
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jeongik Lee | -- | 3584 | 2022-04-29 05:21:52 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 3584 | 2022-04-29 09:36:12 | | |
Video Upload Options
Cancer is an extensive disease and the most common cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. It is characterized by a deregulation of the cell cycle, which primarily results in a progressive loss of control of cellular growth and differentiation. The repurposing of veterinary antiparasitic drugs for the treatment of cancer is gaining traction, as supported by existing literature. A prominent example is the proposal to implement the use of veterinary antiparasitics such as benzimidazole carbamates and halogenated salicylanilides as novel anticancer drugs. These agents have revealed pronounced anti-tumor activities and gained special attention for “double repositioning”, as they are repurposed for different species and diseases simultaneously, acting via different mechanisms depending on their target. As anticancer agents, these compounds employ several mechanisms, including the inhibition of oncogenic signal transduction pathways of mitochondrial respiration and the inhibition of cellular stress responses.
1. Introduction
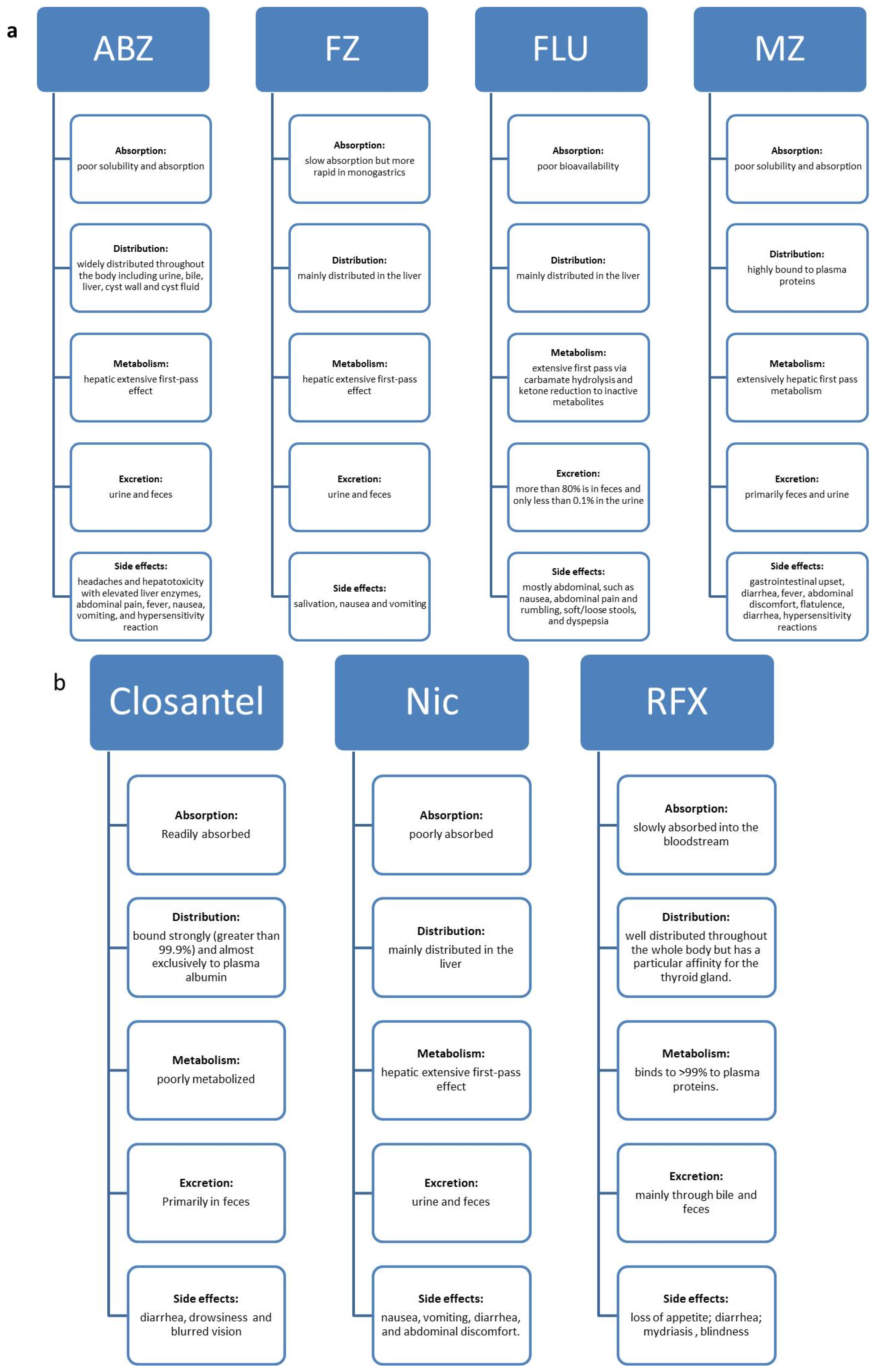
2. BZ Carbamates
2.1. Mechanism of Action of BZ Carbamates
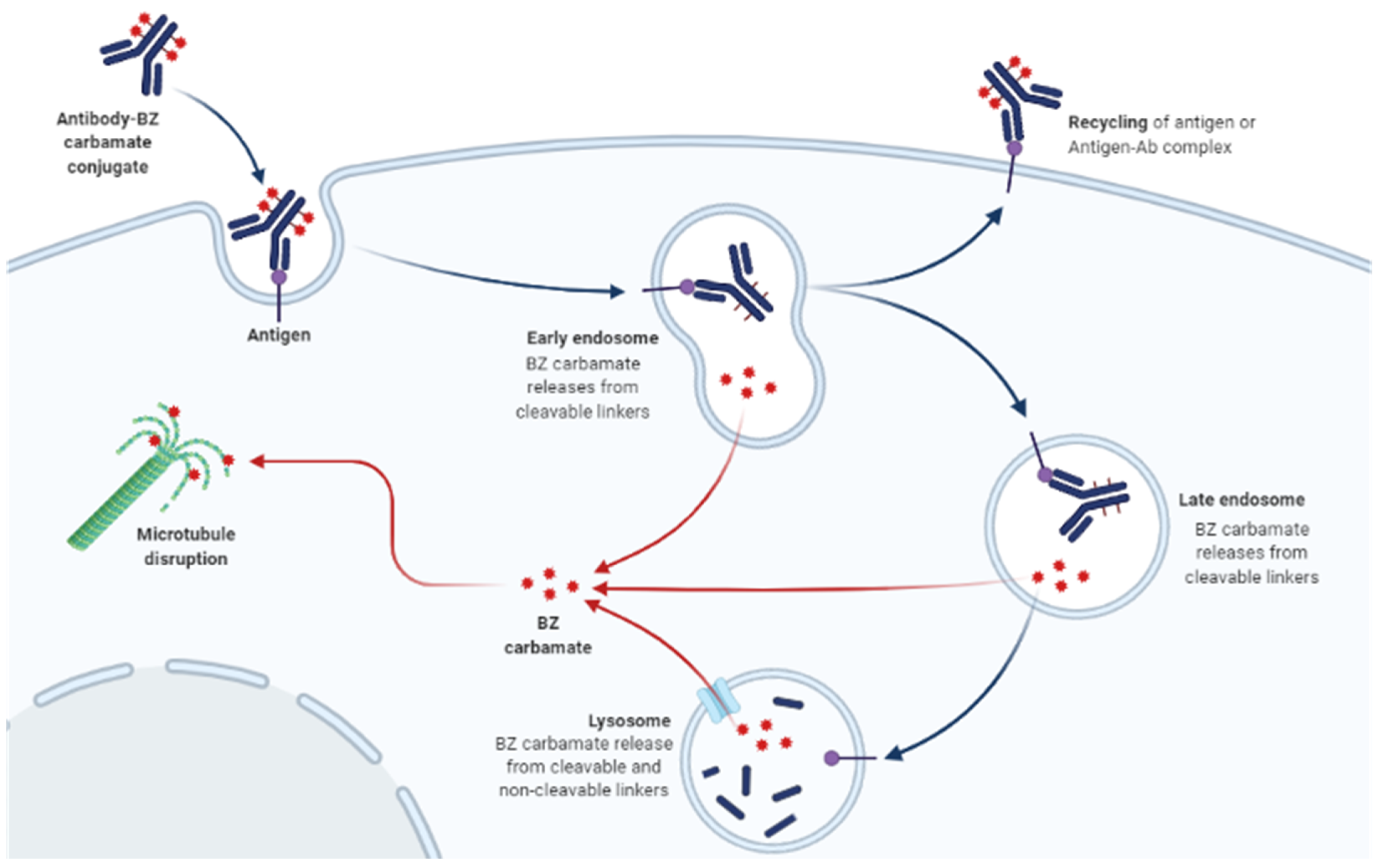
2.2. Anticancer Activity of BZ Carbamates
|
Cell Source |
Cell Lines |
Procedure of Study |
Species |
Antiparasitics |
Cancer Type |
Target Pathway |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Human |
Hep G2 and Hep3B |
in vitro |
Mice |
ABZ |
HCC |
Cytotoxicity |
[12] |
|
Human |
Hep G2 and Hep3B, PLC/PRF/5 and SKHEP-1 |
in vitro |
Mice |
ABZ |
HCC |
Tubulin disruption |
[13] |
|
SKHEP-1 |
in vivo |
||||||
|
Rat |
HTC, Novikoff |
in vitro |
|||||
|
Mice |
Hep1-6 |
in vitro |
|||||
|
Human |
SW480, SW620, HCT8 and Caco2 |
in vitro |
Mice |
ABZ, RBZ, FLU |
Intestinal cancer |
Tubulin disruption |
[14] |
|
Human |
HT-29 |
in vitro |
Mice |
ABZ |
CRC |
Apoptosis |
[15] |
|
Human |
CEM/dEpoB300 |
in vitro |
Mice |
ABZ |
Leukemia |
Apoptosis |
[16] |
|
Human |
1A9Pc TX22 |
in vitro |
Mice |
ABZ |
OC |
Apoptosis |
[17] |
|
Mouse |
EMT6 |
in vitro |
Mice |
FZ |
Mammary carcinoma |
Cytotoxicity |
[18] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
H460 and A549 |
in vitro |
nu/nu mice |
FZ |
LC |
microtubule disruption, p53 activation and down regulation of pivotal glycolytic enzymes |
[19] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
P493-6 |
in vitro |
SCID mice |
FZ |
Lymphoma |
Tubulin disruption |
[20] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Mice |
EMT6 |
in vitro |
BALB/c Rw mice |
FZ |
Mammary carcinoma |
Tubulin disruption |
[21] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
OCI-AML-2 |
in vitro |
SCID mice |
FLU |
Leukaemia and Myeloma |
Tubulin disruption |
[22] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
MDA-MB-231, BT-549, SK-BR-3 and MCF-7 |
in vitro |
Mice |
FLU |
BC |
Tubulin disruption |
[23] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
TNBC cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 |
in vitro |
Mice |
FLU |
BC |
Apoptosis |
[24] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
BT474, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-453, JIMT-1 |
in vitro |
BALB/c mice |
FLU |
BC |
Tubulin disruption |
[25] |
|
in vivo |
Apoptosis |
||||||
|
Human |
HCT116, RKO and SW480 |
in vitro |
BALB/c mice |
FLU |
CRC |
Apoptosis |
[26] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
H295R and SW-13 |
in vitro |
Mice |
MZ |
Adrenocortical carcinoma |
Apoptosis |
[27] |
|
Human |
H460, A549, H1299 and WI-38 |
in vitro |
Mice |
MZ |
LC |
Tubulin disruption, Apoptosis |
[28] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
HCT 116 and RKO |
in silico |
- |
MZ |
CC |
Tubulin disruption |
[29] |
|
Human |
DLD-1, HCT-116, HT-29 and SW480 |
in vitro |
Mice |
MZ |
CC |
Tubulin disruption |
[30] |
|
Human |
ACP-02, ACP-03 and AGP-01 |
in vitro |
Mice |
MZ |
GC |
Tubulin disruption |
[31] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Mouse |
GL261 |
in vitro |
C57BL6 Mice |
MZ |
Brain tumour |
Tubulin disruption |
[32] |
|
in vivo |
Apoptosis |
||||||
|
Human |
GBM U87-MG, D54, H80, H247, H392, H397, H502 and H566 |
in vitro |
C57BL/6 mice |
MZ |
Brain cancer |
Apoptosis |
[33] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Mouse |
GL261 |
||||||
|
Human |
D425 MB |
in vivo |
p53 mice |
MZ |
Medullo-blastoma |
Tubulin disruption |
[34] |
|
Human |
293T and hTERT-RPE1 |
in vitro |
nu/nu athymic mice |
MZ |
Medullo-blastoma |
Hedgehog inhibitor |
[35] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Murine |
CP2 and SP1 |
in vitro |
BALB/c mice |
MZ |
PC |
Tubulin disruption |
[36] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
KKU-M213 |
in vitro |
Nude mice |
MZ |
Bile duct Cancer |
Apoptosis |
[37] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
