
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Abu Baker Sheikh | + 3592 word(s) | 3592 | 2022-03-21 07:08:21 | | | |
| 2 | Conner Chen | -50 word(s) | 3542 | 2022-03-22 05:08:24 | | |
Video Upload Options
SARS-CoV-2 is a member of the Coronaviridae family, a group of enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses. Many extrapulmonary manifestations of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have been reported involving the cardiovascular, renal, gastrointestinal and urinary systems. These widespread manifestations are attributed to the presence of the ACE2 (Angiotensin converting enzyme 2) receptor in these tissues, which is postulated to be at the center of the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Similarly, expression of the ACE2 receptor has also been reported in various endocrine tissues including the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, gonads, and pancreatic islets. Therefore, it is imperative to understand the way COVID-19 can alter the function of these tissues and cause pathology, especially considering the close interplay between various endocrine systems as part of the RAAS (renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system) pathway and the central role of ACE2 in this pathway.
1. COVID-19 and Endocrine System
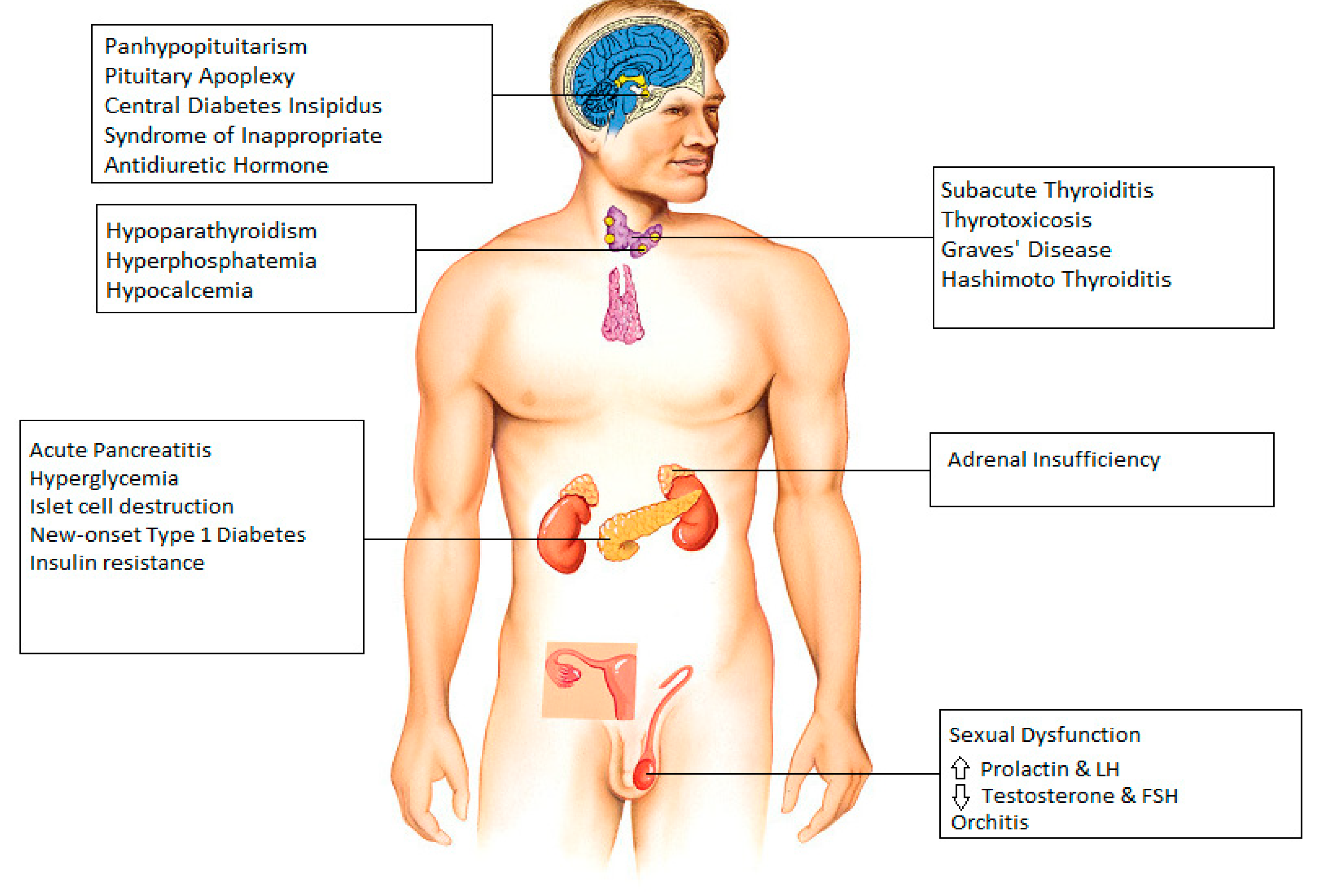
2. Hypothalamus and Pituitary
3. Thyroid
4. Parathyroid
5. Pancreas
6. Adrenal Gland
7. Gonads
8. Endocrinopathies and COVID-19 Vaccines
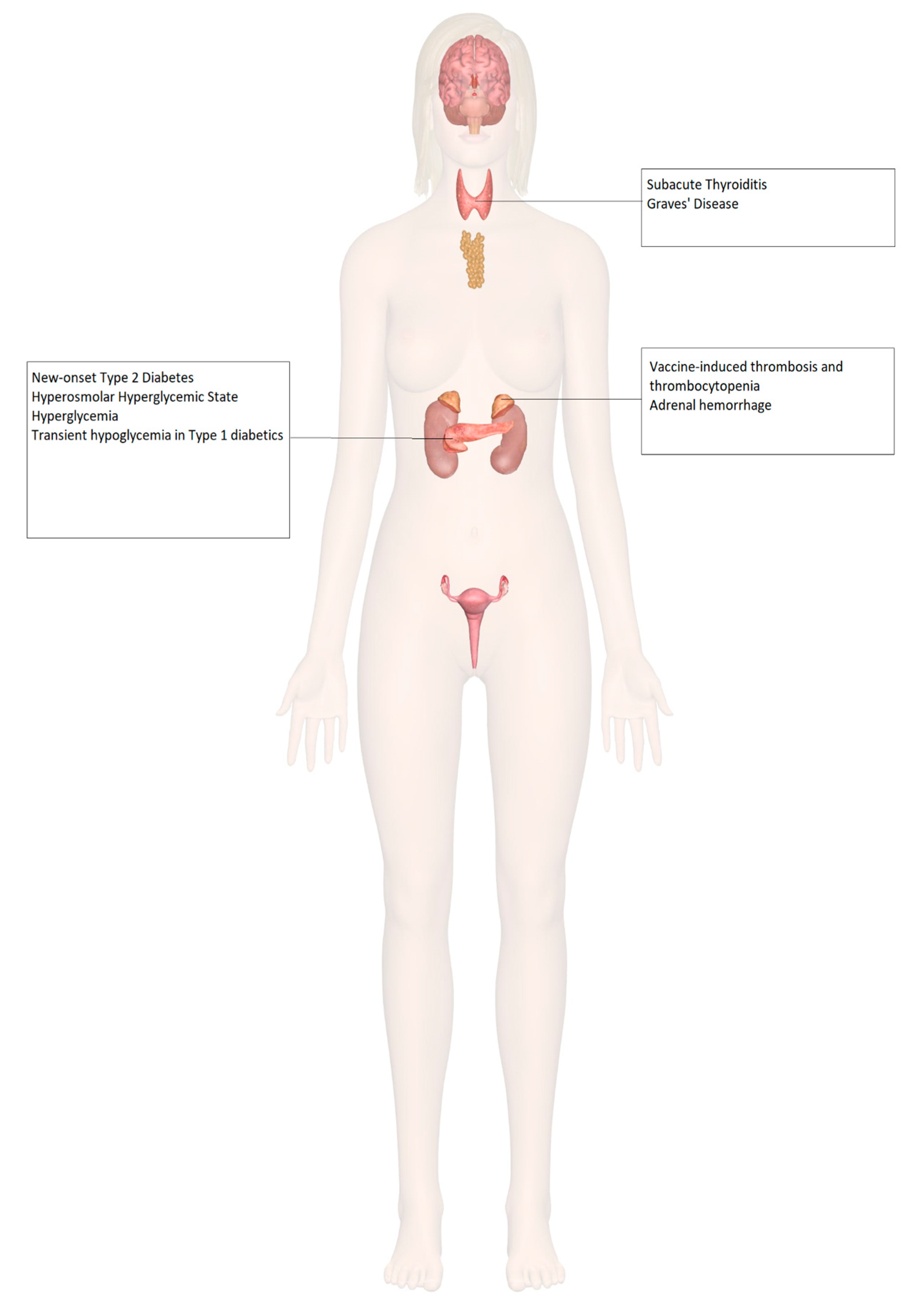
9. Adrenal Insufficiency
10. Diabetes Mellitus
11. Thyroid Disorders
12. Hypogonadism and Infertility
13. Osteoporosis
14. Misinformation: COVID-19 Vaccine and Endocrine System
| Author (Country, Year) |
System Involved | Age and Sex of the Patient | Type of Vaccine |
Onset of Symptom | Presenting Symptoms | Final Diagnosis |
Complications | Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taylor et al. (Wales, 2021) [69] | Adrenal | 38, Male | Astra Zeneca | 8 days after Dose 1 | Severe abdominal pain Vomiting |
Vaccine–Induced Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia with Bilateral Adrenal Hemorrhage | Dural venous sinus thrombosis | Intravenous Immunoglobulin, Hydrocortisone, Argatroban Plasma exchange |
Improved platelet count after plasma exchange |
