| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Daramy Kallon | + 4428 word(s) | 4428 | 2021-09-17 08:45:57 | | | |
| 2 | Lindsay Dong | Meta information modification | 4428 | 2021-09-22 03:28:44 | | |
Video Upload Options
Biofuel, a cost-effective, safe, and environmentally benign fuel produced from renewable sources, has been accepted as a sustainable replacement and a panacea for the damaging effects of the exploration for and consumption of fossil-based fuels.
1. Biofuel as a Renewable Fuel
-
Biofuels are renewable and are carbon- and CO2/GHG-neutral during the progression of the life cycle [6].
2.1. Classification of Biofuels
2.1.1. Classification Based on the Physical State
Solid Biofuels
| Lignocellulosic Biomass | Solid Waste | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Residues | Forest Residues | Energy Crops | |
| Rice straw Rice husk Wheat straw Sorghum straw Corn stover Sugarcane bagasse Sugarcane peel Barley straw Olive pulp Grapeseed |
Firewoods Wood chips Wood branches Sawdust Fruit bunch Willow chips Black locust Pine Spruce Eucalyptus Softwood Hardwood Hybrid poplar |
Switchgrass Miscanthus Energy cane grass Hybrid Pennisetum Triarrhena lutarioriparia Energy cane leaf Energy cane stem Grass leaf Grass stem |
Municipal solid waste Processed paper Plastics Wastewater sludge Food waste Dried animal manure Poultry waste |
Liquid Biofuels
Gaseous Biofuels
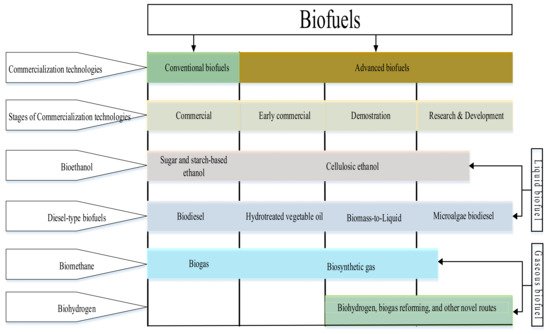
2.1.2. Classification Based on Technology Maturity
2.1.3. Classification Based on the Generation of Feedstock
Feedstocks for biofuel production are divided into three categories in terms of their generation: first-generation feedstock, second-generation feedstock, and third-generation feedstock. The choice of feedstock has a huge influence on the development and utilization of biofuel as a substitute for FB fuels. Feedstocks are chosen based on price, hydrocarbon content, and biodegradability. For example, edible feedstocks and those containing pure sugars are relatively expensive. Simple sugars are preferred as feedstocks because they are easy to decompose with microbes while lignocellulosic biomasses are selected based on their relative affordability.
2.1.4. Classification Based on the Generation of Products
Primary Biofuels
First-Generation Biofuels
Second-Generation Biofuels
Third-Generation Biofuels
Fourth-Generation Biofuels
2. Biofuel as Internal Combustion Engine Fuels
| Fuel | Stored Energy (MJ) |
|---|---|
| Diesel | 36 |
| Gasoline | 33 |
| Biodiesel | 33 |
| Methanol | 16 |
| Ethanol | 21 |
| Liquid H2 (at −253 °C) | 8.5 |
| Compressed H2 (at 250 bar) | 2.5 |
| Property | PBG | PBD | Methanol | Ethanol | DME | Biogas | Hydrogen | Biodiesel | F-T Diesel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | CnH1.87n | CnH1.8n | CH3OH | C2H5OH | CH3OCH3 | CH4 | H2 | C15H31CO2CH3 | C9 to C20 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 720–780 | 820–870 | 800 | 790 | 667 | - | 70 | 850–885 | 774–782 |
| Kinetic viscosity at 40 °C (cSt) | 0.7 | 2.0–3.5 | 0.75 | 1.5 | 0.18 | - | - | 4.43 | 2-4.5 |
| Cetane number | 13–17 | 45–55 | 5 | 8 | 55–60 | - | - | 45-65 | 72 |
| Self-ignition temperature (°C) | 260a | 210 a | 470 | 365 | 320 | 580 | 500 | 220 | 315 |
| Lower heating value (MJ/kg) | 44 | 43 | 19.7 | 28.6 | 28.2 | 24 | 120 | 37 | 43.5 a |
