
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rui Han | -- | 3467 | 2023-09-24 14:40:07 | | | |
| 2 | Lindsay Dong | + 5 word(s) | 3472 | 2023-09-25 04:13:08 | | |
Video Upload Options
Breast cancer (BC) is a lethal malignancy with high morbidity and mortality but lacks effective treatments thus far. Histone deacetylases 2 (HDAC2) inhibitor (HDAC2i) has been proven to exhibit an anti-cancer effect, can act as a sensitizer for immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) therapy. Simultaneously, dietary intervention, as a crucial supportive therapy, has been reported to provide ingredients containing HDAC2 inhibitory activity. Thus, the novel integration of dietary intervention with ICIs therapy may offer promising possibilities for improving treatment outcomes.
1. Introduction
2. Dietary HDAC2i in Breast Cancer
2.1. HDAC2: A Potential Index of Aggressiveness and a Therapeutic Target against BC
2.2. HDAC2 Inhibition for Treating Breast Cancer
2.3. HDAC2 Inhibition Enhances the Therapeutic Effect of ICIs in BC Treatment
The emergence of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) has revolutionized the treatment of breast cancer [29][30][31][32][33][34][35][36]. Adjuvant or neoadjuvant immune checkpoint blockades are used for metastatic breast cancer [30]. Despite ICI therapy being promising, breast cancer cells often find ways to evade the host’s immune system, necessitating combination therapies to overcome these limitations. HDAC inhibitors (HDACi) have demonstrated potent immunomodulatory activity, making them a rational choice for cancer immunotherapies.
2.3.1. HDAC2 Regulates PD-L1 Nuclear Translocation
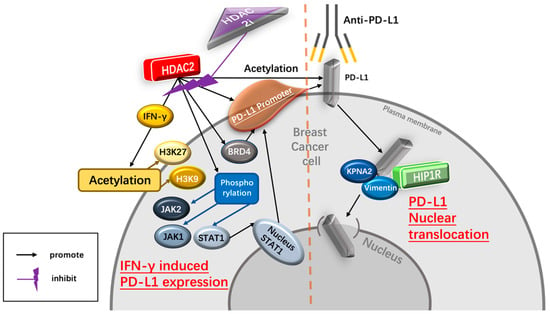
2.3.2. HDAC2 Regulates IFN-γ- Induced PD-L1 Expression
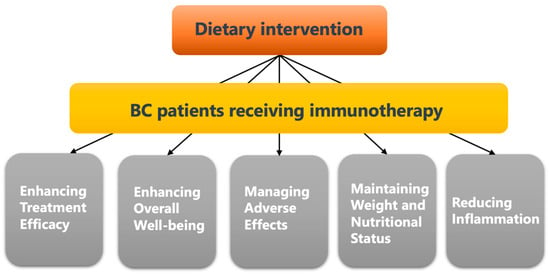
IFN-γ upregulates the expression of PD-L12.4. Dietary Intervention Is Important for Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Anti-Cancer Immunotherapy
2.5. Dietary HDAC2i
2.6. Selected Candidates of HDAC2i
2.6.1. Genistein (GE)
2.6.2. Sulforaphane (SFN)
2.6.3. Chrysin and Its Analogues
2.6.4. Resveratrol (RSV)
2.6.5. Oleuropein (OLE)
2.6.6. Curcumin
2.6.7. Valeric Acid
2.6.8. Rh4
2.6.9. Butyrate (NaB)
2.6.10. Other Potential Candidates
2.7. Potential Approaches of Taking Bioactive Compound
2.8. Nutrients That May Impair the Therapeutic Effect of ICIs
References
- Tao, X.; Li, T.; Gandomkar, Z.; Brennan, P.C.; Reed, W.M. Incidence, mortality, survival, and disease burden of breast cancer in China compared to other developed countries. Asia-Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023.
- Bazzi, T.; Al-Husseini, M.; Saravolatz, L.; Kafri, Z. Trends in Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality in the United States From 2004-2018: A Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Based Study. Cureus 2023, 15, e37982.
- Pedersini, R.; di Mauro, P.; Bosio, S.; Zanini, B.; Zanini, A.; Amoroso, V.; Turla, A.; Vassalli, L.; Ardine, M.; Monteverdi, S.; et al. Changes in eating habits and food preferences in breast cancer patients undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12975.
