
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shailendra Pratap Singh | + 1773 word(s) | 1773 | 2021-08-03 06:09:57 | | | |
| 2 | Beatrix Zheng | + 184 word(s) | 1957 | 2021-08-19 10:42:34 | | | | |
| 3 | Beatrix Zheng | + 184 word(s) | 1957 | 2021-08-19 10:43:01 | | |
Video Upload Options
Mitochondria are clustered around the replication sites of several viruses and decrease the supply routes for energy and metabolites, resulting in increased viral progeny viruses. In a viral infection, viruses generate cellular stress, which causes mitochondrial redistribution.
1. Introduction
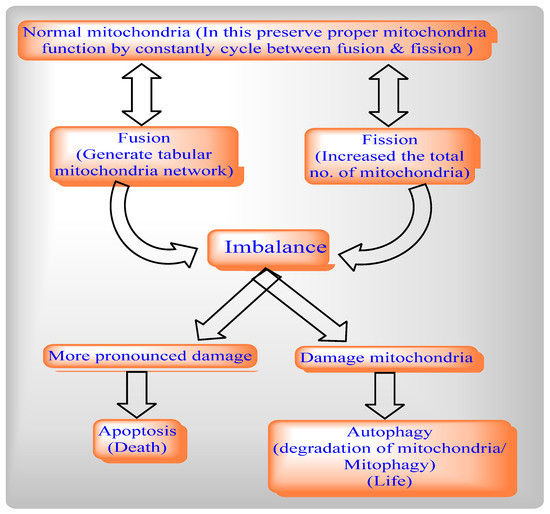
The mitochondrial dynamics network involves two cycles, mitochondrial fission and Mitochondrial Fusion, to help maintain the functional capacity of mitochondria by distribution of mitochondrial contents, energy conductance, and responsiveness to cellular cues. Thus, mitochondrial dynamics govern their communication and interaction with other cellular organelles.
By balancing between two opposite processes, mitochondrial fission and fusion, mammalian cells maintain the overall shapes of their mitochondria. The Fis1 protein has a TM domain with the help of the C-terminal of mitochondria anchored into the mitochondrial outer membrane [1]. Drp1 does not prevent localized mitochondria via the knockdown of Fis1 with RNA interference [2]. By network lengthening, MFF release the Drp1 foci from the mitochondrial outer membrane, whereas, with the help of mitochondrial fission and the physical interaction between the mitochondrial fission factor (MFF) and Drp1, MFF overexpression stimulates mitochondrial fission [3].
Mitochondrial fission includes Drp1 and Fis1, whereas mitochondrial fusion includes Mfn1, Mfn2, and OPA1. The deletion of the Drp1 gene causes mitochondrial enlargement, the increased opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP), apoptosis, and lethal dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) [4] by inhibiting mitochondrial fission, whereas deletion of Mfn1 and Mfn2 disrupts mitochondrial structure and respiratory chain function [5]. An imbalance between mitochondrial fusion and fission compromises mitochondrial integrity during aging [6][7][8]. Mitochondrial from aged C. elegans is indicated by a significantly enlarged and swollen ultrastructure, which is accompanied by decreasing O2 consumption, increasing carbonylated proteins and decreasing mitochondrial SOD activity [9].
In healthy mitochondria, PINK1 contains a mitochondrial target sequence (MTS), which translocates to mitochondria and is imported to the IMM by translocase of the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) and inner mitochondrial membrane (TIM). Following this, PINK1 is degraded by downstream proteolytic events.
