From malignant hypertension to hypertension-MOD: A modern definition for an old but still dangerous emergency. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2016, 30, 463–466.
- Kim, W.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, J.; Shin, J.-H. Clinical implications of cardiac troponin-I in patients with hypertensive crisis visiting the emergency department. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 507–515.
- Janke, A.T.; McNaughton, C.D.; Brody, A.M.; Welch, R.D.; Levy, P.D. Trends in the Incidence of Hypertensive Emergencies in US Emergency Departments From 2006 to 2013. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 5, e004511.
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Beevers, M.; Beevers, G. The failure of malignant hypertension to decline—A survey of 24 years experience in a multiracial population in England. J. Hypertens. 1994, 12, 1297–1305. Available online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cmedm&AN=7868878&site=ehost-live&scope=site (accessed on 6 February 2022).
- Zampaglione, B.; Pascale, C.; Marchisio, M.; Cavallo-Perin, P. Hypertensive urgencies and emergencies. Prevalence and clinical presentation. Hypertension 1996, 27, 144–147.
- Lane, D.A.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Beevers, D.G. Improving Survival of Malignant Hypertension Patients Over 40 Years. Am. J. Hypertens. 2009, 22, 1199–1204.
- Martin, J.F.V.; Higashiama, E.; Garcia, E.; Luizon, M.R.; Cipullo, J.P. Hypertensive crisis profile. Prevalence and clinical presentation. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2004, 83, 130–131.
- Rubin, S.; Cremer, A.; Boulestreau, R.; Rigothier, C.; Kuntz, S.; Gosse, P. Malignant hypertension: Diagnosis, treatment and prognosis with experience from the Bordeaux cohort. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 316–324. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/jhypertension/Fulltext/2019/02000/Malignant_hypertension__diagnosis,_treatment_and.13.aspx (accessed on 8 February 2022).
- Nkoke, C.; Noubiap, J.J.; Dzudie, A.; Jingi, M.A.; Njume, D.; Teuwafeu, D.; Aseneh, J.; Nkouonlack, C.; Menanga, A.; Kingue, S. Epidemiology of hypertensive crisis in the Buea Regional Hospital, Cameroon. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2020, 22, 2105–2110.
- Guiga, H.; Decroux, C.; Michelet, P.; Loundou, A.; Cornand, D.; Silhol, F.; Vaisse, B.; Sarlon-Bartoli, G. Hospital and out-of-hospital mortality in 670 hypertensive emergencies and urgencies. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2017, 19, 1137–1142.
- Vilela-Martin, J.F.; Vaz-de-Melo, R.O.; Kuniyoshi, C.H.; Abdo, A.N.R.; Yugar-Toledo, J.C. Hypertensive crisis: Clinical-epidemiological profile. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 367–371.
- Acosta, G.; Amro, A.; Aguilar, R.; Abusnina, W.; Bhardwaj, N.; Koromia, G.A.; Studeny, M.; Irfan, A. Clinical Determinants of Myocardial Injury, Detectable and Serial Troponin Levels among Patients with Hypertensive Crisis. Cureus 2020, 12, e6787.
- Pattanshetty, D.J.; Bhat, P.K.; Aneja, A.; Pillai, D.P. Elevated troponin predicts long-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in hypertensive crisis: A retrospective study. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 2410–2415.
- Beishon, L.C.; Minhas, J.S. Cerebral Autoregulation and Neurovascular Coupling in Acute and Chronic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 720770.
- Strandgaard, S.; Haunsø, S. Why does antihypertensive treatment prevent stroke but not myocardial infarction? Lancet 1987, 330, 658–661.
- Westerhof, N.; Boer, C.; Lamberts, R.R.; Sipkema, P. Cross-Talk Between Cardiac Muscle and Coronary Vasculature. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 1263–1308.
- van den Born, B.-J.H.; Löwenberg, E.C.; van der Hoeven, N.V.; de Laat, B.; Meijers, J.C.; Levi, M.; van Montfrans, G.A. Endothelial dysfunction, platelet activation, thrombogenesis and fibrinolysis in patients with hypertensive crisis. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 922–927.
- van den Born, B.-J.H.; Koopmans, R.P.; van Montfrans, G.A. The renin-angiotensin system in malignant hypertension revisited: Plasma renin activity, microangiopathic hemolysis, and renal failure in malignant hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2007, 20, 900–906.
- te Riet, L.; van Esch, J.H.M.; Roks, A.J.M.; van den Meiracker, A.H.; Danser, A.H.J. Hypertension: Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system alterations. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 960–975.
- Rocha, R.; Stier, C.T., Jr.; Kifor, I.; Ochoa-Maya, M.R.; Rennke, H.G.; Williams, G.H.; Adler, G.K. Aldosterone: A Mediator of Myocardial Necrosis and Renal Arteriopathy. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 3871–3878.
- Koenig, J.B.; Jaffe, I.Z. Direct Role for Smooth Muscle Cell Mineralocorticoid Receptors in Vascular Remodeling: Novel Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 427.
- Kusche-Vihrog, K.; Jeggle, P.; Oberleithner, H. The role of ENaC in vascular endothelium. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2014, 466, 851–859.
- Galmiche, G.; Pizard, A.; Gueret, A.; El Moghrabi, S.; Ouvrard-Pascaud, A.; Berger, S.; Challande, P.; Jaffe, I.Z.; Labat, C.; Lacolley, P. Smooth Muscle Cell Mineralocorticoid Receptors Are Mandatory for Aldosterone–Salt to Induce Vascular Stiffness. Hypertension 2014, 63, 520–526.
- Tsuda, K. Renin-Angiotensin System and Sympathetic Neurotransmitter Release in the Central Nervous System of Hypertension. Int. J. Hypertens. 2012, 2012, 1–11.
- Gustafsson, F. Hypertensive arteriolar necrosis revisited. Blood Press 1997, 6, 71–77.
- Kincaid-Smith, P.; McMicheal, J.; Murphy, E.A. The clinical course and pathology of hypertension with papilloedema (malignant hypertension). QJM Int. J. Med. 1958, 27, 117–154.
- Olsen, F. Acute hypertensive damage of arterial vessels of the heart. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. Sect. A Pathol. 1978, 86, 199–200.
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D. and Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2231–2264.
- Bularga, A.; Hung, J.; Daghem, M.; Stewart, S.; Taggart, C.; Wereski, R.; Singh, T.; Meah, M.N.; Fujisawa, T.; Ferry, A.V.; et al. Coronary Artery and Cardiac Disease in Patients with Type 2 Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective Cohort Study. Circulation 2022, 145, 1188–1200.
- Neri, E.; Toscano, T.; Papalia, U.; Frati, G.; Massetti, M.; Capannini, G.; Tucci, E.; Buklas, D.; Muzzi, L.; Oricchio, L.; et al. Proximal aortic dissection with coronary malperfusion: Presentation, management, and outcome. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2001, 121, 552–560.
- Marber, M.S.; Mills, N.L.; Morrow, D.A.; Mueller, C. Cardiac myosin-binding protein C as a biomarker of acute myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2021, 10, 963–965.