- Taylor, C.; McGale, P.; Probert, J.; Broggio, J.; Charman, J.; Darby, S.C.; Kerr, A.J.; Whelan, T.; Cutter, D.J.; Mannu, G.; et al. Breast cancer mortality in 500 000 women with early invasive breast cancer in England, 1993–2015: Population based observational cohort study. BMJ 2023, 381, e074684.
- Bertucci, F.; Gonçalves, A. Immunotherapy in Breast Cancer: The Emerging Role of PD-1 and PD-L1. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 19, 64.
- Lu, L.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Z. Elevated T cell activation score is associated with improved survival of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 164, 689–696.
- Jacob, S.L.; Huppert, L.A.; Rugo, H.S. Role of Immunotherapy in Breast Cancer. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2023, 19, 167–179.
- Hattori, M.; Masuda, N.; Takano, T.; Tsugawa, K.; Inoue, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Itoh, M.; Yasojima, H.; Tanabe, Y.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in Japanese patients with triple-negative breast cancer: Results from KEYNOTE-355. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 10280–10293.
- Downs-Canner, S.; Mittendorf, E.A. Correction: Preoperative Immunotherapy Combined with Chemotherapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Perspective on the KEYNOTE-522 Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3286.
- Khalid, A.B.; Calderon, G.; Jalal, S.I.; Durm, G.A. Physician Awareness of Immune-Related Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat 2022, 20, 1316–1320.
- Gumusay, O.; Callan, J.; Rugo, H.S. Immunotherapy toxicity: Identification and management. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 192, 1–17.
- Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T.; Niu, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, G. Antitumor activity and mechanism of resistance of the novel HDAC and PI3K dual inhibitor CUDC-907 in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 415–423.
- Garmpis, N.; Damaskos, C.; Dimitroulis, D.; Kouraklis, G.; Garmpi, A.; Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Patsouras, A.; Psilopatis, I.; Antoniou, E.A.; et al. Clinical Significance of the Histone Deacetylase 2 (HDAC-2) Expression in Human Breast Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1672.
- Shan, W.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, H.; Huang, Q.; Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Mi, Q.; Zhang, K.; Yang, Z. HDAC2 overexpression correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features and DNA-damage response pathway of breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 1213–1226.
- Zhao, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, L.; He, M.; Ren, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, Q.; Yao, W.; Wei, M. HDAC2 overexpression is a poor prognostic factor of breast cancer patients with increased multidrug resistance-associated protein expression who received anthracyclines therapy. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 46, 893–902.
- Maccallini, C.; Ammazzalorso, A.; De Filippis, B.; Fantacuzzi, M.; Giampietro, L.; Amoroso, R. HDAC Inhibitors for the Therapy of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 667.
- Li, Y.; Seto, E. HDACs and HDAC Inhibitors in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026831.
- Xu, P.; Xiong, W.; Lin, Y.; Fan, L.; Pan, H.; Li, Y. Histone deacetylase 2 knockout suppresses immune escape of triple-negative breast cancer cells via downregulating PD-L1 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 779.
- Gao, Y.; Nihira, N.T.; Bu, X.; Chu, C.; Zhang, J.; Kolodziejczyk, A.; Fan, Y.; Chan, N.T.; Ma, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Acetylation-dependent regulation of PD-L1 nuclear translocation dictates the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 1064–1075.
- Bassett, S.A.; Barnett, M.P.G. The Role of Dietary Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) Inhibitors in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4273–4301.
- Muller, B.M.; Jana, L.; Kasajima, A.; Lehmann, A.; Prinzler, J.; Budczies, J.; Winzer, K.-J.; Dietel, M.; Weichert, W.; Denkert, C. Differential expression of histone deacetylases HDAC1, 2 and 3 in human breast cancer—Overexpression of HDAC2 and HDAC3 is associated with clinicopathological indicators of disease progression. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 215.
- Long, M.; Hou, W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, T. A Histone Acetylation Modulator Gene Signature for Classification and Prognosis of Breast Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 928–939.
- Choi, S.R.; Hwang, C.Y.; Lee, J.; Cho, K.-H. Network Analysis Identifies Regulators of Basal-Like Breast Cancer Reprogramming and Endocrine Therapy Vulnerability. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 320–333.
- Harms, K.L.; Chen, X. Histone Deacetylase 2 Modulates p53 Transcriptional Activities through Regulation of p53-DNA Binding Activity. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3145–3152.