PANC-1 |
in vitro |
Mice |
MZ |
Pancreatic cancer |
- |
[38] |
|
Human |
CAL27 and HCC15 |
in vitro |
Nude mice |
MZ |
Head and neck cancer |
Apoptosis |
[39] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
SK-Br-3 |
in vivo |
Mice |
MZ |
BC |
Tubulin disruption |
[40] |
|
Human |
M-14 and SK-Mel-19 |
in vitro |
Mice |
MZ |
Melanoma |
Tubulin disruption |
[41] |
|
Human |
MM622, MM540, D08, MM329, D17, and UACC1097 |
in vitro |
Mice |
MZ |
Melanoma |
Tubulin disruption |
[42] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
NRASQ61K |
in vitro |
Athymic mice |
MZ |
Melanoma |
Apoptosis |
[43] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
in silico |
|||||||
|
Human |
GL261 |
in vitro |
C57BL/6 mice |
MZ |
Brain cancer |
Tubulin disruption |
[44] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
Burkitt’s lymphoma Ramos cells, Hela cells, PANC-1 cells, and HepG2 cells |
in vivo |
Zebra-fish |
Closantel |
Lymphoma, cervical cancer, PC, and LC |
Suppression of antiangiogenesis and Closantel |
[45] |
|
Human |
Du146 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
PC |
Inhibition of STAT3 Pathway |
[46] |
|
Human |
HEK293 cells |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
PC and BC |
Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin Pathway |
[47] |
|
Human |
MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 |
in vitro |
NOD/SCID mice |
Nic |
BC |
Apoptosis and downregulation stem pathways |
[48] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
MDA-MB-231 |
in vitro |
BALB/c nude mice |
Nic and cisplatin |
BC |
Apoptosis and inhibition of Akt, ERK, and Src pathways |
[49] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
MDA-MB-468 and MCF-7 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
BC |
Inhibition of cell motility and STAT3 activity |
[50] |
|
Human |
TNBC MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468 and Hs578T |
in vitro |
Athymic nude mice |
Nic |
BC |
Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin Pathway |
[51] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Mouse |
4T1 |
in vitro |
BALB/c mice |
Nic |
BC |
Apoptosis and suppression of cell migration and invasion |
[52] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468 and MCF-7 |
in vitro |
|||||
|
Human |
2LMP, SUM159, HCC1187, and HCC1143 |
in vitro |
NOD/ SCID mice |
Nic |
BC |
Cytotoxicity |
[53] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
K562 and KBM5-T315I cells |
in vitro |
NOD mice |
Nic |
Chronic myelogenous leukemia |
Inhibition of FOXM1/β-catenin Pathway |
[54] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
HL-60, U937, OCI-AML3, Molm13, MV4-11, and U266 cells |
in vitro |
BALB/c mice |
Nic |
Acute myelogenous leukemia |
Apoptosis and Inhibition of NF-κB pathway |
[55] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
MCF7 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
Adeno-carcinoma |
Inhibition of PI3K-dependent signalling |
[56] |
|
HCC1954 |
Carcinoma |
||||||
|
BT-474 |
in vivo |
Ductal Carcinoma |
|||||
|
MDA-MB-361 and |
Adeno-carcinoma |
||||||
|
SKBR3 cell |
in silico |
Adeno-carcinoma |
|||||
|
Human |
HCT116, SW620, and HT29 |
in vivo |
Mice |
Nic |
CC |
Inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation |
[57] |
|
Human |
HCT116, SW480, DLD1 and 293 cells |
in vitro |
APC-MIN mice |
Nic |
CC |
Inhibition of Wnt/Snail-mediated EMT |
[58] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
HCT116, SW620, LS174T, SW480, and DLD-1 |
in vitro |
NOD/SCID mice |
Nic |
CC |
Inhibition of S100A4-induced metastasis formation |
[59] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
in situ |
|||||||
|
Human |
HT29, HCT116, CaCO2 and MCF-10A |
in vitro |
NOD/SCID mice |
Nic |
CC |
Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin Pathway |
[60] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
HEK293T, U2OS, WIDR, DLD-1, CRC 240, COLO205, CRC57 and HCT116 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
CC |
Induction of autophagy and inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin Pathway |
[61] |
|
Human |
SW480 and SW620 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
CC |
Reduction of Wnt activity |
[62] |
|
Rodent |
CC531 |
in vivo |
|||||
|
Murine |
MC38 |
in vitro |
APCmin/+ mouse |
Nic-EN and oxyclozanide |
CC |
Mitochondrial uncoupling |
[63] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
HCT116 |
in vitro |
|||||
|
Rodent |
C2C12 |
in vitro |
|||||
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
SKOV3 and CP70 |
in vitro |
SCID mice |
Nic |
OC |
Induction of metabolic shift to glycolysis |
[64] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
OVCAR-3, SKOV-3 and A2780 |
in vitro |
NOD/ SCID mice |
Nic |
OC |
Inhibition of CP70sps and primary OTICs |
[65] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
SKOV3.ip1 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
OC |
Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin Pathway |