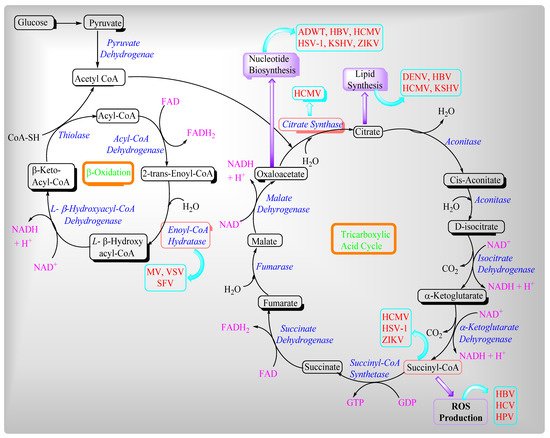
2. Viruses and Their Effects on Mitochondrial Metabolites
2.1. Regulation of Ca2+ Homeostasis by Viruses in Host Cells
2.2. Role of Viruses in Modulating Mitochondrial Antiviral Immunity
-
HCV cleaves MAVS in amino acids (508) and paralyzes the host defense against HCV;
-
The flaviviridae GB virus B, NH3/4A protein cleaves MAVS and prevents any interferon product [23]. MAVS is associated with RLRs which produce type 1 interferon [IFNs] and pro-inflammatory cytokines [24] that act against the pathogen interferon regulatory factor (IRF) and produce type 1 IFN in the cytoplasm [25][26]. Peroxisomal MAVS are involved in the induction of IFN-stimulated genes like encoding viperin [27].
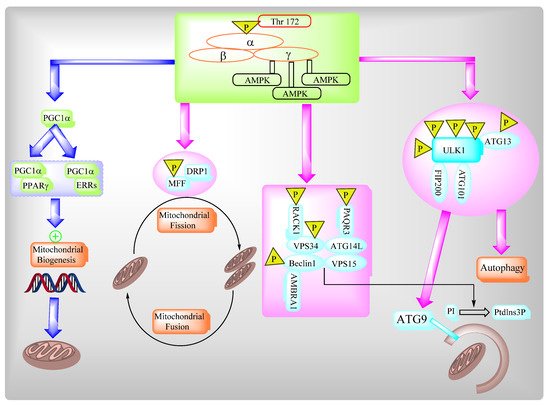
2.3. AMPK Governs Autophagy and Mitochondrial Homeostatsis
2.4. Role of SRV2 in Mitochondrial Dynamics
2.4.1. SRV2 in Various Functions of Mitochondria
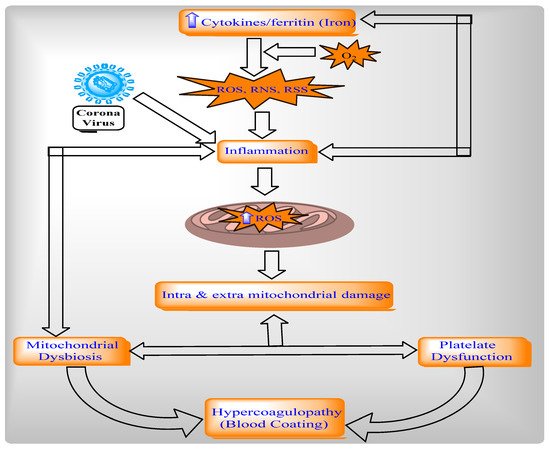
2.4.2. Relationship between Mitochondria, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in COVID-19
2.5. Different Pathways to Reposition Common Approved Drugs against COVID-19
| Therapeutic Category | Mechanism of Action | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autophagy | UPR stress | MPTP | NLRP3 Inflammasome | ||||
| Activator | Modulator | Inhibitor | Suppressor | Modulator | Modulator | Inhibitor | |
| Immunosuppressant | Rapamycin, Tacrolimus, Everolimus [49] | Cyclosporin A [50][51] | |||||
| Anticancer | Rapamycin, Tersirolimus, Everolimus [49], Gefitinib [52], Temozolomide [52] | Bortezomib, Celecoxib [52] | Sunitinib [53] | Thalidomide [54] | |||
| Antidiabetic | Metformin [49] | Pioglitazone [53], Exenatide, Vildagliptin [55], Berberine [56] | Liraglutide [56] | Glyburide [54][57] | |||
| Dietary supplement | Trehalose, Resveratro l [49] | Curcumin [53] | Quercetin [58] | ||||
| Antipsychotic | Lithium [49], Fluspirilene, Trifluperazine, Pimozide [59], Bromperidol, Chlorpromazine [60][61], Sertindole, Olanzapine, Fluphenazine, Methotrimeprazine [62], Prochlorperazine [61] | Clozapine [62] | Haloperidol [63][64][65], Etifoxine [66][67] | ||||
| Antiepileptic | Carbamazepine, Sodium valproate [49] | ||||||
| Antihypertensive | Verapamil, Nimodipine, Nitrendipine [49], Nicardipine, Amidarone [59], Rilmenidine, Clonidine [68], Minoxidil [60] | Isoproterenol [53], Valsartan, Lowsartan, Olmesartan, Telmisartan [55], Guanabenz [69], Bisoprolol, Propranolol, Metoprolol [56] | Ifenprodil [63][64][65], Diazoxide, Nicorandil, Tadalafil, Perhaxiline, Carvedilol [50][51] | ||||
| Antidiarrheal | Loperamide [59] | ||||||
| Ca+ regulator | Calcifediol [68] | ||||||
| Anti-infective | Nitazoxanide [68] | ||||||
| Antidepressant | Nortriptyline [68] | Clomipramine [60] | Trazodone [70] | ||||
| AnticholesteremiC agent | Simvastatin [67] | Atorvastatin [56] | |||||
| Antiemetic | Chlorpromazine [60][61], Prochlorperazine [61] | Haloperidol [63][64][65] | Thalidomide [54] | ||||
