
Video Upload Options
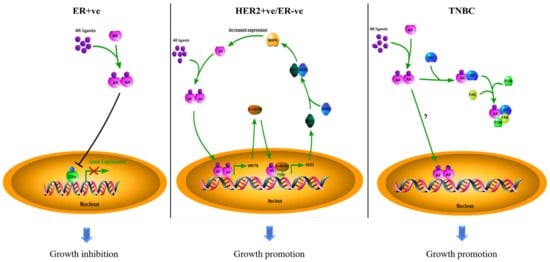
Biomarkers can be used for diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction in targeted therapy. The estrogen receptor α (ERα) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) are standard biomarkers used in breast cancer for guiding disease treatment. The androgen receptor (AR), a nuclear hormone receptor, contributes to the development and progression of prostate tumors and other cancers. With increasing evidence to support that AR plays an essential role in breast cancer, AR has been considered a useful biomarker in breast cancer, depending on the context of breast cancer sub-types. The existing survival analyses suggest that AR acts as a tumor suppressor in ER + ve breast cancers, serving as a favorable prognostic marker. However, AR functions as a tumor promoter in ER-ve breast cancers, including HER2 + ve and triple-negative (TNBC) breast cancers, serving as a poor prognostic factor. AR has also been shown to be predictive of the potential of response to adjuvant hormonal therapy in ER + ve breast cancers and to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in TNBC.
All contents are adapted from You, C.-P.; Leung, M.-H.; Tsang, W.-C.; Khoo, U.-S.; Tsoi, H. Androgen Receptor as an Emerging Feasible Biomarker for Breast Cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010072
1. What Are Cancer Biomarkers
2. AR as a Biomarker in Breast Cancers
| Types | AR Status (Cut-Off Used to Define AR + ve) | Case No. | Indicator of Clinical Outcomes 1 | Hazard Ratio (HR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | p-Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER + ve | Positive (≥10% nuclear-stained) | 470 | DFS | 0.654 | 0.429–0.997 | 0.049 | [10] |
| Negative (<10% nuclear-stained) | 202 | 1 | - | - | |||
| Positive (≥1% nuclear-stained) | 1024 | OS | 0.68 | 0.52–0.88 | - | [11] | |
| Negative (<1% nuclear-stained) | 140 | 1 | - | - | |||
| Positive (≥1% nuclear-stained) | 2833 | BCM | 0.53 | 0.41 –0.69 | < 0.001 | [12] | |
| Negative (<1% nuclear-stained) | 470 | 1 | - | - | |||
| Positive (≥1% nuclear-stained) | 609 | DSS | 0.259 | 0.139–0.482 | 0.000 | [13] | |
| Negative (<1% nuclear-stained) | 250 | 1 | - | - | |||
| High (mRNA Z-score) | 145 | DRFS | - | - | 0.008 | [14] | |
| Low (mRNA Z-score) | 144 | - | - | - | |||
| Positive (N/A) | - | DFS | 0.40 | 0.31–0.52 | < 0.001 | [15] | |
| Negative (N/A) | - | 1 | - | - | |||
| Positive (≥10% nuclear-stained) | 909 | OS | 0.71 | 0.53–0.95 | 0.022 | [16] | |
| Negative (<10% nuclear-stained) | 162 | 1 | - | - | |||
| Positive (≥1% nuclear-stained) | 461 | DFS | 0.606 | 0.388–0.944 | 0.027 | [17] | |
| Negative (<1% nuclear-stained) | 337 | 1 | - | - | |||
| HER2 + ve/ ER-ve |
Positive (≥10% nuclear-stained) | 49 | OS | - | - | 0.074 | [10] |
| Negative (<10% nuclear-stained) | 42 | - | - | - | |||
| High (mRNA level) | 35 | DFS | 1.46 | 1.03–2.06 | 0.03 | [18] | |
| Low (mRNA level) | 49 | 1 | - | - | |||
| TNBC | Positive (≥1% nuclear-stained) | 78 | OS | 1.83 | 1.11–3.01 | 0.02 | [11] |
| Negative (<1% nuclear-stained) | 133 | 1 | - | - | |||
| Positive (≥1% nuclear-stained) | 261 | OS | 2.159 | 1.224–3.808 | 0.008 | [19] | |
| Negative (<1% nuclear-stained) | 231 | 1 | - | - | |||
| Positive (≥1% nuclear-stained) | 23 | DFS | 5.26 | 1.39–19.86 | 0.014 | [20] | |
| Negative (<1% nuclear-stained) | 38 | 1 | - | - | |||
| Positive (≥1% nuclear-stained) | 78 | DDFS | 1.82 | 1.10–3.02 | 0.020 | [21] | |
| Negative (<1% nuclear-stained) | 185 | 1 | - | - |
2.1. The Role of AR in ER + ve Breast Cancer
2.2. The Role of AR in HER2 + ve Breast Cancer
2.3. The Role of AR in TNBC
2.4. Conflicting Results
References
- Strimbu, K.; Tavel, J.A. What are biomarkers? Curr. Opin. Hiv Aids 2010, 5, 463–466.