| Boyle et al. (United Kingdom, 2021) [70] | Adrenal | 55, Female | Astra Zeneca | 8 days after Dose 1 | Left iliac fossa pain Vomiting |
Left Adrenal Hemorrhage | Thrombo-embolism in both lungs, left basilic vein, and left renal vein | Hydrocortisone Apixaban |
Positive response to therapy, conservatively managed further |
| Abu-Rumaileh et al. (Jordan, 2021) [76] | Diabetes | 58, Male | Pfizer/BioNTech | 21 days after Dose 1 (2 days after Dose 2) | Nocturia Polyuria Polydipsia Altered mental status Weight loss |
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State | IV Fluids Insulin drip Glargine 50 units daily plus 10 units pre-meal insulin |
Insulin tapered and stopped in 4 weeks Metformin continued with good glycemic control |
|
| Mishra et al. (India, 2021) [77] | Diabetes | 58, Female | Covishield | 1 day | None Hypertension and tachycardia None |
Exacerbation of hyperglycemia in pre-existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | None | Increased dose of Metformin in patient 1 No interventions in patients 2 and 3 |
Return to previous blood glucose levels in 1 month, 3 days and 15 days, respectively |
| 64, Male | |||||||||
| 1 day | |||||||||
| 65, Male | 6 days | ||||||||
| Heald et al. (United Kingdom, 2021) [78] | Diabetes | 20 patients Median age 53 (range 26–70), 11 Females, 9 Males |
Pfizer/BioNTech [6] Astra Zeneca [10] |
7 days | None | Transient hypoglycemia in Type 1Diabetes Mellitus patients | None | No intervention | Return to previous glucose levels in further 7 days |
| Irlemi et al. (Turkey, 2021) [79] | Thyroid | 35, Female | CoronaVac | 4 days after Dose 2 4 days after Dose 1 7 days after Dose 2 |
Anterior neck pain Fever Palpitations Weight loss Fatigue |
Subacute Thyroiditis (secondary to ASIA syndrome) | Recurrent myalgia and neck pain in patient 2 | Methylprednisolone 16 mg once daily propranolol 25 mg twice daily No intervention in patient 3 |
Complete resolution of symptoms |
| 34, Female | |||||||||
| 37, Female | |||||||||
| Franquemont et al. (USA, 2021) [80] | Thyroid | 42, Female | Pfizer/BioNTech | 5 days after Dose 1 | Sore throat Palpitation Tachycardia |
Subacute Thyroiditis | None | Prednisone 40mg daily and Propranolol 20mg as needed | Rapid improvement of symptoms after therapy |
