Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chien-Hsiu Li | + 2400 word(s) | 2400 | 2021-12-29 04:50:05 | | | |
| 2 | Catherine Yang | -5 word(s) | 2395 | 2022-01-11 08:00:41 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Li, C.; Liao, C. MicroRNA Let-7-Mediated Glycolysis. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/18024 (accessed on 13 February 2026).
Li C, Liao C. MicroRNA Let-7-Mediated Glycolysis. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/18024. Accessed February 13, 2026.
Li, Chien-Hsiu, Chiao-Chun Liao. "MicroRNA Let-7-Mediated Glycolysis" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/18024 (accessed February 13, 2026).
Li, C., & Liao, C. (2022, January 11). MicroRNA Let-7-Mediated Glycolysis. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/18024
Li, Chien-Hsiu and Chiao-Chun Liao. "MicroRNA Let-7-Mediated Glycolysis." Encyclopedia. Web. 11 January, 2022.
Copy Citation
The microRNA (miRNA) Let-7 has been identified as related to glycolysis procedures such as tissue repair, stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, and tumoral metastasis. In many cancers, the expression of glycolysis-related enzymes is correlated with Let-7, in which multiple enzymes are related to the regulation of the autophagy process. However, much recent research has not comprehensively investigated how Let-7 participates in glycolytic reprogramming or its links to autophagic regulations, mainly in tumor progression.
Let-7
microRNA
autophagy
1. Introduction
Cellular energy-related metabolisms involve complex regulation dynamic processes. The current understanding is that the uptake of glucose from the extracellular environment is a primary way for cells to acquire resources for sustaining energy. Intermediate glucose metabolism can be converted by diverse metabolites of lipids and amino acids to maintain cellular functions [1]. In addition, autophagy is recognized as a digesting process to engulf cellular compartments or damaged organelles for maintaining metabolic homeostasis while responding to multiple metabolic stresses [2]. Within such processes, necessary molecules can be recycled by degrading specific factors to adapt cell growth to a rigorous environment. The glucose metabolic networks regulated by glycolysis and autophagy have explained the fundamental nutrients dynamic for maintaining cell growth and survival. Among them, miRNA, a 18–25-nt single-stranded noncoding RNA, serves as an essential modulator involved in cellular metabolisms, conducting post-transcriptional modification by targeting to 3’UTR of specific mRNA [3].
Let-7 is the first miRNA family identified as involved in multiple cellular and biological functions, including glucose metabolism and autophagy. The glucose metabolism is controlled by the miRNA family of Let-7 directly [4], or regulated by an autophagy-associated glycogen recycling system [5][6]. The imbalance of Let-7-mediated processes of glucose metabolism has been found to contribute to disease progression, especially carcinogenesis. In addition, metabolic dysregulation, which causes excessive energy release for unlimited growth, has been a consequential risk for promoting cancer development. However, the crosstalk networks between autophagy and glucose metabolism—especially the linkage of Let-7 miRNA that participates in carcinogenesis and various biological functions—are still obscure and need to be fully addressed.
2. Involvement of Let-7 in Glycolysis Reprogramming
Let-7 was reported in 1990 and contributes to the embryonic development of C. elegans. The artificial manipulation of the expression of Let-7 causes mortality during embryogenesis [7]. Interestingly, several cancer-associated molecules have been identified from embryonic development, including Let-7. The Let-7 family has been classified by its consensus sequence [8] (Table 1). According to the literatures review, the Let-7 family-related expression was associated with the patient’s prognosis (Table 2). Furthermore, numerous studies have indicated that the related expression of Let-7 is lower in tumor cells, whereas an increased level of Let-7 is able to suppress tumor malignancy, which indicates that Let-7 may contribute to the suppression role in most types of tumors [9][10].
Table 1. The Let-7 family in humans.
| Let-7 Family | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Let-7a | UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUAUAGUU |
| Let-7b | UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUGUGGUU |
| Let-7c | UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUAUGGUU |
| Let-7d | AGAGGUAGUAGGUUGCAUAGUU |
| Let-7e | UGAGGUAGGAGGUUGUAUAGUU |
| Let-7f | UGAGGUAGUAGAUUGUAUAGUU |
| Let-7g | UGAGGUAGUAGUUUGUACAGUU |
| Let-7i | UGAGGUAGUAGUUUGUGCUGUU |
| miR-98 | UGAGGUAGUAAGUUGUAUUGUU |
| miR-202 | AGAGGUAGUAGGGCAUGGGAA |
Table 2. Let-7 family in pan-cancer to coordinate the related survival correlation between patients with cancer and the Let-7 family.
