
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manuel Izquierdo | + 4466 word(s) | 4466 | 2022-02-28 09:10:11 | | | |
| 2 | Vivi Li | + 116 word(s) | 4582 | 2022-03-10 02:20:15 | | |
Video Upload Options
Extracellular vesicles (EV) are a very diverse group of cell-derived vesicles released by almost all kind of living cells. EV are involved in intercellular exchange, both nearby and systemically, since they induce signals and transmit their cargo (proteins, lipids, miRNAs) to other cells, which subsequently trigger a wide variety of biological responses in the target cells. However, cell surface receptor-induced EV release is limited to cells from the immune system, including T lymphocytes. T cell receptor activation of T lymphocytes induces secretion of EV containing T cell receptors for antigen and several bioactive molecules, including proapoptotic proteins. These EV are specific for antigen-bearing cells, which make them ideal candidates for a cell-free, EV-dependent cancer therapy.
1. Introduction
1.1 Extracellular Vesicle Types
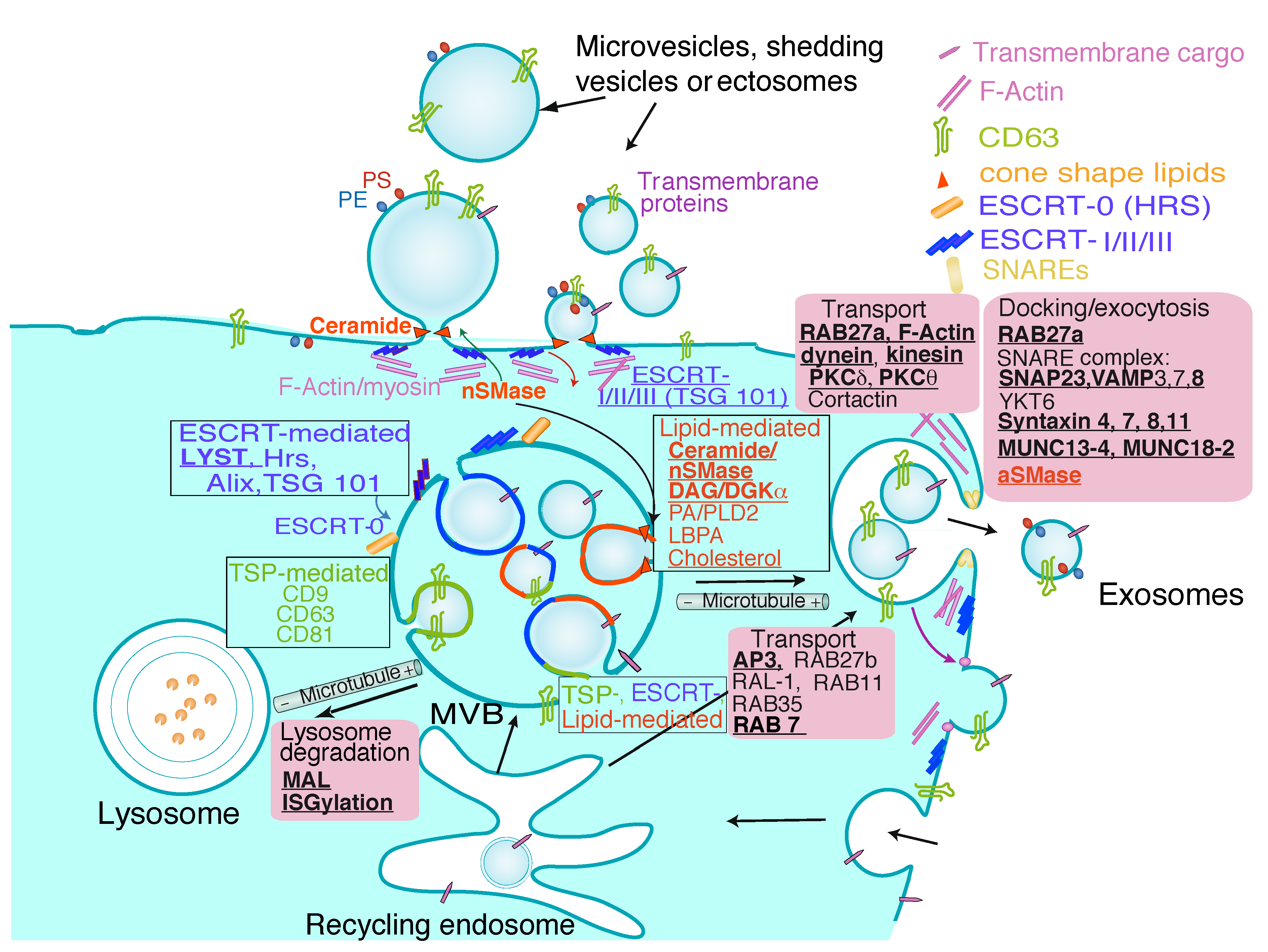
2. Extracellular Vesicles from T Lymphocytes
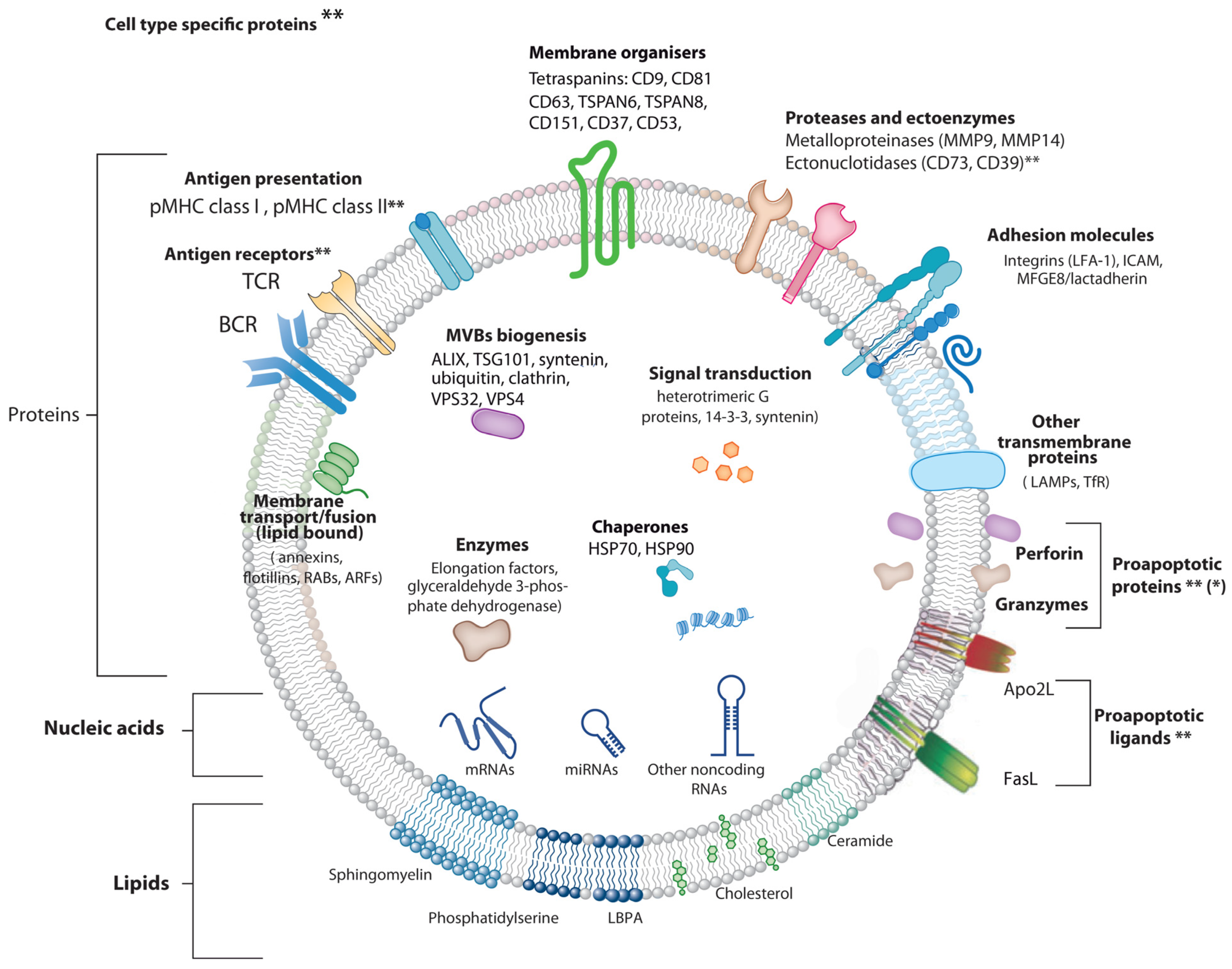
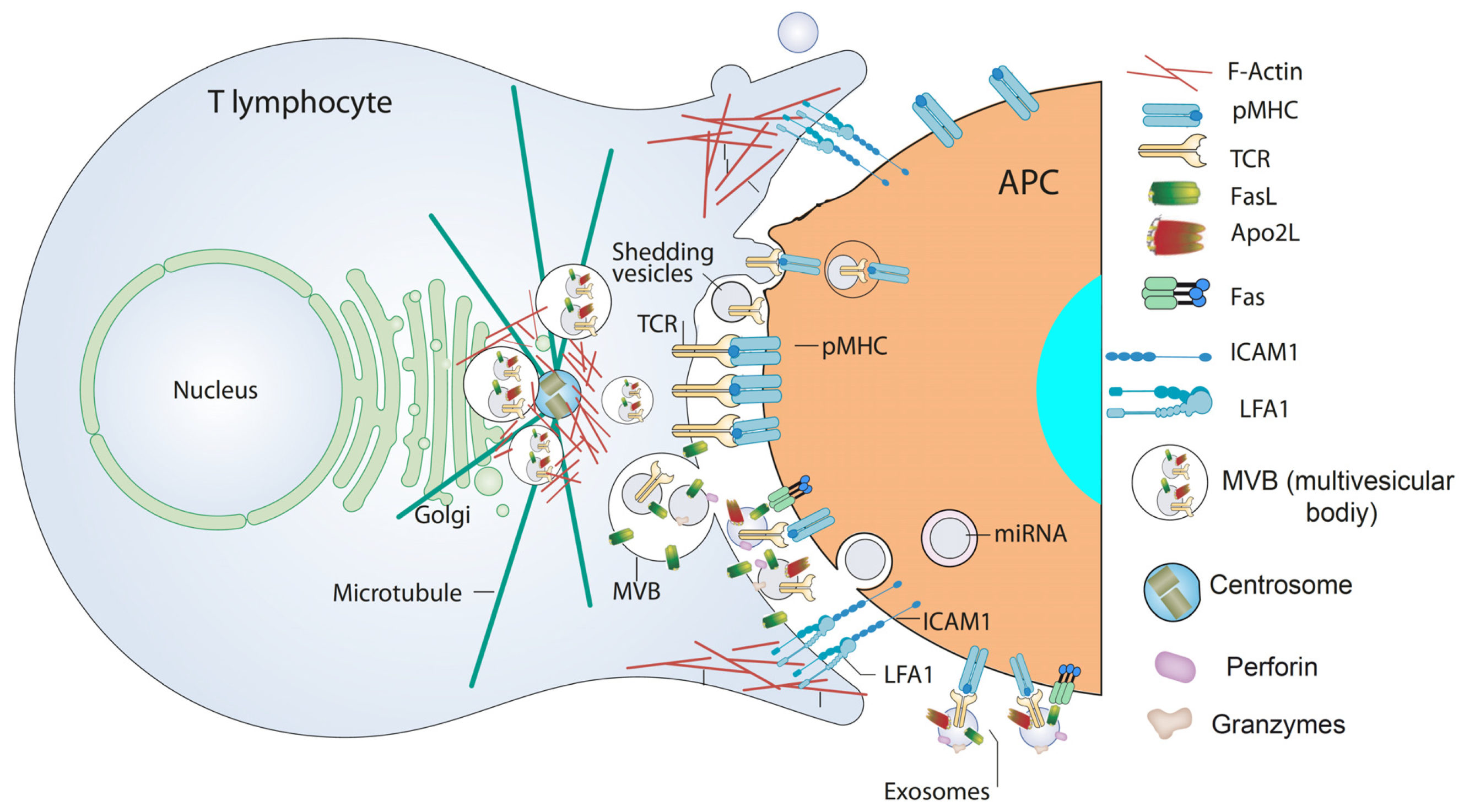
3. Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells and CAR T Cell-Derived EV
3.1 Cancer Therapeutic Approaches
| Target Molecule | EV-Producing Cell | EV Types | EV Phenotype | Anti-Tumor Mechanism | Target Cell |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR, HER2 [81] |
Human CAR T cells (?) 1 |
Exosomes | CAR+, CD3+, CD63+, perforin+, granzyme B+, CD45−, CD28− |