| Lower heating value (liquid) (MJ/L) | 33 | 36 | 16 | 21 | 19 | - | 8.5 | 33 | - |
| Higher heating value (mixture) (kJ/kg) | 3.8 | 3.9 | 3.5 | - | 3.4 | 3.1 | 2.0 | - | - |
| Adiabatic temperature (°C) | 1995 | - | 1950 | 1965 | 2020 | 1954 | 2510 | 2000 | - |
| Boiling temperature (°C) | 25–210 | 180–360 | 65 | 78 | −25 | −162 | −253 | 250–350 | 157.6 |
| Reid vapor pressure at 38 °C (kPa) | 55–100 | <1.5 | 32 | 16 | 800 | - | - | - | - |
| Stoichiometric A/F ratio | 14.5 a | 14 a | 6.4 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 17 | 34.1 | 13 a | 15 |
| Research octane number | 98 | - | 115 | 110 | - | 120 | 106 | - | - |
| Enthalpy of vaporization (kJ/kg) | 350 a | 270 a | 1100 | 900 | 375 | 510 | 455 | - | - |
| Flammability limit (% vol.) | 1.3–8 | 0.6–8 | 7–36 | 4.3–19 | 3.4–19 | - | 4–75 | - | - |
| Flash point (°C) | -40 | 60–80 | 11 | 12 | −41 | - | - | 62 | 500 |
| Oxygen content (wt.%) | - | - | 50 | 35 | 34.8 | - | - | 10.7 | - |
| Carbon content (wt.%) | - | - | - | - | 52.2 | - | - | 76.9 | 86.44 |
| Hydrogen content (wt.%) | - | - | - | - | 13 | - | - | 12.4 | 13.56 |
2.1. Utilization of Biofuels in Spark Ignition Engines
2.2. Utilization of Biofuels in Compression Ignition Engines
| Biofuel Used | Engine Details | Effects | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Emissions | |||
| Biodiesel | 1C, 4S, NA, DI, air-cooled |
|
|
[98] |
| Biodiesel | 1C, common-rail DI, r = 16 |
|
|
[99] |
| Biodiesel | 1C, 4S, DI, VCR, water-cooled |
|
|
[100] |
| Biodiesel | 2C, water-cooled, r = 17.5, N = 1500 rpm |
|
|
[101] |
| Biodiesel | 1C, 4S, constant speed, water-cooled |
|
|
[102] |
| DME | 1S, common-rail injection |
|
|
[103] |
| DME | 1S, 4S, DI, water-cooled, r = 18, N = 2200 rpm | NA |
|
[104] |
| DME | 4C, NA, in-line, common rail, r = 18.5 |
|
|
[105] |
| DME | 1S, common rail, r = 16.7 |
|
|
[106] |
| F-T | 1S, 4S, NA, DI, water-cooled, r = 18 |
|
|
[107] |
3. Implications
References
- Alaswad, A.; Dassisti, M.; Prescott, T.; Olabi, A.G. Technologies and developments of third generation biofuel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1446–1460.
- Saladini, F.; Patrizi, N.; Pulselli, F.M.; Marchettini, N.; Bastianoni, S. Guidelines for emergy evaluation of first, second and third generation biofuels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 221–227.
- Schulte, L.A.; Ontl, T.A.; Larsen, G.L. Biofuels and biodiversity, wildlife habitat restoration. In Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, 2nd ed.; Levin, S.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 540–551.
- Cruz, C.H.B.; Souza, G.M.; Cortez, L.A.B. Biofuels for Transport. In Future Energy; Letcher, T.M., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2014; pp. 215–244.
- Ruan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, S.; Fan, L.; Zhou, N.; Ding, K.; Peng, P.; Addy, M.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Biofuels: Introduction. In Biofuels: Alternative Feedstocks and Conversion Processes for the Production of Liquid and Gaseous Biofuels, 2nd ed.; Pandey, A., Larroche, C., Dussap, C.G., Gnansounou, E., Khanal, S.K., Ricke, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 3–43.
- Janampelli, S.; Darbha, S. Hydrodeoxygenation of vegetable oils and fatty acids over different group VIII metal catalysts for producing biofuels. Catal. Surv. Asia 2019, 23, 90–101.