| Cancer Type | Let-7 Family | Clinical Association | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Let-7a | Associated with poor outcome | 2013 | [11] |
| Let-7a-2-3p | Associated with good outcome | 2015 | [12] | |
| miR-98 | Associated with good outcome | 2019 | [13] | |
| Breast Cancer | Let-7a | Associated with good outcome | 2018 | [14] |
| Let-7a | Associated with good outcome | 2018 | [15] | |
| Let-7a | Associated with good outcome | 2019 | [16] | |
| Let-7a | Associated with good outcome | 2019 | [17] | |
| Let-7a-5p | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [18] | |
| Let-7b | Associated with good outcome | 2018 | [14] | |
| Let-7b | Associated with good outcome | 2019 | [16] | |
| Let-7b | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [19] | |
| Let-7b | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [20] | |
| Let-7b | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [21] | |
| Let-7b | Associated with good outcome | 2016 | [22] | |
| Let-7c | Associated with good outcome | 2016 | [22] | |
| Let-7c | Associated with good outcome | 2018 | [14] | |
| Let-7c | Associated with good outcome | 2019 | [16] | |
| Let-7c | Associated with poor outcome | 2020 | [23] | |
| Let-7d | Associated with good outcome | 2018 | [14] | |
| Let-7d | Associated with good outcome | 2018 | [24] | |
| Let-7d | Associated with good outcome | 2019 | [16] | |
| Let-7e | Associated with good outcome | 2018 | [14] | |
| Let-7e | Associated with poor outcome | 2019 | [16] | |
| Let-7f | Associated with good outcome | 2018 | [14] | |
| Let-7f | Associated with good outcome | 2019 | [16] | |
| Let-7g | Associated with good outcome | 2011 | [25] | |
| Let-7g | Associated with good outcome | 2018 | [14] | |
| Let-7g | Associated with good outcome | 2019 | [16] | |
| Let-7i | Associated with good outcome | 2008 | [26] | |
| Let-7i | Associated with good outcome | 2018 | [14] | |
| Let-7i | Associated with good outcome | 2019 | [16] | |
| Colon Cancer | Let-7a | Associated with poor outcome | 2017 | [27] |
| Let-7g | Associated with good outcome | 2017 | [28] | |
| Esophageal Cancer | Let-7b | Associated with good outcome | 2012 | [29] |
| Let-7c | Associated with good outcome | 2012 | [29] | |
| Let-7c | Associated with good outcome | 2013 | [30] | |
| Glioblastoma | Let-7a | Associated with good outcome | 2013 | [31] |
| Let-7c | Associated with good outcome | 2021 | [32] | |
| Let-7f | Associated with poor outcome | 2018 | [33] | |
| Let-7i | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [34] | |
| Liver Cancer | Let-7a | Associated with poor outcome | 2018 | [35] |
| Let-7a | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [36] | |
| Let-7b | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [36] | |
| Let-7b | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [37] | |
| Let-7c | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [36] | |
| miR-202 | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [38] | |
| Lung Adenocarcinoma | Let-7b | Associated with good outcome | 2021 | [39] |
| Melanoma | miR-98 | Associated with good outcome | 2014 | [40] |
| Mesothelioma | Let-7c | Associated with good outcome | 2017 | [41] |
| Ovarian Cancer | Let-7b | Associated with poor outcome | 2021 | [42] |
| Let-7d | Associated with poor outcome | 2012 | [43] | |
| Let-7e | Associated with good outcome | 2017 | [44] | |
| Let-7f | Associated with good outcome | 2013 | [45] | |
| Let-7g | Associated with poor outcome | 2016 | [46] | |
| Let-7i | Associated with good outcome | 2008 | [26] | |
| miR-98 | Associated with good outcome | 2021 | [47] | |
| miR-98 | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [48] | |
| miR-98 | Associated with poor outcome | 2019 | [49] | |
| miR-98 | Associated with poor outcome | 2018 | [50] | |
| miR-202 | Associated with good outcome | 2020 | [51] | |
| Let-7g | Associated with good outcome | 2017 | [52] | |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Let-7e | Associated with good outcome | 2010 | [53] |
| miR-202 | Associated with good outcome | 2021 | [54] | |
| Prostate Cancer | Let-7b | Associated with poor outcome | 2013 | [55] |
| Let-7c | Associated with good outcome | 2013 | [55] |
There are divergent theories about how carcinogenesis starts. The monosaccharide glucose is the primary nutritarian for cells. After a meal, insulin increases and stimulates cell response to process glucose metabolism. Once cells uptake glucose, they undergo a process of glycolysis to convert glucose to other intermediates via specific enzymes and generate cellular components, including lipids, amino acids, and energy for cell survival [56]. According to the concept of cancer energy uptake raised by Douglas Hanahan and Robert Weinberg, the dysregulation of metabolism contributes to cancer progression [57]. Studies have demonstrated that the glucose level might change the mitochondria respiration in cells by modulating the expression of the Let-7 level [58]. Comprehensive miRNA profiling from 14 global population studies indicated that the top 1% of population-differentiated miRNA was associated with glucose/insulin metabolism and pathogenesis. MiR-202, as one of the Let-7 family members, may contribute to cancer progression by regulating glucose metabolism [59]. Additionally, Serguienko et al. observed that Let-7 is linked to the expression of Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD), Inosine-5’-monophosphate dehydrogenase 2 (IMPDH2), Fatty Acid Synthase (FASN), stearoyl-CoA desaturase, and Aminoadipate-Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase-Phosphopantetheinyl Transferase (AASDHPPT) from a comparable transcriptome analysis [60]. We herein describe the molecular mechanism of Let-7-mediated glucose metabolism and Let-7-associated metabolic reprogramming impacts in tumor plasticity (Figure 1).
