Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jerzy Gebicki | -- | 1167 | 2024-03-12 11:19:05 | | | |
| 2 | Sirius Huang | Meta information modification | 1167 | 2024-03-15 08:58:40 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Marcinek, A.; Katarzynska, J.; Gebicki, J. Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence for Vascular Dysfunction Identification. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/56158 (accessed on 12 January 2026).
Marcinek A, Katarzynska J, Gebicki J. Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence for Vascular Dysfunction Identification. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/56158. Accessed January 12, 2026.
Marcinek, Andrzej, Joanna Katarzynska, Jerzy Gebicki. "Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence for Vascular Dysfunction Identification" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/56158 (accessed January 12, 2026).
Marcinek, A., Katarzynska, J., & Gebicki, J. (2024, March 12). Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence for Vascular Dysfunction Identification. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/56158
Marcinek, Andrzej, et al. "Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence for Vascular Dysfunction Identification." Encyclopedia. Web. 12 March, 2024.
Copy Citation
Arterial blood pressure monitoring plays an important role in preventive medicine, allowing, in selected cases, the identification of vascular dysfunction. Extensive research, encompassing both healthy subjects and patients with a range of vascular issues, has consistently demonstrated the efficacy of the Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF) technique in identifying cases of impaired vascular function, including many cases of silent vascular dysfunction that are not manifested by changes in blood pressure.
FMSF technique
NADH fluorescence
vascular circulation
vascular screening
1. Introduction
The diagnosis and treatment of vascular diseases incurs tremendous costs to the healthcare system. Early diagnosis of vascular dysfunction is not always possible, as it is often not manifested by characteristic symptoms. Hypertension is a common example of such silent vascular dysfunction. Therefore, occasional monitoring of arterial blood pressure is recommended as a preventative measure. However, blood pressure monitoring is only able to identify selected cases of vascular dysfunction. Many other cases of silent vascular dysfunction are not manifested by changes in blood pressure.
Vascular system dysfunction often results in insufficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to tissues, due to hypoxia. There are techniques available for the assessment of the body’s reaction to hypoxia. The classical technique, called flow-mediated dilation (FMD) and regarded as the gold standard [1][2][3], is based on stimulation of the vascular circulation in response to the post-occlusive reactive hyperemia (PORH) [4]. However, FMD only measures the reaction of the macrocirculation to transient hypoxia. Despite great research interest in the use of the FMD technique, its widespread adoption as a routine diagnostic technique has been hindered by the technical complexities involved in its execution.
Changes in the functioning of the endothelium of large blood vessels are often preceded by dysfunction of vascular microcirculation [5]. Because cutaneous microcirculation is representative for the assessment of systemic microcirculation, its dysfunctions and pathologies [6][7][8] and is readily accessible for monitoring, changes in epidermal cell functioning in response to ischemia are a sensitive marker of early vascular circulation disorders.
In light of this, there is growing demand for a diagnostic tool that is both simple and non-invasive, for assessment of the body’s reaction to transient hypoxia. Addressing this need is the Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF) technique [9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17]. The FMSF technique stands out for its ability to provide information on distinguishable macro- and microcirculatory responses to transient hypoxia.
The FMSF technique is based on the measurement of the strongest fluorescence emitted from human skin, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) fluorescence. A significant part of the exciting light is absorbed by the epidermis and papillary dermis [11][18][19][20]; hence, the emission of NADH and its changes are related to changes in the mitochondrial redox balance of the NADH/NAD+ pair in epidermal cells, which are the final recipients of oxygen from the circulatory system.
NADH fluorescence has previously been used to determine mitochondrial function in vivo [21][22][23][24]. Because only the reduced form of the NADH/NAD+ pair fluoresces, limited information can be obtained regarding the redox balance of this coenzyme as an indicator of mitochondrial function. However, the reduced form of the coenzyme (NADH) accumulates under ischemia and hypoxia, while it is oxidized during hyperemia. Hence, changes observed during the PORH test can be used to assess the NADH/NAD+ balance in epidermal cells and vascular response to ischemic conditions.
2. Brief Description of the FMSF Methodology
The Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF) technique measures changes in the in-tensity of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) fluorescence from the skin on the forearm (Figure 1). The changes are stimulated by blocking and releasing blood flow in the brachial artery. The skin is characterized by a specific metabolism. The epidermal layer of skin is not directly vascularized, and oxygen and nutrients are transported from the dermis by diffusion. Therefore, epidermal cell metabolism can be considered a unique and sensitive marker of early dysfunction in vascular circulation and metabolic regulation.
