Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mohamad Hesam Shahrajabian | -- | 2014 | 2023-09-14 08:27:45 | | | |
| 2 | Wendy Huang | Meta information modification | 2014 | 2023-09-14 13:10:17 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H. Classification of Biostimulants. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/49141 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Sun W, Shahrajabian MH. Classification of Biostimulants. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/49141. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Sun, Wenli, Mohamad Hesam Shahrajabian. "Classification of Biostimulants" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/49141 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Sun, W., & Shahrajabian, M.H. (2023, September 14). Classification of Biostimulants. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/49141
Sun, Wenli and Mohamad Hesam Shahrajabian. "Classification of Biostimulants." Encyclopedia. Web. 14 September, 2023.
Copy Citation
Biostimulants provide beneficial properties to plants by increasing plant metabolism, which promotes crop yield and improves the quality of crops; protecting plants against environmental stresses such as water shortage, soil salinization, and exposure to sub-optimal growth temperatures; and promoting plant growth via higher nutrient uptake. Biostimulants are classified as microbial, such as arbuscular mycorrhizae fungi (AMF), plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), non-pathogenic fungi, protozoa, and nematodes, or non-microbial, such as seaweed extract, phosphite, humic acid, other inorganic salts, chitin and chitosan derivatives, protein hydrolysates and free amino acids, and complex organic materials.
biostimulant
arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
microbial biostimulants
pathogens
plants
abiotic stress tolerance
1. Introduction
Biostimulant application is known as an eco-friendly and novel farming practice and is relevant to two otherwise contrasting concepts, namely crop sustainability and intensification [1]. Biostimulant products already form a significant part of the global farming industry, indicating increasing trends over the years and in the future [2]. There are various reports regarding their positive impacts on crops, especially under biotic and abiotic stress conditions, and significant research is continuously conducted to find and/or produce new biostimulatory products, as well as to show the mechanisms of action behind the observed impacts. However, the variance in the composition of biostimulant products, as well as the lack of ordinary application protocols for the different products, may create inconsistencies between the observed results and complicate attempts to reveal the actual mechanisms behind the biostimulatory impacts, which may include physiological procedures, hormonal regulation, and morphological alterations. Biostimulants’ beneficial activities include the improvement of nutrient uptake, the induction of root growth, and the production of phytohormones; osmotic adjustment through the synthesis of organic osmolytes has also been confirmed. Biostimulants can also be applied to decrease the application of mineral inorganic fertilizer and are considered environmentally friendly tools with no significant negative impacts on fruit quality or total yield. Humic acids, fulvic acid, protein seaweed extracts, hydrolysates, N-containing compounds, botanicals, seaweed extracts, chitosan and other related biopolymers, beneficial bacteria and fungi, and inorganic compounds are the major categories of plant biostimulants. Modern crop production has to cope with abiotic and biotic stressors such as soil and irrigation water salinity, extreme and untimely weather phenomena, water limitations, infections from pathogens, and pests, which severely influence crop performance and the quality of the final products [3][4][5]. The most important advantages of biostimulants include improved profits, stimulated plant reactions, decreased operating costs, reduced application of fertilizers, improved root protection from soil pathogens, and enhanced drought tolerance; moreover, they repel pests, accelerate root establishment, boost fertilization, enhance stress tolerance, ameliorate fertilization, alleviate leaching, detoxify heavy metals and chemicals, and improve stomata opening and plant transpiration [3][4][5][6]. Biostimulatory compounds may also have positive effects on soil biology and are recognized as a good technique for recovering semi-arid areas and degraded ecosystems [6][7][8]. However, the variable composition of raw materials applied for the production of biostimulant products makes the task of revealing the mechanisms of action more difficult, and long-term research and standardization processes are needed [9]. Different sources of chitin and chitosan in nature are crustaceans (lobster, shrimp, king crab), fungi (Mucor rouxii, Penicillium chrysogenum, Aspergillus niger, Lactarius vellereus), insects (ladybug, wax worm, silk worm, butterfly), and mollusks (shell oysters, squid pen). Crustacean shells are the most notable chitin source, and chitin recovery involves three steps consisting of demineralization, deproteination, and the elimination of pigments and lipids [10][11][12]. Microbial proteases such as Lactobacillus sp., Bacillus sp., Pseudomonas sp., Serrati marcescens, etc., are the most significant strains applied in chitin and chitosan production [10].
