Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lingyu Zhang | -- | 2070 | 2024-03-08 06:35:18 | | | |
| 2 | Lindsay Dong | Meta information modification | 2070 | 2024-03-11 02:33:50 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Lian, X.; Zhang, L. Types and Applications of Unconventional Feed. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/56009 (accessed on 11 March 2026).
Lian X, Zhang L. Types and Applications of Unconventional Feed. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/56009. Accessed March 11, 2026.
Lian, Xiao, Lingyu Zhang. "Types and Applications of Unconventional Feed" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/56009 (accessed March 11, 2026).
Lian, X., & Zhang, L. (2024, March 08). Types and Applications of Unconventional Feed. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/56009
Lian, Xiao and Lingyu Zhang. "Types and Applications of Unconventional Feed." Encyclopedia. Web. 08 March, 2024.
Copy Citation
Unconventional feed, which is abundant in China, contains anti-nutritional factors and toxins; however, these can be greatly reduced with microbial fermentation, thus improving the nutrient content of the feed, enhancing animal appetites, and ultimately significantly improving the intestinal health and growth performance of animals. When oxidative stress occurs, fermented feed can effectively reduce the damage caused by stress to the gastrointestinal tract, accelerate the removal of gastrointestinal abnormalities, improve the ability to resist intestinal stress, and ensure the efficient production of animals.
unconventional feed
fermented probiotics
feed quality
1. Introduction
Unconventional feed refers to feed that is different in terms of the raw material source or preparation process compared to conventional feed. This kind of feed is usually obtained from diversified raw materials such as agricultural and sideline products, aquatic product by-products, and industrial by-products, which are obtained through special processing or treatment; China possesses rich resources of such materials [1][2]. However, the nutrient composition of unconventional feed is complex, and it has shortcomings such as a high content of anti-nutritional factors and poisons, poor palatability, unstable nutrient composition, and significant quality variations [3]. Therefore, the comprehensive utilization level of unconventional feed is low, resulting in a waste of resources, environmental pollution, and other problems. At present, unconventional feed processed through microbial fermentation technology, crushing, heating, hydrolysis, drying, and other methods, in order to degrade the anti-nutritional factors, toxins, crude fiber, lignin, and other substances present in it and reflect its high nutritional value [4] in terms of protein, minerals, and trace elements required for livestock supplementation, is called “special feed” or “alternative feed”. Therefore, unconventional feed is often used, in part, to replace conventional feed to reduce feed costs, improve the economic value, and achieve sustainable development in the feed industry. In recent years, the popularity of unconventional feeds has gradually increased.
2. Types and Applications of Unconventional Feed
The sources of unconventional feed are very extensive, including, but not limited to, grain and oil processing by-products, livestock and poultry processing by-products, aquatic product processing by-products, and other industrial processing by-products. Unconventional raw materials are abundant resources, but their application in animal feeding is limited due to their high amounts of anti-nutritional factors and toxins [5][6]. Therefore, improving the quality of unconventional raw materials and elevating their utilization rate in animal feeding are important topics of current scientific feed research. Current commonly used unconventional raw materials such as wheat bran, rice bran, bean dregs, distiller’s grains, sweet potatoes, straw, and other processing by-products require physical processing, chemical treatment, or microbial fermentation to decompose crude fiber and increase their feed value. Anti-nutritional factors and toxins in unconventional fermented feed can be reduced in a number of ways. During fermentation, microorganisms and enzymes that digest anti-nutritional factors such as phytic acid and cellulose are produced [7], while high-temperature treatment helps to destroy the structure of some toxins. In addition, regulating the pH and microbial metabolism during fermentation can also reduce the toxin content in feed [8]. Physical treatments such as filtration and sedimentation can also be used to reduce toxin levels [9]. By combining these methods, unconventional fermented feed can be safely provided to animals while improving their nutrient availability and health. Table 1 shows the positive effects of the fermentation of unconventional feed on animal health, nutrition and performance, and antioxidant aspects.