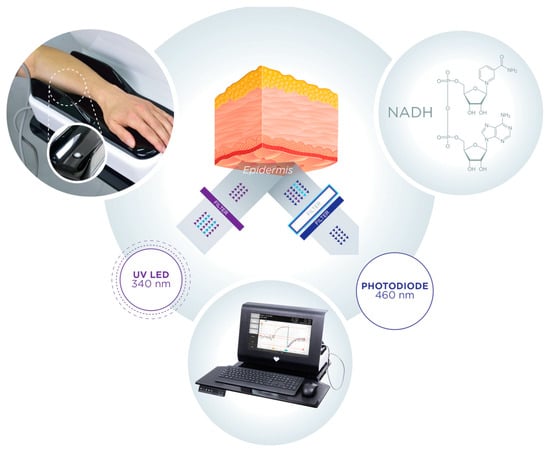

Figure 1. Operating principle of AngioExpert.
AngioExpert is a diagnostic tool based on the FMSF technique, produced by Angionica Ltd. (Lodz, Poland). The measurement protocol has been described in detail elsewhere [12][17]. Figure 2 shows an exemplary FMSF trace, consisting of three parts: the baseline, the ischemic response (IR), and the hyperemic (reperfusion) response (HR).
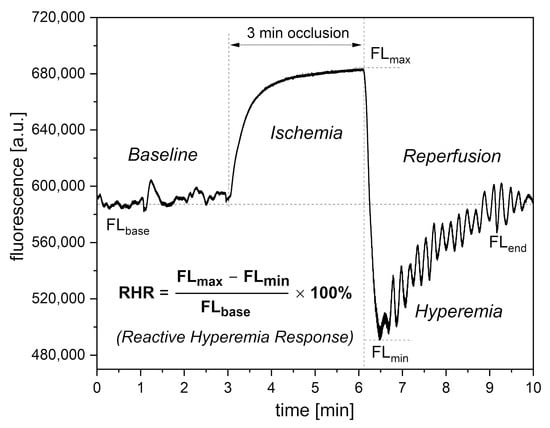
Figure 2. Definition of the RHR parameter.
In the PORH test, an increase in NADH fluorescence is observed during the ischemic response associated with brachial artery occlusion. After 3 min, the occlusion is released and NADH fluorescence drops below the baseline, reaching minimum (hyperemia, 20–30 s), followed by a return to baseline values (reperfusion, approximately 3 min).
On the baseline and reperfusion lines, microcirculation oscillations known as flowmotion are clearly visible [25][26]. These microcirculatory oscillations in the low-frequency range (<0.15 Hz) fit into several periodic activities, classified as endothelial (<0.021 Hz), neurogenic (0.021–0.052 Hz), and myogenic (0.052–0.15 Hz). Characteristic parameters have been defined for each part of the FMSF trace and can be used for precise analysis of the vascular function, as discussed in previous studies [27][28][29]. Based on extensive experience examining hundreds of cases, researchers decided to select only three key parameters for vascular screening purposes: Reactive Hyperemia Response (RHR), Hypoxia Sensitivity (HS), and Normoxia Oscillatory Index (NOI). These parameters will be presented in the subsequent sections.
3. Interpretation of Key FMSF Parameters for Vascular Screening
Of the three parameters selected for vascular screening, the RHR and HS parameters are particularly useful. The RHR parameter is defined in Figure 2. RHR is a unique parameter based on the combined responses from both the ischemic and hyperemic parts of the measured FMSF trace (RHR = IRmax + HRmax). It represents the overall function of the vascular system, including both macro- and microcirculation [14][17]. The HS parameter represents a direct measure of the intensity of microcirculatory oscillations related to myogenic oscillations with frequencies in the range of 0.052–0.15 Hz, recorded during reperfusion [13][14][17]. Myogenic microcirculatory oscillations are a very sensitive measure of the microcirculatory response to hypoxia and can be monitored with high precision using the FMSF technique. As the values of the HS parameter can vary within a quite broad range, it is more practical to use a normally distributed log (HS).