- Wu, B.; Bai, X.; Liu, W.; Lin, S.; Liu, S.; Luo, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, S.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, C.; et al. Non-negligible stack emissions of non-criteria air pollutants from coal-fired power plants in China: Condensable particulate matter and sulfur trioxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6540–6550.
- Appavu, P.; Ramanan, M.V.; Jayaraman, J.; Venu, H. NOx emission reduction techniques in biodiesel-fuelled CI engine: A review. Aust. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 18, 210–220.
- Navas, M.B.; Ruggera, J.F.; Lick, I.D.; Casella, M.L. A sustainable process for biodiesel production using Zn/Mg oxidic species as active, selective and reusable heterogeneous catalysts. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2020, 7, 4.
- Pugazhendhi, A.; Alagumalai, A.; Mathimani, T.; Atabani, A. Optimization, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on sustainable biodiesel production from waste cooking oil: An Indian perspective. Fuel 2020, 273, 117725.
- Darby, H.M.; Callahan, C.W. On-farm oil-based biodiesel production. In Bioenergy; Elsevier: London, UK, 2020; pp. 157–184.
- Smith, N. The Creation of an Inclusive and Safe Biofuel Production Method; Research Paper; Savannah State University: Sannah, GA, USA, 2019.
- Yaghoubi, J.; Yazdanpanah, M.; Komendantova, N. Iranian agriculture advisors’ perception and intention toward biofuel: Green way toward energy security, rural development and climate change mitigation. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 452–459.
- Szabó, Z. Can biofuel policies reduce uncertainty and increase agricultural yields through stimulating investments? Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2019, 13, 1224–1233.
- Chintala, V. Coal versus biofuels: A social and economic assessment. In Second and Third Generation of Feedstocks; Elsevier: London, UK, 2019; pp. 513–529.
- Oyewole, S.O.; Ishola, B.; Oyewole, A.L. Socioeconomic issues associated with campaign for large scale jatropha production to meet the anticipated biofuel demand. Int. J. For. Plant 2019, 2, 19–25.
- Topcu, M.; Tugcu, C.T. The impact of renewable energy consumption on income inequality: Evidence from developed countries. Renew. Energy 2020, 151, 1134–1140.
- Schuenemann, F.; Kerr, W.A. European union non-tariff barriers to imports of African biofuels. Agrekon 2019, 58, 407–425.
- Mattioda, R.A.; Tavares, D.R.; Casela, J.L.; Junior, O.C. Social life cycle assessment of biofuel production. In Biofuels for a More Sustainable Future; Ren, J., Scipioni, A., Manzardo, A., Liang, H., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2020; pp. 255–271.
- Siddiqui, M.R.; Miranda, A.; Mouradov, A. Microalgae as bio-converters of wastewater into biofuel and food. In Water Scarcity and Ways to Reduce the Impact; Pannirselvam, M., Shu, L., Griffin, G., Philip, L., Natarajan, A., Hussain, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 75–94.
- Ingle, A.P.; Ingle, P.; Gupta, I.; Rai, M. Socioeconomic impacts of biofuel production from lignocellulosic biomass. In Sustainable Bioenergy; Rais, M., Ingle, A., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2019; pp. 347–366.
- Vassilev, S.V.; Vassileva, C.G. Composition, properties and challenges of algae biomass for biofuel application: An overview. Fuel 2016, 181, 1–33.
- Meyer, K.; Newman, P. A quota for agricultural GHG emissions (methane and nitrous oxide). In Planetary Accounting; Meyer, K., Newman, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 137–145.
- Patidar, S.K.; Raheman, H. Performance and durability analysis of a single-cylinder direct injection diesel engine operated with water emulsified biodiesel-diesel fuel blend. Fuel 2020, 273, 117779.
- Adewuyi, A. Challenges and prospects of renewable energy in Nigeria: A case of bioethanol and biodiesel production. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 77–88.
- Mandley, S.; Daioglou, V.; Junginger, H.; van Vuuren, D.; Wicke, B. EU bioenergy development to 2050. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 127, 109858.
- Knapczyk, A.; Francik, S.; Fraczek, J.; Slipek, Z. Analysis of research trends in production of solid biofuels. In Proceedings of the 18th International Scientific Conference “Engineering for Rural Development”, Jelgava, Latvia, 22–24 May 2019; Latvia University of Life Sciences and Technologies: Jelgava, Latvia, 2019; pp. 1503–1509.