- He, X.-H.; Zhu, W.; Yuan, P.; Jiang, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.-W.; Liu, M.-F. miR-155 downregulates ErbB2 and suppresses ErbB2-induced malignant transformation of breast epithelial cells. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6015–6025.
- Jo, H.; Shim, K.; Kim, H.-U.; Jung, H.S.; Jeoung, D. HDAC2 as a target for developing anti-cancer drugs. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 2048–2057.
- Biçaku, E.; Marchion, D.C.; Schmitt, M.L.; Münster, P.N. Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 2 Silences Progesterone Receptor–Mediated Signaling. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1513–1519.
- Marchion, D.C.; Bicaku, E.; Turner, J.G.; Schmitt, M.L.; Morelli, D.R.; Munster, P.N. HDAC2 regulates chromatin plasticity and enhances DNA vulnerability. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 794–801.
- Masoumi, E.; Tahaghoghi-Hajghorbani, S.; Jafarzadeh, L.; Sanaei, M.-J.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Bashash, D. The application of immune checkpoint blockade in breast cancer and the emerging role of nanoparticle. J. Control. Release 2021, 340, 168–187.
- Isaacs, J.; Anders, C.; McArthur, H.; Force, J. Biomarkers of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2021, 22, 38.
- Lu, L.; Risch, E.; Halaban, R.; Zhen, P.; Bacchiocchi, A.; Risch, H.A. Dynamic changes of circulating soluble PD-1/PD-L1 and its association with patient survival in immune checkpoint blockade-treated melanoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110092.
- Fan, Z.; Wu, C.; Chen, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Mao, R.; Fan, Y. The generation of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in cancer cells: From nuclear chromatin reorganization to extracellular presentation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1041–1053.
- Xiong, W.; Gao, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhang, J. Extracellular and nuclear PD-L1 in modulating cancer immunotherapy. Trends Cancer 2021, 7, 837–846.
- Koh, Y.W.; Han, J.-H.; Haam, S.; Lee, H.W. HIP1R Expression and Its Association with PD-1 Pathway Blockade Response in Refractory Advanced NonSmall Cell Lung Cancer: A Gene Set Enrichment Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1425.
- Muenst, S.; Schaerli, A.R.; Gao, F.; Däster, S.; Trella, E.; Droeser, R.A.; Muraro, M.G.; Zajac, P.; Zanetti, R.; Gillanders, W.E.; et al. Expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 15–24.
- Lotfinejad, P.; Kazemi, T.; Safaei, S.; Amini, M.; Baghbani, E.; Shotorbani, S.S.; Niaragh, F.J.; Derakhshani, A.; Shadbad, M.A.; Silvestris, N. PD-L1 silencing inhibits triple-negative breast cancer development and upregulates T-cell-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111436.
- Minn, A.J.; Wherry, E.J. Combination Cancer Therapies with Immune Checkpoint Blockade: Convergence on Interferon Signaling. Cell 2016, 165, 272–275.
- Abiko, K.; Matsumura, N.; Hamanishi, J.; Horikawa, N.; Murakami, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Baba, T.; Konishi, I.; Mandai, M. IFN-γ from lymphocytes induces PD-L1 expression and promotes progression of ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1501–1509.
- Bouhet, S.; Lafont, V.; Billard, E.; Gross, A.; Dornand, J. The IFNgamma-induced STAT1-CBP/P300 association, required for a normal response to the cytokine, is disrupted in Brucella-infected macrophages. Microb. Pathog. 2009, 46, 88–97.
- Calder, P.C. Foods to deliver immune-supporting nutrients. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 136–145.
- Calder, P.C.; Carr, A.G.; Gombart, A.F.; Eggersdorfer, M. Reply to Comment on: Optimal Nutritional Status for a Well-Functioning Immune System Is an Important Factor to Protect against Viral Infections. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1181.
- Chen, O.; Mah, E.; Dioum, E.; Marwaha, A.; Shanmugam, S.; Malleshi, N.; Sudha, V.; Gayathri, R.; Unnikrishnan, R.; Anjana, R.M.; et al. The Role of Oat Nutrients in the Immune System: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1048.
- Noor, S.; Piscopo, S.; Gasmi, A. Nutrients Interaction with the Immune System. Arch. Razi. Inst. 2021, 76, 1579–1588.