[66] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
SKOV3 and HO8910 |
in vitro |
Athymic Nude mice |
Nic |
OC |
Mitochondrial Respiration and aerobic glycolysis |
[67] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
A2780ip2, A2780cp20, and SKOV3Trip2 |
in vitro |
SCID mice |
Nic |
OC |
Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin, mTOR and STAT3 pathways |
[68] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
Tumorspheres |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic and its analogs in combination with carboplatin |
OC |
Cytotoxicity |
[69] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
HepG2 and QGY7701 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
HCC |
Apoptosis and suppression of ATF3 expression |
[70] |
|
Human |
NSCLC, NCI-H1299 and HCT116 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
LC |
Apoptosis through ROS-mediated p38 MAPK-c-Jun activation |
[71] |
|
Human |
SK-Hep-1 and Huh7 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
HCC |
Inhibition of metastasis of HCC, and CD10 |
[72] |
|
Human |
HCC827, H1650, and H1975 |
in vitro |
Nu/Nu nude mice |
Nic |
LC |
Inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation |
[73] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
A549/DDP |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic combined with cisplatin (DDP) |
Cisplatin-resistant LC |
Apoptosis and reduction of c-myc protein |
[74] |
|
Human |
HepG2, QGY-7703 and SMMC-7721 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
HCC |
Inhibition of cell growth and STAT3 pathway |
[75] |
|
Human |
Lung adenocarcinoma (549, EKVX, H358, Hop62, H322M, H522, H838, and H23), large cell lung carcinoma (H460, Hop92), NCSLC (H1299, H810) and small cell LC (H82) |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
LC |
Reduction in proliferation and inhibition of S100A4 protein |
[76] |
|
Human |
U-87 MG |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
Glioblastoma |
Cell toxicity and inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin, PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK, and STAT3 |
[77] |
|
Human |
TS15-88, GSC11 |
in vitro |
Athymic nude mice |
Nic and/or temo-zolomide |
Glioblastoma |
Inhibition of the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related markers, Zeb1, N-cadherin, and β-catenin |
[78] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
LN229, T98G, U87(MG), U138, and U373(MG) |
in vitro |
Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− and SCID/ Beige mice |
Nic |
Glioblastoma |
Cytotoxicity and diminished the pGBMs’ malignant potential |
[79] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
C4-2B, LNCaP and DU145 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic with enzalutamide |
Enzalutamide resistance PC |
Inhibition of migration, invasion and IL6-Stat3-AR pathway |
[80] |
|
Human |
LNCaP, VcaP, CWR22Rv1, PC3 and HEK293 |
in vitro |
SCID mice |
Nic with enzalutamide |
Castration-resistant PC |
Inhibition of AR variant and enzalutamide-resistant tumor growth |
[81] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
CaLo, HeLa, SiHa, CasKi, DoTc2, ViBo and C-33A |
in vitro |
SCID mice |
Nic |
Cervical cancer |
Inhibition of mTOR signaling |
[82] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
ESO26, FLO-1, KYAE-1, OE33, SK-GT-4, and OE19 |
in vitro |
SCID mice |
Nic |
Esophageal cancer |
Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin |
[83] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
BE3,CE48T/VGH and CE81T/VGH |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
Esophageal cancer |
Inhibition of cell proliferation and STAT3 pathway |
[84] |
|
Human |
Osteosarcoma cells |
in vitro |
Mouse |
Nic |
Osteosarcoma |
Apoptosis and target multiple signaling pathways |
[85] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
NCI-H295R and SW-13 |
in vitro |
Nu+/Nu+ mice |
Nic |
Adrenocortical Carcinoma |
Induction of G1 cell-cycle arrest mitochondrial uncoupling |
[86] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
A498 and Caki-1 |
in vitro |
Athymic nude mice |
Nic |
Renal cell carcinoma |
Inhibition of cell proliferation, migration and cell cycle progression |
[87] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
SCC4 and SCC25 |
in vitro |
Mice |
Nic |
Oral cancer |
Inhibition of cancer stemness, extracellular matrix remodeling, and metastasis through dysregulation Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway |
[88] |
|
Human |
H929, MM1S, U266 and BMSC |
in vitro |
BALB/c nude mice |
RFX |
Multiple myeloma |
Apoptosis and inhibition of DNA synthesis |
[89] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
A431 and A375 |
in vitro |
BALB/c nude mice |
RFX |
Skin cancer |
Inhibition of CDK4/6 |
[90] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
HCT-116 and HT-29 |
in vitro |
Apcmin/+ mice |
RFX |
CRC |
Inhibition of cell proliferation |
[91] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
HCT-116 and DLD1 cells |