Table 1. Positive effects of the fermentation of unconventional feed on animal health, nutrition and performance, and antioxidant aspects.
| Unconventional Fermented Feed Feeding | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animal | Raw Materials | Probiotics | Regulated Items | Antioxidant Substance |
References |
| Boer goats | Pennisetum giganteum | Bacillus coagulans preparation | Abundance of Lactobacillus and unidentified Clostridiales ↑ Anaerovibrio and Methanobrevibacter ↓ |
CAT, GSH-Px activities and glutathione ↑ | Qiu et al. [10] |
| Laying hens | Corn–soybean meal wheat bran |
Bacillus subtilis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae | In relative Lactobacillus, Megasphaera, and Peptococcus abundance ↑ Campylobacter abundance ↓ |
Immunoglobulin A, immunoglobulin M, and immunoglobulin G ↑ | Guo et al. [11] |
| Broilers | Corn, soybean meal, corn–gluten meal, and corn dried distillers’ grains | Lactobacillus plantarum, Bacillus subtilis, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Abundance of Ruminococcaceae, Lactobacillaceae, and unclassified Clostridiales ↑ Abundance of Rikenellaceae, Lachnospiraceae, and Bacteroidaceae ↓ |
Acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, and lactic acid ↑ | Zhu et al. [12] |
| Laying hens | Astragalus | Lactobacillus plantarum | CAT, GSH-Px, superoxide dismutase and total antioxidant capacity in serum ↑ | CAT ↑ | Hong et al. [13] |
| Cobb male broilers | Corn–soybean meal | Lactobacillus acidophilus | Body weight, ADG, average daily feed intake, and jejunum and ileum V:C ratio at 14 d and 21 d ↑ | The mRNA expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, interleukin-8, and interleukin-1β in the jejunum ↓ | Wu et al. [14] |
| Nursery pig | Corn–soybean meal | Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus acidilactici | ADG and significantly increased fecal acetate, butyrate, and total short-chain fatty acid concentrations ↑ | Short-chain fatty acid ↑ | Yang et al. [15] |
| Berkshire pigs | Rubus coreanus | Lactobacillus plantarum | The mRNA expression of transcription factors and cytokines in Th1 and Treg cells ↑ The mRNA expression of T helper cell 2 and Th17 transcription factors and cytokines ↓ |
The mRNA expression of transcription factors and cytokines in Th1 and Treg cells ↑ | Yu et al. [16] |
| Cyprinus carpio | Wheat, soybean meal, corn–gluten meal, chicken meal | C. somerae XMX-1, S. cerevisiae GCC−1, L. rhamnosus GCC-3, and B. subtilis HGcc-1 | Health and production ↑ | Liver anti-inflammatory factors transforming growth Factor-β↑ | Zhang et al. [17] |
| Juvenile olive flounder | Garlic husks, Tuna | Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis | Weight gain, specific growth rate, and feed efficiency ↑ | Sucrose reductase↑ | Fatma et al. [18] |
↑ indicates an increase in substance content or enzyme activity; ↓ indicates a decrease in substance content or enzyme activity. CAT, catalase; GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase; ADG, average daily gain; Th1, T helper cell 1; Th17, T helper cell 17.
3. The Effects and Mechanism of Fermentation on the Improvement of Unconventional Feed Quality
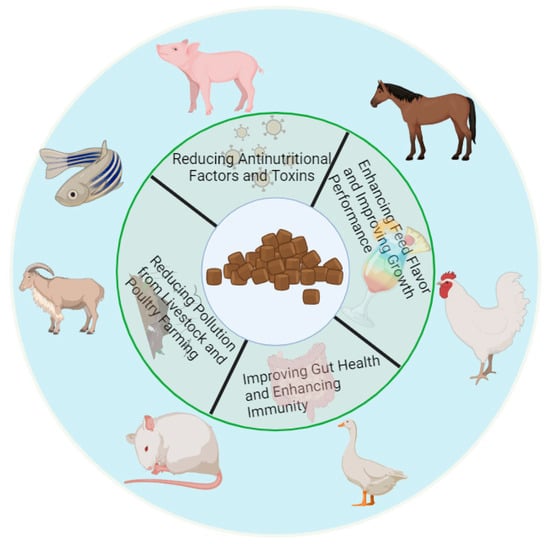
Unconventional feed comes from a wide range of abundantly produced sources. The development and utilization of unconventional raw materials can not only alleviate the problem of food security, but also serve as a way to consolidate the effect of poverty alleviation. As mentioned above, unconventional raw materials have the advantages of low environmental requirements, a wide growth range, rich nutritional value, and high total output. Nowadays, through the use of microbial fermentation technology, anti-nutritional factors and other substances in unconventional raw materials can be degraded to improve the materials’ nutritional value. Figure 1 shows the expected characteristics of unconventional feed after fermentation, which can effectively reduce the amount of anti-nutritional factors and toxins and increase the flavor substances in raw feed. The antioxidant application of unconventional fermented feed in animal production is a key measure. This type of feed protects animal cells from oxidative damage by providing a rich source of antioxidants [19] such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and polyphenolic compounds that effectively inhibit the production of free radicals. In addition, the preparation of unconventional fermented feed may degrade the anti-nutritional factors and toxins in feed, reduce the load of oxidative stress in animals [20], and further reduce the incidence of oxidative damage. These antioxidants are also able to enhance the immune function of animals, making them more resistant and thus reducing the risk of disease. It is worth noting that unconventional feed has stronger antioxidant activity after fermentation treatment [21], which can not only maintain the feed’s nutrient integrity and extend its shelf life, but can also improve its palatability, digestion, and absorption efficiency, ultimately improving the overall health and production performance of animals. Therefore, the antioxidant application of unconventional fermented feed in animal production is of great significance for improving the sustainable development of the aquaculture industry.