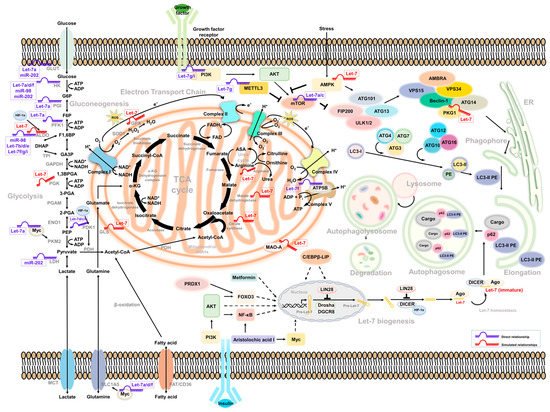
Figure 1. Intermediate mediators/molecules between Let-7-associated glucose metabolism and autophagy.
The diagram summarizes the current participation of the Let-7 family in the regulation of glucose metabolism and autophagy. The direct (marked blue) and indirect (marked red) interrelationship between glycolysis- and autophagy-related pathway were highlighted according to the simulated model. Molecules and factors involved in the biogenesis of Let-7 and the speculation of its interaction with glucose metabolism and autophagic degradation were also illustrated. Possible molecules that regulate the Let-7 homeostasis in between non-carbohydrate metabolism and autophagy processes were indicated.
3. Let-7-Mediated Autophagy Participates in Glucose Metabolism and Cancer Progression
3.1. Let-7 and Autophagy
In lung cancer, Let-7 targets IGF-1R to induce autophagy and blocks the function of BCL2L1/BCL2/PI3K complex to induce apoptosis and pyroptosis and inhibit cell motility [61]. Let-7a targets Rictor’s mTORC2 component, inhibiting AKT/mTORC1 signaling to activate autophagy in gastric cancer [62]. Similar regulation can be observed in human placental trophoblasts, in which the expression of Let-7b was correlated with cell growth and motility. The Let-7b-mediated TGFBR1/ERK/IL-6/TNF-α cascade triggers not only apoptosis but also autophagy. Such regulation may contribute to pre-eclampsia during pregnancy [63]. In glioma, the downregulation of STAT3 was mediated by Let-7a, Let-7d, and Let-7f. Upregulation of Let-7 suppressed the expression of STAT3, resulting in the inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of autophagy and apoptosis [64]. Liang et al. identified that a set of the Let-7 family was downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, with different clinical correlations under a genetic profiling analysis. The expression of Let-7b and Let-7c had a better prognosis; Let-7e had a poor prognosis instead. Among them, Let-7e has been demonstrated to promote tumor growth by suppressing autophagy and apoptosis [65]. A similar strategy was used in cholangiocarcinoma. Clinical evidence showed that the expression of NUAK1 was negatively correlated with Let-7a. NUAK1-mediated cholangiocarcinoma cell motility can be suppressed by increasing Let-7a. In turn, the overexpression of Let-7a inhibited NUAK1-mediated tumor malignancy by the induction of autophagy [66]. Additionally, Let-7 can be regulated by LncRNA H19 and LIN28 in breast cancer. The expression of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) H19 and LIN28 was correlated with breast cancer’s poor prognosis and metastasis ability. Overexpression of H19 and LIN28 increases the expression of several autophagy-related ATG markers as well as its puncta structure formation. Downregulation of Let-7 increased the transcript activity of several EMT-related genes—including Slug, Zeb1, Twist, Snail, β-catenin, and HMGA2—to modulate the metastasis of breast cancer [67]. Another lncRNA MIR99AHG, as well as its Let-7c-associated cluster, were reported to have decreased expression in lung cancer. MIR99AHG increased Let-7c, subsequently promoting autophagy via targeting mTOR, an autophagy suppressor of nucleation, and ANXA2, a negative regulator of elongation, to suppress the growth and motility of lung adenocarcinoma [68]. In view of the controversial role of autophagy in a variety of cancers, the regulation of Let-7-mediated autophagy in tumor progression could be complicated—and condition-, environment-, and tissue-specific.
3.2. Autophagy Activators
Several components have been identified as triggering Let-7-mediated autophagy in cancer cells. Treating cells with recombinant capsid protein viral particle 1 (rVP1) induces autophagy to regulate the motility of macrophages [69] and ovarian cancer cells [70]. In ovarian cancer, autophagy—activated by either a canonical or a rVP1-mediated noncanonical pathway—maintains the homeostasis of the Let-7 level through SQSTM1-mediated degradation of Dicer/AGO2 inhibition of cell migration [70]. In lymphosarcoma, the expression of Let-7g/CTSB may be suppressed by ribonuclease binase to participate in apoptosis and autophagy [71].
