
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wachiranun Sirikul | + 1543 word(s) | 1543 | 2022-03-03 11:33:14 | | | |
| 2 | Vicky Zhou | Meta information modification | 1543 | 2022-03-16 07:50:43 | | | | |
| 3 | Vicky Zhou | + 16 word(s) | 1559 | 2022-03-16 10:11:01 | | |
Video Upload Options
Osteoporosis is a chronic debilitating disease caused by imbalanced bone remodeling processes that impair the structural integrity of bone. Over the last ten years, the association between fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) and osteoporosis has been studied in both pre-clinical and clinical investigations. FGF23 is a bone-derived endocrine factor that regulates mineral homeostasis via the fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs)/αKlotho complex. These receptors are expressed in kidney and the parathyroid gland. Preclinical studies have supported the link between the local actions of FGF23 on the bone remodeling processes. In addition, clinical evidence regarding the effects of FGF23 on bone mass and fragility fractures suggest potential diagnostic and prognostic applications of FGF23 in clinical contexts, particularly in elderly and patients with chronic kidney disease. However, inconsistent findings exist and there are areas of uncertainty requiring exploration.
1. Introduction
2. Role of FGF23 in Postmenopausal and Age-Related Osteoporosis Pathogenesis
3. Potential Clinical Application of FGF23 in Osteoporosis and Chronic Kidney Disease–Mineral and Bone Disease (CKD-MBD)
4. FGF23 Measurement in Routine Clinical Practices
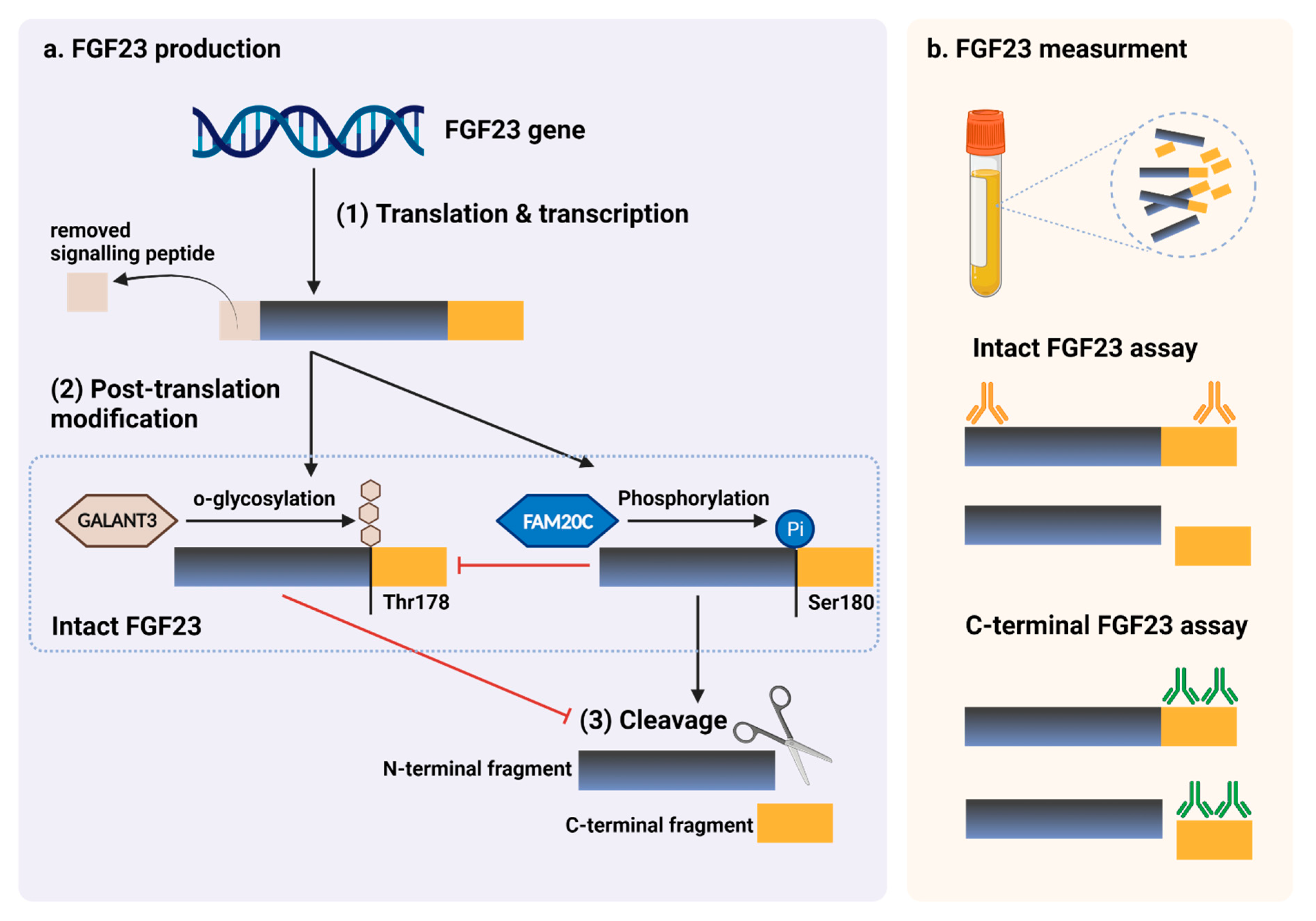 Figure 1. FGF23 production and immunoassay measurements. (a) After completed transcription and translation, FGF23 can be transferred to two post-translation modification pathways, including O-glycosylation with GALNT3 on Thr178, or phosphorylation by the extracellular serine/threonine protein kinase FAM20C at Ser180. O-glycosylation modification by GALANT3, stabilized form, can prevent intact FGF23 from cleavage. In contrast, phosphorylated FGF23 by FAM20C can be cleaved into N-terminal and C-terminal fragments within the osteocyte/osteoblast. These peptides, including full-length (intact) FGF23, N-terminal fragments, and C-terminal fragments, can be detected in the circulation. (b) For C-terminal assays, detecting antibodies bind to C-terminus epitopes to detect both full-length FGF23 and its C-terminal fragments, whereas assays