
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maria De Falco | + 2790 word(s) | 2790 | 2021-09-26 03:43:06 | | | |
| 2 | Conner Chen | Meta information modification | 2790 | 2021-10-21 05:35:29 | | |
Video Upload Options
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) belong to a heterogeneous class of environmental pollutants widely diffused in different aquatic and terrestrial habitats. This implies that humans and animals are continuously exposed to EDCs from different matrices and sources. Moreover, pollution derived from anthropic and industrial activities leads to combined exposure to substances with multiple mechanisms of action on the endocrine system and correlated cell and tissue targets. For this reason, specific organs, such as the prostate gland, which physiologically are under the control of hormones like androgens and estrogens, are particularly sensitive to EDC stimulation. It is now well known that an imbalance in hormonal regulation can cause the onset of various prostate diseases, from benign prostate hyperplasia to prostate cancer.
1. Prostate Gland: Anatomy and Embryology
The prostate is an important accessory gland of the male reproductive system; it secretes a slightly alkaline fluid that in humans usually constitutes roughly 30% of the volume of the semen [1][2]. This gland develops from the pelvic part of the urogenital sinus (UGS), located at the base of the developing urinary bladder [3]. The UGS, responding to androgens, particularly testosterone (T) secreted by fetal testes and 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT), branches to form the prostate, due to a coordinated balance between different mechanisms as well as proliferation, adhesion, and migration [3][4]. All these phenomena are mediated by AR [5]. In rats, the prostatic buds appear at embryonic day E18–E19, but most of the prostate branching occurs after the birth [4]. The rodent prostate has three lobes: anterior, dorsolateral, and ventral; the last one has the most extensive branching [4]. Different from rodents, in humans, the prostate morphogenesis develops into a single organ formed by three different parts: the central, peripheral, and transitional zones [3]. Although prostate formation is completed at birth, its functional activity starts at puberty, when the prostate acquires its secretory ability [3][6]. It has been postulated that disease propensity of the prostate with respect to other accessory male organs can derive from its unique embryologic origin [7][8], different from what happens with the seminal vesicle and vas deferens, which arise from the mesodermal Wolffian ducts [7][9][10].
In adults, the prostate is formed by an epithelium that has low proliferation rates, which, in balance with the control of cell death, allow for the maintenance of a constant size of the prostate, although there is a physiological and continuous stimulation by androgens [4]. Indeed, it is well known that a healthy prostate needs a constant amount of androgens, which are essential throughout development [4]. The prostate epithelium is formed by epithelial cells that present all the features of secretory cells: a large endoplasmic reticulum, a well-developed Golgi apparatus, and many secretory granules widely distributed in the cytoplasm. Epithelial cells, in fact, contribute secretions to semen [4]. The prostate gland also contains composite tubule-alveolar glands that are separated from each other through a stromal tissue [4]. This, specifically, is an interstitial tissue formed by different cell types as well as smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, blood vessels, and nerves [4]. The stromal component, derived from mesenchyma, is equally important, since, working together with prostate epithelium, it helps maintain prostate physiology and contributes to expel secretions to the semen [4][11]. In addition, the proliferation of stromal cells is under the control of high levels of T [4][12]. It has been demonstrated that another important factor in the maintenance and control of prostate size is the epithelial-stromal ratio [4]. Although androgens are essential for prostate growth and function [13], estrogens also play key roles in prostate development, homeostasis, and disease [13][14].
2. Localization and Expression of Estrogen and Androgen Receptors inside the Prostate Gland
In the normal prostate, AR is the dominant steroid receptor. All the components of the prostate gland—stromal cells, epithelium, and smooth muscle cells—express androgen receptors [4] (Figure 1). Interaction between AR and its ligand can strongly guide morphogenesis. On the contrary, it has been shown that estrogens act through multiple ERs, including ERα, ERβ, and GPER, which are expressed in different cell types inside the prostate [5]. During development, 17β-estradiol (E2) plays a physiologic role in the modulation of branching morphogenesis through the activation of ERα and in the differentiation of prostate epithelium through ERβ [5][15][16][17][18]. In particular, lower levels of ERα than AR are localized in stromal cells that surround the proximal ducts during early-life prostate morphogenesis [5]. ERα significantly declines with puberty as androgen levels rise, suggesting a specific role during development [5]. Specifically, it has been demonstrated that mouse ERα expressed by different cell types has different actions: fibroblast ERα modulates branching morphogenesis; smooth muscle ERα regulates stromal cell proliferation and deposition of extracellular matrix [5][17][18]. In humans, ERα is expressed by stromal cells during fetal development [5][19][20], and it has been shown that when it is expressed in the periurethral prostatic epithelium during the last gestational period, it is associated with squamous metaplasia [5][20] (Figure 1). Moreover, recently it has been demonstrated that ERα also plays a role in prostatic epithelial stem cells and has involvement in self-renewal and progenitor cell proliferation after estrogen induction [5][21][22][23]. Different from ERα, rodent ERβ is almost exclusively localized in prostate epithelial cells, and it is involved in differentiation processes of the luminal epithelium [5][24]. On the contrary, in humans, ERβ is widely expressed in epithelial and stromal cells by gestational week seven, and it is activated during gestation and for several months after birth, suggesting that ERβ plays a role in development regulation [5][19][20]. Furthermore, ERβ is also localized in stem cells and seems to be involved in progenitor cell differentiation [5][23][25]. Many studies have focused on the central role of steroid receptors in the onset of different prostate pathologies, since it has been shown that they lead to expression and localization changes, initiate growth and differentiation defects during early development, and maintain these phenotypes throughout life [5]. Indeed, in rodents it has been demonstrated that after exposure to high levels of estrogens during the neonatal critical window (post-natal day PND1-5), ERα and AR immediately change, directly driving the early estrogenized phenotype. Specifically, AR protein is sharply downregulated in both stromal and epithelial cells and remains low throughout life, leading to a reduced response to androgens [5] (Figure 1). On the contrary, ERα is upregulated in periductal stromal cells, which in turn permits a transient induction of the prolactin receptor (PRLR) [5]. Different from ERα and AR, ERβ changes later in development or adulthood [5]. Thus, the developing prostate is no longer under AR regulation but is rather driven by several estrogens, through different receptors such as ERα and PRLR. The resulting effect is that programming signals that normally guide development of the prostate are altered, leading to permanent alterations in prostate structure and activity throughout life [5].