| Oyibo (United Kingdom, 2021) [81] | Thyroid | 55, Female | Astra Zeneca | 21 days after Dose 1 | Neck pain Swelling Headache Sore throat Myalgia Palpitation |
Subacute Thyroiditis | None | Levothyroxine 50 mg daily Propranolol |
Resolution of symptoms after therapy |
| Sahin et al. (Turkey, 2021) [82] | Thyroid | 67, Male | Subacute Thyroiditis | ||||||
| Vera-Lastra et al. (Mexico, 2021) [84] | Thyroid | 3 days | Grave’s disease |
| Author | Study Design | Criteria | Patient Population | Conclusion | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gonzalez et al. [86]. | Single-center prospective study | Inclusion: Men aged 18–50, no underlying fertility issues. |
45 male participants. | No significant decrease in sperm parameters after 2 doses of COVID-19 vaccination. |
|
| Exclusion: COVID-19 symptoms or positive results within the last 90 days. |
|||||
| Lifshitz et al. [87]. | Prospective cohort study | Inclusion: Men < 45 years old, fertile men were considered to be those who had previously successfully impregnated their partners without the use of artificial reproductive technology. |
75 male participants. | Semen parameters found to be within normal parameters after COVID-19 vaccination. |
|
| Exclusion: Previously diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infection, taking medications known to be detrimental to semen parameters. |
|||||
| Lipkind et al. [91] | Retrospective cohort study | Inclusion: Single-gestation pregnancies. |
46,079 participants. | COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy was not significantly associated with increased risk for preterm birth overall or SGA at birth |
|
| Exclusion: Age < 16 or >49 years, multiple gestations, no documented care in the health system, implausible gestational age, pregnancy start date outside the prespecified periods. |
|||||
| Blakeway et al. [92]. | Retrospective cohort study | Inclusion: Pregnant women with known vaccination status, complete maternal and fetal outcome data. |
1328 Participants. | Similar pregnancy outcomes seen in vaccinated and unvaccinated participants. |
|
| Exclusion: Complicated pregnancies with genetic syndromes, fully vaccinated before getting pregnant. |
References
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Pöhlmann, S. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8.
