
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tae-Bum Lee | + 2899 word(s) | 2899 | 2022-02-17 06:44:47 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 2899 | 2022-03-02 02:45:22 | | |
Video Upload Options
Multidrug resistance (MDR) refers to a phenomenon wherein tumors exhibit cross-resistance to an array of drugs with different structures or action mechanisms once they become resistant to one anticancer drug. MDR to anticancer drugs remains a serious obstacle to the success of cancer chemotherapy. Resveratrol, a polyphenol, present in natural products exerts anticancer activity and acts as a potential MDR inhibitor in various drug-resistant cancer cells.
1. Introduction
2. In Vitro and In Vivo Activity of RES in Different Tumor Models
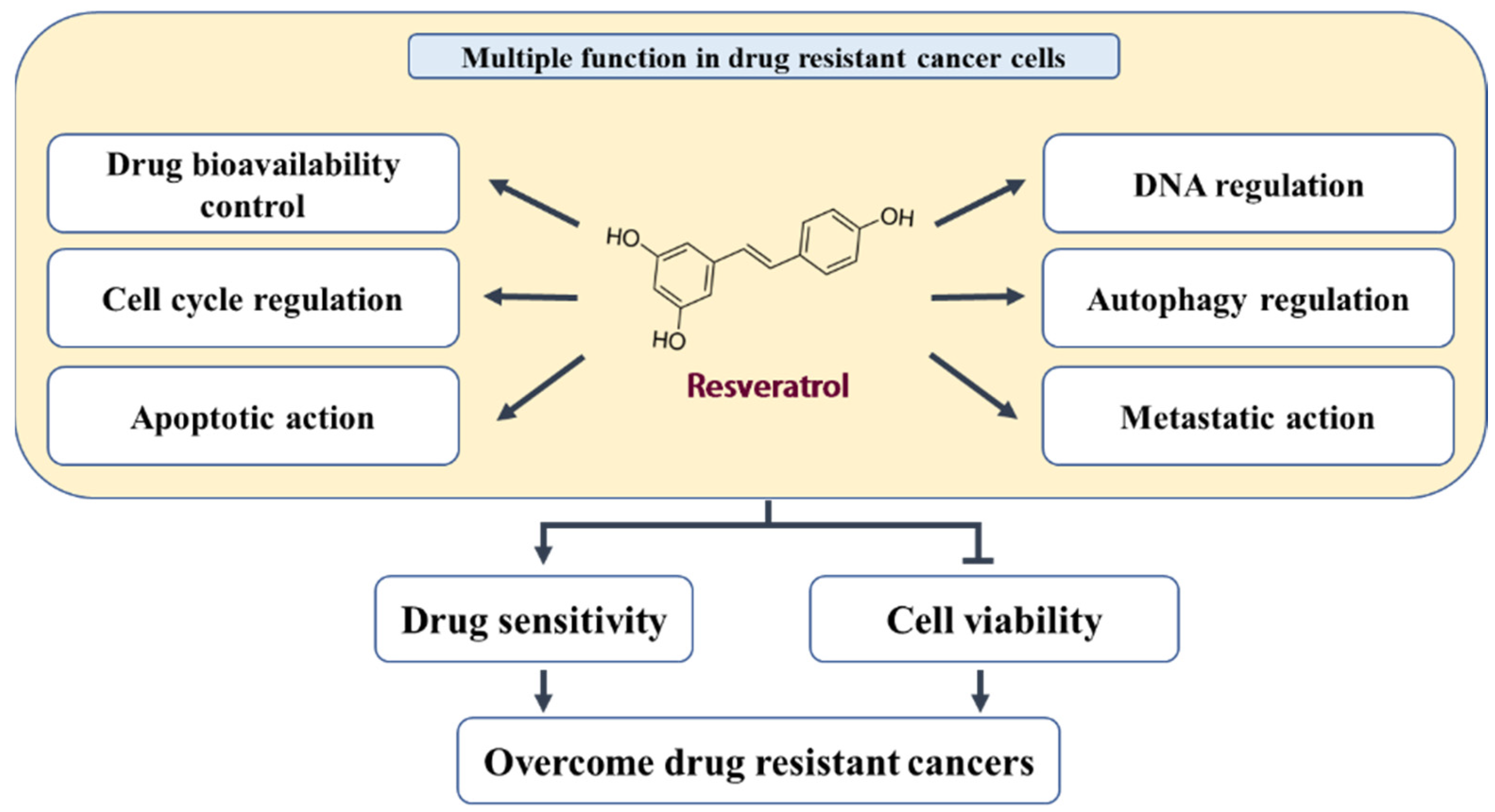
|
Target |
Regulatory Molecules |
Cellular Effect |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
↑ Upregulation |
↓ Downregulation |
↑ Upregulation |
↓ Downregulation |
|
|
Drug transporters and drug-metabolizing enzymes |
AMPK |
ABCG2, GST, LRP1, MDR1, MRP1, Nrf2, p-AKT, p-CREB, p-NF-κB, PI3K |
Cellular accumulation |
ABC transporters ATPase activity Detoxification |
|
DNA damage, repair, and replication |
APC, Topo-II, γ-H2AX |
DDB2, FEN-1, POLH, POL-β, Rad51 |
DNA damage |
DNA repair DNA replication |
|
Cell cycle regulation |
miR-122-5p, p21, p53, PTEN |
CDC2, CDK2, CDK4, CDK6, Cyclin D1, ERα, IRS1 |
Cell cycle arrest |
- |
|
Pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic action |
AIF, AMPK, Apaf-1, Bad, Bax, Caspae-3, Caspase-7, Caspase-8, Caspase-9, CHK2, CK1, Endo G, miR-122-5p, p53, p-p53(S20), PTEN, PUMA, TSC1, TSC2 |
Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, Clusterin, Integrin β1, p-AKT, p-Bad(s136), p-EGFR, p-ERK1/2, p-FAK, PI3K, p-IkBα, p-Jak, p-mTOR, p-NF-κB, p-p53(S15, S46), p-Src, p-Stat1, Survivin, uPAR |