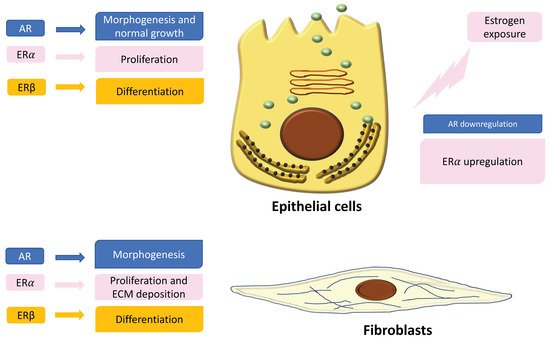
Figure 1. Localization and expression of steroid receptors in epithelial cells and fibroblasts. On the left is shown the role of the receptors in the regulation of cell functions. On the right is shown the different expression of androgen receptors (ARs) and estrogen receptors (ERs) after estrogen exposure during critical windows of exposure.
3. The Role of Estrogens in the Prostate Gland
The wide localization and expression of the main steroid receptors (AR, ERα, ERβ) highlight the relevant role of both androgens and estrogens in the control of prostate function and physiology. Indeed, an imbalance in estrogen levels and actions may contribute to aging-associated prostatic disease [7][9]. Several studies have demonstrated that inappropriate estrogen exposure, mainly E2 but also pharmaceutical estrogens and estrogenic EDCs, in terms of dose, type, and timing during prostate development, result in predisposition to an increased disease susceptibility, a phenotype referred to as estrogenic imprinting or developmental estrogenization [5]. Specifically, an altered estrogenic exposure can lead to abnormal growth of the human prostate, with predisposition to diseases such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and adenocarcinoma [26]. A Swedish cohort study showed strong correlations between indicators of high levels of pregnancy estradiol (E) and increased risk of prostate cancer [27]. Moreover, African-American men have a twofold higher risk of developing prostate cancer with aging than Caucasian men, and it has been shown that there is a link with elevated maternal estrogens during the first trimester of gestation [28]. Estrogens can increase risk of prostate cancer later in life, since estrogenic compounds are able to reprogram the gland, both structurally and epigenetically, driving differentiation defects [13][28][29][30]. Moreover, estrogen can render the prostate more susceptible to prostate cancer with aging [7][31][32], a concept that reinforces the developmental basis of adult disease paradigm [5]. For this reason, increased concern regarding inappropriate estrogenic exposure has led to attention on EDCs due to their ability to mimic estrogens activating different pathways in the prostate gland.
4. Prostate Diseases
Prostate diseases, such as prostatitis, enlarged prostate, BPH, and prostate cancer, become very common with age [1]. BPH is prevalent among older men and increases with age; it is found in approximately 70% of men over 60 and up to 90% of men over 80 [33]. BPH develops in the transition zone of the prostate surrounding the proximal urethra, and with the enlargement of the prostate, it may impede urine flow causing a bladder outlet obstruction (BOO), which can be responsible for bothersome lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) [33]. LUTS encompass a range of clinical complaints, including weak stream, straining to urinate, incomplete bladder emptying, frequency and urgency of urination, nocturia, and small voided volumes [33][34]. In addition to LUTS, BPH can also lead to other urinary tract complications, such as elevated postvoid residual, urinary retention, bladder diverticula, hydronephrosis, bladder calculi, and renal insufficiency [33][35]. These conditions significantly affect the quality of life of a substantial proportion of men, and the associated healthcare costs are in the billions annually [33][36][37][38]. Prostate cancer (PC) is the most common cancer and is the second leading cause of death for Caucasian men [39][40]. In Europe, about 2.6 million new cases per year are diagnosed; in Italy, 35,000 new cases were estimated through an epidemiological study in 2015 [41][42]. The Western lifestyle seems to play a central role in the etiology of prostate cancer; in fact, western men have an incidence rate up to 15 times greater than Asian men [41]. Moreover, during the last 15 years, the annual incidence rate increased in Korea as well [40][43]. The most well-known risk factors are age, race, family history of prostate cancer, inflammation, and diet, but biologic and experimental evidence support the hypothesis that environmental pollution, particularly the presence of EDCs, can strongly contribute to this increase [40].