for intact FGF23 use antibodies to detect epitopes surrounding the FGF23 cleavage site for the detection of only full-length FGF23. This figure was generated with publication licensed by BioRender, Toronto, ON, Canada (Agreement number: DV237SONHF, 19 November 2021). Abbreviations: GALNT3, polypeptide N-acetyl galactosaminyltransferase 3; FAM20C, the extracellular protein kinase FAM20C; Ser, Serine; Thr, Threonine.
Figure 1. FGF23 production and immunoassay measurements. (a) After completed transcription and translation, FGF23 can be transferred to two post-translation modification pathways, including O-glycosylation with GALNT3 on Thr178, or phosphorylation by the extracellular serine/threonine protein kinase FAM20C at Ser180. O-glycosylation modification by GALANT3, stabilized form, can prevent intact FGF23 from cleavage. In contrast, phosphorylated FGF23 by FAM20C can be cleaved into N-terminal and C-terminal fragments within the osteocyte/osteoblast. These peptides, including full-length (intact) FGF23, N-terminal fragments, and C-terminal fragments, can be detected in the circulation. (b) For C-terminal assays, detecting antibodies bind to C-terminus epitopes to detect both full-length FGF23 and its C-terminal fragments, whereas assays for intact FGF23 use antibodies to detect epitopes surrounding the FGF23 cleavage site for the detection of only full-length FGF23. This figure was generated with publication licensed by BioRender, Toronto, ON, Canada (Agreement number: DV237SONHF, 19 November 2021). Abbreviations: GALNT3, polypeptide N-acetyl galactosaminyltransferase 3; FAM20C, the extracellular protein kinase FAM20C; Ser, Serine; Thr, Threonine.5. Conclusions
References
- Shen, J.; Fu, S.; Song, Y. Relationship of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF-23) Serum Levels With Low Bone Mass in Postmenopausal Women. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 4454–4459.
- Marsell, R.; Mirza, M.A.; Mallmin, H.; Karlsson, M.; Mellström, D.; Orwoll, E.; Ohlsson, C.; Jonsson, K.B.; Ljunggren, O.; Larsson, T.E. Relation between fibroblast growth factor-23, body weight and bone mineral density in elderly men. Osteoporos. Int. 2009, 20, 1167–1173.
- Rupp, T.; Butscheidt, S.; Vettorazzi, E.; Oheim, R.; Barvencik, F.; Amling, M.; Rolvien, T. High FGF23 levels are associated with impaired trabecular bone microarchitecture in patients with osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 1655–1662.