- Henry, N.L.; Hayes, D.F. Cancer biomarkers. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 140–146.
- Paik, S.; Shak, S.; Tang, G.; Kim, C.; Baker, J.; Cronin, M.; Baehner, F.L.; Walker, M.G.; Watson, D.; Park, T.; et al. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2817–2826.
- Lin, K.; Lipsitz, R.; Miller, T.; Janakiraman, S.; Force, U.S.P.S.T. Benefits and harms of prostate-specific antigen screening for prostate cancer: An evidence update for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 149, 192–199.
- Jordan, V.C. Selective estrogen receptor modulation: Concept and consequences in cancer. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 207–213.
- Dai, X.F.; Li, T.; Bai, Z.H.; Yang, Y.K.; Liu, X.X.; Zhan, J.L.; Shi, B.Z. Breast cancer intrinsic subtype classification, clinical use and future trends. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2929–2943.
- Hennigs, A.; Riedel, F.; Gondos, A.; Sinn, P.; Schirmacher, P.; Marme, F.; Jager, D.; Kauczor, H.U.; Stieber, A.; Lindel, K.; et al. Prognosis of breast cancer molecular subtypes in routine clinical care: A large prospective cohort study. Bmc Cancer 2016, 16, 734.
- Fallahpour, S.; Navaneelan, T.; De, P.; Borgo, A. Breast cancer survival by molecular subtype: A population-based analysis of cancer registry data. CMAJ Open 2017, 5, E734–E739.
- Gerratana, L.; Basile, D.; Buono, G.; De Placido, S.; Giuliano, M.; Minichillo, S.; Coinu, A.; Martorana, F.; De Santo, I.; Del Mastro, L.; et al. Androgen receptor in triple negative breast cancer: A potential target for the targetless subtype. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 68, 102–110.
- Park, S.; Koo, J.S.; Kim, M.S.; Park, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.I.; Park, B.W.; Lee, K.S. Androgen receptor expression is significantly associated with better outcomes in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1755–1762.
- Hu, R.; Dawood, S.; Holmes, M.D.; Collins, L.C.; Schnitt, S.J.; Cole, K.; Marotti, J.D.; Hankinson, S.E.; Colditz, G.A.; Tamimi, R.M. Androgen Receptor Expression and Breast Cancer Survival in Postmenopausal Women. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1867–1874.
- Kensler, K.H.; Poole, E.M.; Heng, Y.J.J.; Collins, L.C.; Glass, B.; Beck, A.H.; Hazra, A.; Rosner, B.A.; Eliassen, A.H.; Hankinson, S.E.; et al. Androgen Receptor Expression and Breast Cancer Survival: Results From the Nurses’ Health Studies. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 700–708.
- Castellano, I.; Allia, E.; Accortanzo, V.; Vandone, A.M.; Chiusa, L.; Arisio, R.; Durando, A.; Donadio, M.; Bussolati, G.; Coates, A.S.; et al. Androgen receptor expression is a significant prognostic factor in estrogen receptor positive breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 124, 607–617.
- Okano, M.; Oshi, M.; Butash, A.L.; Asaoka, M.; Katsuta, E.; Peng, X.; Qi, Q.Y.; Yan, L.; Takabe, K. Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer with High Expression of Androgen Receptor has Less Cytolytic Activity and Worse Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy but Better Survival. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2655.