in vitro |
BALB/c nude mice |
RFX |
CRC |
Induction of ICD of CRC cells |
[92] |
|
in vivo |
|||||||
|
Human |
SGC-7901 and BGC-823, GES-1 |
in vitro |
BALB/c nude mice |
RFX |
GC |
Apoptosis and inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway |
[93] |
PubMed, Google Scholar, and CTD databases were used to summarize the data for the antitumor effects of BZ carbamates. ABZ—albendazole; BC—breast cancer; CC—colon cancer; CRC—colorectal cancer; EMT—epithelial–mesenchymal transition; FZ—fenbendazole; GC—gastric cancer; HCC—hepatocellular carcinoma; ICD—immunogenic cell death; LC—lung cancer; MZ—Mebendazole; Nic—Niclosamide; Nic-EN—Niclosamide ethanolamine; OC—ovarian cancer; PC—prostate cancer; RBZ—Ricobendazole; RFX—Rafoxanide.
2.3. Anticancer Activity of BZ Carbamates in Clinical Models
|
Antiparasitics |
Cancer Type |
Title |
Phase |
Purpose |
Status/Result |
Identifier/Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ABZ |
HCC or CRC |
Pilot Study Of Albendazole In Patients With Advanced Malignancy. Effect On Serum Tumor Markers/High Incidence Of Neutropenia |
PS |
Evaluation of anticancer activity |
Stabilization of the disease, but because of neutropenia, treatment was stopped on day 19 |
[95] |
|
ABZ |
Refractory solid tumors |
Phase I Clinical Trial To Determine Maximum Tolerated Dose Of Oral Albendazole In Patients With Advanced Cancer |
1 |
To determine the safety, tolerability, and the maximal tolerated dose. To characterize the pharmacokinetics and preliminary evidence of efficacy. |
2400 mg/day from 1200 mg b.d. Decreased plasma VEGF and 16% patients had a tumor marker response with a fall of at least 50% |
[94] |
|
MZ |
Adreno-cortical carcinoma |
Mebendazole Monotherapy and Long-Term Disease Control in Metastatic Adrenocortical Carcinoma |
CS |
To describe successful long-term tumor control |
Well tolerated, and the associated adverse effects of MZ are minor |
[96] |
|
MZ |
CC |
Drug Repositioning From Bench To Bedside: Tumour Remission By The Antihelmintic Drug Mebendazole In Refractory Metastatic Colon Cancer |
CS |
Repositioning drugs for use in advanced CC |
No disease-related symptoms were found |
[97] |
|
MZ |
Glio- blastoma |
Mebendazole In Newly Diagnosed High-Grade Glioma Patients Receiving Temozolomide (Mebendazole) |
1 |
To find the highest dose and the efficiency of MZ to slow the growth of the brain tumor |
Active, not recruiting |
NCT01729260 |
|
MZ |
Pediatric Gliomas |
A Phase I Study of Mebendazole for the Treatment of Pediatric Gliomas |
1 |
To determine the safety and efficacy of MZ |
Recruiting |
NCT01837862 |
|
MZ |
GI Cancer |
A Clinical Safety and Efficacy Study of Mebendazole on GI Cancer or Cancer of Unknown Origin. (RepoMeb) |
1 |
To determine the safety and efficacy of MZ (ReposMZ) |
Terminated (Lack of effect) |
NCT03628079 |
|
Cancer of Unknown Origin |
2 |
|||||
|
MZ |
OC, PC and ovarian epithelial cancer |
Study of the Safety, Tolerability and Efficacy of Metabolic Combination Treatments on Cancer (METRICS) |
3 |
To determine the effectiveness of a regimen of selected metabolic treatments for cancer patients and to perform exploratory analysis on the relationship between the degree of response and changes in biochemical markers |
Not yet recruiting |
NCT02201381 |
|
MZ |
CC |
Mebendazole as Adjuvant Treatment for Colon Cancer |
3 |
MZ as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer |
Recruiting |
NCT03925662 |
|
Nic |
CC |
A Study of Niclosamide in Patients With Resectable Colon Cancer |
1 |
To determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) |
Terminated (low accrual) |
NCT02687009 |
|
Nic |
CRC |
Drug Trial to Investigate the Safety and Efficacy of Niclosamide Tablets in Patients With Metastases of a Colorectal Cancer Progressing After Therapy (Nikolo) |
2 |
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of oral appliqued Nic |
Unknown |
NCT02519582 |
|
Nic |
PC |
Niclosamide and Enzalutamide in Treating Patients With Castration-Resistant, Metastatic PC |
1 |
To determine the side effects and best dose of Nic |
Completed (No result posted) |
NCT02532114 |
|
Nic |
Metastatic PC |
Enzalutamide and Niclosamide in Treating Patients With Recurrent or Metastatic Castration-Resistant PC |
1 |
To determine the best dose and side effects of Nic when given together with enzalutamide |
Recruiting |
NCT03123978 |
|
Recurrent PC |
||||||
|
Stage IV PC |
||||||
|
Nic |
Metastatic PC |
Abiraterone Acetate, Niclosamide, and Prednisone in Treating Patients With Hormone-Resistant PC |
2 |
To determine the side effects and how well abiraterone acetate, Nic, and prednisone work in treating patients with hormone-resistant PC |
Recruiting |
NCT02807805 |
|
Recurrent PC |
||||||
|
Stage IV PC |
NCBI database was used to inquire about the clinical trials on antitumor effects of antiparasitic drugs. ABZ—albendazole; MZ—mebendazole, Nic—niclosamide, CS—clinical study; CC—colon cancer; CRC—colorectal cancer; HCC—hepatocellular carcinoma; PS—pilot Study.