Apoptosis Cell death Senescence Sub-G1 arrest |
Cell proliferation Tumor volume |
|
Autophagy regulation |
Atg3, Atg5, Atg7, Atg14, Atg12, Atg16L1, Beclin-1, LC3-Ⅱ, p62, p-AMPKα, p-JNK |
p-AKT, p-mTOR, Rubicon |
Autophagy |
- |
|
Migration, invasion, metastasis, EMT, and CSC |
E-cadherin, SIRT1, γ-catenin |
ALDH1, CD133, CD44, CXCR4, Fibronectin, MMP-2, MMP-9, N-Cadherin, p-ERK, p-NF-κB, p-p38, p-Smad2, p-Smad3, Slug, Snail, TGF-β, Vimentin, β-Catenin |
Intracellular junction |
Cell migration, invasion, and metastasis Colony formation CSC EMT |
3. Biological Effects and Mechanisms of RES in Acquired Drug-Resistant Cancer Cells
3.1. Inhibition of Drug Transporters and Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes
3.2. Promotion of DNA Damage and Inhibition of DNA Repair and Replication
3.3. Cell Cycle Regulation
3.4. Pro-Apoptotic and Antisurvival Actions
3.5. Autophagy Regulation
3.6. Inhibition of EMT and CSCs
References
- Bugde, P.; Biswas, R.; Merien, F.; Lu, J.; Liu, D.X.; Chen, M.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y. The therapeutic potential of targeting ABC transporters to combat multi-drug resistance. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 511–530.
- Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Shu, X. Resveratrol-mediated reversal of tumor multi-drug resistance. Curr. Drug Metab. 2014, 15, 703–710.
- Li, Y.J.; Lei, Y.H.; Yao, N.; Wang, C.R.; Hu, N.; Ye, W.C.; Zhang, D.M.; Chen, Z.S. Autophagy and multidrug resistance in cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2017, 36, 52.
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug resistance in cancer: An overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792.