Figure 1. Expected characteristics of unconventional feed after fermentation. After fermentation, the anti-nutritional factors and toxins present in unconventional feed are greatly reduced, and the flavor substances of the feed are significantly increased. By eating fermented feed, animals can significantly improve their growth performance, improve their intestinal health, enhance their immunity, and reduce environmental pollution in the process of livestock and poultry breeding.
3.1. Reductions in Anti-Nutritional Factors and Toxins
Unconventional fermented feed uses a variety of effective measures to reduce anti-nutritional factors and toxins. Through microbial action [22], enzyme action [23], and acid base treatment, the microflora and enzymes in the fermentation process can decompose, transform, and reduce the contents of anti-nutritional factors and toxins. At the same time, proper heat treatment [24] and the screening of raw materials can further reduce the presence of these harmful substances. The process of microbial fermentation can effectively decompose anti-nutritional factors and toxins in feed [25], thereby reducing their content, and has the advantages of high treatment efficiency, no reagent residue, safe use, and less nutrient loss, so fermented feed has been widely used in actual livestock and poultry production. Fermentation improves not only the nutritional value, but also the safety of feed, making it more suitable for the digestion and absorption of livestock and poultry. Yeast cell walls can adsorb mycotoxins such as aflatoxin B1, reduce the absorption of mycotoxins by the digestive tract, and protect animals from the toxic effects of mycotoxins [26]. Liu et al. [27] found that microbial fermented feed could further improve the growth performance and immune indexes of offspring mice.
3.2. Increases Feed Flavor and Improves Growth Performance
Fermentation produces a large number of organic acids, small peptides, amino acids, enzymes, and various metabolites that increase the natural flavor of feed, improve the palatability of feed, and promote the appetite of animals [28]. For example, lactic acid, butyric acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, and other organic acids [29] can reduce the pH value of feed and inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms; small peptides and amino acids [30] provide nutrients that help animals grow and develop; and phytase, cellulose, and other enzymes [31] can help to decompose complex polysaccharides and proteins and improve the digestion and absorption rate of feed. Taken together, these effects promote the digestion and absorption of nutrients and improve animal growth performance [32][33]. Yeast produces alcohol and other volatile compounds with a distinctive wine aroma during fermentation. Lactic acid bacteria produce a large amount of lactic acid, which has a sour aroma, during fermentation. Both different types of fermented feed can increase the appetite of animals while also having an increased nutritional value.
3.3. Improves Intestinal Health and Strengthens Immunity
Unconventional fermented feed plays an important role in improving gut health and boosting immunity. First of all, the beneficial microorganisms and metabolites produced by the fermentation process help to maintain the intestinal microecological balance, inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, and reduce the invasion of pathogenic bacteria to the intestine, thereby improving intestinal health [34]. Secondly, the bioactive substances in fermented feed, such as organic acids, enzymes, and peptides, can promote the growth and repair of intestinal mucosal cells, enhance intestinal barrier function, and prevent the penetration of harmful substances [35]. In addition, the bioactive ingredients rich in fermented feed can also regulate the function of the immune system, promote the generation and activity of immune cells, and improve the resistance and immunity of animals [36]. Beneficial microorganisms in fermented feed can improve the structure of the intestinal microbial communities of animals [37][38], promote intestinal health, and improve the digestion and absorption of nutrients. Microbial fermented feed can stimulate the development of immune organs, improve immune function, and increase the weight of immune organs, thereby strengthening the immunity of animals [39][40][41].