Perforin/ granzyme B 2 |
EGFR+, HER2+ human breast cancer cells |
| HER2 [84] |
Human CAR T cells CD4+ (46%) CD8+ (49%) |
EV (small EV, probably exosomes plus larger EV) 3 |
CAR+, CD3+, CD63+, granzyme B+ |
Granzyme B 2 | HER2+ human breast cancer cells, ovarian cancer cells |
| Mesothelin [83] |
Human CAR T cells CD4+ (58%) CD8+ (31%) |
Probably exosomes 4 |
CAR+, CD3+, CD63+, perforin+, granzyme B+ |
Perforin/ granzyme B 2 |
Triple negative human breast cancer cells |
| CD19 [85] |
Human CAR HEK293 cells | Probably exosomes 4 |
CAR+, CD63+, CD81+ |
Indirect induction of proapoptotic genes in target cells |
CD19+ human B cell leukemia |
| CD19 [82] |
Human CAR HEK293 cells | Probably shedding vesicles 4 | CAR+, annexin V binding (PS exposure) |
MYC Gene disruption mediated by CRISPR/Cas9 |
CD19+ human B cell leukemia cell lines |
| Mesothelin CD19 [86] |
Human and mouse CAR T Cells (?) 1 |
EV 4 | Unknown 5 Contain RN7SL1 |
Recruitment of endogenous anti-tumor immunity byRN7SL1 |
Mouse melanoma expressing human CD19 |
| Event | CAR T Cells | CAR T Cell-Derived EV |
|---|---|---|
| Cytokine releasing syndrome | ++ | − |
| Neurotoxicity | ++ | − |
| Cross the blood barrier | − | ++ |
| Efficiency against solid tumors | +/− | ++ |
| Immunosuppression by tumoral PD-L1 | + | − |
| Immunological memory | + 1 | (?) 2 |
References
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228.
- Thery, C.; Ostrowski, M.; Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 581–593.
- Lindenbergh, M.F.S.; Stoorvogel, W. Antigen presentation by extracellular vesicles from professional antigen-presenting cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 435–459.