Androgens physiologically control growth and functions of the prostate during, but it has been shown that they can also be involved in carcinogenesis [44]. The interaction among androgens and AR promotes prostate cell proliferation by activating AR-responsive genes and pathways in androgen-dependent adult prostate growth [45][46]. For this reason, AR has a major drug target in BPH [46][47] and PC [44][48]. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that estrogens play an important role in male sex hormone secretion as well as in the growth, differentiation, and homeostasis of both normal and cancer prostate cells [44][49][50]. Estrogens have a crucial role in prostate hyperplasia in aging [46][51]. In vivo studies have suggested that the combined administration of estrogen and androgen synergistically induce BPH [33][52]. Specifically, it has been shown that when Wistar rats were treated with T and E2, prostate weight increased at a higher rate than with T treatment alone, together with a higher DNA synthesis index [52][53]. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that in Noble rats, the long-term administration of combined T and E2 induces prostatic carcinoma [52][54][55]. Furthermore, even if mouse prostate is less sensitive to T and E2, it has been observed that combined administration of both T and E2 causes significant glandular prostatic growth accompanied by bladder outlet obstruction in C57BL mice [33][52]. The administration of T + E2 synergistically promoted prostatic growth, and interestingly, this was accompanied by an extremely enlarged bladder, probably due to bladder outlet obstruction [52]. Indeed, it is not important to consider the single amount of androgens or estrogens, but it is necessary to evaluate the ratio of the circulating and intra-prostatic E/T ratio. In elderly men, the E/T ratio is higher than younger men, and it is accompanied by an increase of ER expression, particularly in the stromal compartment [50][56]. The decrease of T is due to a lower production by the testes together with an increase of sex hormone binding globulin levels [44][57]. Moreover, in elderly men there is an increase of free circulating estrogens in the blood. The change of E/T ratio in favor of E may be responsible for the reactivation of cell growth and can induce a subsequent neoplastic transformation [31][44][58]. It has been proposed that estrogen could promote prostate epithelial proliferation through the activation of ERα, a key mediator of cell proliferation [46][59]. An autopsy study revealed that the prevalence of pathological benign lesions, such as hyperplasia, increased markedly in 90% of men older than 80, probably due to ER overexpression [60][44].
5. EDCs and Prostate Disease
Although risk assessments have been historically conducted on a chemical-by-chemical basis, regulatory agencies are beginning to consider the cumulative risk of chemicals. Moreover, it is now well known that humans [61][62][63][64][65][66][67], fish [68][69][70][71][72][73], and wildlife [74][75][76][77] are continuously exposed to multiple contaminants [67][78]. In this view, it is essential to study the effect of combined multicomponent mixtures on prostate diseases rather than individual substances in order to highlight the involvement of multiple compounds acting simultaneously in prostate pathologies [40][79][80].
Exposure to various EDCs may disrupt the normal androgen and estrogen balance in animals and humans, potentially leading to sex-hormone-sensitive diseases/disorders [81][82][83][84][85][86]. The “something from nothing” principle proposes that exposure to a single chemical may have no observed effects, but exposure to several of these chemicals in a mixture, due to synergistic or additive effects, may be significant [87][63]. These mixtures may even have significant effects at lower concentrations than the “no observed adverse effect levels” (NOAELS) reported for individual chemicals [87][88]. The combined toxicological effects of two or more compounds can take one of three forms: independent action, dose addition, or interaction [78][89][90] (Figure 2). In a mixture, individual compounds may have a single/specific effect due to a separate mechanism of action; in this case we speak of independent action, also known as response addition [78]. In this case, compounds that exhibit dissimilar modes of action can produce different, non-overlapping toxic effects in different organs and systems; thus, it is difficult to identify a combination effect [90]. In the case of simultaneous exposure to several chemicals with different modes of action, the principle of independence of effects is only applicable when all the chemicals in the mixture act through strictly dissimilar modes by affecting strictly different targets (simple dissimilar action). The EFSA expert panel states the simple dissimilar action “occurs where the modes of action and possibly, but not necessarily, the nature and sites of toxic effects differ between the chemicals in a mixture, and one chemical does not influence the toxicity of another” [90]. Based on the concept that toxic effects resulting from response addition would not be expected if no toxicity would occur from any of the single components of the mixture and given the low levels of pesticide residues in food, it was assumed that “… response-additive toxicity will rarely if ever occur from pesticide residues in food”. In contrast, when in a mixture, individual chemicals share the same mechanism of action, differing only in their potencies; we refer to this as dose addition, also known as simple similar action [78]. Finally, when one or more compounds interact in a mixture, we speak of interaction. The mechanistic basis of the interaction can be at the chemical, physico-chemical, or biological level. Thus, we can observe an interaction between two chemicals in a mixture or an interaction in either the toxicokinetic or toxicodynamic phase in a living organism. However, we need to distinguish between two types of interaction: synergistic (also referred as synergy, potentiation, or supra-additivity), when the combined effects of two or more interacting chemicals is either greater than that predicted based on dose addition or response addition; antagonistic (also called sub-additivity or inhibition), when the combined effects are lower than the individual chemical effect [78]. The basic assumption for the cumulative/combined risk assessment is dose addition, which considers compounds with similar mechanisms of action, or the same target organ [78][91][92]. Dose additivity has also been found for compounds with different mechanisms of action but displaying similar downstream in vivo effects, often indicated by “having effects on the same target organ” [67][78][93]. For this reason, the dose additivity assumption can be considered protective for human health assessments [78].