3.3. Drug Resistance
In gastric cancer, the expression of miR-202 can be restricted by lncRNA MALAT1, resulting in the activation of autophagy, increased tumor malignancy, and an enhanced drug-resistant ability [72]. In agreement with other reports, Yang et al. showed that paclitaxel-based drug-resistant breast cancer cells express a high level of CircRNA ABCB10 and autophagy, which are correlated with clinical paclitaxel-sensitive or resistant data and negatively associated to Let-7a. Mechanistically, the Let-7a/DUSP7 axis is a downstream effector of Circ-ABCB10 resistant to paclitaxel treatment. Knockdown of Circ-ABCB10 not only increases sensitivity to paclitaxel but also decreases tumor weight [73]. Similar regulation was observed in a cisplatin-based resistance model of A549 with a high level of DICER. Overexpression of DICER induces autophagy processes and increased tumor growth and motility, in which DICER-mediated suppression of Let-7i and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis contributes to the autophagy activity [74]. In medulloblastoma, inhibited autophagy was found to promote tumor resistance upon cisplatin treatment. The level of Let-7f in cells was insufficient to repress HMGB1 and led to autophagy-mediated drug resistance. Overexpression of Let-7f could attenuate cisplatin’s drug resistance and induce apoptosis in medulloblastoma cells [75].
3.4. Let-7-Mediated Autophagy in Glucose Metabolism
Recently, Let-7-mediated autophagy has been described as participating in glucose metabolism events. For example, Duan et al. observed that Let-7 targeted BCL-xL to induce autophagic cell death in lung cancer, indicating that Let-7 regulates mitochondria-related autophagy (mitophagy) to regulate metabolism-related events, and BCL-xL with non-apoptotic functions to induce cell death [76]. However, the underlying mechanism of Let-7-mediated autophagy in glucose metabolism that contributes to cell stress and death needs to be further elucidated. According to the above reports, several links may support the correlation between Let-7, autophagy, and glucose metabolism. In turn, Lai et al. found that—in a hypoxic environment—HIF-1α can interact with DICER to regulate miRNA processing in diverse cancer types, including colon, breast, liver, lung, and prostate cancer [77]. HIF-1α changed the glycolysis-related enzyme PDK1 level and induced autophagy-mediated proteolysis by interacting with Parkin/p62 to possess DICER, which decreased Let-7 biogenesis. Overexpression of HIF-1α reduced the levels of Let-7a, Let-7b, and Let-7d as well as its complement downstream target LIN41 and Aurora B to promote tumor metastasis [77]. However, how glycolysis participates in DICER ubiquitination and related autophagy processes has not yet been well explained. So far, Lai et al.’s study provides a possible reason for why the Let-7 level being downregulated under hypoxia is an important factor contributing to tumor microenvironment reprogramming and providing tumor cells with escape from immune surveillance. Recently, bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) have been observed to have anticancer activity. Egea et al. found that Let-7f can be transactivated under hypoxia to induce autophagy in hMSCs and promote migration in tumor cells [78]. Let-7f can be regulated by TGF-β, TNF-α, IL-1β, and SDF-1α to modulate CXCR4 and MMP-9 expression and drive chemotactic invasion. Interestingly, hMSCs have been observed to transport Let-7f by exosome secretion to inhibit the growth and motility of breast cancer; such events can be reversed with the Let-7f inhibitor [78].
3.5. mTOR-Dependent Autophagy and Glucose Metabolism
Several studies have found that Let-7 mediates glucose metabolism through the regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) [74][79][80][62]. It is also a well-known negative regulator of autophagy. Notably, human growth hormone receptors (GHR) have played an essential role in glucose metabolism and are linked to mTOR activity. A murine model revealed that, under limited nutrients, growth hormone maintained the cellular glucose level through gluconeogenesis, accompanied by the induction of autophagy [81]. In addition, GHR has been identified to contribute to breast and prostate cancer malignancy [82][83]. Elzein et al. reported that GHR is the target of miR-202. Increased miR-202 suppresses the expression of GHR in MCF and LNCaP cells [84]. Additionally, it has been reported that PKM2 and mTOR expression is downregulated under glucose restriction in breast cancer, which reverses the Warburg effect of cells [85]. Strikingly, these molecules were all be Let-7 downstream effectors. Such regulation may explain how Let-7 mediates autophagy and glucose metabolism to regulate cancer cell progression (Figure 1).
4. Conclusions
Even though Let-7 was the first miRNA identified, its related biological functions linked to diverse biological processes, including glycolysis and autophagy, remain obscure. The literature review and omics data analysis we performed has generated simulated results to elucidate how Let-7-mediated autophagy participates in glucose metabolism, revealing possible molecules that may participate in this regulatory network. However, the related processes may differ from different genetic backgrounds, cancer types, and therapeutic strategies.
References
- Zhu, J.; Thompson, C.B. Met abolic regulation of cell growth and proliferation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 436–450.
- Lahiri, V.; Hawkins, W.D.; Klionsky, D.J. Watch What You (Self-) Eat: Autophagic Mechanisms that Modulate Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 803–826.
- Michlewski, G.; Caceres, J.F. Post-transcriptional control of miRNA biogenesis. RNA 2019, 25, 1–16.
- Ma, X.Y.; Li, C.C.; Sun, L.C.; Huang, D.; Li, T.T.; He, X.P.; Wu, G.W.; Yang, Z.; Zhong, X.Y.; Song, L.B.; et al. Lin28/let-7 axis regulates aerobic glycolysis and cancer progression via PDK1. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–13.
- Karsli-Uzunbas, G.; Guo, J.Y.; Price, S.; Teng, X.; Laddha, S.V.; Khor, S.; Kalaany, N.Y.; Jacks, T.; Chan, C.S.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; et al. Autophagy Is Required for Glucose Homeostasis and Lung Tumor Maintenance. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 914–927.