- Kichloo, A.; Albosta, M.; Dahiya, D.; Guidi, J.C.; Aljadah, M.; Singh, J.; Shaka, H.; Wani, F.; Kumar, A.; Lekkala, M. Systemic adverse effects and toxicities associated with immunotherapy: A review. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 12, 150–163.
- Ticinesi, A.; Nouvenne, A.; Chiussi, G.; Castaldo, G.; Guerra, A.; Meschi, T. Calcium Oxalate Nephrolithiasis and Gut Microbiota: Not just a Gut-Kidney Axis. A Nutritional Perspective. Nutrients 2020, 12, 548.
- Taraszewska, A. Risk factors for gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms related to lifestyle and diet. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig 2021, 72, 21–28.
- Jadhav, A.; Bajaj, A.; Xiao, Y.; Markandey, M.; Ahuja, V.; Kashyap, P.C. Role of Diet–Microbiome Interaction in Gastrointestinal Disorders and Strategies to Modulate Them with Microbiome-Targeted Therapies. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2023, 43, 355–383.
- Martínez-Garay, C.; Djouder, N. Dietary interventions and precision nutrition in cancer therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 489–511.
- Vernieri, C.; Casola, S.; Foiani, M.; Pietrantonio, F.; De Braud, F.; Longo, V. Targeting Cancer Metabolism: Dietary and Pharmacologic Interventions. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1315–1333.
- Bose, S.; Allen, A.E.; Locasale, J.W. The Molecular Link from Diet to Cancer Cell Metabolism. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 1034–1044.
- Locasale, J.W. Diet and Exercise in Cancer Metabolism. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2249–2257.
- Morita, M.; Kudo, K.; Shima, H.; Tanuma, N. Dietary intervention as a therapeutic for cancer. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 498–504.
- Patra, S.; Pradhan, B.; Nayak, R.; Behera, C.; Das, S.; Patra, S.K.; Efferth, T.; Jena, M.; Bhutia, S.K. Dietary polyphenols in chemoprevention and synergistic effect in cancer: Clinical evidences and molecular mechanisms of action. Phytomedicine 2021, 90, 153554.
- Zhou, Y.; Li, H. Neurological adverse events associated with PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1227049.
- Alturki, N.A. Review of the Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Context of Cancer Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4301.
- Zraik, I.M.; Heß-Busch, Y. Management of chemotherapy side effects and their long-term sequelae. Urologe A 2021, 60, 862–871.
- Buchholz, T.A. Radiation Therapy for Early-Stage Breast Cancer after Breast-Conserving Surgery. New Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 63–70.
- Zhang, C.; Xu, C.; Gao, X.; Yao, Q. Platinum-based drugs for cancer therapy and anti-tumor strategies. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2115–2132.
- Wu, Q.; Gao, Z.-J.; Yu, X.; Wang, P. Dietary regulation in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 252.
- Prado, C.M.; Antoun, S.; Sawyer, M.B.; Baracos, V.E. Two faces of drug therapy in cancer: Drug-related lean tissue loss and its adverse consequences to survival and toxicity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 250–254.
- Soldati, L.; Di Renzo, L.; Jirillo, E.; Ascierto, P.A.; Marincola, F.M.; De Lorenzo, A. The influence of diet on anti-cancer immune responsiveness. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 75.
- Greathouse, K.L.; Wyatt, M.; Johnson, A.J.; Toy, E.P.; Khan, J.M.; Dunn, K.; Clegg, D.J.; Reddy, S. Diet-microbiome interactions in cancer treatment: Opportunities and challenges for precision nutrition in cancer. Neoplasia 2022, 29, 100800.
- Tao, J.; Li, S.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Meng, X.; Li, H.-B. Targeting gut microbiota with dietary components on cancer: Effects and potential mechanisms of action. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1025–1037.
- Dieli-Conwright, C.M.; Harrigan, M.; Cartmel, B.; Chagpar, A.; Bai, Y.; Li, F.-Y.; Rimm, D.L.; Pusztai, L.; Lu, L.; Sanft, T.; et al. Impact of a randomized weight loss trial on breast tissue markers in breast cancer survivors. npj Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 29.
- Puklin, L.; Cartmel, B.; Harrigan, M.; Lu, L.; Li, F.-Y.; Sanft, T.; Irwin, M.L. Randomized trial of weight loss on circulating ghrelin levels among breast cancer survivors. npj Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 49.