- Bilha, S.C.; Bilha, A.; Ungureanu, M.C.; Matei, A.; Florescu, A.; Preda, C.; Covic, A.; Branisteanu, D. FGF23 Beyond the Kidney: A New Bone Mass Regulator in the General Population. Horm. Metab. Res. 2020, 52, 298–304.
- Shimada, T.; Kakitani, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Fujita, T.; Fukumoto, S.; Tomizuka, K.; Yamashita, T. Targeted ablation of Fgf23 demonstrates an essential physiological role of FGF23 in phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 561–568.
- Takeshita, A.; Kawakami, K.; Furushima, K.; Miyajima, M.; Sakaguchi, K. Central role of the proximal tubular αKlotho/FGF receptor complex in FGF23-regulated phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6917.
- Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Galitzer, H.; Lavi-Moshayoff, V.; Goetz, R.; Kuro-o, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Sirkis, R.; Naveh-Many, T.; Silver, J. The parathyroid is a target organ for FGF23 in rats. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 4003–4008.
- Kawaguchi, H.; Manabe, N.; Miyaura, C.; Chikuda, H.; Nakamura, K.; Kuro-o, M. Independent impairment of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation in klotho mouse exhibiting low-turnover osteopenia. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 229–237.
- Masuyama, R.; Stockmans, I.; Torrekens, S.; Van Looveren, R.; Maes, C.; Carmeliet, P.; Bouillon, R.; Carmeliet, G. Vitamin D receptor in chondrocytes promotes osteoclastogenesis and regulates FGF23 production in osteoblasts. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3150–3159.
- Mirza, M.A.; Karlsson, M.K.; Mellström, D.; Orwoll, E.; Ohlsson, C.; Ljunggren, O.; Larsson, T.E. Serum fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF-23) and fracture risk in elderly men. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 857–864.
- Lane, N.E.; Parimi, N.; Corr, M.; Yao, W.; Cauley, J.A.; Nielson, C.M.; Ix, J.H.; Kado, D.; Orwoll, E. Association of serum fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) and incident fractures in older men: The Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 2325–2332.
- Kanda, E.; Yoshida, M.; Sasaki, S. Applicability of fibroblast growth factor 23 for evaluation of risk of vertebral fracture and chronic kidney disease-mineral bone disease in elderly chronic kidney disease patients. BMC Nephrol. 2012, 13, 122.
- Desbiens, L.C.; Sidibé, A.; Ung, R.V.; Fortier, C.; Munger, M.; Wang, Y.P.; Bisson, S.K.; Marquis, K.; Agharazii, M.; Mac-Way, F. FGF23-klotho axis, bone fractures, and arterial stiffness in dialysis: A case-control study. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 2345–2353.
- Wu, Q.; Xiao, D.M.; Fan, W.F.; Ye, X.W.; Niu, J.Y.; Gu, Y. Effect of serum fibroblast growth factor-23, matrix Gla protein and Fetuin-A in predicting osteoporosis in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Ther. Apher Dial 2014, 18, 427–433.
- Smith, E.R.; Cai, M.M.; McMahon, L.P.; Holt, S.G. Biological Variability of Plasma Intact and C-Terminal FGF23 Measurements. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3357–3365.
- Dirks, N.F.; Smith, E.R.; van Schoor, N.M.; Vervloet, M.G.; Ackermans, M.T.; de Jonge, R.; Heijboer, A.C. Pre-analytical stability of FGF23 with the contemporary immunoassays. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 493, 104–106.
- Vervloet, M.G.; van Ittersum, F.J.; Buttler, R.M.; Heijboer, A.C.; Blankenstein, M.A.; ter Wee, P.M. Effects of Dietary Phosphate and Calcium Intake on Fibroblast Growth Factor-23. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 383–389.
- Burnett, S.M.; Gunawardene, S.C.; Bringhurst, F.R.; Jüppner, H.; Lee, H.; Finkelstein, J.S. Regulation of C-terminal and intact FGF-23 by dietary phosphate in men and women. J. Bone Min. Res. 2006, 21, 1187–1196.
- Goetz, R.; Nakada, Y.; Hu, M.C.; Kurosu, H.; Wang, L.; Nakatani, T.; Shi, M.; Eliseenkova, A.V.; Razzaque, M.S.; Moe, O.W.; et al. Isolated C-terminal tail of FGF23 alleviates hypophosphatemia by inhibiting FGF23-FGFR-Klotho complex formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 407–412.