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420.
- Johnstone, R.M. The jeanne manery-fisher memorial lecture 1991. Maturation of reticulocytes: Formation of exosomes as a mechanism for shedding membrane proteins. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1992, 70, 179–190.
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289.
- Babst, M. Mvb vesicle formation: Escrt-dependent, escrt-independent and everything in between. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 452–457.
- Scott, C.C.; Vacca, F.; Gruenberg, J. Endosome maturation, transport and functions. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 31, 2–10.
- Geuze, H.J. The role of endosomes and lysosomes in mhc class ii functioning. Immunol. Today 1998, 19, 282–287.
- Denzer, K.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Heijnen, H.F.; Stoorvogel, W.; Geuze, H.J. Exosome: From internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 19, 3365–3374.
- Pan, B.T.; Teng, K.; Wu, C.; Adam, M.; Johnstone, R.M. Electron microscopic evidence for externalization of the transferrin receptor in vesicular form in sheep reticulocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 942–948.
- Calvo, V.; Izquierdo, M. Inducible polarized secretion of exosomes in t and b lymphocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2631.
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17.
- Nagle, D.L.; Karim, M.A.; Woolf, E.A.; Holmgren, L.; Bork, P.; Misumi, D.J.; McGrail, S.H.; Dussault, B.J., Jr.; Perou, C.M.; Boissy, R.E.; et al. Identification and mutation analysis of the complete gene for chediak-higashi syndrome. Nat. Genet. 1996, 14, 307–311.
- Mittelbrunn, M.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gonzalez, S.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Gonzalez, M.A.; Bernad, A.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Unidirectional transfer of microrna-loaded exosomes from T cells to antigen-presenting cells. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 282.
- Quann, E.J.; Merino, E.; Furuta, T.; Huse, M. Localized diacylglycerol drives the polarization of the microtubule-organizing center in T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 627–635.
- Alonso, R.; Mazzeo, C.; Merida, I.; Izquierdo, M. A new role of diacylglycerol kinase alpha on the secretion of lethal exosomes bearing fas ligand during activation-induced cell death of t lymphocytes. Biochimie 2007, 89, 213–221.
- Alonso, R.; Mazzeo, C.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Marsh, M.; Fraile-Ramos, A.; Calvo, V.; Avila-Flores, A.; Merida, I.; Izquierdo, M. Diacylglycerol kinase alpha regulates the formation and polarisation of mature multivesicular bodies involved in the secretion of fas ligand-containing exosomes in t lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1161–1173.
- Alonso, R.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Pindado, J.; Merino, E.; Merida, I.; Izquierdo, M. Diacylglycerol kinase alpha regulates the secretion of lethal exosomes bearing fas ligand during activation-induced cell death of t lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 28439–28450.