| Minercorticoid replacement agent | Fludraocortisone [60][61] | ||||||
| Antitussive | Noscapine [60][61] | Carbetapentane, Dextromethorphan [63][64][65] | |||||
| Anti-allergic | Clemastine [60] | ||||||
| Chelating agent | Defeiprone [71] | ||||||
| Antihelmintic | Niclosamide [72] | Quimacrine [73][74] | |||||
| Skeletal muscle relaxant | Baclofen [75] | ||||||
| Gastrointestinal | Pantoprazole [52] | ||||||
| Macrolide antibiotic | Azithromycin [60] | ||||||
| Ocular drug | Verteporfin [60] | ||||||
| Antiprotozoal drug | Quimacrine [73][74], Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine [68] | ||||||
| Urea cycle disorder agent | Thenylbutyrate [52][53] | ||||||
| Hypolipidemic agent | Pravastatin [53], Fenofibrate [55] | ||||||
| Anti-Alzheimer’s | Donepeziol [63][64][65] | ||||||
| Anti-Parkinsonian | Pramipexole [76] | ||||||
| Neuroprotective agent; anti-ALS drug | Edaravone [50][77] | ||||||
| Anti-arthritic | Anakinra [54] | ||||||
| Anti-inflammatory agent | Celecoxib [52] | Anakinra [54], Tranilast [54][78] | |||||
| Anti-insomia agent | Melatonin [79] | ||||||
3. Expert Opinion
Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles which produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as well as regulating various intracellular functions like metabolism, bioenergetics, cell death, innate immune signaling, and cellular homeostasis. Mitochondria are self-governed by mitochondrial dynamics and mitochondria-selective autophagy or mitophagy. During infection, viruses altered mitochondrial dynamics in order to modulate mitochondria-mediated antiviral immune responses via the alteration of mitochondrial events such as autophagy, mitophagy, and cellular metabolism to facilitate their proliferation.
The pro-fission protein of SRV2 activates mitochondrial fission via the loss of MMP, the ROS-overloading suppression antioxidant system, the depletion of cellular ATP, the release of the apoptotic factor, the activation of the caspase family, and NLRP3 inflammasomes. The protein SRV2 also promotes mitochondria-associated cardiomyocyte apoptosis to cause cardiomyocyte death and mitochondrial damage. The World Health Organization reported that most repositioned drugs modulators, under clinical investigation against COVID-19, act through different pathways such as UPR, autophagy, the NLRP3 inflammasome, and mitochondrial permeability transition pores (MPTP) to inhibit SARS-COV2 propagation. Analysis of the functional significance of mitochondrial dynamics and viral pathogenesis will open up new possibilities for the therapeutic design of approaches to combat viral infections and associated diseases.
References
- James, D.I.; Parone, P.A.; Mattenberger, Y.; Martinou, J.-C. hFis1, a Novel Component of the Mammalian Mitochondrial Fission Machinery. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36373–36379.