- Bozovic-Spasojevic, I.; Zardavas, D.; Brohee, S.; Ameye, L.; Fumagalli, D.; Ades, F.; de Azambuja, E.; Bareche, Y.; Piccart, M.; Paesmans, M.; et al. The Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor in Patients with Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Clinical and Gene Expression Data. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2702–2712.
- Kraby, M.R.; Valla, M.; Opdahl, S.; Haugen, O.A.; Sawicka, J.E.; Engstrom, M.J.; Bofin, A.M. The prognostic value of androgen receptors in breast cancer subtypes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 172, 283–296.
- Tsang, J.Y.S.; Ni, Y.B.; Chan, S.K.; Shao, M.M.; Law, B.K.B.; Tan, P.H.; Tse, G.M. Androgen Receptor Expression Shows Distinctive Significance in ER Positive and Negative Breast Cancers. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 2218–2228.
- Venema, C.M.; Bense, R.D.; Steenbruggen, T.G.; Nienhuis, H.H.; Qiu, S.Q.; van Kruchten, M.; Brown, M.; Tamimi, R.M.; Hospers, G.A.P.; Schroder, C.P.; et al. Consideration of breast cancer subtype in targeting the androgen receptor. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2019, 200, 135–147.
- Choi, J.E.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Bae, Y.K. Androgen receptor expression predicts decreased survival in early stage triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 82–89.
- Asano, Y.; Kashiwagi, S.; Onoda, N.; Kurata, K.; Morisaki, T.; Noda, S.; Takashima, T.; Ohsawa, M.; Kitagawa, S.; Hirakawa, K. Clinical verification of sensitivity to preoperative chemotherapy in cases of androgen receptor-expressing positive breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 14–20.
- Dieci, M.V.; Tsvetkova, V.; Griguolo, G.; Miglietta, F.; Mantiero, M.; Tasca, G.; Cumerlato, E.; Giorgi, C.A.; Giarratano, T.; Faggioni, G.; et al. Androgen Receptor Expression and Association With Distant Disease-Free Survival in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Analysis of 263 Patients Treated With Standard Therapy for Stage I-III Disease. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 452.
- Kensler, K.H.; Regan, M.M.; Heng, Y.J.J.; Baker, G.M.; Pyle, M.E.; Schnitt, S.J.; Hazra, A.; Kammler, R.; Thurlimann, B.; Colleoni, M.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of androgen receptor expression in postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: Results from the Breast International Group Trial 1-98. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21.
- Park, S.; Koo, J.; Park, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, B.W.; Lee, K.S. Expression of androgen receptors in primary breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 488–492.
- Witzel, I.; Graeser, M.; Karn, T.; Schmidt, M.; Wirtz, R.; Schutze, D.; Rausch, A.; Janicke, F.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Muller, V. Androgen receptor expression is a predictive marker in chemotherapy-treated patients with endocrine receptor-positive primary breast cancers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. 2013, 139, 809–816.
- Aleskandarany, M.A.; Abduljabbar, R.; Ashankyty, I.; Elmouna, A.; Jerjees, D.; Ali, S.; Buluwela, L.; Diez-Rodriguez, M.; Caldas, C.; Green, A.R.; et al. Prognostic significance of androgen receptor expression in invasive breast cancer: Transcriptomic and protein expression analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 159, 215–227.
- Hickey, T.E.; Selth, L.A.; Chia, K.M.; Laven-Law, G.; Milioli, H.H.; Roden, D.; Jindal, S.; Hui, M.; Finlay-Schultz, J.; Ebrahimie, E.; et al. The androgen receptor is a tumor suppressor in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 310.
- Rizza, P.; Barone, I.; Zito, D.; Giordano, F.; Lanzino, M.; De Amicis, F.; Mauro, L.; Sisci, D.; Catalano, S.; Wright, K.D.; et al. Estrogen receptor beta as a novel target of androgen receptor action in breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16.
- Giovannelli, P.; Di Donato, M.; Galasso, G.; Di Zazzo, E.; Bilancio, A.; Migliaccio, A. The Androgen Receptor in Breast Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 492.
- Iqbal, N.; Iqbal, N. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) in Cancers: Overexpression and Therapeutic Implications. Mol. Biol. Int. 2014, 2014, 852748.