- Thomas, G.A.; Alvarez-Reeves, M.; Lu, L.; Yu, H.; Irwin, M.L. Effect of Exercise on Metabolic Syndrome Variables in Breast Cancer Survivors. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 168797.
- Zeng, H.; Irwin, M.L.; Lu, L.; Risch, H.; Mayne, S.; Mu, L.; Deng, Q.; Scarampi, L.; Mitidieri, M.; Katsaros, D.; et al. Physical activity and breast cancer survival: An epigenetic link through reduced methylation of a tumor suppressor gene L3MBTL1. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 127–135.
- Garbiec, E.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Kowalówka, M.; Hołubiec, M.; Zalewski, P. Genistein—Opportunities Related to an Interesting Molecule of Natural Origin. Molecules 2022, 27, 815.
- Sharma, M.; Arora, I.; Chen, M.; Wu, H.; Crowley, M.R.; Tollefsbol, T.O.; Li, Y. Therapeutic Effects of Dietary Soybean Genistein on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer via Regulation of Epigenetic Mechanisms. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3944.
- Çakır, I.; Pan, P.L.; Hadley, C.K.; El-Gamal, A.; Fadel, A.; Elsayegh, D.; Mohamed, O.; Rizk, N.M. Is a corresponding author Masoud Ghamari-Langroudi. Sulforaphane reduces obesity by reversing leptin resistance. Elife 2022, 11, e67368.
- Xie, Q.; Bai, Q.; Zou, L.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, H.; Yi, L.; Zhu, J.-D.; Mi, M.-T. Genistein inhibits DNA methylation and increases expression of tumor suppressor genes in human breast cancer cells. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2014, 53, 422–431.
- Tortorella, S.M.; Royce, S.G.; Licciardi, P.V.; Karagiannis, T.C. Dietary Sulforaphane in Cancer Chemoprevention: The Role of Epigenetic Regulation and HDAC Inhibition. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 1382–1424.
- Paul, B.; Li, Y.; Tollefsbol, T.O. The Effects of Combinatorial Genistein and Sulforaphane in Breast Tumor Inhibition: Role in Epigenetic Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1754.
- Middleton, E., Jr.; Kandaswami, C.; Theoharides, T.C. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 673–751.
- Chang, H.; Mi, M.; Ling, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, N.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, J. Structurally related cytotoxic effects of flavonoids on human cancer cells in vitro. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2008, 31, 1137–1144.
- Androutsopoulos, V.; Papakyriakou, A.; Vourloumis, D.; Spandidos, D.A. Comparative CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 substrate and inhibitor profile of dietary flavonoids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 2842–2849.
- Pal-Bhadra, M.; Ramaiah, M.J.; Reddy, T.L.; Krishnan, A.; Pushpavalli, S.; Babu, K.S.; Tiwari, A.K.; Rao, J.M.; Yadav, J.S.; Bhadra, U. Plant HDAC inhibitor chrysin arrest cell growth and induce p21 WAF1 by altering chromatin of STAT response element in A375 cells. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 180.
- Sedlak, L.; Wojnar, W.; Zych, M.; Wyględowska-Promieńska, D.; Mrukwa-Kominek, E.; Kaczmarczyk-Sedlak, I. Effect of Resveratrol, a Dietary-Derived Polyphenol, on the Oxidative Stress and Polyol Pathway in the Lens of Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1423.
- Galiniak, S.; Aebisher, D.; Bartusik-Aebisher, D. Health benefits of resveratrol administration. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2019, 66, 13–21.
- Venturelli, S.; Berger, A.; Böcker, A.; Busch, C.; Weiland, T.; Noor, S.; Leischner, C.; Schleicher, S.; Mayer, M.; Weiss, T.S.; et al. Resveratrol as a pan-HDAC inhibitor alters the acetylation status of histone proteins in human-derived hepatoblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73097.
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Ahn, K.S. An updated review on the potential antineoplastic actions of oleuropein. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 365–379.
- Bayat, S.; Derakhshan, S.M.; Derakhshan, N.M.; Khaniani, M.S.; Alivand, M.R. Downregulation of HDAC2 and HDAC3 via oleuropein as a potent prevention and therapeutic agent in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9172–9180.
- Jabczyk, M.; Nowak, J.; Hudzik, B.; Zubelewicz-Szkodzińska, B. Curcumin in Metabolic Health and Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4440.