- Brosnahan, S.B.; Jonkman, A.H.; Kugler, M.C.; Munger, J.S.; Kaufman, D.A. COVID-19 and Respiratory System Disorders: Current Knowledge, Future Clinical and Translational Research Questions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2586–2597.
- Chigr, F.; Merzouki, M.; Najimi, M. Autonomic Brain Centers and Pathophysiology of COVID-19. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 1520–1522.
- Poyiadji, N.; Shahin, G.; Noujaim, D.; Stone, M.; Patel, S.; Griffith, B. COVID-19-associated Acute Hemorrhagic Necrotizing Encephalopathy: Imaging Features. Radiology 2020, 296, E119–E120.
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Gao, J. Sars-Cov-2: Underestimated damage to nervous system. Travel Med. Infect Dis. 2020, 36, 101642.
- Kaya, M.G.; Ertürk, C.; Güven, M. Pituitary Insufficiency Diagnosed After Coronavirus Disease-19: A Case Report. Erciyes Med. J. 2021, 44, 3.
- Martinez-Perez, R.; Kortz, M.W.; Carroll, B.W.; Duran, D.; Neill, J.S.; Luzardo, G.D.; Zachariah, M.A. Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Pituitary Apoplexy: A Single-Center Case Series and Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2021, 152, e678–e687.
- Zhang, X.; Cai, H.; Hu, J.; Lian, J.; Gu, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y. Epidemiological, clinical characteristics of cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection with abnormal imaging findings. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 81–87.
- Sheikh, A.B.; Javed, N.; Sheikh, A.A.E.; Upadhyay, S.; Shekhar, R. Diabetes Insipidus and Concomitant Myocarditis: A Late Sequelae of COVID-19 Infection. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2021, 9, 2324709621999954.
- Ho, K.S.; Narasimhan, B.; Kumar, A.; Flynn, E.; Salonia, J.; El-Hachem, K.; Mathew, J.P. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone as the initial presentation of COVID-19: A novel case report. Nefrol. Engl. Ed. 2021, 41, 219–220.
- Yousaf, Z.; Al-Shokri, S.D.; Al-Soub, H.; Mohamed, M.F.H. COVID-19-associated SIADH: A clue in the times of pandemic! Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E882–E885.
- Li, M.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.S. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 45.
- Rotondi, M.; Coperchini, F.; Ricci, G.; Denegri, M.; Croce, L.; Ngnitejeu, S.T.; Chiovato, L. Detection of SARS-COV-2 receptor ACE-2 mRNA in thyroid cells: A clue for COVID-19-related subacute thyroiditis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1085–1090.
- Brancatella, A.; Ricci, D.; Viola, N.; Sgro, D.; Santini, F.; Latrofa, F. Subacute Thyroiditis After Sars-COV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 2367–2370.
- Brancatella, A.; Ricci, D.; Cappellani, D.; Viola, N.; Sgro, D.; Santini, F.; Latrofa, F. Is Subacute Thyroiditis an Underestimated Manifestation of SARS-CoV-2 Infection? Insights from a Case Series. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e3742–e3746.
- Chakraborty, U.; Ghosh, S.; Chandra, A.; Ray, A.K. Subacute thyroiditis as a presenting manifestation of COVID-19: A report of an exceedingly rare clinical entity. BMJ Case Rep. CP 2020, 13, e239953.