- Lee, Y.-J.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Karbowski, M.; Smith, C.L.; Youle, R.J. Roles of the Mammalian Mitochondrial Fission and Fusion Mediators Fis1, Drp1, and Opa1 in Apoptosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 5001–5011.
- Otera, H.; Wang, C.; Cleland, M.M.; Setoguchi, K.; Yokota, S.; Youle, R.J.; Mihara, K. Mff is an essential factor for mitochondrial recruitment of Drp1 during mitochondrial fission in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 1141–1158.
- Song, M.; Mihara, K.; Chen, Y.; Scorrano, L.; Dorn, G.W. Mitochondrial Fission and Fusion Factors Reciprocally Orchestrate Mitophagic Culling in Mouse Hearts and Cultured Fibroblasts. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 273–286.
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dorn, G.W. Mitochondrial Fusion is Essential for Organelle Function and Cardiac Homeostasis. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 1327–1331.
- Miyamoto, S. Autophagy and cardiac aging. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 653–664.
- Seo, A.Y.; Joseph, A.-M.; Dutta, D.; Hwang, J.C.Y.; Aris, J.P.; Leeuwenburgh, C. New insights into the role of mitochondria in aging: Mitochondrial dynamics and more. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 2533–2542.
- Wu, N.N.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J. Mitophagy, Mitochondrial Dynamics, and Homeostasis in Cardiovascular Aging. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–15.
- Yasuda, K.; Ishii, T.; Suda, H.; Akatsuka, A.; Hartman, P.S.; Goto, S.; Miyazawa, M.; Ishii, N. Age-related changes of mitochondrial structure and function in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2006, 127, 763–770.
- Dasgupta, A.; Wilson, D.W. ATP depletion blocks herpes simplex virus DNA packaging and capsid maturation. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2006–2015.
- Hui, E.K.-W.; Nayak, D.P. Role of ATP in Influenza Virus Budding. Virology 2001, 290, 329–341.
- Tritel, M.; Resh, M.D. The Late Stage of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Assembly Is an Energy-Dependent Process. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5473–5481.
- Green, D.R.; Reed, J.C. Mitochondria and Apoptosis. Science 1998, 281, 1309.
- Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Xue, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Liu, M.; Wen, Y.; Guan, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Voltage-dependent anion channel involved in the mitochondrial calcium cycle of cell lines carrying the mitochondrial DNA A4263G mutation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 364–369.
- Hüttemann, M.; Lee, I.; Pecinova, A.; Pecina, P.; Przyklenk, K.; Doan, J.W. Regulation of oxidative phosphorylation, the mitochondrial membrane potential, and their role in human disease. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2008, 40, 445–456.
- Gradzka, I. Mechanisms and regulation of the programmed cell death. Postępy Biochem. 2006, 52, 157–165.
- Yoneyama, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Natsukawa, T.; Shinobu, N.; Imaizumi, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Taira, K.; Akira, S.; Fujita, T. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 730–737.
- Maniatis, T.; Falvo, J.V.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, T.K.; Lin, C.H.; Parekh, B.S.; Wathelet, M.G. Structure and function of the interferon-beta enhanceosome. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1998, 63, 609–620.
- Seth, R.B.; Sun, L.; Ea, C.K.; Chen, Z.J. Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3. Cell 2005, 122, 669–682.
- Meylan, E.; Curran, J.; Hofmann, K.; Moradpour, D.; Binder, M.; Bartenschlager, R.; Tschopp, J. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 437, 1167–1172.
- Retracted article: MAVS protects cells from apoptosis by negatively regulating VDAC1. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2013, 375, 219.
- Li, X.D.; Sun, L.; Seth, R.B.; Pineda, G.; Chen, Z.J. Hepatitis C virus protease NS3/4A cleaves mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein off the mitochondria to evade innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17717–17722.
- Chen, Z.; Benureau, Y.; Rijnbrand, R.; Yi, J.; Wang, T.; Warter, L.; Lanford, R.E.; Weinman, S.A.; Lemon, S.M.; Martin, A.; et al. GB virus B disrupts RIG-I signaling by NS3/4A-mediated cleavage of the adaptor protein MAVS. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 964–976.
