
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Razvan Adrian Covache-Busuioc | -- | 3751 | 2023-12-27 11:34:12 | | | |
| 2 | Lindsay Dong | Meta information modification | 3751 | 2023-12-28 02:13:01 | | |
Video Upload Options
Pituitary adenomas is a type of brain tumor with diverse behaviors and complexities. About half of pituitary adenomas are known to secrete specific hormones, most frequently prolactin, growth hormone, or adrenocorticotropic hormone. Despite being histologically benign, these tumors can cause significant endocrine disturbances, leading to considerable morbidity and potentially shortening lifespan. Due to their pathophysiological endocrine secretion and proximity to critical neural and vascular structures, hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas require comprehensive management.
1. Introduction
2. Epigenetics of Pituitary Adenomas
2.1. Introduction to the Role of Epigenetics in Tumor Development—Specific Changes Associated with Pituitary Adenomas
2.2. Potential Therapeutic Avenues Targeting Epigenetic Modifications
3. Transcriptomic Insights into Pituitary Adenomas
3.1. Overview of Transcriptomics and Its Significance in Cancer Biology
3.2. Implications for Targeted Therapy Based on Transcriptomic Data
4. Immunological Aspects of Pituitary Adenomas
4.1. Introduction to the Immune Response in Intracranial Tumors
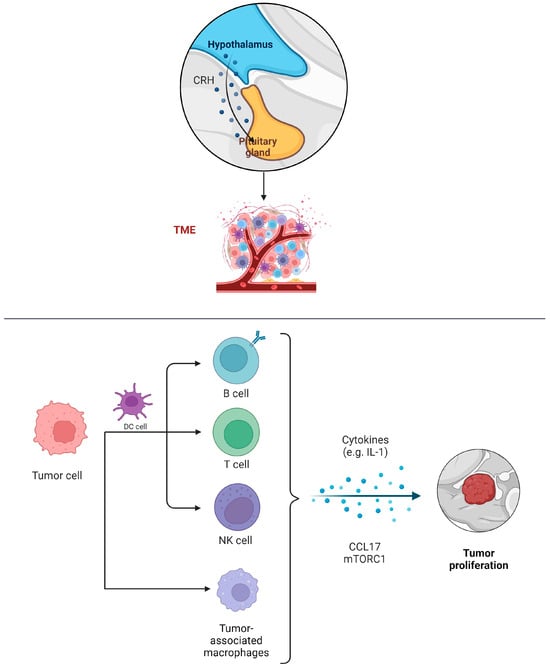
4.2. Opportunities and Challenges for Immunotherapy in Pituitary Adenomas
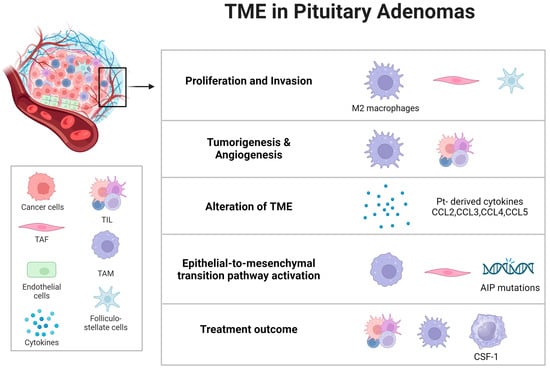
5. The Tumor Microenvironment in Pituitary Adenomas
5.1. Exploring the Microenvironment’s Contribution to Pituitary Adenoma Progression
5.2. Strategies to Target and Modulate the Tumor Microenvironment for Therapeutic Advantage
6. Biomarkers: The Future of Diagnosis and Treatment
6.1. The Importance of Biomarkers in Oncology
6.2. Exploring Potential Biomarkers Specific to Intracranial Tumors and Pituitary Adenomas
6.3. Role of Biomarkers in Early Diagnosis and Targeted Therapies
7. Old and Emerging Targets for Therapy
7.1. Historical Treatment Options: A Static Landscape
7.1.1. Analysis of Traditional Treatments over the Past 20 Years
7.1.2. The Exceptions: Pituitary Adenomas and the Alternative Treatments
7.2. Targeted Therapies
Pituitary adenomas are linked with several related disorders, including prolactinoma, acromegaly, Cushing’s disease, and non-functioning pituitary adenoma. Treatment often requires a combination of surgery, medical therapies (such as dopamine agonists or somatostatin receptor ligands), and radiotherapy, due to their significant impact on patient mortality, morbidity, and quality of life [44][45]. Transsphenoidal surgery is usually the first-line treatment for pituitary tumors, except for prolactinomas. However, the tumor’s local invasiveness may complicate surgical resection, occasionally necessitating initial medical therapy [46].