- Chua, S.Y.; Goh, C.M.H.; Tan, Y.H.; Mubarak, N.M.; Kansedo, J.; Khalid, M.; Walvekar, R.; Abdullah, E. Biodiesel synthesis using natural solid catalyst derived from biomass waste—A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 81, 41–60.
- Morato, T.; Vaezi, M.; Kumar, A. Assessment of energy production potential from agricultural residues in Bolivia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 102, 14–23.
- Islas, J.; Manzini, F.; Masera, O.; Vargas, V. Solid biomass to heat and power. In The Role of Bioenergy in the Bioeconomy; Lago, C., Caldés, N., Lechón, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2019; pp. 145–177.
- Carrasco-Diaz, G.; Perez-Verdin, G.; Escobar-Flores, J.; Marquez-Linares, M.A. A technical and socioeconomic approach to estimate forest residues as a feedstock for bioenergy in northern Mexico. Ecosyst 2019, 6, 45.
- Rupp, S.P.; Ribic, C.A. Second-generation feedstocks from dedicated energy crops. In Renewable Energy and Wildlife Conservation; Moorman, C.E., Grodsky, S.M., Rupp, S.P., Eds.; Baltimore University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2019; pp. 64–66.
- Ho, D.P.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. A mini review on renewable sources for biofuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 742–749.
- Jacobson, M.Z. Why Not Liquid Biofuels for Transportation as Part of a 100% Wind-Water-Solar (WWS) and Storage Solution to Global Warming, Air Pollution, and Energy Security. 2020. Available online: https://web.stanford.edu/group/efmh/jacobson/Articles/I/BiofuelVsWWS.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2020).
- Huang, H.; Jin, Q. Industrial waste valorization: Applications to the case of liquid biofuels. green energy to sustainability: Strategies for global industries. In Green Energy to Sustainability: Strategies for Global Industries; Vertès, A.A., Qureshi, N., Blaschek, H.P., Yukawa, H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 515–537.
- Guo, M. The global scenario of biofuel production and development. In Practices and Perspectives in Sustainable Bioenergy; Mitra, M., Nagchaudhuri, A., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2020; pp. 29–56.
- IEA. Technology Roadmap. Biofuels for Transport. Available online: https://www.ieabioenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/IEA-Biofuel-Roadmap.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2020).
- Noraini, M.; Ong, H.C.; Badrul, M.J.; Chong, W. A review on potential enzymatic reaction for biofuel production from algae. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 24–34.
- Knapczyk, A.; Francik, S.; Wójcik, A.; Ślipek, Z. Application of methods for scheduling tasks in the production of biofuels. In Renewable Energy Sources: Engineering, Technology, Innovation; Wróbel, M., Jewiarz, M., Szlęk, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 863–873.
- Isah, S.; Ozbay, G. Valorization of food loss and wastes: Feedstocks for biofuels and valuable chemicals. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 82.
- Rajak, U.; Verma, T.N. Effect of emission from ethylic biodiesel of edible and non-edible vegetable oil, animal fats, waste oil and alcohol in CI engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 166, 704–718.
- Ahamed, M.; Dash, S.; Kumar, A.; Lingfa, P. A critical review on the production of biodiesel from Jatropha, Karanja and Castor feedstocks. In Bioresource Utilization and Bioprocess; Ghosh, S., Sen, R., Chanakya, H., Pariatamby, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 107–115.
- Hadin, A.; Eriksson, O. Horse manure as feedstock for anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 506–518.
- Ajanovic, A. Biofuels versus food production: Does biofuels production increase food prices? Energy 2011, 36, 2070–2076.
- Callegari, A.; Bolognesi, S.; Cecconet, D.; Capodaglio, A.G. Production technologies, current role, and future prospects of biofuels feedstocks: A state-of-the-art review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 384–436.
- Al Hatrooshi, A.S.; Eze, V.C.; Harvey, A.P. Production of biodiesel from waste shark liver oil for biofuel applications. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 99–105.
- Patel, A.; Sartaj, K.; Pruthi, P.A.; Pruthi, V.; Matsakas, L. Utilization of clarified butter sediment waste as a feedstock for cost-effective production of biodiesel. Foods 2019, 8, 234.
- Ekeoma, M.; Okoye, P.; Ajiwe, V.; Hameed, B. Modified coconut shell as active heterogeneous catalyst for the transesterification of waste cooking oil. J. Chem. Soc. Niger. 2020, 45, 107.