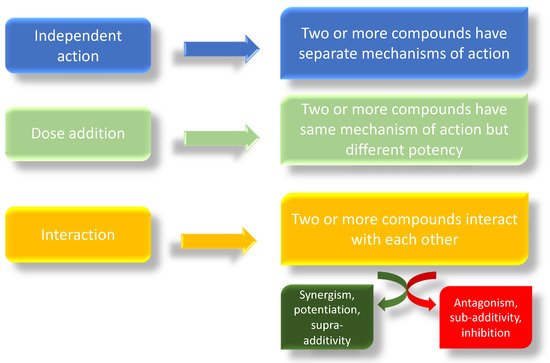
Figure 2. Possible mechanisms of action of combined exposure of different compounds.
Many chemicals with anti-androgenic actions have been shown to act together in combination, producing effects at doses that individually are not associated with any observable responses [67][94][95][96][97][98][99]. Anti-androgens are compounds that can act on male sexual development but with different modes of action, such as the inhibition of androgen hormone biosynthesis or blocking of receptor-mediated signaling [77][100][101]. Chemicals with estrogenic action can also disturb the development of male reproductive organs [99][102][103][104][105][106][107], but little is known about the effects of mixtures of estrogenic and anti-androgenic chemicals [99].
References
- Gan, W.; Zhou, M.; Xiang, Z.; Han, X.; Li, D. Combined effects of nonylphenol and bisphenol A on the human prostate epithelial cell line RWPE-1. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 4141–4155.
- Huggins, C.; Scott, W.W.; Heinen, J.H. Chemical composition of human semen and of the secretions of the prostate and seminal vesicles. Am. J. Physiol.-Leg. Content 1942, 136, 467–473.
- Scarano, W.R.; Pinho, C.F.; Pissinatti, L.; Goncalves, B.F.; Mendes, L.O.; Campos, S.G.P. Cell junction in the prostate: An overview about the effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in different experimental models. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 81, 147–154.
- Klukovich, R.; Nilsson, E.; Sadler-Riggleman, I.; Beck, D.; Xie, Y.; Yan, W.; Skinner, M.K. Environmental toxicant induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of prostate pathology and stromal-epithelial cell epigenome and transcriptome alterations: Ancestral origins of prostate disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2209.
- Prins, G.S. Developmental estrogenization: Prostate gland reprogramming leads to increased disease risk with aging. Differentiation 2021, 118, 72–81.
- Sugimura, Y.; Cunha, G.R.; Donjacour, A.A. Morphogenesis of ductal networks in the mouse prostate. Biol. Reprod. 1986, 34, 961–971.
- Calderon-Gierszal, E.L.; Prins, G.L. Directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into prostate organoids in vitro and its perturbation by low-dose bisphenol A exposure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133238.
- Leong, K.G.; Wang, B.E.; Johnson, L.; Gao, W.Q. Generation of a prostate from a single adult stem cell. Nature 2008, 456, 804–808.
- Prins, G.S.; Putz, O. Molecular signaling pathways that regulate prostate gland development. Differentiation 2008, 76, 641–659.
- Venditti, M.; Aniello, F.; Santillo, A.; Minucci, S. Study on PREP localization in mouse seminal vesicles and its possible involvement during regulated exocytosis. Zygote 2019, 27, 160–165.
- Flickinger, C.J. The fine structure of the interstitial tissue of the rat prostate. Am. J. Anat. 1972, 134, 107–125.
- Haynes, J.M.; Frydenberg, M.; Majewski, H. Testosterone- and phorbol ester-stimulated proliferation in human cultured prostatic stromal cells. Cell. Signal. 2001, 13, 703–709.
- Prins, G.S.; Ye, S.H.; Birch, L.; Zhang, X.; Cheong, A.; Lin, H.; Calderon-Gierszal, E.; Groen, J.; Hu, W.-Y.; Ho, S.-M.; et al. Prostate cancer risk and DNA methylation signatures in aging rats following developmental BPA exposure: A dose-response analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 077007.
- Nelles, J.L.; Hu, W.Y.; Prins, G.S. Estrogenaction and prostate cancer. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 6, 437–451.
- Prins, G.S.; Marmer, M.; Woodham, C.; Chang, W.; Kuiper, G.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Birch, L. Estrogen receptor-beta messenger ribonucleic acid ontogeny in the prostate of normal and neonatally estrogenized rats. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 874–883.
- Omoto, Y.; Imamov, O.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen receptor alpha and imprinting of the neonatal mouse ventral prostate by estrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1484–1489.
- Chen, M.; Hsu, I.; Wolfe, A.; Radovick, S.; Huang, K.; Yu, S.; Chang, C.; Messing, E.M.; Yeh, S. Defects of prostate development and reproductive system in the estrogen receptor-alpha null male mice. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 251–259.
- Vitkus, S.; Yeh, C.R.; Lin, H.H.; Hsu, I.; Yu, J.; Chen, M.; Yeh, S. Distinct function of estrogen receptor alpha in smooth muscle and fibroblast cells in prostate development. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 38–49.