- Lania, A.; Sandri, M.T.; Cellini, M.; Mirani, M.; Lavezzi, E.; Mazziotti, G. Thyrotoxicosis in patients with COVID-19: The THYRCOV study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, 381–387.
- Mateu-Salat, M.; Urgell, E.; Chico, A. SARS-COV-2 as a trigger for autoimmune disease: Report of two cases of Graves’ disease after COVID-19. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 1527–1528.
- Muller, I.; Cannavaro, D.; Dazzi, D.; Covelli, D.; Mantovani, G.; Muscatello, A.; Ferrante, E.; Orsi, E.; Resi, V.; Longari, V.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-related atypical thyroiditis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 739–741.
- Dixit, N.M.; Truong, K.P.; Rabadia, S.V.; Li, D.; Srivastava, P.K.; Mosaferi, T.; Calfon Press, M.A.; Donangelo, I.; Kelesidis, T. Sudden Cardiac Arrest in a Patient with Myxedema Coma and COVID-19. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvaa130.
- Tee, L.Y.; Harjanto, S.; Rosario, B.H. COVID-19 complicated by Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Singap. Med. J. 2021, 62, 265.
- Trimboli, P.; Camponovo, C.; Scappaticcio, L.; Bellastella, G.; Piccardo, A.; Rotondi, M. Thyroid sequelae of COVID-19: A systematic review of reviews. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021, 22, 485–491.
- Cippa, P.E.; Cugnata, F.; Ferrari, P.; Brombin, C.; Ruinelli, L.; Bianchi, G.; Beria, N.; Schulz, L.; Bernasconi, E.; Merlani, P.; et al. A data-driven approach to identify risk profiles and protective drugs in COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2016877118.
- Scappaticcio, L.; Pitoia, F.; Esposito, K.; Piccardo, A.; Trimboli, P. Impact of COVID-19 on the thyroid gland: An update. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 22, 803–815.
- Ding, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Che, X.; Hou, J.; Hou, J.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Qiu, L.; et al. Organ distribution of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) in SARS patients: Implications for pathogenesis and virus transmission pathways. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 622–630.
- He, L.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Che, X.; He, Y.; Shen, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Geng, J.; et al. Expression of elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in SARS-CoV-infected ACE2+ cells in SARS patients: Relation to the acute lung injury and pathogenesis of SARS. J. Pathol. 2006, 210, 288–297.
- Elkattawy, S.; Alyacoub, R.; Ayad, S.; Pandya, M.; Eckman, A. A Novel Case of Hypoparathyroidism Secondary to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cureus 2020, 12, e10097.
- Liu, J.; Han, P.; Wu, J.; Gong, J.; Tian, D. Prevalence and predictive value of hypocalcemia in severe COVID-19 patients. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1224–1228.
- Liu, F.; Long, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. ACE2 Expression in Pancreas May Cause Pancreatic Damage After SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2128–2130.e2.
- de Sa, T.C.; Soares, C.; Rocha, M. Acute pancreatitis and COVID-19: A literature review. World, J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 13, 574–584.
- Ceriello, A. Hyperglycemia and COVID-19: What was known and what is really new? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 167, 108383.
- Saand, A.R.; Flores, M.; Kewan, T.; Alqaisi, S.; Alwakeel, M.; Griffiths, L.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Burton, R.; Al-Jaghbeer, M.J.; et al. Does inpatient hyperglycemia predict a worse outcome in COVID-19 intensive care unit patients? J. Diabetes 2021, 13, 253–260.
- Brufsky, A. Hyperglycemia, hydroxychloroquine, and the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 770–775.
- Gianchandani, R.; Esfandiari, N.H.; Ang, L.; Iyengar, J.; Knotts, S.; Choksi, P.; Pop-Busui, R. Managing Hyperglycemia in the COVID-19 Inflammatory Storm. Diabetes 2020, 69, 2048–2053.
- Mao, Y.; Xu, B.; Guan, W.; Xu, D.; Li, F.; Ren, R.; Zhu, X.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, L. The Adrenal Cortex, an Underestimated Site of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 593179.
- Heidarpour, M.; Vakhshoori, M.; Abbasi, S.; Shafie, D.; Rezaei, N. Adrenal insufficiency in coronavirus disease 2019: A case report. J. Med. Case. Rep. 2020, 14, 134.