- Ndiaye, M.; Arhaliass, A.; Legrand, J.; Roelens, G.; Kerihuel, A. Reuse of waste animal fat in biodiesel: Biorefining heavily-degraded contaminant-rich waste animal fat and formulation as diesel fuel additive. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1073–1079.
- Nikhom, R.; Mueanmas, C.; Suppalakpanya, K.; Tongurai, C. Utilization of oil recovered from biodiesel wastewater as an alternative feedstock for biodiesel production. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2020, 39, 13365.
- Hess, J.R.; Ray, A.E.; Rials, T.G. Advancements in biomass feedstock preprocessing: Conversion ready feedstocks. Front. Energy Res. 2019, 7, 140.
- Puettmann, M.; Sahoo, K.; Wilson, K.; Oneil, E. Life cycle assessment of biochar produced from forest residues using portable systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119564.
- Du, C.; Zhao, X.; Liu, D.; Lin, C.S.K.; Wilson, K.; Luque, R.; Clark, J. Introduction: An overview of biofuels and production technologies. In Handbook of Biofuels Production; Luque, R., Ki Lin, C.S., Wilson, K., Clark, J., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2016; pp. 3–12.
- Abdulkareem-Alsultan, G.; Asikin-Mijan, N.; Lee, H.; Taufiq-Yap, Y. Biofuels: Past, Present, Future. In Innovations in Sustainable Energy and Cleaner Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 489–504.
- Jamwal, V.L.; Kapoor, N.; Gandhi, S.G. Biotechnology of biofuels: Historical overview, business outlook and future perspectives. In Biotechnology Business—Concept to Delivery; Saxena, A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 109–127.
- Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A.; Ankaram, S.; Duan, Y.; Awasthi, M.K. Biofuel production from biomass: Toward sustainable development. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Larroche, C., Sanroman, M., Du, G., Pandey, A., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2019; pp. 79–92.
- Nwoba, E.G.; Vadiveloo, A.; Ogbonna, C.N.; Ubi, B.E.; Ogbonna, J.C.; Moheimani, N.R. Algal cultivation for treating wastewater in African developing countries: A review. Clean Soil Air Water 2020, 48, 2000052.
- Veeramuthu, A.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C. Potential of microalgal biodiesel: Challenges and applications. IntechOpen 2020, 9, 51–60.
- Chew, B.; Shen, X.; Ansell, J.; Hamid, S.; Oh, Y. Review a decade of BP’s Technology roadmap on the next generation biofuels development. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 268, 012009.
- Subramanian, K.A. Biofueled Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; p. 15.
- IEA. Key World Energy Statistics. 2018. Available online: https://webstore.iea.org/key-world-energy-statistics-2018 (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- TERM. Transport Indicators Tracking Progress towards Environmental Targets in Europe; No 7/2015; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/term-report-2015 (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- EIA—Energy Information Administration. International Energy Outlook. 2017. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/ieo/ (accessed on 4 August 2020).
- Staffell, I.; Scamman, D.; Abad, A.V.; Balcombe, P.; Dodds, P.E.; Ekins, P.; Shah, N.; Ward, K.R. The role of hydrogen and fuel cells in the global energy system. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 463–491.
- IRENA. Global Energy Transformation: The REmap Transition Pathway (Background Report to 2019 Edition); International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2019; Available online: https://www.irena.org/publications/2019/Apr/Global-energy-transformation-The-REmap-transition-pathway (accessed on 4 August 2020).
- Martins, J.; Brito, F. Alternative fuels for internal combustion engines. Energies 2020, 13, 4086.
- Lisý, M.; Lisá, H.; Jecha, D.; Baláš, M.; Križan, P. Characteristic properties of alternative biomass fuels. Energies 2020, 13, 1448.
- Aladejare, A.E.; Onifade, M.; Lawal, A.I. Application of metaheuristic based artificial neural network and multilinear regression for the prediction of higher heating values of fuels. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2020, 1–22.
- Noushabadi, A.S.; Dashti, A.; Raji, M.; Zarei, A.; Mohammadi, A.H. Estimation of cetane numbers of biodiesel and diesel oils using regression and PSO-ANFIS models. Renew. Energy 2020, 4, 146.