- Vaidya, F.U.; Sufiyan Chhipa, A.; Mishra, V.; Gupta, V.K.; Rawat, S.G.; Kumar, A.; Pathak, C. Molecular and cellular paradigms of multidrug resistance in cancer. Cancer Rep. 2020, 13, e1291.
- Shnaider, P.V.; Ivanova, O.M.; Malyants, I.K.; Anufrieva, K.S.; Semenov, I.A.; Pavlyukov, M.S.; Lagarkova, M.A.; Govorun, V.M.; Shender, V.O. New Insights into Therapy-Induced Progression of Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7872.
- Beaudeux, J.L.; Nivet-Antoine, V.; Giral, P. Resveratrol: A relevant pharmacological approach for the treatment of metabolic syndrome? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 729–736.
- Gusman, J.; Malonne, H.; Atassi, G. A reappraisal of the potential chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic properties of resveratrol. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 1111–1117.
- Jang, M.; Cai, L.; Udeani, G.O.; Slowing, K.V.; Thomas, C.F.; Beecher, C.W.; Fong, H.H.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Mehta, R.G.; et al. Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes. Science 1997, 275, 218–220.
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Bhardwaj, A.; Aggarwal, R.S.; Seeram, N.P.; Shishodia, S.; Takada, Y. Role of resveratrol in prevention and therapy of cancer: Preclinical and clinical studies. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 2783–2840.
- Bishayee, A. Cancer prevention and treatment with resveratrol: From rodent studies to clinical trials. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 409–418.
- Sinha, D.; Sarkar, N.; Biswas, J.; Bishayee, A. Resveratrol for breast cancer prevention and therapy: Preclinical evidence and molecular mechanisms. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40–41, 209–232.
- Ozben, T. Mechanisms and strategies to overcome multiple drug resistance in cancer. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 2903–2909.
- Zhou, J.; Kang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zeng, S.; Yu, L. The Drug-Resistance Mechanisms of Five Platinum-Based Antitumor Agents. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 343.
- Lovly, C.M.; Shaw, A.T. Molecular pathways: Resistance to kinase inhibitors and implications for therapeutic strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2249–2256.
- Bhullar, K.S.; Lagaron, N.O.; McGowan, E.M.; Parmar, I.; Jha, A.; Hubbard, B.P.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Kinase-targeted cancer therapies: Progress, challenges and future directions. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 48.
- Chang, M. Tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 256–267.
- Leon-Galicia, I.; Diaz-Chavez, J.; Albino-Sanchez, M.E.; Garcia-Villa, E.; Bermudez-Cruz, R.; Garcia-Mena, J.; Herrera, L.A.; Garcia-Carranca, A.; Gariglio, P. Resveratrol decreases Rad51 expression and sensitizes cisplatinresistant MCF7 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 3025–3033.
- Wang, S.; Meng, Q.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, M. Effect and mechanism of resveratrol on drug resistance in human bladder cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 1179–1187.
- Buhrmann, C.; Yazdi, M.; Popper, B.; Shayan, P.; Goel, A.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol Chemosensitizes TNF-beta-Induced Survival of 5-FU-Treated Colorectal Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 888.
- Xu, J.; Liu, D.; Niu, H.; Zhu, G.; Xu, Y.; Ye, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Resveratrol reverses Doxorubicin resistance by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through modulating PTEN/Akt signaling pathway in gastric cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 19.
- Kourti, M.; Vavatsi, N.; Gombakis, N.; Sidi, V.; Tzimagiorgis, G.; Papageorgiou, T.; Koliouskas, D.; Athanassiadou, F. Expression of multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1), multidrug resistance-related protein 1 (MRP1), lung resistance protein (LRP), and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) genes and clinical outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2007, 86, 166–173.
- Choi, Y.H.; Yu, A.M. ABC transporters in multidrug resistance and pharmacokinetics, and strategies for drug development. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 793–807.
- Kaur, G.; Gupta, S.K.; Singh, P.; Ali, V.; Kumar, V.; Verma, M. Drug-metabolizing enzymes: Role in drug resistance in cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 1667–1680.