- Yamada, S.; Shimojima, M.; Narita, R.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Kato, H.; Saijo, M.; Fujita, T. RIG-I-Like Receptor and Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways Cause Aberrant Production of Inflammatory Cytokines/Chemokines in a Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection Mouse Model. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02246-17.
- Hou, F.; Sun, L.; Zheng, H.; Skaug, B.; Jiang, Q.X.; Chen, Z.J. MAVS forms functional prion-like aggregates to activate and propagate antiviral innate immune response. Cell 2011, 146, 448–461.
- Xu, H.; He, X.; Zheng, H.; Huang, L.J.; Hou, F.; Yu, Z.; Michael, J.D.L.C.; Brian, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.J.; et al. Structural basis for the prion-like MAVS filaments in antiviral innate immunity. eLife 2014, 3, e01489.
- Dixit, E.; Boulant, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, A.S.; Odendall, C.; Shum, B.; Hacohen, N.; Chen, Z.; Whelan, S.; Fransen, M.; et al. Peroxisomes Are Signaling Platforms for Antiviral Innate Immunity. Cell 2010, 141, 668–681.
- Ibáñez Cabellos, J.S.; Pérez-Machado, G.; Seco-Cervera, M.; Berenguer-Pascual, E.; García-Giménez, J.; Pallardó, F. Acute telomerase components depletion triggers oxidative stress as an early event previous to telomeric shortening. Redox Biol. 2017, 14, 398–408.
- Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Dai, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cao, R.; Zhang, R.; Wang, G.; Jiang, R.; Zhou, B.P.; et al. Twist promotes tumor metastasis in basal-like breast cancer by transcriptionally upregulating ROR1. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2739–2751.
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541.
- Liu, L.; Jin, X.; Hu, C.-F.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Zhou, Z.; Li, R.; Shen, C.-X. Amphiregulin enhances cardiac fibrosis and aggravates cardiac dysfunction in mice with experimental myocardial infarction partly through activating EGFR-dependent pathway. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2018, 113, 12.
- Itteboina, R.; Ballu, S.; Sivan, S.K.; Manga, V. Molecular docking, 3D-QSAR, molecular dynamics, synthesis and anticancer activity of tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK 2) inhibitors. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2018, 38, 462–474.
- Aanhane, E.; Schulkens, I.A.; Heusschen, R.; Castricum, K.; Leffler, H.; Griffioen, A.W.; Thijssen, V.L. Different angioregulatory activity of monovalent galectin-9 isoforms. Angiogenesis 2018, 21, 545–555.
- Audia, J.P.; Yang, X.-M.; Crockett, E.S.; Housley, N.; Haq, E.U.; O’Donnell, K.; Cohen, M.V.; Downey, J.M.; Alvarez, D.F. Caspase-1 inhibition by VX-765 administered at reperfusion in P2Y12 receptor antagonist-treated rats provides long-term reduction in myocardial infarct size and preservation of ventricular function. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2018, 113, 32.
- Erland, L.A.E.; Yasunaga, A.; Li, I.T.S.; Murch, S.J.; Saxena, P.K. Direct visualization of location and uptake of applied melatonin and serotonin in living tissues and their redistribution in plants in response to thermal stress. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 66, e12527.
- Ko, A.; Han, S.Y.; Choi, C.H.; Cho, H.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Song, J.S.; Hong, K.-M.; Lee, H.-W.; Hewitt, S.M.; et al. Oncogene-induced senescence mediated by c-Myc requires USP10 dependent deubiquitination and stabilization of p14ARF. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1050–1062.
- Jain, R.; Mintern, J.D.; Tan, I.; Dewson, G.; Strasser, A.; Gray, D.H.D. How do thymic epithelial cells die? Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1002–1004.
- Dickinson, J.D.; Sweeter, J.M.; Warren, K.J.; Ahmad, I.; De Deken, X.; Zimmerman, M.C.; Brody, S.L. Autophagy regulates DUOX1 localization and superoxide production in airway epithelial cells during chronic IL-13 stimulation. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 272–284.