Biostimulants containing organic substances, humic acids, amino acids, algae extracts, and carbon and boron increased plant growth, yield, and shelf life of onion bulbs [13], and the application of diluted honey extract (DHE) improved photosynthetic parameters, antioxidant activity, biomass production, and yield [14]. The use of seaweed extracts, vermicompost, and a mixture of animal waste increased yield and bulb traits [15]. Foliar application of vermicompost leachate, smoke-water, Ecklonia maxima extracts, and indole-3-butyric acid on seedlings of mustard greens grown in soils from goldmines boosted phytoremediation activities through the accumulation of heavy metals [16]. Foliar application of Kelpak SL and Asahi SL increased the nutritional value and improved the storage life of carrots [17], while root and foliar application of protein hydrolysates in lettuce plants grown under salinity conditions mitigated oxidative stress and increased glucosinolate and osmolyte content [18][19]. In intensive cropping sectors such as horticulture and floriculture, biostimulants can also boost nutrient use efficiency, partly substitute chemical fertilizer inputs, and ameliorate the quality and yield of crops [20][21]. Biostimulants based on microorganisms are a subgroup of the heterogeneous family of biostimulants, related to a microorganism (or mix of microorganisms) that can stimulate biochemical and physiological processes that benefit the nutrient efficiency, nutrient uptake, abiotic stress tolerance, crop quality, and/or yield of plants [22], which can moderately mitigate the damaging effects of intensive agriculture [23][24][25]. The most common microorganisms included in this group of biostimulatory products are the non-pathogenic and non-toxigenic bacteria of Azotobacter spp., Rhizobium spp., and Azospirillum spp., as well as different mycorrhizal fungi [24]. Mycorrhizas are a symbiotic association between fungi and plant roots and are present in several forms according to the fungal taxonomy and the host plant. Two important parameters that influence the distribution of these forms are the climatic and soil conditions and the host plant distribution [26][27] (Hart and Reader, 2002; Yang et al., 2012), and mycorrhiza can significantly boost the efficiency of mineral absorption, falling into two major categories: endotrophic and ectotrophic [28]. The main types of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) are related to the sub-phylum Glomeromycotina of the phylum Mucoromycota [29], and four orders of AMF, namely Glomerales, Paraglomerales, Archaeosporales, and Diversisporales, have been recognized in this sub-phylum, which contains 25 genera [30][31]. The protective mechanisms are credited to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-assisted alleviation of oxidative stress, rapid water uptake and nutrient absorption, and changes in the transcript levels of genes involved in signaling pathways or stress response [32][33][34], and the effectiveness of AMF is usually influenced by environmental variables and soil conditions [35].
2. Biostimulant Categories
Biostimulants are classified into two distinct groups based on their origin; one category includes products that have biological origins in pathogens or plants, and the second group consists of products that do not have biological origins [36][37][38]. Another classification approach divides biostimulant products into microbial biostimulants, which are obtained from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant-growth-promoting bacteria, and non-microbial biostimulants, which include plant micro-algae extracts, humic substances, and biopolymers such as chitosan [39][40][41][42][43]. Different compounds with bioactive properties can be used as biostimulants to boost plant growth and development under normal and stress conditions [44][45][46][47][48][49][50][51][52]. Salicylic acid is economical and quick in action, environmentally sound, and it also links with other elicitors to boost the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites [53][54][55]. Humic acid can increase plant growth, retain water, enrich nutrients, and suppress disease [56][57]. Fulvic acids are used in sustainable horticulture and can change plant primary and secondary metabolism and increase nutrient uptake, root growth, and crop tolerance to environmental stresses [58][59]. Protein hydrolysate biostimulants, mostly produced by chemical and enzymatic hydrolysis of plant- and animal-derived proteins, are based on a mixture of soluble amino acids and peptides and can increase the yield and quality of products as well as improve the nutrient uptake and abiotic stress tolerance of plants [60][61][62][63]. They are largely prepared from brown seaweeds, such as Ecklonia maxima, Ascophyllum nodosum, and Macrocystis pyrifera, and they include promoting hormones or trace elements such as Zn, Fe, Mn, and Cu [64][65]. Humic-like substances such as fulvic and humic acids may also show biostimulatory activity, since several reports have suggested improved crop performance attributed mainly to auxin- and cytokinin-like impacts; they are obtained from organic matter decomposition and metabolic products of soil microbes, and they have roles in plant growth via the improvement of soil physical–chemical properties and the boosted availability of nutrients in the rhizosphere [66][67][68]. The actual mechanisms of action seem to be the result