3. HS
3.1. Mechanism of Action of HS
3.2. Anticancer Activity of HS
3.3. Anticancer Activity of HS in Clinical Models
References
- Ahlan, S.; Kumar, S.; Kakkar, S.; Narasimhan, B. Benzimidazole scaffolds as promising antiproliferative agents: A review. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 66.
- Kato, S.; Moulder, S.L.; Ueno, N.T.; Wheler, J.J.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Kurzrock, R.; Janku, F. Challenges and perspective of drug repurposing strategies in early phase clinical trials. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 576–580.
- Scannell, J.W.; Blanckley, A.; Boldon, H.; Warrington, B. Diagnosing the decline in pharmaceutical R&D efficiency. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 191–200.
- Cha, Y.; Erez, T.; Reynolds, I.J.; Kumar, D.; Ross, J.; Koytiger, G.; Kusko, R.; Zeskind, B.; Risso, S.; Kagan, E.; et al. Drug repurposing from the perspective of pharmaceutical companies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 175, 168–180.
- Castro, L.; Kviecinski, M.R.; Ourique, F.; Parisotto, E.; Grinevicius, V.; Correia, J.; Filho, D.W.; Pedrosa, R. Albendazole as a promising molecule for tumor control. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 90–99.
- Pantziarka, P.; Bouche, G.; Meheus, L.; Sukhatme, V.; Sukhatme, V.P.; Vikas, P. The Repurposing Drugs in Oncology (ReDO) Project. Ecancermedicalscience 2014, 8, 442.
- Gull, K.; Dawson, P.J.; Davis, C.; Byard, E.H. Microtubules as target organelles for benzimidazole anthelmintic chemotherapy. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1987, 15, 59–60.
- Lacey, E.; Watson, T.R. Structure-activity relationships of benzimidazole carbamates as inhibitors of mammalian tubulin, in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1985, 34, 1073–1077.
- Jordan, M.A.; Wilson, L. Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 253–265.
- Junquera, P. Fenbendazole, Anthelmintic for Veterinary Use in Cattle, Sheep, Goats, Pig, Poultry, Horses, Dogs and Cats Against Roundworms and Tapeworms. Parasitipedia.net. 2015. Available online: https://parasitipedia.net/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=2512&Itemid=2785 (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Lacey, E.; Watson, T.R. Activity of benzimidazole carbamates against L1210 mouse leukaemia cells: Correlation with in vitro tubulin polymerization assay. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1985, 34, 3603–3605.
- Rolin, S.; Amri, H.S.-E.; Batt, A.-M.; Levy, M.; Bagrel, D.; Siest, G. Study of the in vitro bioactivation of albendazole in human liver microsomes and hepatoma cell lines. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 1989, 5, 1–14.
- Pourgholami, M.; Woon, L.; Almajd, R.; Akhter, J.; Bowery, P.; Morris, D. In vitro and in vivo suppression of growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by albendazole. Cancer Lett. 2001, 165, 43–49.
- Králová, V.; Hanušová, V.; Staňková, P.; Knoppová, K.; Čáňová, K.; Skálová, L. Antiproliferative effect of benzimidazole anthelmintics albendazole, ricobendazole, and flubendazole in intestinal cancer cell lines. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2013, 24, 911–919.
- Pourgholami, M.H.; Akhter, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Morris, D.L. Antitumor activity of albendazole against the human colorectal cancer cell line HT-29: In vitro and in a xenograft model of peritoneal carcinomatosis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2004, 55, 425–432.
- Khalilzadeh, A.; Wangoo, K.T.; Morris, D.L.; Pourgholami, M.H. Epothilone-paclitaxel resistant leukemic cells CEM/dEpoB300 are sensitive to albendazole: Involvement of apoptotic pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 407–414.
- Chu, S.W.L.; Badar, S.; Morris, D.L.; Pourgholami, M.H. Potent inhibition of tubulin polymerisation and proliferation of paclitaxel-resistant 1A9PTX22 human ovarian cancer cells by albendazole. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 3791–3796.
- Sharma, Y. Veterinary Drug May Be Repurposed for Human Cancers: Study. The Hindu Business Line, 27 August 2018.
- Duan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Rockwell, S. Fenbendazole as a potential anticancer drug. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 355–362.
- Dogra, N.; Kumar, A.; Mukhopadhyay, T. Fenbendazole acts as a moderate microtubule destabilizing agent and causes cancer cell death by modulating multiple cellular pathways. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11926.
- Gao, P.; Dang, C.V.; Watson, J. Unexpected antitumorigenic effect of fenbendazole when combined with supplementary vitamins. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2008, 47, 37–40.
- Duan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Booth, C.J.; Rockwell, S. Use of fenbendazole-containing therapeutic diets for mice in experimental cancer therapy studies. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2012, 51, 224–230.