- Zirin, J.; Nieuwenhuis, J.; Perrimon, N. Role of Autophagy in Glycogen Breakdown and Its Relevance to Chloroquine Myopathy. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001708.
- Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.J.; Basson, M.; Pasquinelli, A.E.; Bettinger, J.C.; Rougvie, A.E.; Horvitz, H.R.; Ruvkun, G. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2000, 403, 901–906.
- Roush, S.; Slack, F.J. The let-7 family of microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 505–516.
- Biamonte, F.; Santamaria, G.; Sacco, A.; Perrone, F.M.; Di Cello, A.; Battaglia, A.M.; Salatino, A.; Di Vito, A.; Aversa, I.; Venturella, R.; et al. MicroRNA let-7g acts as tumor suppressor and predictive biomarker for chemoresistance in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12.
- Al-Harbi, B.; Hendrayani, S.F.; Silva, G.; Aboussekhra, A. Let-7b inhibits cancer-promoting effects of breast cancer-associated fibroblasts through IL-8 repression. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17825–17838.
- Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Yang, J.; Qian, J.; Qian, W.; Yao, D.M.; Deng, Z.Q.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.X.; Xie, D.; et al. Overexpressed let-7a-3 is associated with poor outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 1642–1647.
- Shi, J.L.; Fu, L.; Li, Y.H.; Yu, L.; Wang, W.D. Identification of let-7a-2-3p or/and miR-188-5p as Prognostic Biomarkers in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118099.
- Hu, N.; Cheng, Z.H.; Pang, Y.F.; Zhao, H.M.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Qin, T.; Li, Q.Y.; Han, Y.; Shi, J.L.; et al. High expression of MiR-98 is a good prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia patients treated with chemotherapy alone. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 178–185.
- Liang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Tang, S.C.; Xiao, G.D.; Sun, X.; Li, G.; Du, N.; Liu, D.P.; Ren, H. MiR-146a promotes the asymmetric division and inhibits the self-renewal ability of breast cancer stem-like cells via indirect upregulation of Let-7. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 1445–1456.
- Guo, Q.N.; Wen, R.Y.; Shao, B.; Li, Y.D.; Jin, X.; Deng, H.R.; Wu, J.N.; Su, F.X.; Yu, F.Y. Combined Let-7a and H19 Signature: A Prognostic Index of Progression-Free Survival in Primary Breast Cancer Patients. J. Breast Cancer 2018, 21, 142–149.
- Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Xiao, G.D.; Zheng, X.Q.; Wang, J.C.; Xu, C.W.; Qin, S.; Ren, H.; Tang, S.C.; Sun, X. H19 regulation of oestrogen induction of symmetric division is achieved by antagonizing Let-7c in breast cancer stem-like cells. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12534.
- Du, J.; Fan, J.J.; Dong, C.; Li, H.T.; Ma, B.L. Inhibition effect of exosomes-mediated Let-7a on the development and metastasis of triple negative breast cancer by down-regulating the expression of c-Myc. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5301–5314.
- Shi, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.N.; Ran, F.; Liu, J.; Lin, J.; Hao, X.P.; Ding, L.H.; Ye, Q.N. Let-7a-5p inhibits triple-negative breast tumor growth and metastasis through GLUT12-mediated warburg effect. Cancer Lett. 2020, 495, 53–65.
- Ju, Z.L.; Bhardwaj, A.; Embury, M.D.; Singh, H.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Bedrosian, I.; Wang, J. Integrative Analyses of Multilevel Omics Reveal Preneoplastic Breast to Possess a Molecular Landscape That Is Globally Shared with Invasive Basal-Like Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 722.
- Bozgeyik, E. Bioinformatic Analysis and in Vitro Validation of Let-7b and Let-7c in Breast Cancer. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2020, 84, 107191.
- Li, X.; Liang, T.; Chen, S.S.; Wang, M.; Wang, R.; Li, K.; Wang, J.C.; Xu, C.W.; Du, N.; Qin, S.D.; et al. Matrine suppression of self-renewal was dependent on regulation of LIN28A/Let-7 pathway in breast cancer stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 2139–2149.
- Sun, X.; Xu, C.; Tang, S.C.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Du, N.; Qin, S.; Li, G.; Xu, S.; et al. Let-7c blocks estrogen-activated Wnt signaling in induction of self-renewal of breast cancer stem cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 83–89.
- Chen, D.N.; Bao, C.; Zhao, F.; Yu, H.G.; Zhong, G.S.; Xu, L.; Yan, S.X. Exploring Specific miRNA-mRNA Axes with Relationship to Taxanes-Resistance in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1397.
- Wei, Y.C.; Liu, G.H.; Wu, B.L.; Yuan, Y.F.; Pan, Y.B. Let-7d Inhibits Growth and Metastasis in Breast Cancer by Targeting Jab1/Cops5. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 2126–2135.
- Qian, P.X.; Zuo, Z.H.; Wu, Z.S.; Meng, X.Y.; Li, G.P.; Wu, Z.Z.; Zhang, W.J.; Tan, S.; Pandey, V.; Yao, Y.D.; et al. Pivotal Role of Reduced let-7g Expression in Breast Cancer Invasion and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6463–6474.