7.3. Potential Novel Targets
References
- Rutenberg, M.S.; Rotondo, R.L.; Rao, D.; Holtzman, A.L.; Indelicato, D.J.; Huh, S.; Morris, C.G.; Mendenhall, W.M. Clinical outcomes following proton therapy for adult craniopharyngioma: A single-institution cohort study. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 147, 387–395.
- Asa, S.L.; Mete, O.; Perry, A.; Osamura, R.Y. Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Pituitary Tumors. Endocr. Pathol. 2022, 33, 6–26.
- Vergeer, R.A.; Postma, M.R.; Schmidt, I.; Korsten-Meijer, A.G.; Feijen, R.A.; Kruijff, S.; Nagengast, W.B.; van Dijk, J.M.C.; Dunnen, W.F.A.D.; van Beek, A.P.; et al. Detection by fluorescence of pituitary neuroendocrine tumour (PitNET) tissue during endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery using bevacizumab-800CW (DEPARTURE trial): Study protocol for a non-randomised, non-blinded, single centre, feasibility and dose-finding trial. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e049109.
- Guo, X.; Zhang, D.; Pang, H.; Wang, Z.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Lian, W.; Xing, B. Safety of Withholding Perioperative Hydrocortisone for Patients with Pituitary Adenomas with an Intact Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2242221.
- Sharma, S.; Kelly, T.K.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 27–36.
- Liu, A.P.Y.; Gudenas, B.; Lin, T.; Orr, B.A.; Klimo, P.; Kumar, R.; Bouffet, E.; Gururangan, S.; Crawford, J.R.; Kellie, S.J.; et al. Risk-adapted therapy and biological heterogeneity in pineoblastoma: Integrated clinico-pathological analysis from the prospective, multi-center SJMB03 and SJYC07 trials. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 259–271.
- Hauser, B.M.; Lau, A.; Gupta, S.; Bi, W.L.; Dunn, I.F. The Epigenomics of Pituitary Adenoma. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 290.
- Fuks, F.; Burgers, W.A.; Brehm, A.; Hughes-Davies, L.; Kouzarides, T. DNA methyltransferase Dnmt1 associates with histone deacetylase activity. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 88–91.
- LaPierre, M.P.; Godbersen, S.; Esteban, M.T.; Schad, A.N.; Treier, M.; Ghoshdastider, U.; Stoffel, M. MicroRNA-7a2 Regulates Prolactin in Developing Lactotrophs and Prolactinoma Cells. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqaa220.
- Armagan, D.M.; Akdemir, A.S.; Ozkaya, H.M.; Korkmaz, O.P.; Gazioglu, N.; Kadioglu, P.; Tanriover, N.; Dagistanli, K.-F.; Dirican, A.; Ozturk, M. SNPs of miR-23b, miR-107 and HMGA2 and their Relations with the Response to Medical Treatment in Acromegaly Patients. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2021, 129, 593–600.
- Zhao, P.; Cheng, J.; Li, B.; Nie, D.; Li, C.; Gui, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Up-regulation of the expressions of MiR-149-5p and MiR-99a-3p in exosome inhibits the progress of pituitary adenomas. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2021, 37, 633–651.
- Bi, K.; He, M.X.; Bakouny, Z.; Kanodia, A.; Napolitano, S.; Wu, J.; Grimaldi, G.; Braun, D.A.; Cuoco, M.S.; Mayorga, A.; et al. Tumor and immune reprogramming during immunotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 649–661.e5.