- Spagnuolo, P.A.; Hu, J.; Hurren, R.; Wang, X.; Gronda, M.; Sukhai, M.A.; Di Meo, A.; Boss, J.; Ashali, I.; Zavareh, R.B.; et al. The antihelmintic flubendazole inhibits microtubule function through a mechanism distinct from Vinca alkaloids and displays preclinical activity in leukemia and myeloma. Blood 2010, 115, 4824–4833.
- Hou, Z.-J.; Luo, X.; Zhang, W.; Peng, F.; Cui, B.; Wu, S.-J.; Zheng, F.-M.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.-Z.; Long, Z.-J.; et al. Flubendazole, FDA-approved anthelmintic, targets breast cancer stem-like cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6326–6340.
- Kim, Y.; Oh, E.; Cho, T.; Jang, S.; Park, J.M.; Park, S.; Park, M.; Kim, J.Y.; Seo, J.H. An anthelmintic drug, flubendazole, exerts antitumor effects in triple-negative breast cancer via targeting cancer stem-like properties. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 703.
- Kim, Y.-J.; Sung, D.; Oh, E.; Cho, Y.; Cho, T.-M.; Farrand, L.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, J.Y. Flubendazole overcomes trastuzumab resistance by targeting cancer stem-like properties and HER2 signaling in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 118–130.
- Lin, S.; Yang, L.; Yao, Y.; Xu, L.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Zuo, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhao, C. Flubendazole demonstrates valid antitumor effects by inhibiting STAT3 and activating autophagy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 293.
- Martarelli, D.; Pompei, P.; Baldi, C.; Mazzoni, G. Mebendazole inhibits growth of human adrenocortical carcinoma cell lines implanted in nude mice. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 61, 809–817.
- Sasaki, J.-I.; Ramesh, R.; Chada, S.; Gomyo, Y.; Roth, J.; Mukhopadhyay, T. The anthelmintic drug mebendazole induces mitotic arrest and apoptosis by depolymerizing tubulin in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 1201–1209.
- Nygren, P.; Fryknäs, M.; Ågerup, B.; Larsson, R. Repositioning of the anthelmintic drug mebendazole for the treatment for colon cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 2133–2140.
- Williamson, T.; Bai, R.-Y.; Staedtke, V.; Huso, D.; Riggins, G.J. Mebendazole and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory combine to reduce tumor initiation in a colon cancer preclinical model. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68571–68584.
- Pinto, L.C.; Soares, B.M.; Pinheiro, J.d.J.; Riggins, G.J.; Assumpcao, P.P.; Burbano, R.M.; Montenegro, R.C. The anthelmintic drug mebendazole inhibits growth, migration and invasion in gastric cancer cell model. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 2038–2044.
- Bai, R.-Y.; Staedtke, V.; Wanjiku, T.; Rudek, M.A.; Joshi, A.; Gallia, G.L.; Riggins, G.J. Brain Penetration and Efficacy of Different Mebendazole Polymorphs in a Mouse Brain Tumor Model. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3462–3470.
- Bai, R.-Y.; Staedtke, V.; Aprhys, C.M.; Gallia, G.L.; Riggins, G.J. Antiparasitic mebendazole shows survival benefit in 2 preclinical models of glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 974–982.
- Bodhinayake, I.; Symons, M.; Boockvar, J.A. Repurposing Mebendazole for the Treatment of Medulloblastoma. Neurosurgery 2015, 76, N15–N16.
- Larsen, A.R.; Bai, R.-Y.; Chung, J.; Borodovsky, A.; Rudin, C.; Riggins, G.J.; Bunz, F. Repurposing the Antihelmintic Mebendazole as a Hedgehog Inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 14, 3–13.
- Rushworth, L.; Hewit, K.; Munnings-Tomes, S.; Somani, S.; James, D.; Shanks, E.; Dufès, C.; Straube, A.; Patel, R.; Leung, H.Y. Repurposing screen identifies mebendazole as a clinical candidate to synergise with docetaxel for prostate cancer treatment. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 122, 517–527.
- Sawanyawisuth, K.; Williamson, T.; Wongkham, S.; Riggins, G.J. Effect of the antiparasitic drug mebendazole on cholangiocarcinoma growth. South Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2014, 45, 1264–1270.
- Varbanov, H.P.; Kuttler, F.; Banfi, D.; Turcatti, G.; Dyson, P.J. Repositioning approved drugs for the treatment of problematic cancers using a screening approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171052.
- Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, E.; Gao, L.; Luo, W.; Wei, Q.; Fan, J.; Song, D.; Liao, J. Anthelmintic mebendazole enhances cisplatin’s effect on suppressing cell proliferation and promotes differentiation of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12968–12982.
- Coyne, C.P.; Jones, T.; Bear, R. Anti-Neoplastic Cytotoxicity of Gemcitabine-(C4-amide)- in Dual-combination with Epirubicin-(C3-amide)- against Chemotherapeutic-Resistant Mammary Adenocarcinoma (SKBr-3) and the Complementary Effect of Mebendazole. J. Cancer Res. Ther. Oncol. 2014, 2, 203.
- Doudican, N.; Rodriguez, A.; Osman, I.; Orlow, S. Mebendazole Induces Apoptosis via Bcl-2 Inactivation in Chemoresistant Melanoma Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1308–1315.
- Doudican, N.A.; Byron, S.A.; Pollock, P.M.; Orlow, S.J. XIAP downregulation accompanies mebendazole growth inhibition in melanoma xenografts. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2013, 24, 181–188.
- Simbulan-Rosenthal, C.M.; Dakshanamurthy, S.; Gaur, A.; Chen, Y.S.; Fang, H.B.; Abdussamad, M.; Zhou, H.; Zapas, J.; Calvert, V.; Petricoin, E.F. The repurposed anthelmintic mebendazole in combination with trametinib suppresses refractory NRASQ61K melanoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12576–12595.
- Prichard, R.K. The metabolic profile of adult Fasciola hepatica obtained from rafoxanide-treated sheep. Parasitology 1978, 76, 277–288.
- Li, Y.; Guo, B.; Xu, Z.; Li, B.; Cai, T.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, J.; Zhu, W. Repositioning organohalogen drugs: A case study for identification of potent B-Raf V600E inhibitors via docking and bioassay. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31074.
- Zhu, X.-Y.; Xia, B.; Liu, H.-C.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Huang, C.-J.; Gao, J.-M.; Dong, Q.-X.; Li, C.-Q. Closantel Suppresses Angiogenesis and Cancer Growth in Zebrafish Models. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2016, 14, 282–290.