3.4. Reduces Pollution from Livestock and Poultry Farming
Unconventional fermented feed plays an important role in reducing pollution from livestock and poultry farming. First of all, the use of unconventional raw materials as the main component of fermented feed can effectively use resources such as agricultural and sideline products and aquatic product by-products, reduce the demand for traditional raw feed materials, and thus reduce resource consumption and environmental pressure in the agricultural production process [11]. Secondly, the microorganisms and enzymes in the fermentation process can degrade organic matter in organic waste, such as straw and manure, which reduces the emission of organic waste and reduces the pollution of livestock and poultry breeding to the environment [42]. In addition, the antioxidants and bioactive components in fermented feed can also improve the digestion and absorption capacity of animals, reduce the emission of nutrients in manure, and further reduce the pollution of water and soil by livestock and poultry farming. Pathogens in feces can pollute the farm environment, including the water and soil, which is harmful to human and animal health [43]. The main pathogen on farms is Enterobacteriaceae, which leads to impaired barrier function and malnutrition by colonizing the intestinal mucosa of pigs [44]. The use of fermented feed in livestock and poultry farming can significantly reduce environmental impacts. This is mainly due to the fact that fermented feed can reduce the discharge of manure, eliminate the foul smell of manure, and reduce the number of mosquitoes and flies, thus effectively reducing environmental pollution.
References
- Liang, J.; Nie, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, S.; Nian, F.; Tang, D. Effects of Jujube Powder on Growth Performance, Blood Biochemical Indices, and Intestinal Microbiota of Broiler. Animals 2023, 13, 3398.
- Ren, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Chen, W.; Zhao, S. Effects of Different Proportions of Amaranthus hypochondriacus Stem and Leaf Powder Inclusions on Growth Performance, Carcass Traits, and Blood Biochemical Parameters of Broilers. Animals 2023, 13, 2818.
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Samak, D.H.; Noreldin, A.E.; Arif, M.; Yaqoob, H.S.; Swelum, A.A. Towards saving freshwater: Halophytes as unconventional feedstuffs in livestock feed: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 14397–14406.
- Sugiharto, S.; Ranjitkar, S. Recent advances in fermented feeds towards improved broiler chicken performance, gastrointestinal tract microecology and immune responses: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 5, 1–10.
- Sun, H.; Kang, X.; Tan, H.; Cai, H.; Chen, D. Progress in Fermented Unconventional Feed Application in Monogastric Animal Production in China. Fermentation 2023, 9, 947.
- Araiza Ponce, K.A.; Gurrola Reyes, J.N.; Martínez Estrada, S.C.; Salas Pacheco, J.M.; Palacios Torres, J.; Murillo Ortiz, M. Fermentation Patterns, Methane Production and Microbial Population under In Vitro Conditions from Two Unconventional Feed Resources Incorporated in Ruminant Diets. Animals 2023, 13, 2940.
- Zhang, X.; Long, J.; Liu, J.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Fermentation Characteristics, Antinutritional Factor Level and Flavor Compounds of Soybean Whey Yogurt. Foods 2024, 13, 330.
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, S.; Shao, T.; Tao, X.; Yuan, X. Effect of Lactic Acid Bacteria on the Fermentation Quality and Mycotoxins Concentrations of Corn Silage Infested with Mycotoxigenic Fungi. Toxins 2021, 13, 699.
- Kulabhusan, P.K.; Campbell, K. Physico-chemical treatments for the removal of cyanotoxins from drinking water: Current challenges and future trends. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170078.
- Qiu, Y.; Zhao, H.; He, X.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, F.; Liu, B.; Liu, Q. Effects of fermented feed of Pennisetum giganteum on growth performance, oxidative stress, immunity and gastrointestinal microflora of Boer goats under thermal stress. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1030262.
- Guo, W.; Xu, L.N.; Guo, X.J.; Wang, W.; Hao, Q.H.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhu, B.C. The impacts of fermented feed on laying performance, egg quality, immune function, intestinal morphology and microbiota of laying hens in the late laying cycle. Animal 2022, 16, 100676.
- Zhu, X.; Tao, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, G. Effects of fermented feed on growth performance, immune organ indices, serum biochemical parameters, cecal odorous compound production, and the microbiota community in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102629.
- Shi, H.T.; Wang, B.Y.; Bian, C.Z.; Han, Y.Q.; Qiao, H.X. Fermented Astragalus in diet improved laying performance, egg quality, antioxidant and immunological status and intestinal microbiota in laying hens. AMB Express 2020, 10, 159.