- Köhler, D.; Bibli, S.-I.; Klammer, L.P.; Roth, J.M.; Lehmann, R.; Fleming, I.; Granja, T.F.; Straub, A.; Benz, P.M.; Rosenberger, P. Phosphorylation of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein contributes to myocardial ischemic preconditioning. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2018, 113, 11.
- Gandarillas, A.; Molinuevo, R.; Sanz-Gómez, N. Mammalian endoreplication emerges to reveal a potential developmental timer. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 471–476.
- Li, X.; Fang, P.; Mai, J.; Choi, E.T.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.-F. Targeting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species as novel therapy for inflammatory diseases and cancers. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 19.
- Jo, E.-K.; Kim, J.K.; Shin, D.-M.; Sasakawa, C. Molecular mechanisms regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 148–159.
- Naik, E.; Dixit, V.M. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species drive proinflammatory cytokine production. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 417–420.
- Twig, G.; Shirihai, O.S. The Interplay Between Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitophagy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1939–1951.
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive Oxygen Species in Inflammation and Tissue Injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167.
- West, A.P.; Khoury-Hanold, W.; Staron, M.; Tal, M.; Pineda, C.M.; Lang, S.M.; Bestwick, M.; Duguay, B.A.; Raimundo, N.; MacDuff, D.A.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA stress primes the antiviral innate immune response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 520, 553–557.
- Nakahira, K.; Haspel, J.A.; Rathinam, V.A.; Lee, S.-J.; Dolinay, T.; Lam, H.C.; Englert, J.A.; Rabinovitch, M.; Cernadas, M.; Kim, H.P.; et al. Autophagy proteins regulate innate immune responses by inhibiting the release of mitochondrial DNA mediated by the NALP3 inflammasome. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 222–230.
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062.
- Thellung, S.; Corsaro, A.; Nizzari, M.; Barbieri, F.; Florio, T. Autophagy Activator Drugs: A New Opportunity in Neuroprotection from Misfolded Protein Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 901.
- Szewczyk, A.; Wojtczak, L. Mitochondria as a pharmacological target. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 101–127.
- Javadov, S.; Karmazyn, M. Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore Opening as an Endpoint to Initiate Cell Death and as a Putative Target for Cardioprotection. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 20, 1–22.
- Kondapuram, S.K.; Sarvagalla, S.; Coumar, M.S. Targeting autophagy with small molecules for cancer therapy. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2019, 2019.
- Minamino, T.; Komuro, I.; Kitakaze, M. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress As a Therapeutic Target in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1071–1082.
- Xu, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Chang, R.; Zhang, C. Inflammasome inhibitors: Promising therapeutic approaches against cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1–13.
- Jung, T.W.; Choi, K.M. Pharmacological Modulators of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 192.
- Amen, O.M.; Sarker, S.D.; Ghildyal, R.; Arya, A. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Activates Unfolded Protein Response Signaling and Mediates Inflammation, Obesity, and Cardiac Dysfunction: Therapeutic and Molecular Approach. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 977.
- Zahid, A.; Li, B.; Kombe, A.J.K.; Jin, T.; Tao, J. Pharmacological Inhibitors of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2538.
- Rivas, A.; Vidal, R.L.; Hetz, C. Targeting the unfolded protein response for disease intervention. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 1–16.
- Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Pan, H.; Hu, P.; Hao, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhu, H.; Yu, A.D.; Xie, X.; Ma, D.; et al. Small molecule regulators of autophagy identified by an image-based high-throughput screen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19023–19028.
- Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg, H.; Xia, H.-G.; Yuan, J. Pharmacologic agents targeting autophagy. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 5–13.
- Shaw, S.Y.; Tran, K.; Castoreno, A.B.; Peloquin, J.M.; Lassen, K.G.; Khor, B.; Aldrich, L.; Tan, P.H.; Graham, D.B.; Kuballa, P.; et al. Selective Modulation of Autophagy, Innate Immunity, and Adaptive Immunity by Small Molecules. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2724–2733.