of synergy between the several bioactive components in raw materials, although the impacts may change depending on the crop, soil type, and soil microbes present in the rhizosphere [69][70][71][72]. The most important impacts of chitin and its derivatives’ applications are that they stimulate and protect seed germination, stimulate stress resistance, mitigate negative impacts of abiotic stress, induce plant growth and development, improve soil properties and prevent nutrient leaching, improve the shelf-life of crops, chelate heavy metals, increase crop yield and quality, and protect against pests and pathogens, e.g., bacteria, viruses, fungi, insects, and nematodes [73][74][75]. Amino acids are the best candidates to boost stress tolerance through osmo-protection, ROS scavenging, metal chelation, and nutrient availability [76], which can notably impact the synthesis and stimulation of some enzymes and gene expression [77][78][79]. They can also be applied as signal molecules, like for inducing stomatal closure, as sensors of the nutrient contents of cells, or as regulators for inducing their own catabolism. Amino acids can manage the procedure of protein synthesis, strengthening plant growth, photosynthesis, and yield formation. They can increase nutrient assimilation, use, and translocation, as well as increase the quality of constituents [79]. Amino acids are well-known biostimulants due to their positive effects on yield and plant growth, and can mitigate injuries from abiotic stresses [80][81]. Amino acids also have a significant role in ammonium fixation and C4 metabolism and in the biosynthesis of different components, including isoflavonoids, flavonoids, cutin, aurones, sporopollenin, stilbenes, proanthocyanidins, suberin, lignins, catechins, phenylpropenes, lignans, acylated polyamines, and other different alkaloid derivatives. The largest and most diverse group of secondary metabolites in plants is phenols, which have good antioxidant effects and are involved in the regulation of photosynthesis, physiological activities, oxidation reduction procedures, and plant breathing [82]. Phenolic acids and their derivatives are coumarins, stilbenes, quinones, lignans, flavonoids, curcuminoids, and tannins, which have meaningful roles in plant development, especially in pigment and lignin biosynthesis, and of course, they have a significant role in protecting plants from stress [83].
Protein hydrolysate biostimulants, mostly produced by enzymatic and chemical hydrolysis of plant-derived and animal proteins, are based on a mixture of peptides and soluble amino acids, and can increase the quality and yield of products as well as the uptake and abiotic stress tolerance of plants [84]. Glomus, the largest and most common genus in the phylum Glomeromycota, forms symbiotic relationships with plant roots [85][86], which can boost the drought tolerance of the host plant, mediated by proteins with chaperone-like activity [87]. Trichoderma fungi have important functions in nature as plant growth promoters and antagonists of phytopathogenic fungi [88], and as rhizosphere inhabitants, they contribute to interactions with microorganisms, soil, arthropods, and plants at multiple trophic levels [89], and can be used as biocontrol and biopesticide agents [90]. Members of the genus Trichoderma are also used in different industry branches, like in the production of biofuel, antibiotics, and enzymes [91]. The main Trichoderma–plant interactions include their impacts on plant morphology, plant physiology, nutrient absorption and solubilization, disease resistance, yield improvement, and abiotic stress tolerance [92]. Trichoderma reesei is a genus of filamentous fungi and a superior cellulose source for industrial uses, and it can produce proteins, including different enzymes, cellulases, hemicellulases, and hydrophobins [93][94]. The endophytic fungus Heteroconium chaetospira can also penetrate through the outer epidermal cells of its host, pass into the inner cortex, and grow all over the cortical cells, consisting of those of the root tip region, without causing apparent pathogenic symptoms [95], and it can provide even more nitrogen to the plant than mineralizing plant-available organic nitrogen [96]. Arthrobacter species, which are Gram-positive chemoorganotrophs and obligate aerobes, are commonly identified among soil bacteria [97], being dominant aerobic bacteria under the class of families Micrococcaceae and Actinobacteria [98], and nutritional versatility is the principal feature of arthrobacters [99]. Acinetobacter spp. are Gram-negative coccobacilli that are aerobic, non-motile, and oxidative negative, with no glucose fermentation ability; they can be found in different environments [100] and can fix nitrogen, solubilize minerals, produce siderophores, and act as plant endophytes or epiphytes, which can help hosts in detaching pollutants and tolerating environmental stresses [101]. Moreover, the plant-growth-promoting traits of Actinobacteria entail phosphate solubilization, IAA, and siderophores [102]. They can also promote higher phosphorus content and plant growth and increase radical scavenging, plant phenolic components, and antioxidant activity [103]. Other important bacteria are Enterobacter spp., Pseudomonas spp., Ochrobactrum spp., Bacilus spp., and Rhodococcus spp. [104][105][106][107][108][109][110][111][112][113]. Figure 1 shows different classifications of plant biostimulants.