- Hashim, M.; Athar, S.; Gaba, W.H. New onset adrenal insufficiency in a patient with COVID-19. BMJ Case Rep. CP 2021, 14, e237690.
- Sheikh, A.B.; Javaid, M.A.; Sheikh, A.A.E.; Shekhar, R. Central adrenal insufficiency and diabetes insipidus as potential endocrine manifestations of COVID-19 infection: A case report. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2021, 38, 222.
- Pal, R. COVID-19, hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis and clinical implications. Endocrine 2020, 68, 251–252.
- Massarotti, C.; Garolla, A.; Maccarini, E.; Scaruffi, P.; Stigliani, S.; Anserini, P.; Foresta, C. SARS-CoV-2 in the semen: Where does it come from? Andrology 2021, 9, 39–41.
- Selek, A.; Guclu, M.; Bolu, S.E. COVID-19 pandemic: What about the gonads? Hormones Athens 2021, 20, 259–268.
- Dutta, S.; Sengupta, P. SARS-CoV-2 and Male Infertility: Possible Multifaceted Pathology. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 28, 23–26.
- Bhasin, S.; Brito, J.P.; Cunningham, G.R.; Hayes, F.J.; Hodis, H.N.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Snyder, P.J.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Wu, F.C.; Yialamas, M.A. Testosterone Therapy in Men with Hypogonadism: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1715–1744.
- Seymen, C.M. The other side of COVID-19 pandemic: Effects on male fertility. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1396–1402.
- Mannur, S.; Jabeen, T.; Khader, M.A.; Rao, L.S.S. Post-COVID-19 Associated Decline in Long-Term Male Fertility and Embryo Quality during Assisted Reproductive Technology. QJM 2021, 114, 328–330.
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615.
- Bridwell, R.E.; Merrill, D.R.; Griffith, S.A.; Wray, J.; Oliver, J.J. A coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patient with bilateral orchitis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 42, 260.e3–260.e5.
- Segars, J.; Katler, Q.; McQueen, D.B.; Kotlyar, A.; Glenn, T.; Knight, Z.; Feinberg, E.C.; Taylor, H.S.; Toner, J.P.; Kawwass, J.F.L. Prior and novel coronaviruses, Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), and human reproduction: What is known? Fertil. Steril. 2020, 113, 1140–1149.
- Stanley, K.E.; Thomas, E.; Leaver, M.; Wells, D. Coronavirus disease-19 and fertility: Viral host entry protein expression in male and female reproductive tissues. Fertil. Steril. 2020, 114, 33–43.
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416.
- Luger, A.; Giustina, A.; Peeters, R. European Society of Endocrinology (ESE)’s Statement Concerning COVID 19 Vaccination: ‘Follow the Same Recommendations for Patients with Stable Endocrine Disorders as for the General Population’; European Society of Endocrinology: Bristol, UK, 2021.
- Puig-Domingo, M.; Marazuela, M.; Yildiz, B.O.; Giustina, A. COVID-19 and endocrine and metabolic diseases. An updated statement from the European Society of Endocrinology. Endocrine 2021, 72, 301–316.
- Katznelson, L.; Gadelha, M. Glucocorticoid use in patients with adrenal insufficiency following administration of the COVID-19 vaccine: A pituitary society statement. Pituitary 2021, 24, 143–145.
- Fauci, A.S.; Dale, D.C. The effect of in vivo hydrocortisone on subpopulations of human lymphocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1974, 53, 240–246.
- Fauci, A.S.; Pratt, K.R.; Whalen, G. Activation of human B lymphocytes. IV. Regulatory effects of corticosteroids on the triggering signal in the plaque-forming cell response of human peripheral blood B lymphocytes to polyclonal activation. J. Immunol. 1977, 119, 598–603.
- Yasir, M.; Goyal, A.; Bansal, P.; Sonthalia, S. Corticosteroid Adverse Effects; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021.
- Inoue, S.; Shibata, Y.; Takabatake, N.; Igarashi, A.; Abe, S.; Kubota, I. Influence of corticosteroid therapy on the serum antibody response to influenza vaccine in elderly patients with chronic pulmonary diseases. EXCLI J. 2013, 12, 760–765.
- Fischer, L.; Gerstel, P.F.; Poncet, A.; Siegrist, C.A.; Laffitte, E.; Gabay, C.; Seebach, J.D.; Ribi, C. Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination in adults undergoing immunosuppressive treatment for inflammatory diseases—A longitudinal study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 151.