- Huang, Y.; Li, F.; Bao, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, H. Estimation of kinematic viscosity of biodiesel fuels from fatty acid methyl ester composition and temperature. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 2476–2485.
- SAE International Hybrid-EV Committee. J2841: Utility Factor Definitions for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles Using Travel Survey Data; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010.
- Arat, H.T.; Baltacioglu, M.K.; Özcanli, M.; Aydin, K. Effect of using Hydroxy–CNG fuel mixtures in a non-modified diesel engine by substitution of diesel fuel. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 8354–8363.
- McCormick, R.L.; Fioroni, G.; Fouts, L.; Christensen, E.; Yanowitz, J.; Polikarpov, E.; Albrecht, K.; Gaspar, D.; Gladden, J.; George, A. Selection criteria and screening of potential biomass-derived streams as fuel blendstocks for advanced spark-ignition engines. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2017, 10, 442–460.
- Mustafa, A.; Lougou, B.G.; Shuai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tan, H. Current technology development for CO2 utilization into solar fuels and chemicals: A review. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 49, 96–123.
- Chintala, V. Production, upgradation and utilization of solar assisted pyrolysis fuels from biomass–a technical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 120–130.
- Jiao, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhou, G.; Dong, S.; Liu, W. Comparison of combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with diesel and methanol-Fischer-Tropsch diesel-biodiesel-diesel blends at various altitudes. Fuel 2019, 243, 52–59.
- Bongartz, D.; Doré, L.; Eichler, K.; Grube, T.; Heuser, B.; Hombach, L.E.; Robinius, M.; Pischinger, S.; Stolten, D.; Walther, G.; et al. Comparison of light-duty transportation fuels produced from renewable hydrogen and green carbon dioxide. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 757–767.
- Bae, C.J.; Kim, J. Alternative fuels for internal combustion engines. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 3389–3413.
- Dupnock, T.L. Development of a High Performance, Biological Trickling Filter to Upgrade Raw Biogas to Renewable Natural Gas Standards. Master’s Thesis, Duke University, Durham, NC, USA, 2019.
- Bora, D.; Barbora, L.; Borah, A.J.; Mahanta, P. A Comparative Assessment of Biogas Upgradation Techniques and Its Utilization as an Alternative Fuel in Internal Combustion Engines. In Alternative Fuels and Advanced Combustion Techniques as Sustainable Solutions for Internal Combustion Engines. Energy, Environment, and Sustainability; Singh, A.P., Kumar, D., Agarwal, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 95–115.
- Pramanik, S.K.; Suja, F.B.; Zain, S.M.; Pramanik, B.k. The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste: Prospects and constraints. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 8, 100310.
- Baena-Moreno, F.M.; Rodríguez-Galán, M.; Vega, F.; Vilches, L.F.; Navarrete, B. Recent advances in biogas purifying technologies. Int. J. Green Energy 2019, 16, 401–412.
- Baena-Moreno, F.M.; le Saché, E.; Pastor-Pérez, L.; Reina, T. Biogas as a renewable energy source: Focusing on principles and recent advances of membrane-based technologies for biogas upgrading. In Membranes for Environmental Applications; Zhang, Z., Zhang, W., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 95–120.
- Saboor, A.; Khan, S.; Ali Shah, A.; Hasan, F.; Khan, H.; Badshah, M. Enhancement of biomethane production from cattle manure with codigestion of dilute acid pretreated lignocellulosic biomass. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 14, 632–637.
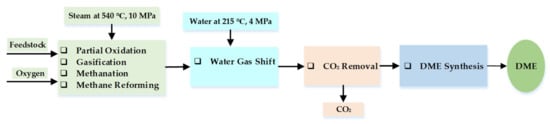
- Stepanenko, D.; Kneba, Z. DME as alternative fuel for compression ignition engines-a review. Combust. Eng. 2019, 177, 172–179.
- Inayat, A.; Ghenai, C.; Naqvi, M.; Ammar, M.; Ayoub, M.; Hussin, M.N.B. Parametric Study for Production of Dimethyl Ether (DME) As a Fuel from Palm Wastes. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 1242–1249.
- Evans, C.; Smith, C. Biomass to Liquids Technology. In Comprehensive Renewable Energy; Sayigh, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2012; Volume 5, pp. 155–204.