The baseline microcirculatory oscillations hold interesting diagnostic potential. The intensity and relative distribution of these oscillations in the low frequency range (<0.15 Hz) have been found to be sensitive to various stress factors. These include emotional stress, physical exhaustion, post-infection states, and hormonal deficiencies. The NOI parameter can be used for universal characterization of stress of various origins. The NOI parameter represents the contribution of endothelial and neurogenic oscillations relative to all oscillations detected at low-frequency intervals (<0.15 Hz). For emotional stress, physical exhaustion, or post-infection stress, the NOI parameters have values below 60%. In the case of hormonal deficiency frequently associated with erectile dysfunction, the NOI parameter values are in the range of 90–100% [15][17].
Based on extensive experience, the function of the RHR, HS, and NOI parameters can be presented in the form of a colored strip, as shown in Figure 3. The most optimal values are shown in green and values indicating potential vascular dysfunction are shown in yellow.
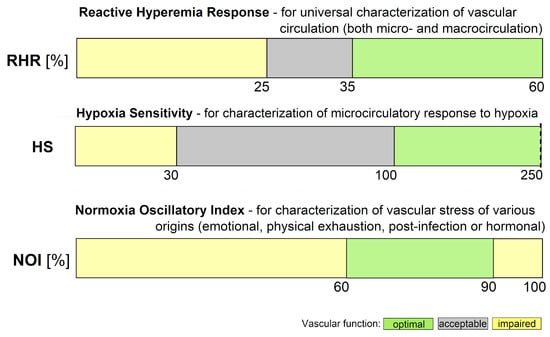
Figure 3. Ranges of key FMSF parameters (RHR—Reactive Hyperemia Response, HS—Hypoxia Sensitivity, NOI—Normoxia Oscillatory Index).
References
- Kelm, M. Flow-mediated dilatation in human circulation: Diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2002, 282, H1–H5.
- Tremblay, J.C.; Pyke, K.E. Flow-mediated dilation stimulated by sustained increases in shear stress: A useful tool for assessing endothelial function in humans? Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2017, 314, H508–H520.
- Mućka, S.; Miodońska, M.; Jakubiak, G.K.; Starzak, M.; Cieślar, G.; Stanek, A. Endothelial Function Assessment by Flow-Mediated Dilation Method: A Valuable Tool in the Evaluation of the Cardiovascular System. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11242.
- Roustit, M.; Cracowski, J.L. Assessment of endothelial and neurovascular function in human skin microcirculation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 373–384.
- Hellmann, M.; Roustit, M.; Cracowski, J.L. Skin microvascular endothelial function as a biomarker in cardiovascular diseases? Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 803–810.
- Cracowski, J.-L.; Roustit, M. Human Skin Microcirculation. In Comprehensive Physiology; Prakash, Y.S., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Chapter 3; Volume 10, pp. 1105–1154.
- IJzerman, R.G.; De Jongh, R.T.; Beijk, M.A.M.; Van Weissenbruch, M.M.; Delemarre-van de Waal, H.A.; Serné, E.H.; Stehouwer, C.D.A. Individuals at increased coronary heart disease risk are characterized by an impaired microvascular function in skin. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 33, 536–542.
- Rossi, M.; Matteucci, E.; Pesce, M.; Consani, C.; Franzoni, F.; Santoro, G.; Giampietro, O. Peripheral microvascular dysfunction as an independent predictor of atherosclerotic damage in type 1 diabetes patients: A preliminary study. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2013, 54, 381–391.
- Katarzynska, J.; Lipinski, Z.; Cholewinski, T.; Piotrowski, L.; Dworzynski, W.; Urbaniak, M.; Borkowska, A.; Cypryk, K.; Purgal, R.; Marcinek, A.; et al. Non-invasive evaluation of microcirculation and metabolic regulation using flow mediated skin fluorescence (FMSF): Technical aspects and methodology. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 104104.
- Hellmann, M.; Tarnawska, M.; Dudziak, M.; Dorniak, K.; Roustit, M.; Cracowski, J.L. Reproducibility of flow mediated skin fluorescence to assess microvascular function. Microvasc. Res. 2017, 113, 60–64.
- Hou, H.; Du, G.; Wang, Y.; Su, C.; Guo, L.; Chen, X. Noninvasive in vivo study of NADH fluorescence and its real-time intrinsic dynamical changes: Experiments and seven-layered skin model Monte Carlo simulations. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2022, 15, 2230006.
- Katarzynska, J.; Cholewinski, T.; Sieron, L.; Marcinek, A.; Gebicki, J. Flowmotion Monitored by Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF): A Tool for Characterization of Microcirculatory Status. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 702.