- Yang, N.; Kaur, S.; Volinia, S.; Greshock, J.; Lassus, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Liang, S.; Leminen, A.; Deng, S.; Smith, L.; et al. MicroRNA Microarray Identifies Let-7i as a Novel Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 10307–10314.
- Xu, M.; Kuang, Y.; Wang, M.; Han, X.; Yang, Q. A microRNA expression signature as a predictor of survival for colon adenocarcinoma. Neoplasma 2017, 64, 56–64.
- Monzo, M.; Santasusagna, S.; Moreno, I.; Martinez, F.; Hernandez, R.; Munoz, C.; Castellano, J.J.; Moreno, J.; Navarro, A. Exosomal microRNAs isolated from plasma of mesenteric veins linked to liver metastases in resected patients with colon cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30859–30869.
- Sugimura, K.; Miyata, H.; Tanaka, K.; Hamano, R.; Takahashi, T.; Kurokawa, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Nakajima, K.; Takiguchi, S.; Mori, M.; et al. Let-7 Expression Is a Significant Determinant of Response to Chemotherapy through the Regulation of IL-6/STAT3 Pathway in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5144–5153.
- Tanaka, K.; Miyata, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Sugimura, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kurokawa, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Takiguchi, S.; Mori, M.; Doki, Y. Circulating miR-200c Levels Significantly Predict Response to Chemotherapy and Prognosis of Patients Undergoing Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Esophageal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 607–615.
- Wang, X.R.; Luo, H.; Li, H.L.; Cao, L.; Wang, X.F.; Yan, W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Jiang, T.; Kang, C.S.; et al. Overexpressed let-7a inhibits glioma cell malignancy by directly targeting K-ras, independently of PTEN. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 1491–1501.
- Santangelo, A.; Rossato, M.; Lombardi, G.; Benfatto, S.; Lavezzari, D.; de Salvo, G.L.; Indraccolo, S.; Dechecchi, M.C.; Prandini, P.; Gambari, R.; et al. A molecular signature associated with prolonged survival in glioblastoma patients treated with regorafenib. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 264–276.
- Matos, B.; Bostjancic, E.; Matjasic, A.; Popovic, M.; Glavac, D. Dynamic expression of 11 miRNAs in 83 consecutive primary and corresponding recurrent glioblastoma: Correlation to treatment, time to recurrence, overall survival and MGMT methylation status. Radiol. Oncol. 2018, 52, 422–432.
- Erhart, F.; Hackl, M.; Hahne, H.; Buchroithner, J.; Meng, C.; Klingenbrunner, S.; Reitermaier, R.; Fischhuber, K.; Skalicky, S.; Berger, W.; et al. Combined proteomics/miRNomics of dendritic cell immunotherapy-treated glioblastoma patients as a screening for survival-associated factors. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 1–13.
- Wang, G.; Bi, C. Correlations of pri-Let-7 gene polymorphisms with the recurrence and metastasis of primary liver cancer after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 667–672.
- Tsai, Y.S.; Yeh, M.L.; Tsai, P.C.; Huang, C.I.; Huang, C.F.; Hsieh, M.H.; Liu, T.W.; Lin, Y.H.; Liang, P.C.; Lin, Z.Y.; et al. Clusters of Circulating let-7 Family Tumor Suppressors Are Associated with Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Hepatitis C. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4945.
- Li, H.; Fang, Z.; Yuan, B.; Ma, S.L.; Li, A.J.; Zhou, W.P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yin, L. MicroRNA let-7b inhibits cell proliferation via upregulation of p21 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 1–12.
- Wang, J.G.; Chen, J.L.; Sun, F.; Wang, Z.W.; Xu, W.F.; Yu, Y.F.; Ding, F.; Shen, H.J. miR-202 functions as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting HK2. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2265–2271.
- Li, Y.M.; Dong, R.; Lu, M.; Cheng, C.L.; Feng, Z.T.; Zhao, R.C.; Liang, J.H.; Han, J.Y.; Jiang, J.; Xu-Welliver, M.; et al. Let-7b-3p inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the BRF2-mediated MAPK/ERK pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1841–1856.
- Li, F.; Li, X.J.; Qiao, L.; Shi, F.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Dang, Y.P.; Gu, W.J.; Wang, X.G.; Liu, W. miR-98 suppresses melanoma metastasis through a negative feedback loop with its target gene IL-6. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, e116.
- Truini, A.; Coco, S.; Nadal, E.; Genova, C.; Mora, M.; Dal Bello, M.G.; Vanni, I.; Alama, A.; Rijavec, E.; Biello, F.; et al. Downregulation of miR-99a/let-7c/miR-125b miRNA cluster predicts clinical outcome in patients with unresected malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68627–68640.
- Huang, X.J.; Dong, H.X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, F.; Yang, S.S.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.Y. Silencing of let-7b-5p inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and stemness characteristics by Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp-box helicase 19A. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7666–7677.
- Ye, H.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Guo, A.; Hao, P. Construction of let-7d expression vector and its inhibitory effect on HMGA2 and ras expression in human ovarian cancer cells in vitro. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao = J. South. Med. Univ. 2012, 32, 1752–1757.