- Chauveau, A.; Le Floc’h, A.; Bantilan, N.S.; Koretzky, G.A.; Huse, M. Diacylglycerol kinase alpha establishes t cell polarity by shaping diacylglycerol accumulation at the immunological synapse. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra82.
- Herz, J.; Pardo, J.; Kashkar, H.; Schramm, M.; Kuzmenkina, E.; Bos, E.; Wiegmann, K.; Wallich, R.; Peters, P.J.; Herzig, S.; et al. Acid sphingomyelinase is a key regulator of cytotoxic granule secretion by primary t lymphocytes. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 761–768.
- Ventimiglia, L.N.; Alonso, M.A. Biogenesis and function of t cell-derived exosomes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 84.
- Ventimiglia, L.N.; Fernandez-Martin, L.; Martinez-Alonso, E.; Anton, O.M.; Guerra, M.; Martinez-Menarguez, J.A.; Andres, G.; Alonso, M.A. Cutting edge: Regulation of exosome secretion by the integral mal protein in T cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 810–814.
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Baixauli, F.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Fernández-Delgado, I.; Torralba, D.; Moreno-Gonzalo, O.; Baldanta, S.; Enrich, C.; Guerra, S.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Isgylation controls exosome secretion by promoting lysosomal degradation of mvb proteins. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13588.
- Clark, R.H.; Stinchcombe, J.C.; Day, A.; Blott, E.; Booth, S.; Bossi, G.; Hamblin, T.; Davies, E.G.; Griffiths, G.M. Adaptor protein 3-dependent microtubule-mediated movement of lytic granules to the immunological synapse. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 1111–1120.
- Stinchcombe, J.C.; Barral, D.C.; Mules, E.H.; Booth, S.; Hume, A.N.; Machesky, L.M.; Seabra, M.C.; Griffiths, G.M. Rab27a is required for regulated secretion in cytotoxic t lymphocytes. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 825–834.
- Daniele, T.; Hackmann, Y.; Ritter, A.T.; Wenham, M.; Booth, S.; Bossi, G.; Schintler, M.; Auer-Grumbach, M.; Griffiths, G.M. A role for rab7 in the movement of secretory granules in cytotoxic t lymphocytes. Traffic 2011, 12, 902–911.
- Combs, J.; Kim, S.J.; Tan, S.; Ligon, L.A.; Holzbaur, E.L.; Kuhn, J.; Poenie, M. Recruitment of dynein to the jurkat immunological synapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14883–14888.
- Kurowska, M.; Goudin, N.; Nehme, N.T.; Court, M.; Garin, J.; Fischer, A.; de Saint Basile, G.; Ménasché, G. Terminal transport of lytic granules to the immune synapse is mediated by the kinesin-1/slp3/rab27a complex. Blood 2012, 119, 3879–3889.
- Ritter, A.T.; Asano, Y.; Stinchcombe, J.C.; Dieckmann, N.M.; Chen, B.C.; Gawden-Bone, C.; van Engelenburg, S.; Legant, W.; Gao, L.; Davidson, M.W.; et al. Actin depletion initiates events leading to granule secretion at the immunological synapse. Immunity 2015, 42, 864–876.
- Herranz, G.; Aguilera, P.; Davila, S.; Sanchez, A.; Stancu, B.; Gomez, J.; Fernandez-Moreno, D.; de Martin, R.; Quintanilla, M.; Fernandez, T.; et al. Protein kinase c delta regulates the depletion of actin at the immunological synapse required for polarized exosome secretion by T cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 851.
- Bello-Gamboa, A.; Velasco, M.; Moreno, S.; Herranz, G.; Ilie, R.; Huetos, S.; Dávila, S.; Sánchez, A.; Bernardino De La Serna, J.; Calvo, V.; et al. Actin reorganization at the centrosomal area and the immune synapse regulates polarized secretory traffic of multivesicular bodies in t lymphocytes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1759926.
- Fernández-Hermira, S.; Sanz-Fernández, I.; Botas, M.; Calvo, V.; Izquierdo, M. Analysis of centrosomal area actin reorganization and centrosome polarization upon lymphocyte activation at the immunological synapse. In Methods in Cell Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021.
- Ma, J.S.; Monu, N.; Shen, D.T.; Mecklenbrauker, I.; Radoja, N.; Haydar, T.F.; Leitges, M.; Frey, A.B.; Vukmanovic, S.; Radoja, S. Protein kinase cdelta regulates antigen receptor-induced lytic granule polarization in mouse cd8+ ctl. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 7814–7821.