- Velten, L.; Story, B.A.; Hernández-Malmierca, P.; Raffel, S.; Leonce, D.R.; Milbank, J.; Paulsen, M.; Demir, A.; Szu-Tu, C.; Frömel, R.; et al. Identification of leukemic and pre-leukemic stem cells by clonal tracking from single-cell transcriptomics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1366.
- Xing, X.; Yang, F.; Huang, Q.; Guo, H.; Li, J.; Qiu, M.; Bai, F.; Wang, J. Decoding the multicellular ecosystem of lung adenocarcinoma manifested as pulmonary subsolid nodules by single-cell RNA sequencing. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd9738.
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. Recharacterizing Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1040–1046.
- Bi, W.L.; Horowitz, P.; Greenwald, N.F.; Abedalthagafi, M.; Agarwalla, P.K.; Gibson, W.J.; Mei, Y.; Schumacher, S.E.; Ben-David, U.; Chevalier, A.; et al. Landscape of genomic alterations in pituitary adenomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1841–1851.
- Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Xie, W.; Guo, J.; Fang, Q.; Zhao, P.; Liu, C.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of pituitary adenomas reveals the impacts of copy number variations on gene expression and clinical prognosis among prolactin-secreting subtype. Aging 2020, 13, 1276–1293.
- Taniguchi-Ponciano, K.; Andonegui-Elguera, S.; Peña-Martínez, E.; Silva-Román, G.; Vela-Patiño, S.; Gomez-Apo, E.; Chavez-Macias, L.; Vargas-Ortega, G.; Espinosa-De-Los-Monteros, L.; Gonzalez-Virla, B.; et al. Transcriptome and methylome analysis reveals three cellular origins of pituitary tumors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19373.
- Oh, J.Y.; Osorio, R.C.; Jung, J.; Carrete, L.; Choudhary, N.; Lad, M.; Saha, A.; Aghi, M.K. Transcriptomic Profiles of Normal Pituitary Cells and Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumor Cells. Cancers 2022, 15, 110.
- Boyle, J.; Patronas, N.J.; Smirniotopoulos, J.; Herscovitch, P.; Dieckman, W.; Millo, C.; Maric, D.; Chatain, G.P.; Hayes, C.P.; Benzo, S.; et al. CRH stimulation improves 18F-FDG-PET detection of pituitary adenomas in Cushing’s disease. Endocrine 2019, 65, 155–165.
- Xiao, D.; Hu, X.; Peng, M.; Deng, J.; Zhou, S.; Xu, S.; Wu, J.; Yang, X. Inhibitory role of proguanil on the growth of bladder cancer via enhancing EGFR degradation and inhibiting its downstream signaling pathway to induce autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 499.
- Gadelha, M.R.; Bronstein, M.D.; Brue, T.; Coculescu, M.; Fleseriu, M.; Guitelman, M.; Pronin, V.; Raverot, G.; Shimon, I.; Lievre, K.K.; et al. Pasireotide versus continued treatment with octreotide or lanreotide in patients with inadequately controlled acromegaly (PAOLA): A randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 875–884.
- Yeung, J.T.; Vesely, M.D.; Miyagishima, D.F. In silico analysis of the immunological landscape of pituitary adenomas. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 147, 595–598.
- Ilie, M.D.; Vasiljevic, A.; Raverot, G.; Bertolino, P. The Microenvironment of Pituitary Tumors—Biological and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2019, 11, 1605.
- Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Gao, L.; Deng, K.; Lian, W.; Bao, X.; Feng, M.; Duan, L.; Zhu, H.; Xing, B. The Immune Profile of Pituitary Adenomas and a Novel Immune Classification for Predicting Immunotherapy Responsiveness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e3207–e3223.
- Zhao, S.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of the Prognostic and Immunological Role of HSPB1 in Pituitary Adenoma: A Potential Target for Therapy. Medicina 2023, 59, 885.
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 582–598.
- Luga, V.; Wrana, J.L. Tumor–Stroma Interaction: Revealing Fibroblast-Secreted Exosomes as Potent Regulators of Wnt-Planar Cell Polarity Signaling in Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6843–6847.