- Wu, Z.; Yang, K.; Zhang, A.; Chang, W.; Zheng, A.; Chen, Z.; Cai, H.; Liu, G. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus on the growth performance, immune response, and intestinal barrier function of broiler chickens challenged with Escherichia coli O157. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101323.
- Yang, Y.; Yan, G.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus acidilactici co-fermented feed on growth performance and gut microbiota of nursery pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1076906.
- Yu, D.Y.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, G.I.; Kim, J.A.; Moon, Y.S.; Jang, J.C.; Lee, S.S.; Jung, J.H.; Park, J.; et al. Intestinal microbial composition changes induced by Lactobacillus plantarum GBL 16, 17 fermented feed and intestinal immune homeostasis regulation in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2022, 64, 1184–1198.
- Zhang, Q.; Jing, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, D.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Hao, Q.; Wang, M.; Yu, Z.; Li, S.; et al. Partial replacement of pelleted feed by moist fermented feed improved the feed conversion efficiency, liver and intestine health, and gut microbiota structure in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquac. Rep. 2023, 32, 101690.
- Oncul, F.O.; Aya, F.A.; Ali, H.; Seonghun, W.; Geon, L.; Han, K.R.; Bai, S.C. Effects of the dietary fermented tuna by-product meal on growth, blood parameters, nonspecific immune response, and disease resistance in juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2018, 50, 65–77.
- Zou, S.; Sun, C.; Li, F.; Xie, Y.; Liang, T.; Yang, Y.; Shi, B.; Ma, Q.; Shi, Z.; Chai, S.; et al. Effect of Gardenia Pomace Supplementation on Growth Performance, Blood Metabolites, Immune and Antioxidant Indices, and Meat Quality in Xiangcun Pigs. Animals 2022, 12, 2280.
- Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Han, T.; Wang, J. Excessive Substitution of Fish Meal with Fermented Soybean Meal Induces Oxidative Stress by Impairing Glutathione Metabolism in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2096.
- Wu, H.; Barrow, C.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A.R. Phenolic bioaccessibility, antioxidant, and antidiabetic effects of indigenous fermented coffee beans after simulated gastrointestinal digestion and colonic fermentation. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102920.
- Zhou, R.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Lu, L.; Zang, R.; Xu, H. Effects of Tail Vegetable Fermented Feed on the Growth and Rumen Microbiota of Lambs. Animals 2024, 14, 303.
- Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. Effects of tea residues-fermented feed on production performance, egg quality, antioxidant capacity, caecal microbiota, and ammonia emissions of laying hens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1195074.
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, F.; Shi, T.; Xiong, Z.; Gao, R.; Yuan, L. Suanyu fermentation strains screening, process optimization and the effect of thermal processing methods on its flavor. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113296.
- Li, S.; Jin, Z.; Hu, D.; Yang, W.; Yan, Y.; Nie, X.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gai, D.; Ji, Y.; et al. Effect of solid-state fermentation with Lactobacillus casei on the nutritional value, isoflavones, phenolic acids and antioxidant activity of whole soybean flour. LWT 2020, 125, 109264.
- Yiannikouris, A.; Apajalahti, J.; Siikanen, O.; Dillon, G.P.; Moran, C.A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cell Wall-Based Adsorbent Reduces Aflatoxin B1 Absorption in Rats. Toxins 2021, 13, 209.
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Chen, T.; Xi, Q.; Sun, J.; Wei, L.; Zhang, Y. Synergism of fermented feed and ginseng polysaccharide on growth performance, intestinal development, and immunity of Xuefeng black-bone chickens. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 13.
- Olukomaiya, O.O.; Pan, L.; Zhang, D.; Mereddy, R.; Sultanbawa, Y.; Li, X. Performance and ileal amino acid digestibility in broilers fed diets containing solid-state fermented and enzyme-supplemented canola meals. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 275, 114876.
- Adisa, A.M.; Badejo, A.A.; Ifesan, B.O.T.; Enujiugha, V.N. Phenotypic and molecular differentiation of lactic acid bacteria in fonio millet ogi fermentation and their potential as starter cultures. Food Humanit. 2024, 2, 100230.
- Gao, Y.; Hu, M.; Meng, W.; Wen, W.; Zhang, P.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.; Li, S. Study on the quality of soybean proteins fermented by Bacillus subtilis BSNK-5: Insights into nutritional, functional, safety, and flavor properties. Food Chem. 2024, 443, 138523.