- Han, R.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Ling, C.; Lu, L. Valeric acid acts as a novel HDAC3 inhibitor against prostate cancer. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 213.
- Wu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Qu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D. Gastroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rh4 against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury by inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 5167–5181.
- Dong, F.; Qu, L.; Duan, Z.; He, Y.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rh4 inhibits breast cancer growth through targeting histone deacetylase 2 to regulate immune microenvironment and apoptosis. Bioorganic Chem. 2023, 135, 106537.
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; He, T.; Becker, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, D.; Ma, X. Butyrate: A Double-Edged Sword for Health? Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 21–29.
- Fan, P.; Li, L.; Rezaei, A.; Eslamfam, S.; Che, D.; Ma, X. Metabolites of Dietary Protein and Peptides by Intestinal Microbes and their Impacts on Gut. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2015, 16, 646–654.
- Canani, R.B.; Di Costanzo, M.; Leone, L.; Pedata, M.; Meli, R.; Calignano, A. Potential beneficial effects of butyrate in intestinal and extraintestinal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1519–1528.
- Andrade, F.; Nagamine, M.; De Conti, A.; Chaible, L.; Fontelles, C.; Junior, A.J.; Vannucchi, H.; Dagli, M.; Bassoli, B.; Moreno, F.; et al. Efficacy of the dietary histone deacetylase inhibitor butyrate alone or in combination with vitamin A against proliferation of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 841–850.
- Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, C.-C.; Li, S.; Zhan, J.; Ho, C.-T. Immunomodulatory Effects of Green Tea Polyphenols. Molecules 2021, 26, 3755.
- Thakur, V.S.; Gupta, K.; Gupta, S. Green tea polyphenols causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by suppressing class I histone deacetylases. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 377–384.
- Dima, C.; Assadpour, E.; Nechifor, A.; Dima, S.; Li, Y.; Jafari, S.M. Oral bioavailability of bioactive compounds; modulating factors, in vitro analysis methods, and enhancing strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–39.
- Rosenfeld, R.M.; Juszczak, H.M.; Wong, M.A. Scoping review of the association of plant-based diet quality with health out-comes. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1211535.
- Li, B.; Shao, H.; Gao, L.; Li, H.; Sheng, H.; Zhu, L. Nano-drug co-delivery system of natural active ingredients and chemotherapy drugs for cancer treatment: A review. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2130–2161.
- Nakagawa, Y.; Mukai, S.; Yamada, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Tarumi, E.; Hashimoto, T.; Tamura, C.; Imaizumi, A.; Nishihira, J.; Nakamura, T. Short-term effects of highly-bioavailable curcumin for treating knee osteoarthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled prospective study. J. Orthop. Sci. 2014, 19, 933–939.
- Kanai, M.; Imaizumi, A.; Otsuka, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Hashiguchi, M.; Tsujiko, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Ishiguro, H.; Chiba, T. Dose-escalation and pharmacokinetic study of nanoparticle curcumin, a potential anticancer agent with improved bioavailability, in healthy human volunteers. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 65–70.
- Sasaki, H.; Sunagawa, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Imaizumi, A.; Fukuda, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Wada, H.; Katanasaka, Y.; Kakeya, H.; Fujita, M.; et al. Innovative Preparation of Curcumin for Improved Oral Bioavailability. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 660–665.
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, X.; Shen, L.; Feng, Y. Drug delivery for bioactive polysaccharides to improve their drug-like properties and curative efficacy. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24 (Suppl. 1), 70–80.
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, a component of golden spice: From bedside to bench and back. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1053–1064.
- Passos, C.L.A.; Polinati, R.M.; Ferreira, C.; dos Santos, N.A.N.; Lima, D.G.V.; da Silva, J.L.; Fialho, E. Curcumin and melphalan cotreatment induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13446.
- Nootim, P.; Kapol, N.; Bunchuailua, W.; Poompruek, P.; Tungsukruthai, P. Current state of cancer patient care incorporating Thai traditional medicine in Thailand: A qualitative study. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 18, 41–45.
- Yazdi, N.; Salehi, A.; Vojoud, M.; Sharifi, M.H.; Hoseinkhani, A. Use of complementary and alternative medicine in pregnant women: A cross-sectional survey in the south of Iran. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 17, 392–395.
- Ouyang, W.; Meng, Y.; Guo, G.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, X. Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 600.