- Ren, X.; Duan, L.; He, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, D.; Pan, J.; Pei, D.; Ding, K. Identification of Niclosamide as a New Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the STAT3 Signaling Pathway. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 454–459.
- Lu, W.; Lin, C.; Roberts, M.J.; Waud, W.R.; Piazza, G.A.; Li, Y. Niclosamide suppresses cancer cell growth by inducing Wnt co-receptor LRP6 degradation and inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29290.
- Wang, Y.C.; Chao, T.K.; Chang, C.C.; Yo, Y.T.; Yu, M.H.; Lai, H.C. Drug screening identifies niclosamide as an inhibitor of breast cancer stem-like cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74538.
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Ward, T.; Pegram, M.; Shen, K. Combined niclosamide with cisplatin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor growth in cisplatin-resistant triple-negative breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 9825–9835.
- Gyamfi, J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Min, B.S.; Choi, J. Niclosamide reverses adipocyte induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells via suppression of the interleukin-6/STAT3 signalling axis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11336.
- Yin, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H. Niclosamide sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation in association with the inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42126–42138.
- Ye, T.; Xiong, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Song, X.; Liu, L.; Li, D.; Wang, N.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; et al. The Anthelmintic Drug Niclosamide Induces Apoptosis, Impairs Metastasis and Reduces Immunosuppressive Cells in Breast Cancer Model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85887.
- Londoño-Joshi, A.I.; Arend, R.C.; Aristizabal, L.; Lu, W.; Samant, R.S.; Metge, B.J.; Hidalgo, B.; Grizzle, W.E.; Conner, M.; Forero-Torres, A.; et al. Effect of Niclosamide on Basal-like Breast Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 800–811.
- Jin, B.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Du, X.; Ding, K.; Pan, J. Anthelmintic Niclosamide Disrupts the Interplay of p65 and FOXM1/beta-catenin and Eradicates Leukemia Stem Cells in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 789–803.
- Jin, Y.; Lu, Z.; Ding, K.; Li, J.; Du, X.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Pan, J. Antineoplastic mechanisms of niclosamide in acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells: Inactivation of the NF-kappaB pathway and generation of reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2516–2527.
- Carrella, D.; Manni, I.; Tumaini, B.; Dattilo, R.; Papaccio, F.; Mutarelli, M.; Sirci, F.; Amoreo, C.A.; Mottolese, M.; Iezzi, M.; et al. Computational drugs repositioning identifies inhibitors of oncogenic PI3K/AKT/P70S6K-dependent pathways among FDA-approved compounds. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 58743–58758.
- Shi, L.; Zheng, H.; Hu, W.; Zhou, B.; Dai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhao, C.; Liang, G. Niclosamide inhibition of STAT3 synergizes with erlotinib in human colon cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 1767–1776.
- Ahn, S.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, K.; Cha, Y.H.; Yang, J.H.; Cha, S.; Cho, E.S.; Lee, Y.; Cha, J.S.; Cho, H.S.; et al. Niclosamide is a potential therapeutic for familial adenomatosis polyposis by disrupting Axin-GSK3 interaction. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31842–31855.
- Sack, U.; Walther, W.; Scudiero, D.; Selby, M.; Kobelt, D.; Lemm, M.; Fichtner, I.; Schlag, P.M.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Stein, U. Novel Effect of Antihelminthic Niclosamide on S100A4-Mediated Metastatic Progression in Colon Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1018–1036.
- Osada, T.; Chen, M.; Yang, X.Y.; Spasojevic, I.; VanDeusen, J.B.; Hsu, D.; Clary, B.M.; Clay, T.M.; Chen, W.; Morse, M.A.; et al. Antihelminth Compound Niclosamide Downregulates Wnt Signaling and Elicits Antitumor Responses in Tumors with Activating APC Mutations. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4172–4182.
- Wang, J.; Ren, X.-R.; Piao, H.; Zhao, S.; Osada, T.; Premont, R.T.; Mook, R.A.; Morse, M.A.; Lyerly, H.K.; Chen, W. Niclosamide-induced Wnt signaling inhibition in colorectal cancer is mediated by autophagy. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 535–546.
- Monin, M.B.; Krause, P.; Stelling, R.; Bocuk, D.; Niebert, S.; Klemm, F.; Pukrop, T.; Koenig, S. The anthelmintic niclosamide inhibits colorectal cancer cell lines via modulation of the canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling pathway. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 203, 193–205.
- Alasadi, A.; Chen, M.; Swapna, G.V.T.; Tao, H.; Guo, J.; Collantes, J.; Fadhil, N.; Montelione, G.T.; Jin, S. Effect of mitochondrial uncouplers niclosamide ethanolamine (NEN) and oxyclozanide on hepatic metastasis of colon cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 215.
- Lin, C.-K.; Bai, M.-Y.; Hu, T.-M.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chao, T.-K.; Weng, Y.-C.; Huang, R.-L.; Su, P.-H.; Lai, H.-C. Preclinical evaluation of a nanoformulated antihelminthic, niclosamide, in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8993–9006.
- Yo, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-W.; Wang, Y.-C.; Balch, C.; Huang, R.L.; Chan, M.; Sytwu, H.-K.; Chen, C.-K.; Chang, C.-C.; Nephew, K.P.; et al. Growth Inhibition of Ovarian Tumor–Initiating Cells by Niclosamide. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1703–1712.
- Arend, R.C.; Londono-Joshi, A.I.; Samant, R.S.; Li, Y.; Conner, M.; Hidalgo, B.; Alvarez, R.D.; Landen, C.N.; Straughn, J.M.; Buchsbaum, D.J. Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by niclosamide: A therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 134, 112–120.
- Shangguan, F.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Qu, G.; Lv, Q.; An, J.; Yang, S.; Lu, B.; Cao, Q. Niclosamide inhibits ovarian carcinoma growth by interrupting cellular bioenergetics. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3454–3466.
- Arend, R.C.; Londono-Joshi, A.I.; Gangrade, A.; Katre, A.A.; Kurpad, C.; Li, Y.; Samant, R.S.; Li, P.-K.; Landen, C.N.; Yang, E.S.; et al. Niclosamide and its analogs are potent inhibitors of Wnt/beta-catenin, mTOR and STAT3 signaling in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 86803–86815.
- Walters Haygood, C.L.; Arend, R.C.; Gangrade, A.; Chettiar, S.; Regan, N.; Hassmann, C.J.; Li, P.-K.; Hidalgo, B.; Straughn, J.M.; Buchsbaum, D.J. Niclosamide Analogs for Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2015, 25, 1377–1385.