- Gebicki, J.; Marcinek, A.; Zielinski, J. Assessment of Microcirculatory Status Based on Stimulation of Myogenic Oscillations by Transient Ischemia: From Health to Disease. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2021, 17, 33–36.
- Katarzyńska, J.; Zieliński, J.; Marcinek, A.; Gebicki, J. New Approach to Non-Invasive Assessment of Vascular Circulation Based on the Response to Transient Ischemia. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 113–116.
- Gebicki, J.; Katarzynska, J.; Marcinek, A. Effect of Psychological Stress on Microcirculation Oscillations: Diagnostic Aspects. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2023, 19, 79–82.
- Gebicki, J.; Filipiak, T.; Marcinek, A.; Wozniacka, A. Assessment of NADH/NAD+ Redox Imbalance in Psoriatic Lesions Using the FMSF Technique: Therapeutic Aspects. Sensors 2023, 23, 8718.
- Marcinek, A.; Katarzynska, J.; Sieron, L.; Skokowski, R.; Zielinski, J.; Gebicki, J. Non-Invasive Assessment of Vascular Circulation Based on Flow Mediated Skin Fluorescence (FMSF). Biology 2023, 12, 385.
- McMullen, R.L.; Chen, S.; Moore, D.J. Spectrofluorescence of skin and hair. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2012, 34, 246–256.
- Cicchi, R.; Vogler, N.; Kapsokalyvas, D.; Dietzek, B.; Popp, J.; Pavone, F.S. From molecular structure to tissue architecture: Collagen organization probed by SHG microscopy. J. Biophotonics 2013, 6, 129–142.
- Dunaev, A.V.; Dremin, V.V.; Zherebtsov, E.A.; Rafailov, I.E.; Litvinova, K.S.; Palmer, S.G.; Stewart, N.A.; Sokolovski, S.G.; Rafailov, E.U. Individual variability analysis of fluorescence parameters measured in skin with different levels of nutritive blood flow. Med. Eng. Phys. 2015, 37, 574–583.
- Mayevsky, A.; Rogatsky, G.G. Mitochondrial function in vivo evaluated by NADH fluorescence: From animal models to human studies. Am. J. Physiol. 2007, 292, C615–C640.
- Mayevsky, A.; Barbiro-Michaely, E. Use of NADH fluorescence to determine mitochondrial function in vivo. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1977–1988.
- Balu, M.; Mazhar, A.; Hayakawa, C.K.; Mittal, R.; Krasieva, T.B.; König, K.; Venugopalan, V.; Tromberg, B.J. In vivo multiphoton NADH fluorescence reveals depth-dependent keratinocyte metabolism in human skin. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 258–267.
- Pouli, D.; Balu, M.; Alonzo, C.A.; Liu, Z.; Quinn, K.P.; Rius-Diaz, F.; Harris, R.M.; Kelly, K.M.; Tromberg, B.J.; Georgakoudi, I. Imaging mitochondrial dynamics in human skin reveals depth-dependent hypoxia and malignant potential for diagnosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 367ra169.
- Nilsson, H.; Aalkjaer, C. Vasomotion: Mechanisms and physiological importance. Mol. Interv. 2003, 3, 79–89.
- Kvandal, P.; Landsverk, S.A.; Bernjak, A.; Stefanovska, A.; Kvernmo, H.D.; Kirkebøen, K.A. Low-frequency oscillations of the laser Doppler perfusion signal in human skin. Microvasc. Res. 2006, 72, 120–127.
- Bernjak, A.; Clarkson, P.B.M.; McClintock, P.V.E.; Stefanovska, A. Low-frequency blood flow oscillations in congestive heart failure and after β1-blockade treatment. Microvasc. Res. 2008, 76, 224–232.
- Ticcinelli, V.; Stankovski, T.; McClintock, P.V.E.; Stefanovska, A. Ageing of the couplings between cardiac; respiratory and myogenic activity in humans. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 7366–7369.
- Clough, G.F.; Kuliga, K.Z.; Chipperfield, A.J. Flow motion dynamics of microvascular blood flow and oxygenation: Evidence of adaptive changes in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus/insulin resistance. Microcirculation 2017, 24, e12331.
More
Information
Subjects:
Cardiac & Cardiovascular Systems
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
712
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
15 Mar 2024
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