- Chia, K.M.; Liu, J.; Francis, G.D.; Naderi, A. A Feedback Loop between Androgen Receptor and ERK Signaling in Estrogen Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 154–166.
- He, L.C.; Du, Z.Y.; Xiong, X.S.; Ma, H.; Zhu, Z.F.; Gao, H.W.; Cao, J.W.; Li, T.; Li, H.Z.; Yang, K.Y.; et al. Targeting Androgen Receptor in Treating HER2 Positive Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7.
- McGhan, L.J.; McCullough, A.E.; Protheroe, C.A.; Dueck, A.C.; Lee, J.J.; Nunez-Nateras, R.; Castle, E.P.; Gray, R.J.; Wasif, N.; Goetz, M.P.; et al. Androgen receptor-positive triple negative breast cancer: A unique breast cancer subtype. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 361–367.
- Loibl, S.; Muller, B.M.; von Minckwitz, G.; Schwabe, M.; Roller, M.; Darb-Esfahani, S.; Ataseven, B.; du Bois, A.; Fissler-Eckhoff, A.; Gerber, B.; et al. Androgen receptor expression in primary breast cancer and its predictive and prognostic value in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 130, 477–487.
- Christenson, J.L.; Butterfield, K.T.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Norris, J.D.; Josan, J.S.; Pollock, J.A.; McDonnell, D.P.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Richer, J.K. MMTV-PyMT and Derived Met-1 Mouse Mammary Tumor Cells as Models for Studying the Role of the Androgen Receptor in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Progression. Horm. Cancer 2017, 8, 69–77.
- Giovannelli, P.; Di Donato, M.; Auricchio, F.; Castoria, G.; Migliaccio, A. Androgens Induce Invasiveness of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells Through AR/Src/PI3-K Complex Assembly. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9.
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Schafer, J.M.; Pendleton, C.S.; Tang, L.; Johnson, K.C.; Chen, X.; Balko, J.M.; Gomez, H.; Arteaga, C.L.; et al. PIK3CA mutations in androgen receptor-positive triple negative breast cancer confer sensitivity to the combination of PI3K and androgen receptor inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 406.
- Gong, Y.; Wei, W.; Wu, Y.; Ueno, N.T.; Huo, L. Expression of androgen receptor in inflammatory breast cancer and its clinical relevance. Cancer 2014, 120, 1775–1779.
- Qu, Q.; Mao, Y.; Fei, X.C.; Shen, K.W. The impact of androgen receptor expression on breast cancer survival: A retrospective study and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e82650.
- Kim, Y.; Jae, E.; Yoon, M. Influence of Androgen Receptor Expression on the Survival Outcomes in Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. J. Breast Cancer 2015, 18, 134–142.
- Asano, Y.; Kashiwagi, S.; Goto, W.; Tanaka, S.; Morisaki, T.; Takashima, T.; Noda, S.; Onoda, N.; Ohsawa, M.; Hirakawa, K.; et al. Expression and Clinical Significance of Androgen Receptor in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2017, 9, 4.
- McNamara, K.M.; Yoda, T.; Miki, Y.; Chanplakorn, N.; Wongwaisayawan, S.; Incharoen, P.; Kongdan, Y.; Wang, L.; Takagi, K.; Mayu, T.; et al. Androgenic pathway in triple negative invasive ductal tumors: Tts correlation with tumor cell proliferation. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 639–646.
- Sutton, L.M.; Cao, D.; Sarode, V.; Molberg, K.H.; Torgbe, K.; Haley, B.; Peng, Y. Decreased androgen receptor expression is associated with distant metastases in patients with androgen receptor-expressing triple-negative breast carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 138, 511–516.
- Thike, A.A.; Yong-Zheng Chong, L.; Cheok, P.Y.; Li, H.H.; Wai-Cheong Yip, G.; Huat Bay, B.; Tse, G.M.; Iqbal, J.; Tan, P.H. Loss of androgen receptor expression predicts early recurrence in triple-negative and basal-like breast cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 352–360.
- Wang, C.; Pan, B.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, F.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Q. Prognostic value of androgen receptor in triple negative breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46482–46491.