- Paraiso, K.H.T.; Smalley, K.S.M. Fibroblast-mediated drug resistance in cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1033–1041.
- Sapochnik, M.; Fuertes, M.; Arzt, E. Programmed cell senescence: Role of IL-6 in the pituitary. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017, 58, R241–R253.
- Chiloiro, S.; Capoluongo, E.D.; Tartaglione, T.; Giampietro, A.; Bianchi, A.; Giustina, A.; Pontecorvi, A.; De Marinis, L. The Changing Clinical Spectrum of Hypophysitis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 590–602.
- Marques, P.; Barry, S.; Carlsen, E.; Collier, D.; Ronaldson, A.; Awad, S.; Dorward, N.; Grieve, J.; Balkwill, F.; Korbonits, M. MON-460 Pasireotide Treatment Inhibits Cytokine Release from Pituitary Adenoma-Associated Fibroblasts: Is This Mechanism Playing a Key Role in Its Effect? J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3 (Suppl. S1), MON-460.
- Bodaghi, A.; Fattahi, N.; Ramazani, A. Biomarkers: Promising and valuable tools towards diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of COVID-19 and other diseases. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13323.
- Bhatt, A.N.; Mathur, R.; Farooque, A.; Verma, A.; Dwarakanath, B.S. Cancer biomarkers—Current perspectives. Indian J. Med. Res. 2010, 132, 129–149.
- Nixon, A.B.; Schalper, K.A.; Jacobs, I.; Potluri, S.; Wang, I.-M.; Fleener, C. Peripheral immune-based biomarkers in cancer immunotherapy: Can we realize their predictive potential? J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 325.
- Hurvitz, S.A.; Martin, M.; Press, M.F.; Chan, D.; Fernandez-Abad, M.; Petru, E.; Rostorfer, R.; Guarneri, V.; Huang, C.-S.; Barriga, S.; et al. Potent Cell-Cycle Inhibition and Upregulation of Immune Response with Abemaciclib and Anastrozole in neoMONARCH, Phase II Neoadjuvant Study in HR+/HER2− Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 566–580.
- Lamb, L.S.; Sim, H.-W.; McCormack, A.I. Case Report: A Case of Pituitary Carcinoma Treated with Sequential Dual Immunotherapy and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibition Therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 576027.
- Xu, L.; Khaddour, K.; Chen, J.; Rich, K.M.; Perrin, R.J.; Campian, J.L. Pituitary carcinoma: Two case reports and review of literature. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 11, 91–102.
- Pan, Q.; Chegini, N. MicroRNA Signature and Regulatory Functions in the Endometrium during Normal and Disease States. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2008, 26, 479–493.
- Paumier, A.; Le Péchoux, C. Post-operative radiation therapy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 423–432.
- Mondin, A.; Manara, R.; Voltan, G.; Tizianel, I.; Denaro, L.; Ferrari, M.; Barbot, M.; Scaroni, C.; Ceccato, F. Pasireotide-Induced Shrinkage in GH and ACTH Secreting Pituitary Adenoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 935759.
- Sebastian, P.; Balakrishnan, R.; Yadav, B.; John, S. Outcome of radiotherapy for pituitary adenomas. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2016, 21, 466–472.
- Sundlöv, A.; Sjögreen-Gleisner, K.; Tennvall, J.; Dahl, L.; Svensson, J.; Åkesson, A.; Bernhardt, P.; Lindgren, O. Pituitary Function after High-Dose 177Lu-DOTATATE Therapy and Long-Term Follow-Up. Neuroendocrinology 2021, 111, 344–353.
- Melmed, S. Pituitary-Tumor Endocrinopathies. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 937–950.
- Brue, T.; Castinetti, F. The risks of overlooking the diagnosis of secreting pituitary adenomas. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2016, 11, 135.
- Molitch, M.E. Diagnosis and Treatment of Pituitary Adenomas: A. Review. JAMA 2017, 317, 516–524.