- Shangguan, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yao, L.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Dai, J. Improved umami taste of the enzymatic hydrolysate of soybean protein isolate by Corynebacterium glutamicum P-45 fermentation. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103565.
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Xv, J.; Hou, Y.; Wu, X.; Du, E.; Ding, B. Partial Substitution of Fermented Soybean Meal for Soybean Meal Influences the Carcass Traits and Meat Quality of Broiler Chickens. Animals 2020, 10, 225.
- Cheng, Y.H.; Horng, Y.B.; Chen, W.J.; Hua, K.F.; Dybus, A.; Yu, Y.H. Effect of Fermented Products Produced by Bacillus licheniformis on the Growth Performance and Cecal Microbial Community of Broilers under Coccidial Challenge. Animals 2021, 11, 1245.
- Neves, N.; De Dea Lindner, J.; Stockhausen, L.; Delziovo, F.R.; Bender, M.; Serzedello, L.; Cipriani, L.A.; Ha, N.; Skoronski, E.; Gisbert, E.; et al. Fermentation of Plant-Based Feeds with Lactobacillus acidophilus Improves the Survival and Intestinal Health of Juvenile Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Reared in a Biofloc System. Animals 2024, 14, 332.
- Zhang, H.; Liu, M.; Song, F.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Q.; Liu, R. Fermentation enhances the amelioration effect of bee pollen on Caco-2 monolayer epithelial barrier dysfunction based on NF-κB-mediated MLCK-MLC signaling pathway. Food Res. Int. 2024, 178, 113938.
- Mirsalami, S.M.; Mirsalami, M. Impact of solid-state fermentation utilizing Saccharomyces boulardii on the chemical composition and bioactive constituents of rice husk. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 15, 100957.
- Wang, C.; Shi, C.; Su, W.; Jin, M.; Xu, B.; Hao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; et al. Dynamics of the Physicochemical Characteristics, Microbiota, and Metabolic Functions of Soybean Meal and Corn Mixed Substrates during Two-Stage Solid-State Fermentation. mSystems 2020, 5, e00501-19.
- Koo, B.; Kim, J.W.; Nyachoti, C.M. Nutrient and energy digestibility, and microbial metabolites in weaned pigs fed diets containing Lactobacillus–fermented wheat. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 241, 27–37.
- Kulprachakarn, K.; Chaipoot, S.; Phongphisutthinant, R.; Paradee, N.; Prommaban, A.; Ounjaijean, S.; Rerkasem, K.; Parklak, W.; Prakit, K.; Saengsitthisak, B.; et al. Antioxidant Potential and Cytotoxic Effect of Isoflavones Extract from Thai Fermented Soybean (Thua-Nao). Molecules 2021, 26, 7432.
- de Oliveira, N.S.; Ha, N.; da Cunha, L.; Cipriani, L.A.; Neto, A.T.; Skoronski, E.; Gisbert, E.; Perez Fabregat, T.E.H. Fermentation of Soybean Meal with Lactobacillus acidophilus Allows Greater Inclusion of Vegetable Protein in the Diet and Can Reduce Vibrionacea in the Intestine of the South American Catfish (Rhamdia quelen). Animals 2022, 12, 690.
- Wang, W.; Tan, Z.; Gu, L.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, G.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y.; Pang, H. Dynamics Changes of Microorganisms Community and Fermentation Quality in Soybean Meal Prepared with Lactic Acid Bacteria and Artemisia argyi through Fermentation and Aerobic Exposure Processes. Foods 2022, 11, 795.
- Krueger, L.A.; Koester, L.R.; Jones, D.F.; Spangler, D.A. Carbon dioxide equivalent emissions from corn silage fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1092315.
- Delahoy, M.J.; Wodnik, B.; McAliley, L.; Penakalapati, G.; Swarthout, J.; Freeman, M.C.; Levy, K. Pathogens transmitted in animal feces in low- and middle-income countries. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 661–676.
- Mollenkopf, D.F.; Mathys, D.A.; Feicht, S.M.; Stull, J.W.; Bowman, A.S.; Daniels, J.B.; Wittum, T.E. Maintenance of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in a Farrow-to-Finish Swine Production System. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 372–376.
More
Information
Subjects:
Agriculture, Dairy & Animal Science
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
982
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
11 Mar 2024
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No