- Hurley, L.H. DNA and its associated processes as targets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 188–200.
- Salehan, M.R.; Morse, H.R. DNA damage repair and tolerance: A role in chemotherapeutic drug resistance. Br. J. Biomed. Sci 2013, 70, 31–40.
- Beck, W.T.; Danks, M.K. Mechanisms of resistance to drugs that inhibit DNA topoisomerases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1991, 2, 235–244.
- Beck, W.T.; Danks, M.K.; Wolverton, J.S.; Granzen, B.; Chen, M.; Schmidt, C.A.; Bugg, B.Y.; Friche, E.; Suttle, D.P. Altered DNA topoisomerase II in multidrug resistance. Cytotechnology 1993, 11, 115–119.
- Kellner, U.; Sehested, M.; Jensen, P.B.; Gieseler, F.; Rudolph, P. Culprit and victim—DNA topoisomerase II. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 235–243.
- Das, D.; Preet, R.; Mohapatra, P.; Satapathy, S.R.; Kundu, C.N. 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea enhances the inhibitory effect of resveratrol on 5-fluorouracil sensitive/resistant colon cancer cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 7374–7388.
- Shah, M.A.; Schwartz, G.K. Cell cycle-mediated drug resistance: An emerging concept in cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 2168–2181.
- Zhao, W.; Bao, P.; Qi, H.; You, H. Resveratrol down-regulates survivin and induces apoptosis in human multidrug-resistant SPC-A-1/CDDP cells. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 279–286.
- Zhu, Y.; He, W.; Gao, X.; Li, B.; Mei, C.; Xu, R.; Chen, H. Resveratrol overcomes gefitinib resistance by increasing the intracellular gefitinib concentration and triggering apoptosis, autophagy and senescence in PC9/G NSCLC cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17730.
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ren, F. Resveratrol chemosensitizes adriamycin-resistant breast cancer cells by modulating miR-122-5p. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 16283–16292.
- Hernandez-Valencia, J.; Garcia-Villa, E.; Arenas-Hernandez, A.; Garcia-Mena, J.; Diaz-Chavez, J.; Gariglio, P. Induction of p53 Phosphorylation at Serine 20 by Resveratrol Is Required to Activate p53 Target Genes, Restoring Apoptosis in MCF-7 Cells Resistant to Cisplatin. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1148.
- Sherr, C.J.; Roberts, J.M. CDK inhibitors: Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1501–1512.
- Joe, A.K.; Liu, H.; Suzui, M.; Vural, M.E.; Xiao, D.; Weinstein, I.B. Resveratrol induces growth inhibition, S-phase arrest, apoptosis, and changes in biomarker expression in several human cancer cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 893–903.
- Singh, S.K.; Banerjee, S.; Acosta, E.P.; Lillard, J.W.; Singh, R. Resveratrol induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis with docetaxel in prostate cancer cells via a p53/p21WAF1/CIP1 and p27KIP1 pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17216–17228.
- De Amicis, F.; Giordano, F.; Vivacqua, A.; Pellegrino, M.; Panno, M.L.; Tramontano, D.; Fuqua, S.A.; Ando, S. Resveratrol, through NF-Y/p53/Sin3/HDAC1 complex phosphorylation, inhibits estrogen receptor alpha gene expression via p38MAPK/CK2 signaling in human breast cancer cells. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3695–3707.
- Osman, A.M.; Al-Malki, H.S.; Al-Harthi, S.E.; El-Hanafy, A.A.; Elashmaoui, H.M.; Elshal, M.F. Modulatory role of resveratrol on cytotoxic activity of cisplatin, sensitization and modification of cisplatin resistance in colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1368–1374.
- Sui, X.; Chen, R.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Kong, N.; Zhang, M.; Han, W.; Lou, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Autophagy and chemotherapy resistance: A promising therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e838.
- Portt, L.; Norman, G.; Clapp, C.; Greenwood, M.; Greenwood, M.T. Anti-apoptosis and cell survival: A review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 238–259.