- Xu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, P.; Jiang, J.; Ma, P.; Niu, X.; Ma, S.; Cai, H.; Yang, K. Prognostic Significance of Androgen Receptor Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Breast Cancer 2020, 20, e385–e396.
- Ensenyat-Mendez, M.; Llinas-Arias, P.; Orozco, J.I.J.; Iniguez-Munoz, S.; Salomon, M.P.; Sese, B.; DiNome, M.L.; Marzese, D.M. Current Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes: Dissecting the Most Aggressive Form of Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 681476.
- Burstein, M.D.; Tsimelzon, A.; Poage, G.M.; Covington, K.R.; Contreras, A.; Fuqua, S.A.; Savage, M.I.; Osborne, C.K.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Chang, J.C.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis identifies novel subtypes and targets of triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1688–1698.
- Masuda, H.; Baggerly, K.A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Valero, V.; Lehmann, B.D.; Pietenpol, J.A.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; et al. Differential response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy among 7 triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtypes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5533–5540.
- Ding, Y.C.; Steele, L.; Warden, C.; Wilczynski, S.; Mortimer, J.; Yuan, Y.; Neuhausen, S.L. Molecular subtypes of triple-negative breast cancer in women of different race and ethnicity. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 198–208.
- Bhattarai, S.; Klimov, S.; Mittal, K.; Krishnamurti, U.; Li, X.B.; Oprea-Ilies, G.; Wetherilt, C.S.; Riaz, A.; Aleskandarany, M.A.; Green, A.R.; et al. Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Multi-Institutional Study. Cancers 2019, 11, 995.
- Anestis, A.; Sarantis, P.; Theocharis, S.; Zoi, I.; Tryfonopoulos, D.; Korogiannos, A.; Koumarianou, A.; Xingi, E.; Thomaidou, D.; Kontos, M.; et al. Estrogen receptor beta increases sensitivity to enzalutamide in androgen receptor-positive triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 1221–1233.
- Zhang, L.; Fang, C.; Xu, X.Q.; Li, A.L.; Cai, Q.; Long, X.H. Androgen Receptor, EGFR, and BRCA1 as Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015.
- Cuenca-Lopez, M.D.; Montero, J.C.; Morales, J.C.; Prat, A.; Pandiella, A.; Ocana, A. Phospho-kinase profile of triple negative breast cancer and androgen receptor signaling. Bmc Cancer 2014, 14, 302.
- Park, J.J.; Irvine, R.A.; Buchanan, G.; Koh, S.S.; Park, J.M.; Tilley, W.D.; Stallcup, M.R.; Press, M.F.; Coetzee, G.A. Breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1) is a coactivator of the androgen receptor. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 5946–5949.
- Kinoshita, H.; Shi, Y.; Sandefur, C.; Meisner, L.F.; Chang, C.S.; Choon, A.; Reznikoff, C.R.; Bova, G.S.; Friedl, A.; Jarrard, D.F. Methylation of the androgen receptor minimal promoter silences transcription in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3623–3630.
- Fletcher, C.E.; Sulpice, E.; Combe, S.; Shibakawa, A.; Leach, D.A.; Hamilton, M.P.; Chrysostomou, S.L.; Sharp, A.; Welti, J.; Yuan, W.; et al. Androgen receptor-modulatory microRNAs provide insight into therapy resistance and therapeutic targets in advanced prostate cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5700–5724.
- Peters, K.M.; Edwards, S.L.; Nair, S.S.; French, J.D.; Bailey, P.J.; Salkield, K.; Stein, S.; Wagner, S.; Francis, G.D.; Clark, S.J.; et al. Androgen receptor expression predicts breast cancer survival: The role of genetic and epigenetic events. Bmc Cancer 2012, 12.
- Takayama, K.; Misawa, A.; Inoue, S. Significance of microRNAs in Androgen Signaling and Prostate Cancer Progression. Cancers 2017, 9, 102.
- Imani, S.; Wu, R.C.; Fu, J.J. MicroRNA-34 family in breast cancer: From research to therapeutic potential. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3765–3775.
- Xiao, Y.J.; Humphries, B.; Yang, C.F.; Wang, Z.S. MiR-205 Dysregulations in Breast Cancer: The Complexity and Opportunities. Non-Coding Rna 2019, 5, 53.