- Barbosa, F.R.P.; Silva, C.M.d.S.; Lima, G.A.B.; Warszawski, L.; Domingues, R.C.; Dominic, M.; Fontes, R.; Neto, L.V.; Gadelha, M.R. Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea in patients with prolactinoma before and after treatment with dopamine agonists. Pituitary 2014, 17, 441–449.
- Searle, L.; McDowell, S.; Willink, R.; Krebs, J. A cannulated prolactin series reduces the need for further investigations in women with infertility and lowers the number of false positive screening prolactin measurements. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2021, 61, 949–954.
- Petersenn, S.; Houchard, A.; Sert, C.; Caron, P.J. PRIMARYS Study Group, Predictive factors for responses to primary medical treatment with lanreotide autogel 120 mg in acromegaly: Post hoc analyses from the PRIMARYS study. Pituitary 2020, 23, 171–181.
- Walia, R.; Gupta, R.; Bhansali, A.; Pivonello, R.; Kumar, R.; Singh, H.; Ahuja, C.; Chhabra, R.; Singh, A.; Dhandapani, S.; et al. Molecular Imaging Targeting Corticotropin-releasing Hormone Receptor for Corticotropinoma: A Changing Paradigm. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e1816–e1826.
- Graffeo, C.S.; Carlstrom, L.P.; Cohen, S.C.; Perry, A.; Choby, G.; Van Gompel, J.J. Perioperative Tranexamic Acid for ACTH-Secreting Pituitary Adenomas: Implementation Protocol Results and Trial Prospectus. World Neurosurg. 2021, 153, e359–e364.
- Batista, R.L.; Musolino, N.R.; Cescato, V.A.; da Silva, G.O.; Medeiros, R.S.; Herkenhoff, C.G.; Trarbach, E.B.; Cunha-Neto, M.B. Cabergoline in the Management of Residual Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenoma: A Single-Center, Open-Label, 2-Year Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 42, 221–227.
- Yu, S.; Wang, X.-S.; Cao, K.-C.; Bao, X.-J.; Yu, J. Identification of CDK6 and RHOU in Serum Exosome as Biomarkers for the Invasiveness of Non-functioning Pituitary Adenoma. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2019, 34, 168–176.
- Patel, A.J.; Suki, D.; Hatiboglu, M.A.; Abouassi, H.; Shi, W.; Wildrick, D.M.; Lang, F.F.; Sawaya, R. Factors influencing the risk of local recurrence after resection of a single brain metastasis. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 181–189.
- Patel, A.J.; Suki, D.; Hatiboglu, M.A.; Rao, V.Y.; Fox, B.D.; Sawaya, R. Impact of surgical methodology on the complication rate and functional outcome of patients with a single brain metastasis. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 1132–1143.
- Burman, P.; Casar-Borota, O.; Perez-Rivas, L.G.; Dekkers, O.M. Aggressive Pituitary Tumors and Pituitary Carcinomas: From Pathology to Treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 1585–1601.
- Wang, S.; Lu, J.; You, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, K. The mTOR/AP-1/VEGF signaling pathway regulates vascular endothelial cell growth. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 53269–53276.
- Korman, A.J.; Garrett-Thomson, S.C.; Lonberg, N. The foundations of immune checkpoint blockade and the ipilimumab approval decennial. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 509–528.
- Klein, S.; Persa, O.-D.; Mauch, C.; Noh, K.-W.; Pappesch, R.; Wagener-Ryczek, S.; Buettner, R.; Quaas, A.; Helbig, D. First report on two cases of pleomorphic dermal sarcoma successfully treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. OncoImmunology 2019, 8, e1665977.
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Feng, G.; Hu, S.; Bai, Y. The Impact of NOTCH Pathway Alteration on Tumor Microenvironment and Clinical Survival of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in NSCLC. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 638763.
- Caccese, M.; Barbot, M.; Ceccato, F.; Padovan, M.; Gardiman, M.P.; Fassan, M.; Denaro, L.; Emanuelli, E.; D’avella, D.; Scaroni, C.; et al. Rapid disease progression in patient with mismatch-repair deficiency pituitary ACTH-secreting adenoma treated with checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab. Anticancer Drugs 2020, 31, 199–204.