- Tarasov, V.V.; Chubarev, V.N.; Ashraf, G.M.; Dostdar, S.A.; Sokolov, A.V.; Melnikova, T.I.; Sologova, S.S.; Grigorevskich, E.M.; Makhmutova, C.A.; Kinzirsky, A.S.; et al. How Cancer Cells Resist Chemotherapy: Design and Development of Drugs Targeting Protein-Protein Interactions. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 394–412.
- Eskelinen, E.L.; Saftig, P. Autophagy: A lysosomal degradation pathway with a central role in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 664–673.
- Ganley, I.G.; Wong, P.M.; Gammoh, N.; Jiang, X. Distinct autophagosomal-lysosomal fusion mechanism revealed by thapsigargin-induced autophagy arrest. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 731–743.
- Suzuki, K.; Kirisako, T.; Kamada, Y.; Mizushima, N.; Noda, T.; Ohsumi, Y. The pre-autophagosomal structure organized by concerted functions of APG genes is essential for autophagosome formation. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5971–5981.
- Ye, X.; Zhou, X.J.; Zhang, H. Exploring the Role of Autophagy-Related Gene 5 (ATG5) Yields Important Insights Into Autophagy in Autoimmune/Autoinflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2334.
- Chang, C.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Lu, C.C.; Tsai, F.J.; Hsu, Y.M.; Tsao, J.W.; Juan, Y.N.; Chiu, H.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Wang, C.C. Resveratrol-induced autophagy and apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant human oral cancer CAR cells: A key role of AMPK and Akt/mTOR signaling. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 873–882.
- Puissant, A.; Robert, G.; Fenouille, N.; Luciano, F.; Cassuto, J.P.; Raynaud, S.; Auberger, P. Resveratrol promotes autophagic cell death in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells via JNK-mediated p62/SQSTM1 expression and AMPK activation. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1042–1052.
- Baribeau, S.; Chaudhry, P.; Parent, S.; Asselin, E. Resveratrol inhibits cisplatin-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86987.
- Du, B.; Shim, J.S. Targeting Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer. Molecules 2016, 21, 965.
- Petpiroon, N.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Phoyunnanin E inhibits migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells via suppression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and integrin alphav and integrin beta3. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 553.
- Phi, L.T.H.; Sari, I.N.; Yang, Y.G.; Lee, S.H.; Jun, N.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kwon, H.Y. Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) in Drug Resistance and their Therapeutic Implications in Cancer Treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 5416923.
- Wang, C.; Xie, J.; Guo, J.; Manning, H.C.; Gore, J.C.; Guo, N. Evaluation of CD44 and CD133 as cancer stem cell markers for colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1301–1308.
- Loret, N.; Denys, H.; Tummers, P.; Berx, G. The Role of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Ovarian Cancer Progression and Therapy Resistance. Cancers 2019, 11, 838.
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629.
- Chen, J.M.; Bai, J.Y.; Yang, K.X. Effect of resveratrol on doxorubicin resistance in breast neoplasm cells by modulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 491–500.
- Jin, X.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Ding, F.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. Resveratrol promotes sensitization to Doxorubicin by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition and modulating SIRT1/beta-catenin signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1246–1257.
- Shi, X.P.; Miao, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.F.; Ma, H.Z.; Xin, H.L.; Feng, J.; Wen, A.D.; Li, Y. Resveratrol sensitizes tamoxifen in antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer cells with epithelial-mesenchymal transition features. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 15655–15668.
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Kraehe, P.; Popper, B.; Goel, A.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol induces chemosensitization to 5-fluorouracil through up-regulation of intercellular junctions, Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis in colorectal cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 98, 51–68.
- Chang, W.S.; Tsai, C.W.; Yang, J.S.; Hsu, Y.M.; Shih, L.C.; Chiu, H.Y.; Bau, D.T.; Tsai, F.J. Resveratrol inhibited the metastatic behaviors of cisplatin-resistant human oral cancer cells via phosphorylation of ERK/p-38 and suppression of MMP-2/9. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13666.