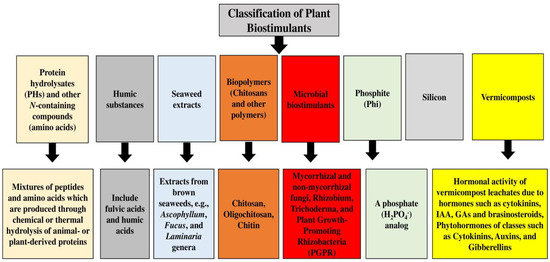
Figure 1. Different classifications of plant biostimulants.
References
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H. Therapeutic potential of phenolic compounds in medicinal plants-natural health products for human health. Molecules 2023, 28, 1845.
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Shahrajabian, N. Developing sustainable agriculture systems in medicinal and aromatic plant production by using chitosan and chitin-based biostimulants. Plants 2023, 12, 2469.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q.; Sun, W. The effects of amino acids, phenols and protein hydrolysates as biostimulants on sustainable crop production and alleviated stress. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2022, 16, 319–328.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Sun, W. Survey of the influences of microbial biostimulants on horticultural crops: Case studies and successful paradigms. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 193.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. Five important seeds in traditional medicine, and pharmacological benefits. Seeds 2023, 2, 290–308.
- Calvo, P.; Nelson, L.; Kloepper, J.W. Agricultural uses of plant biostimulants. Plant Soil 2014, 383, 3–41.
- Karapouloutidou, S.; Gasparatos, D. Effects of biostimulant and organic amendment on soil properties and nutrient status of Lactuca sativa in a Calcareous saline-sodic soil. Agriculture 2019, 9, 164.
- Tejada, M.; Benitez, C.; Gomez, I.; Parrado, J. Use of biostimulants on soil restoration: Effects on soil biochemical properties and microbial community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 49, 11–17.
- Yakhin, O.I.; Lubyanov, A.A.; Yakhin, I.A.; Brown, P.H. Biostimulants in plants science: A global perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2049.
- Philibert, T.; Lee, B.H.; Fabien, N. Current status and new perspectives on chitin and chitosan as functional biopolymers. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 1314–1337.
- Meramo-Hurtado, S.I.; Gonzalez-Delgado, A.D. Application of techno-economic and sensitivity analyses as decision-making tools for assessing emerging large-scale technologies for production of chitosan-based adsorbents. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17601–17610.
- Koleska, I.; Hasanagic, D.; Todorovic, V.; Murtic, S.; Klokic, I.; Paradikovic, N.; Kukavica, B. Biostimulants prevents yield loss and reduces oxidative damage in tomato plants grown on reduced NPK nutrition. J. Plant Interact. 2017, 12, 209–218.
- Shehata, S.A.; AbdelGawad, K.F.; Elmogy, M. Quality and shelf-life of onion bulbs influenced by biostimulants. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2017, 23, 362–371.
- Semida, W.M.; El-Mageed, T.A.A.; Hemida, K.; Rady, M.M. Natural bee-honey based biostimulants confer salt tolerance in onion via modulation of the antioxidant defense system. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 632–642.
- Anbarasi, D.; Haripriya, K. Response of aggregatum onion (Allium cepa L. var. aggregatum Don.) to organic inputs, biofertilizer and biostimulants. Plant Arch. 2020, 20, 759–762.
- Arthur, G.D.; Aremua, A.O.; Kulkarni, M.G.; Okem, A.; Stirk, W.A.; Davies, T.C.; Van Staden, J. Can the use of natural biostimulants be a potential means of phytoremediating contaminated soils from goldmines in South Africa? Int. J. Phytoremediation 2015, 18, 427–434.