- Yildiz, N.; Sever, L.; Kasapcopur, O.; Cullu, F.; Arisoy, N.; Caliskan, S. Hepatitis B virus vaccination in children with steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome: Immunogenicity and safety? Vaccine 2013, 31, 3309–3312.
- Taylor, P.; Allen, L.; Shrikrishnapalasuriyar, N.; Stechman, M.; Rees, A. Vaccine-induced thrombosis and thrombocytopenia with bilateral adrenal haemorrhage. Clin. Endocrinol. 2021.
- Boyle, L.D.; Morganstein, D.L.; Mitra, I.; Nogueira, E.F. A rare case of multiple thrombi and left adrenal haemorrhage following COVID-19 vaccination. Endocr. Abstr. 2021, 74, NCC4.
- Lampasona, V.; Secchi, M.; Scavini, M.; Bazzigaluppi, E.; Brigatti, C.; Marzinotto, I.; Davalli, A.; Caretto, A.; Laurenzi, A.; Martinenghi, S.; et al. Antibody response to multiple antigens of SARS-CoV-2 in patients with diabetes: An observational cohort study. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 2548–2558.
- Frasca, D.; Diaz, A.; Romero, M.; Mendez, N.V.; Landin, A.M.; Ryan, J.G.; Blomberg, B.B. Young and elderly patients with type 2 diabetes have optimal B cell responses to the seasonal influenza vaccine. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3603–3610.
- Li Volti, S.; Caruso-Nicoletti, M.; Biazzo, F.; Sciacca, A.; Mandara, G.; Mancuso, M.; Mollica, F. Hyporesponsiveness to intradermal administration of hepatitis B vaccine in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Arch. Dis. Child. 1998, 78, 54–57.
- Looijmans-Van den Akker, I.; Verheij, T.J.; Buskens, E.; Nichol, K.L.; Rutten, G.E.; Hak, E. Clinical effectiveness of first and repeat influenza vaccination in adult and elderly diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1771–1776.
- Smith, S.A.; Poland, G.A. Use of influenza and pneumococcal vaccines in people with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 95–108.
- Abu-Rumaileh, M.A.; Gharaibeh, A.M.; Gharaibeh, N.E. COVID-19 Vaccine and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State. Cureus 2021, 13, e14125.
- Mishra, A.; Ghosh, A.; Dutta, K.; Tyagi, K.; Misra, A. Exacerbation of hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes after vaccination for COVID19: Report of three cases. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 102151.
- Heald, A.; Rea, R.; Horne, L.; Metters, A.; Steele, T.; Leivesley, K.; Whyte, M.B.; Stedman, M.; Ollier, W. Analysis of continuous glucose tracking data in people with Type 1 Diabetes (T1DM) after COVID-19 Vaccination reveals unexpected link between immune and metabolic response, augmented by adjunctive oral medication. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14714.
- Iremli, B.G.; Sendur, S.N.; Unluturk, U. Three Cases of Subacute Thyroiditis Following SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine: Post-vaccination ASIA Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 2600–2605.
- Franquemont, S.; Galvez, J. Subacute Thyroiditis After mRNA Vaccine for Covid-19. J. Endocr. Soc. 2021, 5, A956–A957.
- Oyibo, S.O. Subacute Thyroiditis After Receiving the Adenovirus-Vectored Vaccine for Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Cureus 2021, 13, e16045.
- Sahin Tekin, M.; Saylisoy, S.; Yorulmaz, G. Subacute thyroiditis following COVID-19 vaccination in a 67-year-old male patient: A case report. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 4090–4092.
- Watad, A.; Sharif, K.; Shoenfeld, Y. The ASIA syndrome: Basic concepts. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 28, 64–69.
- Vera-Lastra, O.; Ordinola Navarro, A.; Cruz Domiguez, M.P.; Medina, G.; Sanchez Valadez, T.I.; Jara, L.J. Two Cases of Graves’ Disease Following SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination: An Autoimmune/Inflammatory Syndrome Induced by Adjuvants. Thyroid 2021, 31, 1436–1439.
- Acheampong, D.O.; Barffour, I.K.; Boye, A.; Aninagyei, E.; Ocansey, S.; Morna, M.T. Male predisposition to severe COVID-19: Review of evidence and potential therapeutic prospects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110748.
- Shimabukuro, T.T.; Cole, M.; Su, J.R. Reports of Anaphylaxis After Receipt of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines in the US-December 14, 2020-January 18, 2021. JAMA 2021, 325, 1101–1102.