- Quann, E.J.; Liu, X.; Altan-Bonnet, G.; Huse, M. A cascade of protein kinase c isozymes promotes cytoskeletal polarization in T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 647–654.
- Liu, X.; Kapoor, T.M.; Chen, J.K.; Huse, M. Diacylglycerol promotes centrosome polarization in T cells via reciprocal localization of dynein and myosin ii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11976–11981.
- Dressel, R.; Elsner, L.; Novota, P.; Kanwar, N.; Fischer von Mollard, G. The exocytosis of lytic granules is impaired in vti1b- or vamp8-deficient ctl leading to a reduced cytotoxic activity following antigen-specific activation. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1005–1014.
- Spessott, W.A.; Sanmillan, M.L.; Kulkarni, V.V.; McCormick, M.E.; Giraudo, C.G. Syntaxin 4 mediates endosome recycling for lytic granule exocytosis in cytotoxic t-lymphocytes. Traffic 2017, 18, 442–452.
- Pattu, V.; Qu, B.; Marshall, M.; Becherer, U.; Junker, C.; Matti, U.; Schwarz, E.C.; Krause, E.; Hoth, M.; Rettig, J. Syntaxin7 is required for lytic granule release from cytotoxic t lymphocytes. Traffic 2011, 12, 890–901.
- Bhat, S.S.; Friedmann, K.S.; Knörck, A.; Hoxha, C.; Leidinger, P.; Backes, C.; Meese, E.; Keller, A.; Rettig, J.; Hoth, M.; et al. Syntaxin 8 is required for efficient lytic granule trafficking in cytotoxic t lymphocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 1653–1664.
- zur Stadt, U.; Schmidt, S.; Kasper, B.; Beutel, K.; Diler, A.S.; Henter, J.I.; Kabisch, H.; Schneppenheim, R.; Nürnberg, P.; Janka, G.; et al. Linkage of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (fhl) type-4 to chromosome 6q24 and identification of mutations in syntaxin 11. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 827–834.
- Choudhuri, K.; Llodra, J.; Roth, E.W.; Tsai, J.; Gordo, S.; Wucherpfennig, K.W.; Kam, L.C.; Stokes, D.L.; Dustin, M.L. Polarized release of t-cell-receptor-enriched microvesicles at the immunological synapse. Nature 2014, 507, 118–123.
- Tchernev, V.T.; Mansfield, T.A.; Giot, L.; Kumar, A.M.; Nandabalan, K.; Li, Y.; Mishra, V.S.; Detter, J.C.; Rothberg, J.M.; Wallace, M.R.; et al. The chediak-higashi protein interacts with snare complex and signal transduction proteins. Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 56–64.
- de Saint Basile, G.; Menasche, G.; Fischer, A. Molecular mechanisms of biogenesis and exocytosis of cytotoxic granules. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 568–579.
- Trams, E.G.; Lauter, C.J.; Salem, N., Jr.; Heine, U. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 645, 63–70.
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mrnas and micrornas is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659.
- Robbins, P.D.; Morelli, A.E. Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 195–208.
- Fooksman, D.R.; Vardhana, S.; Vasiliver-Shamis, G.; Liese, J.; Blair, D.A.; Waite, J.; Sacristan, C.; Victora, G.D.; Zanin-Zhorov, A.; Dustin, M.L. Functional anatomy of t cell activation and synapse formation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 79–105.
- de la Roche, M.; Asano, Y.; Griffiths, G.M. Origins of the cytolytic synapse. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 421–432.
- Xie, J.; Tato, C.M.; Davis, M.M. How the immune system talks to itself: The varied role of synapses. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 251, 65–79.
- Huse, M.; Quann, E.J.; Davis, M.M. Shouts, whispers and the kiss of death: Directional secretion in T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1105–1111.
- Friedl, P.; den Boer, A.T.; Gunzer, M. Tuning immune responses: Diversity and adaptation of the immunological synapse. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 532–545.
- Huse, M. Microtubule-organizing center polarity and the immunological synapse: Protein kinase c and beyond. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 235.
- Calvo, V.; Izquierdo, M. Imaging polarized secretory traffic at the immune synapse in living t lymphocytes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 684.
- Peters, P.J.; Geuze, H.J.; Van der Donk, H.A.; Slot, J.W.; Griffith, J.M.; Stam, N.J.; Clevers, H.C.; Borst, J. Molecules relevant for t cell-target cell interaction are present in cytolytic granules of human t lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 1989, 19, 1469–1475.