- Wszelaczynska, E.; Szczepanek, M.; Poberezny, J.; Kazula, M.J. Effect of biostimulant application and long-term storage on the nutritional value of carrot. Hortic. Bras. 2019, 37, 451–457.
- Halpern, M.; Bar-Tal, A.; Ofek, M.; Minz, D.; Muller, T.; Yermiyahu, U. The use of biostimulants for enhancing nutrient uptake. Adv. Agron. 2015, 130, 141–174.
- Lucini, L.; Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Canaguier, R.; Kumar, P.; Colla, G. The effect of a plant-derived biostimulant on metabolic profiling and crop performance of lettuce grown under saline condition. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 182, 124–133.
- Petropoulos, S.A.; Fernandes, A.; Plexida, S.; Chrysargyris, A.; Tzortzakis, N.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Biostimulants application alleviates water stress effects on yield and chemical composition of greenhouse green bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 181.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Chaski, C.; Polyzos, N.; Tzortzakis, N.; Petropoulos, S.A. Sustainable agriculture systems in vegetable production using chitin and chitosan as plant biostimulants. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 819.
- Joly, P.; Calteau, A.; Wauquier, A.; Dumas, R.; Beuvin, M.; Vallenet, D.; Crovadore, J.; Cochard, B.; Lefort, F.; Berthon, J.-Y. From strain characterization to field authorization: Highlights on Bacillus velezensis strain B2 beneficial properties for plants and its activities on phytopathogenic fungi. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1924.
- Tomas, M.S.J.; Carrasco, M.G.; Lobo, C.B.; Alessandrello, M.J.; Sanchez, L.; Ferrero, M.A. PAH removal simultaneous and sequential inoculation of Pseudomonas monteilii P26 and Gordonia sp. H19 in the presence of biostimulants. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 144, 104752.
- Barros-Rodriguez, A.; Rangseekawe, P.; Lasudee, K.; Pathom-aree, W.; Manzanera, M. Regulatory risks associated with bacteria as biostimulants and biofertilizers in the frame of the European Regulation (EU) 2019/1009. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140239.
- Mickan, B.S.; Alsharmani, A.R.; Solaiman, Z.M.; Leopold, M.; Abbott, L.K. Plant-dependent soil bacterial responses following amendment with a multispecies microbial biostimulant compared to rock mineral and chemical fertilizers. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 550169.
- Hart, M.M.; Reader, R.J. Taxonomic basis for varition in the colonizatio strategy of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. N. Phytol. 2002, 153, 335–344.
- Yang, H.; Zang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, X. Selectivity by host plants affects the distribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal funi: Evidence from ITS rDNA sequence metadata. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 50.
- Cruz, C.; Vishwakarma, K.; Kumar, D.; Varma, A. (Eds.) Soil Nitrogen Ecology; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2021.
- Spatafora, J.W.; Chang, Y.; Benny, G.L.; Lazarus, K.; Smith, M.E.; Berbee, M.L.; Bonito, G.; Corradi, N.; Grigoriev, I.; Gryganskyi, A.; et al. A phylum-level phylogenetic classification of zygomycete fungi based on genome-scale data. Mycologia 2016, 108, 1028–1046.
- Redecker, D.; Schussler, A.; Stockinger, H.; Sturmer, S.L.; Morton, J.B.; Walker, C. An evidence-based consensus for the classification of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomeromycota). Mycorrhiza 2013, 23, 515–531.
- Zhu, B.; Gao, T.; Zhang, D.; Fing, K.; Li, C.; Ma, F. Functions of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in horticultural crops. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 303, 111219.
- Cui, X.; Jia, B.; Diao, F.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.Y.; Guo, W. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the molecular mechanisms of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and nitrilotriacetic acid on Suaeda salsa tolerance to combined stress of cadmium and salt. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 160, 210–220.
- Sales, L.R.; Silva, A.O.; Sales, F.R.; Rodrigues, T.L.; Barbosa, M.V.; Santos, J.V.D.; Kemmelmeier, K.; Siqueira, J.O.; Carneiro, M.A.C. On farm inoculation of native arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improves efficiency in increasing sugarcane productivity in the field. Rhizosphere 2022, 22, 100539.