- Fischinger, S.; Boudreau, C.M.; Butler, A.L.; Streeck, H.; Alter, G. Sex differences in vaccine-induced humoral immunity. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 239–249.
- Ruggieri, A.; Anticoli, S.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Giordani, L.; Viora, M. The influence of sex and gender on immunity, infection and vaccination. Ann. Dell’istituto Super. Sanita 2016, 52, 198–204.
- Trigunaite, A.; Dimo, J.; Jorgensen, T.N. Suppressive effects of androgens on the immune system. Cell. Immunol. 2015, 294, 87–94.
- Tsourdi, E.; Yu, E.W.; Jan de Beur, S.M.; Drake, M.T. Vaccination for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Relationship to Osteoporosis Care: Current Evidence and Suggested Approaches. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2021, 36, 1042–1047.
- Roozenbeek, J.; Schneider, C.R.; Dryhurst, S.; Kerr, J.; Freeman, A.L.J.; Recchia, G.; Van Der Bles, A.M.; Van Der Linden, S. Susceptibility to misinformation about COVID-19 around the world. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 201199.
- Sallam, M.; Dababseh, D.; Eid, H.; Al-Mahzoum, K.; Al-Haidar, A.; Taim, D.; Yaseen, A.; Ababneh, N.A.; Bakri, F.G.; Mahafzah, A. High Rates of COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy and Its Association with Conspiracy Beliefs: A Study in Jordan and Kuwait among Other Arab Countries. Vaccines 2021, 9, 42.
- Sajjadi, N.B.; Nowlin, W.; Nowlin, R.; Wenger, D.; Beal, J.M.; Vassar, M.; Hartwell, M. United States internet searches for “infertility” following COVID-19 vaccine misinformation. J. Osteopath. Med. 2021, 121, 583–587.
- Berry, S.D.; Johnson, K.S.; Myles, L.; Herndon, L.; Montoya, A.; Fashaw, S.; Gifford, D. Lessons learned from frontline skilled nursing facility staff regarding COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 69, 1140–1146.
- Gonzalez, D.C.; Nassau, D.E.; Khodamoradi, K.; Ibrahim, E.; Blachman-Braun, R.; Ory, J.; Ramasamy, R. Sperm Parameters Before and After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination. JAMA 2021, 326, 273–274.
- Lifshitz, D.; Haas, J.; Lebovitz, O.; Raviv, G.; Orvieto, R.; Aizer, A. Does mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine detrimentally affect male fertility, as reflected by semen analysis? Reprod. Biomed. Online 2022, 44, 145–149.
- Available online: https://www.deseret.com/u-s-world/2021/2/13/22278041/pregnant-women-covid-19-vaccine-dr-anthony-fauci (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Gray, K.J.; Bordt, E.A.; Atyeo, C.; Deriso, E.; Akinwunmi, B.; Young, N.; Baez, A.M.; Shook, L.L.; Cvrk, D.; James, K.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine response in pregnant and lactating women: A cohort study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 225, 303-e1.
- Wang, C.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Long, C.Y. Impact of COVID-19 on Pregnancy. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 763–767.
- Lipkind, H.S.; Vazquez-Benitez, G.; DeSilva, M.; Vesco, K.K.; Ackerman-Banks, C.; Zhu, J.; Boyce, T.G.; Daley, M.F.; Fuller, C.C.; Getahun, D.; et al. Receipt of COVID-19 Vaccine During Pregnancy and Preterm or Small-for-Gestational-Age at Birth—Eight Integrated Health Care Organizations, United States, December 15, 2020–July 22, 2021. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 26–30.
- Blakeway, H.; Prasad, S.; Kalafat, E.; Heath, P.T.; Ladhani, S.N.; Le Doare, K.; Magee, L.A.; O’Brien, P.; Rezvani, A.; von Dadelszen, P.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy: Coverage and safety. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, 236.e1–236.e14.
- Zambrano, L.D.; Ellington, S.; Strid, P.; Galang, R.R.; Oduyebo, T.; Tong, V.T.; Woodworth, K.R.; Nahabedian, J.F., III; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Gilboa, S.M.; et al. CDC COVID-19 Response Pregnancy and Infant Linked Outcomes Team. Update: Characteristics of symptomatic women of reproductive age with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection by pregnancy status—United States, January 22–October 3, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1641–1647.