- Peters, P.J.; Borst, J.; Oorschot, V.; Fukuda, M.; Krahenbuhl, O.; Tschopp, J.; Slot, J.W.; Geuze, H.J. Cytotoxic t lymphocyte granules are secretory lysosomes, containing both perforin and granzymes. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 173, 1099–1109.
- Golstein, P.; Griffiths, G.M. An early history of t cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 527–535.
- Peters, P.J.; Geuze, H.J.; van der Donk, H.A.; Borst, J. A new model for lethal hit delivery by cytotoxic t lymphocytes. Immunol. Today 1990, 11, 28–32.
- Bossi, G.; Griffiths, G.M. Degranulation plays an essential part in regulating cell surface expression of fas ligand in T cells and natural killer cells. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 90–96.
- Martinez-Lorenzo, M.J.; Anel, A.; Gamen, S.; Monle n, I.; Lasierra, P.; Larrad, L.; Pineiro, A.; Alava, M.A.; Naval, J. Activated human T cells release bioactive fas ligand and apo2 ligand in microvesicles. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 1274–1281.
- Monleon, I.; Martinez-Lorenzo, M.J.; Monteagudo, L.; Lasierra, P.; Taules, M.; Iturralde, M.; Pineiro, A.; Larrad, L.; Alava, M.A.; Naval, J.; et al. Differential secretion of fas ligand- or apo2 ligand/tnf-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-carrying microvesicles during activation-induced death of human T cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 6736–6744.
- Nagata, S. Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 1997, 88, 355–365.
- Krammer, P.H.; Arnold, R.; Lavrik, I.N. Life and death in peripheral T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 532–542.
- Nagata, S.; Suda, T. Fas and fas ligand: Lpr and gld mutations. Immunol. Today 1995, 16, 39–43.
- Dustin, M.L. What counts in the immunological synapse? Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 255–262.
- Dustin, M.L.; Choudhuri, K. Signaling and polarized communication across the t cell immunological synapse. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 32, 303–325.
- Calvo, V.; Izquierdo, M. Role of actin cytoskeleton reorganization in polarized secretory traffic at the immunological synapse. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 109.
- Mittelbrunn, M.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Intercellular communication: Diverse structures for exchange of genetic information. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 328–335.
- Blanchard, N.; Lankar, D.; Faure, F.; Regnault, A.; Dumont, C.; Raposo, G.; Hivroz, C. Tcr activation of human T cells induces the production of exosomes bearing the tcr/cd3/zeta complex. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 3235–3241.
- van der Vlist, E.J.; Arkesteijn, G.J.; van de Lest, C.H.; Stoorvogel, W.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Wauben, M.H. Cd4(+) t cell activation promotes the differential release of distinct populations of nanosized vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2012, 1, 18364.
- Saliba, D.G.; Cespedes-Donoso, P.F.; Balint, S.; Compeer, E.B.; Korobchevskaya, K.; Valvo, S.; Mayya, V.; Kvalvaag, A.; Peng, Y.; Dong, T.; et al. Composition and structure of synaptic ectosomes exporting antigen receptor linked to functional cd40 ligand from helper T cells. eLife 2019, 8, e47528.
- Menck, K.; Sönmezer, C.; Worst, T.S.; Schulz, M.; Dihazi, G.H.; Streit, F.; Erdmann, G.; Kling, S.; Boutros, M.; Binder, C.; et al. Neutral sphingomyelinases control extracellular vesicles budding from the plasma membrane. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1378056.
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brugger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247.
- Wen, C.; Seeger, R.C.; Fabbri, M.; Wang, L.; Wayne, A.S.; Jong, A.Y. Biological roles and potential applications of immune cell-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1400370.
- Vergani, E.; Daveri, E.; Vallacchi, V.; Bergamaschi, L.; Lalli, L.; Castelli, C.; Rodolfo, M.; Rivoltini, L.; Huber, V. Extracellular vesicles in anti-tumor immunity. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, in press.
- June, C.H.; O’Connor, R.S.; Kawalekar, O.U.; Ghassemi, S.; Milone, M.C. Car t cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Science 2018, 359, 1361–1365.
- Chan, J.D.; Lai, J.; Slaney, C.Y.; Kallies, A.; Beavis, P.A.; Darcy, P.K. Cellular networks controlling t cell persistence in adoptive cell therapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021. 21, 769–784.
- Sterner, R.C.; Sterner, R.M. Car-t cell therapy: Current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 69.