- Xiao, M.; Cai, J.; Cai, L.Q.; Jia, J.H.; Xie, L.S.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, B.X.; Jin, D.D.; Wang, Z.H. Let-7e sensitizes epithelial ovarian cancer to cisplatin through repressing DNA double strand break repair. J. Ovarian Res. 2017, 10, 1–13.
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, L.N.; Zhao, Y.R.; Yang, D.; Song, F.J.; Wen, Y.; Hao, Q.; Hu, Z.B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, K.X. Plasma miRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Ovarian Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77853.
- Petrillo, M.; Zannoni, G.F.; Beltrame, L.; Martinelli, E.; DiFeo, A.; Paracchini, L.; Craparotta, I.; Mannarino, L.; Vizzielli, G.; Scambia, G.; et al. Identification of high-grade serous ovarian cancer miRNA species associated with survival and drug response in patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A retrospective longitudinal analysis using matched tumor biopsies. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 625–634.
- Yang, F.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Cai, S.Y.; Ling, L.; Hong, L.Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, Q. Detailed Molecular Mechanism and Potential Drugs for COL1A1 in Carboplatin-Resistant Ovarian Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 3363.
- Dong, L.N.; Cao, X.J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Zhang, D.D. A Positive Feedback Loop of lncRNA DSCR8/miR-98-5p/STAT3/HIF-1 alpha Plays a Role in the Progression of Ovarian Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1713.
- Qi, X.; Yu, C.J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.X.; Shen, B.R. Network vulnerability-based and knowledge-guided identification of microRNA biomarkers indicating platinum resistance in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 1–11.
- Wang, Y.A.; Bao, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Xu, S.J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.L.; Wu, S.F. miR-98-5p contributes to cisplatin resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer by suppressing miR-152 biogenesis via targeting Dicer1. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–17.
- Yu, H.Y.; Pan, S.S. MiR-202-5p suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion in ovarian cancer via regulating HOXB2. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2256–2263.
- Calatayud, D.; Dehlendorff, C.; Boisen, M.K.; Hasselby, J.P.; Schultz, N.A.; Werner, J.; Immervoll, H.; Molven, A.; Hansen, C.P.; Johansen, J.S. Tissue MicroRNA profiles as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and periampullary cancers. Biomark. Res. 2017, 5, 1–18.
- Ali, S.; Almhanna, K.; Chen, W.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. Differentially expressed miRNAs in the plasma may provide a molecular signature for aggressive pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2011, 3, 28–47.
- Wang, S.J.; Li, X.D.; Wu, L.P.; Guo, P.; Feng, L.X.; Li, B. MicroRNA-202 suppresses glycolysis of pancreatic cancer by targeting hexokinase 2. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 1144–1153.
- Schubert, M.; Spahn, M.; Kneitz, S.; Scholz, C.J.; Joniau, S.; Stroebel, P.; Riedmiller, H.; Kneitz, B. Distinct microRNA Expression Profile in Prostate Cancer Patients with Early Clinical Failure and the Impact of let-7 as Prognostic Marker in High-Risk Prostate Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65064.
- Lam, W.Y.; Bhattacharya, D. Metabolic Links between Plasma Cell Survival, Secretion, and Stress. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 19–27.
- Pavlova, N.N.; Thompson, C.B. The Emerging Hallmarks of Cancer Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 27–47.
- Katayama, M.; Sjogren, R.J.O.; Egan, B.; Krook, A. miRNA let-7 expression is regulated by glucose and TNF-α by a remote upstream promoter. Biochem. J. 2015, 472, 147–156.
- Rawlings-Goss, R.A.; Campbell, M.C.; Tishkoff, S.A. Global population-specific variation in miRNA associated with cancer risk and clinical biomarkers. BMC Med. Genom. 2014, 7, 53.
- Serguienko, A.; Grad, I.; Wennerstrom, A.B.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A.; Thiede, B.; Stratford, E.W.; Myklebost, O.; Munthe, E. Metabolic reprogramming of metastatic breast cancer and melanoma by let-7a microRNA. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2451–2465.
- Duan, S.; Yu, S.; Yuan, T.; Yao, S.; Zhang, L. Exogenous Let-7a-5p Induces A549 Lung Cancer Cell Death Through BCL2L1-Mediated PI3Kgamma Signaling Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 808.
- Fan, H.; Jiang, M.; Li, B.; He, Y.; Huang, C.; Luo, D.; Xu, H.; Yang, L.; Zhou, J. MicroRNA-let-7a regulates cell autophagy by targeting Rictor in gastric cancer cell lines MGC-803 and SGC-7901. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1207–1214.
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Meng, T. Overexpression of let-7b exerts beneficial effects on the functions of human placental trophoblasts by activating the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2021, 1–15.
- Yang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wu, M. microRNA cluster MC-let-7a-1~let-7d promotes autophagy and apoptosis of glioma cells by down-regulating STAT3. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 319–331.
- Liang, H.; Xu, M.X.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Hu, K.P.; Yang, J.R.; Cao, M.B.; Zhong, Z.Z.; Yao, Z.C.; Deng, M.H.; Liu, B. Identification of miRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging 2021, 13, 6115–6133.
- Pan, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, B. MicroRNA-1182 and let-7a exert synergistic inhibition on invasion, migration and autophagy of cholangiocarcinoma cells through down-regulation of NUAK1. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 161.