- Vucicevic, L.; Misirkic-Marjanovic, M.; Harhaji-Trajkovic, L.; Maric, N.; Trajkovic, V. Mechanisms and therapeutic significance of autophagy mdulation by antipsychotic drugs. Cell Stress 2018, 2, 282–291.
- Christ, M.G.; Clement, A.M.; Behl, C. The Sigma-1 Receptor at the Crossroad of Proteostasis, Neurodegeneration, and Autophagy. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 79–81.
- Hayashi, T.; Tsai, S.-Y.; Mori, T.; Fujimoto, M.; Su, T.-P. Targeting ligand-operated chaperone sigma-1 receptors in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 557–577.
- Albayrak, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Sigma-1 Receptor Agonists and Their Clinical Implications in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 964, 153–161.
- Liere, P.; Pianos, A.; Oudinet, J.-P.; Schumacher, M.; Akwa, Y. Differential effects of the 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) ligand etifoxine on steroidogenesis in rat brain, plasma and steroidogenic glands: Pharmacodynamic studies. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 83, 122–134.
- Costa, B.; Cavallini, C.; Da Pozzo, E.; Taliani, S.; Da Settimo, F.; Martini, C. The Anxiolytic Etifoxine Binds to TSPO Ro5-4864 Binding Site with Long Residence Time Showing a High Neurosteroidogenic Activity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1448–1454.
- Panda, P.K.; Fahrner, A.; Vats, S.; Seranova, E.; Sharma, V.; Chipara, M.; Desai, P.; Torresi, J.; Rosenstock, T.; Kumar, D.; et al. Chemical Screening Approaches Enabling Drug Discovery of Autophagy Modulators for Biomedical Applications in Human Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 38.
- Tsaytler, P.; Harding, H.; Ron, D.; Bertolotti, A. Selective Inhibition of a Regulatory Subunit of Protein Phosphatase 1 Restores Proteostasis. Science 2011, 332, 91–94.
- Pérez-Arancibia, R.; Rivas, A.; Hetz, C.; Pérez, R. (off)Targeting UPR signaling: The race toward intervening ER proteostasis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 22, 97–100.
- Allen, G.F.G.; Toth, R.; James, J.; Ganley, I. Loss of iron triggers PINK1/Parkin-independent mitophagy. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 1127–1135.
- Renna, M.; Jimenez-Sanchez, M.; Sarkar, S.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Chemical Inducers of Autophagy That Enhance the Clearance of Mutant Proteins in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 11061–11067.
- Goodall, M.L.; Wang, T.; Martin, K.R.; Kortus, M.G.; Kauffman, A.L.; Trent, J.M.; Gately, S.; MacKeigan, J.P. Development of potent autophagy inhibitors that sensitize oncogenic BRAF V600E mutant melanoma tumor cells to vemurafenib. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1120–1136.
- Khurana, A.; Roy, D.; Kalogera, E.; Mondal, S.; Wen, X.; He, X.; Dowdy, S.; Shridhar, V. Quinacrine promotes autophagic cell death and chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer and attenuates tumor growth. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 36354–36369.
- Liu, L.; Li, C.-J.; Lu, Y.; Zong, X.-G.; Luo, C.; Sun, J.; Guo, L.-J. Baclofen mediates neuroprotection on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells through the regulation of autophagy under chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep14474.
- Ferrari-Toninelli, G.; Maccarinelli, G.; Uberti, D.L.; Buerger, E.; Memo, M. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant effects of S(-) and R(+) pramipexole. BMC Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 2.
- Takayasu, Y.; Nakaki, J.; Kawasaki, T.; Koda, K.; Ago, Y.; Baba, A.; Matsuda, T. Edaravone, a Radical Scavenger, Inhibits Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore in Rat Brain. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 103, 434–437.
- Huang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Tao, J.; Deng, X.; Liang, G.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.; et al. Tranilast directly targets NLRP 3 to treat inflammasome-driven diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8689.
- Almanza, A.; Carlesso, A.; Chintha, C.; Creedican, S.; Doultsinos, D.; Leuzzi, B.; Luís, A.; McCarthy, N.; Montibeller, L.; More, S.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling—from basic mechanisms to clinical applications. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 241–278.