- Weng, S.; Zhou, L.; Deng, Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, Y. Niclosamide induced cell apoptosis via upregulation of ATF3 and activation of PERK in Hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 25.
- Lee, S.-L.; Son, A.-R.; Ahn, J.; Song, J.-Y. Niclosamide enhances ROS-mediated cell death through c-Jun activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 619–624.
- Chien, M.-H.; Ho, Y.-C.; Yang, S.-F.; Yang, Y.-C.; Lai, S.-Y.; Chen, W.-S.; Chen, M.-J.; Yeh, C.-B. Niclosamide, an oral antihelmintic drug, exhibits antimetastatic activity in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through downregulating twist-mediated CD10 expression. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 659–669.
- Li, R.; Hu, Z.; Sun, S.-Y.; Chen, Z.G.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Sica, G.L.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Curran, W.J.; Khuri, F.R.; Deng, X. Niclosamide Overcomes Acquired Resistance to Erlotinib through Suppression of STAT3 in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2200–2212.
- Zuo, Y.; Yang, D.; Yu, Y.; Xiang, M.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Z.; et al. Niclosamide enhances the cytotoxic effect of cisplatin in cisplatin-resistant human lung cancer cells via suppression of lung resistance-related protein and c-myc. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 17, 3497–3502.
- Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Xu, H.; Shi, X.; Zhao, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Jin, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Niclosamide Inhibits Cell Growth and Enhances Drug Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via STAT3 Signaling Pathway. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 4150–4155.
- Stewart, R.L.; Carpenter, B.L.; West, D.S.; Knifley, T.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Weiss, H.L.; Gal, T.S.; Durbin, E.B.; Arnold, S.M.; et al. S100A4 drives non-small cell lung cancer invasion, associates with poor prognosis, and is effectively targeted by the FDA-approved anti-helminthic agent niclosamide. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34630–34642.
- Cheng, B.; Morales, L.D.; Zhang, Y.; Mito, S.; Tsin, A. Niclosamide induces protein ubiquitination and inhibits multiple pro-survival signaling pathways in the human glioblastoma U-87 MG cell line. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184324.
- Oh, H.-C.; Shim, J.-K.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, R.J.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.S.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, E.H.; Chang, J.H.; et al. Combined effects of niclosamide and temozolomide against human glioblastoma tumorspheres. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 2817–2828.
- Wieland, A.; Trageser, D.; Gogolok, S.; Reinartz, R.; Höfer, H.; Keller, M.; Leinhaas, A.; Schelle, R.; Normann, S.; Klaas, L.; et al. Anticancer Effects of Niclosamide in Human Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4124–4136.
- Liu, C.; Lou, W.; Armstrong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. Niclosamide suppresses cell migration and invasion in enzalutamide resistant prostate cancer cells via Stat3-AR axis inhibition. Prostate 2015, 75, 1341–1353.
- Liu, C.; Lou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Nadiminty, N.; Schwartz, C.T.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. Niclosamide Inhibits Androgen Receptor Variants Expression and Overcomes Enzalutamide Resistance in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3198–3210.
- Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Lin, H.; Li, D. Anthelminthic drug niclosamide sensitizes the responsiveness of cervical cancer cells to paclitaxel via oxidative stress-mediated mTOR inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 484, 416–421.
- Wei, W.; Liu, H.; Yuan, J.; Yao, Y. Targeting Wnt/beta-catenin by anthelmintic drug niclosamide overcomes paclitaxel resistance in esophageal cancer. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 165–173.
- Lee, M.; Chen, Y.; Hsu, Y.; Lin, B. Niclosamide inhibits the cell proliferation and enhances the responsiveness of esophageal cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 43, 549–561.
- Liao, Z.; Nan, G.; Yan, Z.; Zeng, L.; Deng, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qiao, M.; Li, R.; Denduluri, S.; et al. The Anthelmintic Drug Niclosamide Inhibits the Proliferative Activity of Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting Multiple Signal Pathways. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2015, 15, 726–738.
- Satoh, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chelluri, R.; Boufraqech, M.; Nilubol, N.; Patel, D.; Shen, M.; Kebebew, E. Identification of Niclosamide as a Novel Anticancer Agent for Adrenocortical Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3458–3466.
- Swan, G.E. The pharmacology of halogenated salicylanilides and their anthelmintic use in animals. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1999, 70, 61–70.
- Xiao, W.; Xu, Z.; Chang, S.; Li, B.; Yu, D.; Wu, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, B.; Sun, X.; et al. Rafoxanide, an organohalogen drug, triggers apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in multiple myeloma by enhancing DNA damage responses and suppressing the p38 MAPK pathway. Cancer Lett. 2018, 444, 45–59.
- Gooyit, M.; Janda, K.D. Reprofiled anthelmintics abate hypervirulent stationary-phase Clostridium difficile. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33642.
- Shi, X.; Li, H.; Shi, A.; Yao, H.; Ke, K.; Dong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Ding, Y.; He, Y.H.; et al. Discovery of rafoxanide as a dual CDK4/6 inhibitor for the treatment of skin cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 1592–1600.
- Laudisi, F.; Di Grazia, A.; De Simone, V.; Cherubini, F.; Colantoni, A.; Ortenzi, A.; Franzè, E.; Dinallo, V.; Di Fusco, D.; Monteleone, I.; et al. Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibition of colon carcinogenesis by the anti-helmintic drug rafoxanide. Cancer Lett. 2019, 462, 1–11.
- Morris, D.L.; Jourdan, J.-L.; Pourgholami, M.H. Pilot Study of Albendazole in Patients with Advanced Malignancy. Oncology 2001, 61, 42–46.
- De Witt, M.; Gamble, A.; Hanson, D.; Markowitz, D.; Powell, C.; Dimassi, S.; Atlas, M.; Boockvar, J.; Ruggieri, R.; Symons, M. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Repurposing mebendazole as a replacement for vincristine for the treatment of brain tumors. Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 50–56.
- Tippens, J. My Cancer Story Rocks. Get Busy Living. 2018. Available online: https://www.mycancerstory.rocks/ (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Dobrosotskaya, I.Y.; Hammer, G.D.; Schteingart, D.E.; Maturen, K.E.; Worden, F.P. Mebendazole monotherapy and long-term disease control in metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocr. Pract. 2011, 17, e59–e62.
- Williamson, R.L.; Metcalf, R.L. Salicylanilides: A New Group of Active Uncouplers of Oxidative Phosphorylation. Science 1967, 158, 1694–1695.
- Cornish, R.; Behm, C.; Butler, R.; Bryant, C. The in vivo effects of rafoxanide on the energy metabolism of Fasciola hepatica. Int. J. Parasitol. 1977, 7, 217–220.