- Adams, J.Y.; Leav, I.; Lau, K.M.; Ho, S.M.; Pflueger, S.M. Expression of estrogen receptor beta in the fetal, neonatal, and prepubertal human prostate. Prostate 2002, 52, 69–81.
- Shapiro, E.; Huang, H.; Masch, R.J.; McFadden, D.E.; Wilson, E.L.; Wu, X.R. Immunolocalization of estrogen receptor alpha and beta in human fetal prostate. J. Urol. 2005, 174, 2051–2053.
- Hu, W.Y.; Shi, G.B.; Hu, D.P.; Nelles, J.L.; Prins, G.S. Actions of estrogens and endocrine disrupting chemicals on human prostate stem/progenitor cells and prostate cancer risk. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 354, 63–73.
- Prins, G.S.; Hu, W.Y.; Shi, G.B.; Hu, D.P.; Majumdar, S.; Li, G.; Huang, K.; Nelles, J.L.; Ho, S.M.; Walker, C.L.; et al. Bisphenol A promotes human prostate stem-progenitor cell self-renewal and increases in vivo carcinogenesis in human prostate epithelium. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 805–817.
- Prins, G.S.; Calderon-Gierszal, E.L.; Hu, W.Y. Stem cells as hormone targets that lead to increased cancer susceptibility. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3451–3457.
- Imamov, O.; Morani, A.; Shim, G.J.; Omoto, Y.; Thulin-Andersson, C.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen receptor beta regulates epithelial cellular differentiation in the mouse ventral prostate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9375–9380.
- Majumdar, S.; Rinaldi, J.C.; Malhotra, N.R.; Xie, L.; Hu, D.P.; Gauntner, T.D.; Grewal, H.S.; Hu, W.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; et al. Differential actions of estrogen receptor α and β via nongenomic signaling in human prostate stem and progenitor cells. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2692–2708.
- Prins, G.S.; Ho, S.M. Early life estrogens and prostate cancer in an animal model. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2010, 1, 365–370.
- Ekbom, A. Growing evidence that several human cancers may originate in utero. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; Volume 8, pp. 237–244.
- Rohrmann, S.; Nelson, W.G.; Rifai, N.; Brown, T.R.; Dobs, A.; Kanarek, N.; Yager, J.D.; Platz, E.A. Serum estrogen, but not testosterone, levels differ between black and white men in a nationally representative sample of Americans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2519–2525.
- Prins, G.S.; Ye, S.H.; Birch, L.; Ho, S.M.; Kannan, K. Serum bisphenol A pharmacokinetics and prostate neoplastic responses following oral and subcutaneous exposures in neonatal Sprague-Dawley rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 1–9.
- Wang, Q.; Trevino, L.S.; Wong, R.L.Y.; Medvedovic, M.; Chen, J.; Ho, S.M.; Shen, J.; Foulds, C.E.; Coarfa, C.; O’Malley, B.W.; et al. Reprogramming of the epigenome by MLL1 links early-life environmental exposures to prostate cancer risk. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 30, 856–871.
- Ho, S.M.; Tang, W.Y.; Belmonte de Frausto, J.; Prins, G.S. Developmental exposure to estradiol and bisphenol A increases susceptibility to prostate carcinogenesis and epigenetically regulates phosphodiesterase type 4 variant 4. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5624–5632.
- Prins, G.S.; Huang, L.; Birch, L.; Pu, Y. The role of estrogens in normal and abnormal development of the prostate gland. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1089, 1–13.
- Nicholson, T.M.; Ricke, E.A.; Marker, P.C.; Miano, J.M.; Mayer, R.D.; Timms, B.G.; vom Saal, F.S.; Wood, R.W.; Ricke, W.A. Testosterone and 17β-Estradiol Induce Glandular Prostatic Growth, Bladder Outlet Obstruction, and Voiding Dysfunction in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 5556–5565.
- Roehrborn, C.G. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: An overview. Rev. Urol. 2005, 7, S3–S14.
- Oelke, M.; Kirschner-Hermanns, R.; Thiruchelvam, N.; Heesakkers, J. Can we identify men who will have complications from benign prostatic obstruction (BPO)?: ICI-RS 2011. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2012, 31, 322–326.
- Irwin, D.E.; Milsom, I.; Kopp, Z.; Abrams, P.; Artibani, W.; Herschorn, S. Prevalence, severity, and symptom bother of lower urinary tract symptoms among men in the EPIC study: Impact of overactive bladder. Eur. Urol. 2009, 56, 14–20.
- Welch, G.; Weinger, K.; Barry, M.J. Quality-of-life impact of lower urinary tract symptom severity: Results from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. Urology 2002, 59, 245–250.
- Parsons, J.K. Benign prostatic hyperplasia and male lower urinary tract symptoms: Epidemiology and risk factors. Curr. Bladder Dysfunct. Rep. 2010, 5, 212–218.
- American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Prostate Cancer. 2016. Available online: http://www.cancer.org/cancer/prostatecancer/detailedguide/prostate-cancer-key-statistics (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Lim, J.-E.; Nam, C.; Yang, J.; Rha, K.H.; Lim, K.-M.; Jee, S.H. Serum persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and prostate cancer risk: A case-cohort study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 849–856.