- Zang, G.; Sun, P.; Elgowainy, A.A.; Bafana, A.; Wang, M. Performance and cost analysis of liquid fuel production from H2 and CO2 based on the Fischer-Tropsch process. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 46, 101459.
- IRENA. Hydrogen: A Renewable Energy Perspective; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2019; Available online: https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2019/Sep/IRENA_Hydrogen_2019.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- Qureshy, A.M.M.I.; Dincer, I. A new integrated renewable energy system for clean electricity and hydrogen fuel production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 20944–20955.
- Afanasiev, A.; Pavlov, D.; Epishkin, V.; Gapchenko, U. Application of hydrogen and hydrogen-containing gases in internal combustion engines. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 734, 012198.
- Asoyan, A.R.; Danilov, I.K.; Asoyan, I.A.; Polishchuk, G.M. Hydrogen application in internal combustion engines. RUDN J. Eng. Res. 2020, 21, 14–19.
- Chandran, D. Compatibility of diesel engine materials with biodiesel fuel. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 89–99.
- Méndez, C.I.; Ancheyta, J. Kinetic models for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis for the production of clean fuels. Catal. Today 2020, 335, 3–16.
- Dimethyl Ether (DME) Market. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2018/09/09/1568236/0/en/Global-Dimethyl-Ether-Market-Will-Reach-USD-9-100-Million-By-2024-Zion-Market-Research.html (accessed on 31 July 2020).
- Farsi, M.; Fekri Lari, M.; Rahimpour, M.R. Development of a green process for DME production based on the methane tri-reforming. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 106, 9–19.
- Mondal, U.; Yadav, G.D. Perspective of dimethyl ether as fuel: Part I. Catalysis. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 32, 299–320.
- Simsek, S. Effects of biodiesel obtained from Canola, sefflower oils and waste oils on the engine performance and exhaust emissions. Fuel 2020, 265, 117026.
- Hirner, F.S.; Hwang, J.; Bae, C.; Patel, C.; Gupta, T.; Agarwal, A.K. Performance and emission evaluation of a small-bore biodiesel compression-ignition engine. Energy 2019, 183, 971–982.
- Rosha, P.; Mohapatra, S.K.; Mahla, S.K.; Cho, H.; Chauhan, B.S.; Dhir, A. Effect of compression ratio on combustion, performance, and emission characteristics of compression ignition engine fueled with palm (B20) biodiesel blend. Energy 2019, 178, 676–684.
- Srikanth, H.; Venkatesh, J.; Godiganur, S.; Manne, B.; Bharath Kumar, S.; Spurthy, S. Combustion, performance, and emission characteristics of dairy-washed milk scum biodiesel in a dual cylinder compression ignition engine. Energy Source Part A 2019, 42, 1–18.
- Nirmala, N.; Dawn, S.S.; Harindra, C. Analysis of performance and emission characteristics of waste cooking oil and Chlorella variabilis MK039712.1 biodiesel blends in a single cylinder, four strokes diesel engine. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 284–292.
- Park, S.H.; Lee, C.S. Combustion performance and emission reduction characteristics of automotive DME engine system. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2013, 39, 147–168.
- Yang, S.; Lee, C. Exhaust gas characteristics according to the injection conditions in diesel and DME engines. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 647.
- Raza, M.; Chen, L.; Ruiz, R.; Chu, H. Influence of pentanol and dimethyl ether blending with diesel on the combustion performance and emission characteristics in a compression ignition engine under low temperature combustion mode. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 1658–1669.
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Shuai, S. Study on combustion and emission characteristics of Polyoxymethylene Dimethyl Ethers/diesel blends in light-duty and heavy-duty diesel engines. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 1393–1402.
- Yongcheng, H.; Longbao, Z.; Shangxue, W.; Shenghua, L. Study on the performance and emissions of a compression ignition engine fuelled with Fischer-Tropsch diesel fuel. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D 2006, 220, 827–835.
- Malode, S.J.; Prabhu, K.K.; Mascarenhas, R.J.; Shetti, N.P.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Recent advances and viability in biofuel production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 10, 100070.
- Adegboye, M.F.; Ojuederie, O.B.; Talia, P.M.; Babalola, O.O. Bioprospecting of microbial strains for biofuel production: Metabolic engineering, applications, and challenges. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 5.
- Lin, C.Y.; Lu, C. Development perspectives of promising lignocellulose feedstocks for production of advanced generation biofuels: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 136, 110445.