- Xiong, H.; Shen, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Xie, B.; Jia, Y.; Jayasinghe, U.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Xie, S.; et al. H19/let7/Lin28 ceRNA network mediates autophagy inhibiting epithelialmesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 794–806.
- Han, C.C.; Li, H.; Ma, Z.F.; Dong, G.Z.; Wang, Q.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Fang, P.Q.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, T.Y.; et al. MIR99AHG is a noncoding tumor suppressor gene in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1–16.
- Liao, C.C.; Ho, M.Y.; Liang, S.M.; Liang, C.M. Recombinant protein rVP1 upregulates BECN1-independent autophagy, MAPK1/3 phosphorylation and MMP9 activity via WIPI1/WIPI2 to promote macrophage migration. Autophagy 2013, 9, 5–19.
- Liao, C.C.; Ho, M.Y.; Liang, S.M.; Liang, C.M. Autophagic degradation of SQSTM1 inhibits ovarian cancer motility by decreasing DICER1 and AGO2 to induce MIRLET7A-3P. Autophagy 2018, 14, 2065–2082.
- Mohamed, I.S.E.; Sen’kova, A.V.; Nadyrova, A.I.; Savin, I.A.; Markov, A.V.; Mitkevich, V.A.; Makarov, A.A.; Ilinskaya, O.N.; Mironova, N.L.; Zenkova, M.A. Antitumour Activity of the Ribonuclease Binase from Bacillus pumilus in the RLS40 Tumour Model Is Associated with the Reorganisation of the miRNA Network and Reversion of Cancer-Related Cascades to Normal Functioning. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1509.
- Xu, W.; Ding, M.; Wang, B.; Cai, Y.; Guo, C.; Yuan, C. Molecular mechanism of the canonical oncogenic lncRNA MALAT1 in gastric cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021.
- Yang, W.; Gong, P.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yang, B.; Ren, L. Circ-ABCB10 Contributes to Paclitaxel Resistance in Breast Cancer through Let-7a-5p/DUSP7 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 2327–2337.
- Li, C.; Chen, L.; Song, W.; Peng, B.; Zhu, J.; Fang, L. DICER activates autophagy and promotes cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by binding with let-7i-5p. Acta Histochem. 2021, 123, 151788.
- Pannuru, P.; Dontula, R.; Khan, A.A.; Herbert, E.; Ozer, H.; Chetty, C.; Lakka, S.S. miR-let-7f-1 regulates SPARC mediated cisplatin resistance in medulloblastoma cells. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 2193–2201.
- Duan, S.Y.; Li, J.X.; Tian, J.Q.; Yin, H.Y.; Zhai, Q.F.; Wu, Y.J.; Yao, S.Q.; Zhang, L. Crosstalk between let-7a-5p and BCL-xL in the Initiation of Toxic Autophagy in Lung Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2019, 15, 69–78.
- Lai, H.H.; Li, J.N.; Wang, M.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Croce, C.M.; Sun, H.L.; Lyu, Y.J.; Kang, J.W.; Chiu, C.F.; Hung, M.C.; et al. HIF-1alpha promotes autophagic proteolysis of Dicer and enhances tumor metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 625–643.
- Egea, V.; Kessenbrock, K.; Lawson, D.; Bartelt, A.; Weber, C.; Ries, C. Let-7f miRNA regulates SDF-1alpha- and hypoxia-promoted migration of mesenchymal stem cells and attenuates mammary tumor growth upon exosomal release. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 516.
- Reinsborough, C.W.; Ipas, H.; Abell, N.S.; Gouws, E.B.; Williams, J.P.; Mercado, M.; Van den Berg, C.; Xhemalce, B. BCDIN3D RNA methyltransferase stimulates Aldolase C expression and glycolysis through let-7 microRNA in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2395–2406.
- Lin, Y.; Wei, X.L.; Jian, Z.X.; Zhang, X.W. METTL3 expression is associated with glycolysis metabolism and sensitivity to glycolytic stress in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 2859–2867.
- Fang, F.; Shi, X.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L.; Liang, G. Growth hormone acts on liver to stimulate autophagy, support glucose production, and preserve blood glucose in chronically starved mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7449–7454.
- Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Fu, C. Growth hormone receptor promotes breast cancer progression via the BRAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. FEBS Open Bio 2020, 10, 1013–1020.
- Recouvreux, M.V.; Wu, J.B.; Gao, A.C.; Zonis, S.; Chesnokova, V.; Bhowmick, N.; Chung, L.W.; Melmed, S. Androgen Receptor Regulation of Local Growth Hormone in Prostate Cancer Cells. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2255–2268.
- Elzein, S.; Goodyer, C.G. Regulation of human growth hormone receptor expression by microRNAs. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 1448–1459.
- Tahtouh, R.; Wardi, L.; Sarkis, R.; Hachem, R.; Raad, I.; El Zein, N.; Hilal, G. Glucose restriction reverses the Warburg effect and modulates PKM2 and mTOR expression in breast cancer cell lines. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2019, 65, 26–33.
More
Information
Subjects:
Biochemistry & Molecular Biology
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
529
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
11 Jan 2022
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No