- Bu, Z.-J.; Liu, Y.-N.; Shahjalal, M.; Zheng, Y.-Y.; Liu, C.-J.; Ye, M.-M.; Xu, J.-Y.; Peng, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-H.; Chen, X.; et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of Chinese medicine belly button application for childhood diarrhea: A Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1180694.
- Kromhout, D.; Yasuda, S.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Shimokawa, H. Fish oil and omega-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular disease: Do they really work? Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 436–443.
- Björkström, N.K.; Strunz, B.; Ljunggren, H.-G. Natural killer cells in antiviral immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 112–123.
- Thies, F.; Nebe-von-Caron, G.; Powell, J.R.; Yaqoob, P.; Newsholme, E.A.; Calder, P.C. Dietary supplementation with eicosapentaenoic acid, but not with other long-chain n-3 or n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, decreases natural killer cell activity in healthy subjects aged >55 y. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 539–548.
- Fortmann, S.P.; Burda, B.U.; Senger, C.A.; Lin, J.S.; Whitlock, E.P. Vitamin and Mineral Supplements in the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer: An Updated Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 824–834.
- Beck, K.L.; von Hurst, P.R.; O’Brien, W.J.; Badenhorst, C.E. Micronutrients and athletic performance: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 158, 112618.
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Lv, X.; Hu, L.; Li, W.; Zi, M.; He, Y. Impact of Diets on Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs) Therapy against Tumors. Life 2022, 12, 409.
- Kim, S.-K.; Guevarra, R.B.; Kim, Y.-T.; Kwon, J.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, J.-H. Role of Probiotics in Human Gut Microbiome-Associated Diseases. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1335–1340.
- Bedada, T.L.; Feto, T.K.; Awoke, K.S.; Garedew, A.D.; Yifat, F.T.; Birri, D.J. Probiotics for cancer alternative prevention and treatment. BioMedicine 2020, 129, 110409.
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Mor, U.; Dori-Bachash, M.; Bashiardes, S.; Zur, M.; Regev-Lehavi, D.; Brik, R.B.-Z.; Federici, S.; et al. Post-Antibiotic Gut Mucosal Microbiome Reconstitution Is Impaired by Probiotics and Improved by Autologous FMT. Cell 2018, 174, 1406–1423.e16.
- Spencer, C.N.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; McQuade, J.; Andrews, M.C.; Helmink, B.; Khan, M.W.; Sirmans, E.; Haydu, L.; Cogdill, A.; Burton, E.; et al. Abstract 2838: The gut microbiome (GM) and immunotherapy response are influenced by host lifestyle factors. Cancer Res 2019, 79 (Suppl. 13), 2838.
- Kuang, R.; Binion, D.G. Should high-fiber diets be recommended for patients with inflammatory bowel disease? Curr. Opin. Gas-Troenterol. 2022, 38, 168–172.
- Marques, F.Z.; Nelson, E.; Chu, P.-Y.; Horlock, D.; Fiedler, A.; Ziemann, M.; Tan, J.K.; Kuruppu, S.; Rajapakse, N.W.; El-Osta, A.; et al. High-Fiber Diet and Acetate Supplementation Change the Gut Microbiota and Prevent the Development of Hypertension and Heart Failure in Hypertensive Mice. Circulation 2017, 135, 964–977.
- Kocher, F.; Amann, A.; Zimmer, K.; Geisler, S.; Fuchs, D.; Pichler, R.; Wolf, D.; Kurz, K.; Seeber, A.; Pircher, A. High indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO) activity is linked to primary resistance to immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 304–313.
- Weber, D.D.; Aminzadeh-Gohari, S.; Tulipan, J.; Catalano, L.; Feichtinger, R.G.; Kofler, B. Ketogenic diet in the treatment of cancer—Where do we stand? Mol. Metab. 2020, 33, 102–121.
- Lussier, D.M.; Woolf, E.C.; Johnson, J.L.; Brooks, K.S.; Blattman, J.N.; Scheck, A.C. Enhanced immunity in a mouse model of malignant glioma is mediated by a therapeutic ketogenic diet. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 310.
- Orillion, A.R.; Damayanti, N.P.; Shen, L.; Adelaiye-Ogala, R.; Affronti, H.C.; Elbanna, M.; Chintala, S.; Ciesielski, M.J.; Fontana, L.; Kao, C.; et al. Dietary Protein Restriction Reprograms Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Enhances Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6383–6395.