- Dong, Y.; Wan, Z.; Gao, X.; Yang, G.; Liu, L. Reprogramming immune cells for enhanced cancer immunotherapy: Targets and strategies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 609762.
- Tang, X.J.; Sun, X.Y.; Huang, K.M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.S.; Zou, D.D.; Wang, B.; Warnock, G.L.; Dai, L.J.; Luo, J. Therapeutic potential of car-t cell-derived exosomes: A cell-free modality for targeted cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44179–44190.
- Fu, W.; Lei, C.; Liu, S.; Cui, Y.; Wang, C.; Qian, K.; Li, T.; Shen, Y.; Fan, X.; Lin, F.; et al. Car exosomes derived from effector car-T cells have potent antitumour effects and low toxicity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4355.
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qin, Y.; Cai, H.; Geng, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; et al. Tropism-facilitated delivery of crispr/cas9 system with chimeric antigen receptor-extracellular vesicles against b-cell malignancies. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 455–467.
- Yang, P.; Cao, X.; Cai, H.; Feng, P.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; An, W.; Yang, Y.; Jie, J. The exosomes derived from car-t cell efficiently target mesothelin and reduce triple-negative breast cancer growth. Cell. Immunol. 2021, 360, 104262.
- Aharon, A.; Horn, G.; Bar-Lev, T.H.; Zagagi Yohay, E.; Waks, T.; Levin, M.; Deshet Unger, N.; Avivi, I.; Globerson Levin, A. Extracellular vesicles derived from chimeric antigen receptor-t cells: A potential therapy for cancer. Hum. Gene Ther. 2021, 32, 1224–1241.
- Haque, S.; Vaiselbuh, S.R. Cd19 chimeric antigen receptor-exosome targets cd19 positive b-lineage acute lymphocytic leukemia and induces cytotoxicity. Cancers 2021, 13, 1401.
- Johnson, L.R.; Lee, D.Y.; Eacret, J.S.; Ye, D.; June, C.H.; Minn, A.J. The immunostimulatory rna rn7sl1 enables car-t cells to enhance autonomous and endogenous immune function. Cell 2021, 184, 4981–4995.e14.
- Ruella, M.; Xu, J.; Barrett, D.M.; Fraietta, J.A.; Reich, T.J.; Ambrose, D.E.; Klichinsky, M.; Shestova, O.; Patel, P.R.; Kulikovskaya, I.; et al. Induction of resistance to chimeric antigen receptor t cell therapy by transduction of a single leukemic b cell. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1499–1503.
- Del Vecchio, F.; Martinez-Rodriguez, V.; Schukking, M.; Cocks, A.; Broseghini, E.; Fabbri, M. Professional killers: The role of extracellular vesicles in the reciprocal interactions between natural killer, cd8+ cytotoxic t-cells and tumour cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12075.
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 29, 116–125.
- Sinha, S.; Hoshino, D.; Hong, N.H.; Kirkbride, K.C.; Grega-Larson, N.E.; Seiki, M.; Tyska, M.J.; Weaver, A.M. Cortactin promotes exosome secretion by controlling branched actin dynamics. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 214, 197–213.
- Tsutsumi, R.; Hori, Y.; Seki, T.; Kurauchi, Y.; Sato, M.; Oshima, M.; Hisatsune, A.; Katsuki, H. Involvement of exosomes in dopaminergic neurodegeneration by microglial activation in midbrain slice cultures. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 511, 427–433.
- Lugini, L.; Cecchetti, S.; Huber, V.; Luciani, F.; Macchia, G.; Spadaro, F.; Paris, L.; Abalsamo, L.; Colone, M.; Molinari, A.; et al. Immune surveillance properties of human nk cell-derived exosomes. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2833–2842.
- Wu, C.H.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Fabbri, M.; Wayne, A.S.; Seeger, R.C.; Jong, A.Y. Extracellular vesicles derived from natural killer cells use multiple cytotoxic proteins and killing mechanisms to target cancer cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1588538.
- Lettau, M.; Janssen, O. Intra- and extracellular effector vesicles from human t and nk cells: Same-same, but different? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 804895.
- Wu, F.; Xie, M.; Hun, M.; She, Z.; Li, C.; Luo, S.; Chen, X.; Wan, W.; Wen, C.; Tian, J. Natural killer cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Novel players in cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 1970.
- Hu, W.; Wang, G.; Huang, D.; Sui, M.; Xu, Y. Cancer immunotherapy based on natural killer cells: Current progress and new opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1205.