- Quagliariello, V.; Rossetti, S.; Cavaliere, C.; Di Palo, R.; Lamantia, E.; Castaldo, L.; Nocerino, F.; Ametrano, G.; Cappuccio, F.; Malzone, G.; et al. Metabolic syndrome, endocrine disruptors and prostate cancer associations: Biochemical and pathophysiological evidences. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30606–30616.
- Capocaccia, R.; Foschi, R.; Zucchetto, A.; Valdagni, R.; Nicolai, N.; Maffezzini, M.; Gatta, G. Estimates of prostate cancer burden in Italy. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 166–172.
- National Cancer Information Center, Korea. Available online: http://www.cancer.go.kr/mbs/cancer/subview.jsp?id=cancer040104000000 (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Di Donato, M.; Cernera, G.; Giovannelli, P.; Galasso, G.; Bilancio, A.; Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G. Recent advances on bisphenol-A and endocrine disruptors effects on huma prostate cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 457, 35–42.
- Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A.; Lin, W.J.; Lai, K.-P.; Chang, C. Androgen receptor roles in the development of benign prostate hyperplasia. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1942–1949.
- Wu, S.; Huang, D.; Su, X.; Yan, H.; Wu, J.; Sun, Z. Oral exposure to low-dose bisphenol A induces hyperplasia of dorsolateral prostate and upregulates EGFR expression in adult Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2019, 35, 647–659.
- Sun, W.G.; Gan, L.P.; Yu, G.Q.; Ye, Z.Q.; Mi, Z.G.; Wang, Q.H.; Han, C.Z.; Ren, L.S.; Wang, H.Z. Testosterone induces different-featured prostate hyperplasia in castrated and uncastrated mice. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 2009, 15, 153–157.
- Heinlein, C.A.; Chang, C. Androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 276–308.
- Härkönen, P.L.; Mäkelä, S.I. Role of estrogens in development of prostate cancer. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 92, 297–305.
- Prezioso, D.; Denis Louis, J.; Klocker, H.; Sciarra, A.; Reis, M.; Naber, K.; Lobe, B.L.; Pacik, D.; Griffiths, K. Estrogens and aspects of prostate disease. Int. J. Urol. 2007, 14, 1–16.
- Wang, C.; Du, X.; Yang, R.; Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Shi, J.; Chen, L.; Shao, R.; Fan, G.; Gao, X.; et al. The prevention and treatment effects of tanshinone IIA on oestrogen/androgen-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 145, 28–37.
- Fujimoto, N.; Kanno, J. Increase in prostate stem cell antigen expression in prostatic hyperplasia induced by testosterone and 17β-estradiol in C57BL mice. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 158, 56–62.
- Suzuki, K.; Ito, K.; Suzuki, T.; Honma, S.; Yamanaka, H. Synergistic effects of estrogen and androgen on the prostate: Effects of estrogen on androgen- and estrogen-receptors, BrdU uptake, immunohistochemical study of AR, and responses to antiandrogens. Prostate 1995, 26, 151–163.
- Drago, J.R. The induction of NB rat prostatic carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 1984, 4, 255–256.
- Noble, R.L. The development of prostatic adenocarcinoma in Nb rats following prolonged sex hormone administration. Cancer Res. 1977, 37, 1929–1933.
- Nicholson, T.M.; Ricke, W.A. Androgens and estrogens in benign prostatic hyperplasia: Past, present and future. Differentiation 2011, 82, 184–199.
- Kaufman, J.M.; Vermeulen, A. The decline of androgen levels in elderly men and its clinical and therapeutic implications. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 833–876.
- King, K.J.; Nicholson, H.D.; Assinder, S.J. Effect of increasing ratio of estrogen: Androgen on proliferation of normal human prostate stromal and epithelial cells, and the malignant cell line LNCaP. Prostate 2006, 66, 105–114.
- Risbridger, G.; Wang, H.; Young, P.; Kurita, T.; Wang, Y.Z.; Lubahn, D.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Cunha, G. Evidence that epithelial and mesenchymal estrogen receptor-alpha mediates effects of estrogen on prostatic epithelium. Dev. Biol. 2001, 229, 432–442.
- Bleak, T.C.; Calaf, G.M. Breast and prostate glands affected by environmental substances. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 20–37.
- Eskenazi, B.; Bradman, A.; Castorina, R. Exposures of children to organophosphate pesticides and their potential adverse health effects. Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 409–419.
- Landrigan, P.J.; Claudio, L.; Markowitz, S.B.; Berkowitz, G.S.; Brenner, B.L.; Romero, H.; Wetmur, J.G.; Matte, T.D.; Gore, A.C.; Godbold, J.H.; et al. Pesticides and inner-city children: Exposures, risks, and prevention. Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 431–437.
- Silva, E.; Rajapakse, N.; Kortenkamp, A. Something from “nothing”—Eight weak estrogenic chemicals combined at concentrations below NOECs produce significant mixture effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1751–1756.
- Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Wong, L.Y.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L. Exposure of the U.S. population to bisphenol A and 4-tertiary-octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 39–44.
- Wolff, M.S.; Teitelbaum, S.L.; Windham, G.; Pinney, S.M.; Britton, J.A.; Chelimo, C.; Godbold, J.; Biro, F.; Kushi, L.H.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; et al. Pilot study of urinary biomarkers of phytoestrogens, phthalates, and phenols in girls. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 116–121.
- Wolff, M.S.; Engel, S.M.; Berkowitz, G.S.; Ye, X.; Silva, M.J.; Zhu, C.; Wetmur, J.; Calafat, A.M. Prenatal phenol and phthalate exposures and birth outcomes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1092–1097.
- Rider, C.V.; Furr, J.R.; Wilson, V.S.; Gray, L.E., Jr. Cumulative effects of in utero administration of mixtures of reproductive toxicants that disrupt common target tissues via diverse mechanisms of toxicity. Int. J. Androl. 2010, 33, 443–462.
- Di Lorenzo, M.; Barra, T.; Rosati, L.; Valiante, S.; Capaldo, A.; De Falco, M.; Laforgia, V. Adrenal gland response to endocrine disrupting chemicals in fishes, amphibians and reptiles: A comparative overview. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 297, 113550.
- Jobling, S.; Nolan, M.; Tyler, C.R.; Brighty, G.; Sumpter, J.P. Widespread sexual disruption in wild fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2498–2506.
- Ankley, G.T.; Brooks, B.W.; Huggett, D.B.; Sumpter, J.P. Repeating history: Pharmaceuticals in the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8211–8217.
- Jobling, S.; Tyler, C.R. Introduction: The ecological relevance of chemically induced endocrine disruption in wildlife. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 7–8.
- Jobling, S.; Williams, R.; Johnson, A.; Taylor, A.; Gross-Sorokin, M.; Nolan, M.; Tyler, C.R.; van Aerle, R.; Santos, E.; Brighty, G. Predicted exposures to steroid estrogens in U.K. rivers correlate with widespread sexual disruption in wild fish populations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 32–39.
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Russo, G.; Rossi, S.; Golianova, K.; Moore, F.; Guida, M.; De Falco, M.; Grumetto, L. Emerging endocrine disruptors in two edible fish from the Persian Gulf: Occurrence, congener profile, and human health risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112241.
- Hall, A.J.; Thomas, G.O. Polychlorinated biphenyls, DDT, polybrominated diphenyl ethers, and organic pesticides in United Kingdom harbor seals (Phoca vitulina)—Mixed exposures and thyroid homeostasis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 851–861.
- Di Lorenzo, M.; Sciarrillo, R.; Rosati, L.; Sellitti, A.; Barra, T.; De Luca, A.; Laforgia, V.; De Falco, M. Effects of alkylphenols mixture on the adrenal gland of the lizard Podarcis sicula. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127239.
- Di Lorenzo, M.; Mileo, A.; Laforgia, V.; De Falco, M.; Rosati, L. Alkyphenol Exposure Alters Steroidogenesis in Male Lizard Podarcis siculus. Animals 2021, 11, 1003.
- Sciarrillo, R.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Valiante, S.; Rosati, L.; De Falco, M. OctylPhenol (OP) Alone and in Combination with NonylPhenol (NP) Alters the Structure and the Function of Thyroid Gland of the Lizard Podarcis siculus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 567–578.
- Schneider, S.; Fussell, K.C.; Melching-Kollmuss, S.; Buesen, R.; Gröters, S.; Strauss, V.; Jiang, X.; van Ravenzwaay, B. Investigations on the dose-response relationship of combined exposure to low doses of three anti-androgens in Wistar rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3961–3989.
- Lee, Y.M.; Bae, S.G.; Lee, S.H.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Lee, D.H. Persistent organic pollutants and hyperuricemia in the U.S. general population. Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 1–5.
- Lim, J.E.; Park, S.H.; Jee, S.H.; Park, H. Body concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and prostate cancer: A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 11275–11284.
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: An endocrine society scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342.
- Scott, H.M.; Mason, J.I.; Sharpe, R.M. Steroidogenesis in the fetal testis and its susceptibility to disruption by exogenous compounds. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 883–925.
- Habauzit, D.; Flouriot, G.; Pakdel, F.; Saligaut, C. Effects of estrogens and endocrine-disrupting chemicals on cell differentiation-survival-proliferation in brain: Contributions of neuronal cell lines. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2011, 14, 300–327.
- Jones, L.A.; Hajek, R.A. Effects of estrogenic chemicals on development. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 63–67.
- Kortenkamp, A. Ten years of mixing cocktails: A review of combination effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 98–105.
- Riad, M.A.; Abd-Rabo, M.M.; Abd El Aziz, S.A.; El Behairy, A.M.; Badawy, M.M. Reproductive toxic impact of subchronic treatment with combined butylparaben and triclosan in weanling male rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22037.
- Patrick, S.M.; Bornman, M.S.; Joubert, A.M.; Pitts, N.; Naidoo, V.; de Jager, C. Effects of environmental endocrine disruptors, including insecticides used for malaria vector control on reproductive parameters of male rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 61, 19–27.
- Hass, U.; Boberg, J.; Christiansen, S.; Jacobsen, P.R.; Vinggaard, A.M.; Taxvig, C.; Poulsen, M.E.; Herrmann, S.S.; Jensen, B.H.; Petersen, A.; et al. Adverse effects on sexual development in rat offspring after low dose exposure to a mixture of endocrine disrupting pesticides. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 34, 261–274.
- Wilkinson, C.F.; Christoph, G.R.; Julien, E.; Kelley, J.M.; Kronenberg, J.; McCarthy, J.; Reiss, R. Assessing the risks of exposures to multiple chemicals with a common mechanism of toxicity: How to cumulate? Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2000, 31, 30–43.
- Feron, V.J.; Groten, J.P. Toxicological evaluation of chemical mixtures. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 825–839.
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on the identification of pesticides to be included in cumulative assessment groups on the basis of their toxicological profile. In EFSA J.; 2013; 11, p. 3293.
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on the relevance of dissimilar mode of action and its appropriate application for cumulative risk assessment of pesticides residues in food. In EFSA J.; 2013; 11, p. 3472.
- Blystone, C.R.; Lambright, C.S.; Cardon, M.C.; Furr, J.; Rider, C.V.; Hartig, P.C.; Wilson, V.S.; Gray, L.E., Jr. Cumulative and antagonistic effects of a mixture of the antiandrogens vinclozolin and iprodione in the pubertal male rat. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 111, 179–188.
- Hass, U.; Scholze, M.; Christiansen, S.; Dalgaard, M.; Vinggaard, A.M.; Axelstad, M.; Metzdorff, S.B.; Kortenkamp, A. Combined exposure to anti-androgens exacerbates disruption of sexual differentiation in the rat. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 122–128.
- Metzdorff, S.B.; Dalgaard, M.; Christiansen, S.; Axelstad, M.; Hass, U.; Kiersgaard, M.K.; Scholze, M.; Kortenkamp, A.; Vinggaard, A.M. Dysgenesis and histological changes of genitals and perturbations of gene expression in male rats after in utero exposure to antiandrogen mixtures. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 98, 87–98.
- Howdeshell, K.L.; Wilson, V.S.; Furr, J.; Lambright, C.R.; Rider, C.V.; Blystone, C.R.; Hotchkiss, A.K.; Gray, L.E., Jr. A mixture of five phthalate esters inhibits fetal testicular testosterone production in the sprague-dawley rat in a cumulative, dose-additive manner. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 105, 153–165.
- Rider, C.V.; Furr, J.; Wilson, V.S.; Gray, L.E., Jr. A mixture of seven antiandrogens induces reproductive malformations in rats. Int. J. Androl. 2008, 31, 249–262.
- Christiansen, S.; Scholze, M.; Dalgaard, M.; Vinggaard, A.M.; Axelstad, M.; Kortenkamp, A.; Hass, U. Synergistic disruption of external male sex organ development by a mixture of four antiandrogens. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1839–1846.
- Christiansen, S.; Kortenkamp, A.; Axelstad, M.; Boberg, J.; Scholze, M.; Jacobsen, P.R.; Faust, M.; Lichtensteiger, W.; Schlumpf, M.; Burdorf, A.; et al. Mixtures of endocrine disrupting contaminants modelled on human high end exposures: An exploratory study in rats. Int. J. Androl. 2012, 35, 303–316.
- Hellwig, J.; van Ravenzwaay, B.; Mayer, M.; Gembardt, C. Pre- and postnatal oral toxicity of vinclozolin in Wistar and Long-Evans rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2000, 32, 42–50.
- Gray, L.E., Jr.; Wilson, V.S.; Stoker, T.; Lambright, C.; Furr, J.; Noriega, N.; Howdeshell, K.; Ankley, G.T.; Guillette, L. Adverse effects of environmental antiandrogens and androgens on reproductive development in mammals. Int. J. Androl. 2006, 29, 96–104.
- Kang, K.S.; Che, J.H.; Ryu, D.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Li, G.X.; Lee, Y.S. Decreased sperm number and motile activity on the F1 offspring maternally exposed to butyl p-hydroxybenzoic acid (butyl paraben). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2002, 64, 227–235.
- Timms, B.G.; Howdeshell, K.L.; Barton, L.; Bradley, S.; Richter, C.A.; vom Saal, F.S. Estrogenic chemicals in plastic and oral contraceptives disrupt development of the fetal mouse prostate and urethra. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7014–7019.
- Durrer, S.; Ehnes, C.; Fuetsch, M.; Maerkel, K.; Schlumpf, M.; Lichtensteiger, W. Estrogen sensitivity of target genes and expression of nuclear receptor co-regulators in rat prostate after pre- and postnatal exposure to the ultraviolet filter 4-methylbenzylidene camphor. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 42–50.
- Prins, G.S.; Tang, W.Y.; Belmonte, J.; Ho, S.M. Perinatal exposure to oestradiol and bisphenol A alters the prostate epigenome and increases susceptibility to carcinogenesis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 102, 134–138.
- Salian, S.; Doshi, T.; Vanage, G. Perinatal exposure of rats to Bisphenol A affects the fertility of male offspring. Life Sci. 2009, 85, 742–752.
- Axelstad, M.; Boberg, J.; Hougaard, K.S.; Christiansen, S.; Jacobsen, P.R.; Mandrup, K.R.; Nellemann, C.; Lund, S.P.; Hass, U. Effects of pre- and postnatal exposure to the UV-filter octyl methoxycinnamate (OMC) on the reproductive, auditory and neurological development of rat offspring. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 250, 278–290.