- Liang, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, G.; Ma, L.; Xue, S. Secondary vegetation succession on the Loess Plateau altered the interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 530, 120744.
- Paymaneh, Z.; Sarcheshmehpour, M.; Mohammadi, H.; Hesni, M.A. Vermicompost and/or compost and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are conducive to improving the growth of pistachio seedlings to drought stress. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 182, 104717.
- Rafiee, H.; Badi, H.N.; Mehrafarin, A.; Qaderi, A.; Zarinpanjeh, N.; Sekara, A.; Zand, E. Application of plant biostimulants as new approach to improve the biological responses of medicinal plants—A critical review. J. Med. Plants. 2016, 15, 6–39.
- Bosi, S.; Negri, L.; Accorsi, M.; Baffoni, L.; Gaggia, F.; Gioia, D.D.; Dinelli, G.; Marotti, I. Biostimulants for sustainable management of sport turfgrass. Plants 2023, 12, 539.
- Vasconsuelo, A.; Boland, R. Molecular aspects of the early stages of elicitation of secondary metabolites in plants. Plant Sci. 2007, 172, 861–875.
- Ahemad, M.; Kibret, M. Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: Current perspective. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1–20.
- Perez-Montano, F.; Alias-Villegas, C.; Bellogin, R.; del Cerro, P.; Espuny, M.; Jimenez-Guerrero, I.; Lopez-Baena, F.; Ollero, F.; Cubo, T. Plant growth promotion in cereal and leguminous agricultural important plants: From microorganism capacities to crop production. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 325–336.
- Lugtenberg, B.; Kamilova, F. Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 63, 541–556.
- De Vries, F.T.; Griffiths, R.I.; Knight, C.G.; Nicolitch, O.; Williams, A. Harnessing rhizosphere microbiomes for drought-resilient crop production. Science 2020, 368, 270–274.
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Toward a sustainable agriculture through plant biostimulants: From experimental data to practical applications. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1461.
- Askari-Khorasgani, O.; Hatterman-Valenti, H.; Pardo, F.B.F.; Pessarakli, M. Plant and symbiont metabolic regulation and biostimulants application improve symbiotic performance and cold acclimation. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 2151–2163.
- Massa, D.; Lenzi, A.; Montoneri, E.; Ginepro, M.; Prisa, D.; Burchi, G. Plant response to biowaste soluble hydrolysates in hibiscus grown under limiting nutrient availability. J. Plant Nutr. 2017, 41, 396–409.
- Kloepper, J.W.; Ryu, C.-M.; Zhang, S. Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 1259–1266.
- Glick, R.B. Bacteria with ACC deaminase can promote plant growth and help to feed the world. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 30–39.
- Ruzzi, M.; Aroca, R. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria act as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 124–134.
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Editorial: Biostimulants in Agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 40.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, C. The importance of flavonoids and phytochemicals of medicinal plants with antiviral activities. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2022, 19, 293–318.
- Nazir, A.; Shafiq, M.; Bareen, F. Fungal biostimulant-driven phytoextraction of heavy metals from tannery solid waste contaminated soil. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2021, 24, 47–58.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. The golden spice for life: Turmeric with the pharmacological benefits of curcuminoids components, including curcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, and demethoxycurcumin. Curr. Org. Synth. 2023, 20, 1–12.
- Ali, B. Salicylic acid: An efficient elicitor of secondary metabolite production in plants. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 101884.
- Eraslan, F.; Inal, A.; Gunes, A.; Alpaslan, M. Impact of exogenous salicylic acid on the growth, antioxidant activity and physiology of carrot plants subjected to combined salinity and boron toxicity. Sci. Hortic. 2007, 113, 120–128.
- Lefevere, H.; Bauters, L.; Gheysen, G. Salicylic acid biosynthesis in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 338.
- Guo, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, S. Humic substances developed during organic waste composting: Formation mechanisms, structural properties, and agronomic functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 501–510.
- Xiang, Y.; Kang, F.; Xiang, Y.; Jiao, Y. Effects of humic acid-modified magnetic Fe3O4/MgAl-layered double hydroxide on the plant growth, soil enzyme activity, and metal availability. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109424.
- Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L.; Aguiar, N.O.; Jones, D.L.; Nebbioso, A.; Mazzeri, P.; Piccolo, A. Humic and fulvic acids as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 15–27.
- Ouni, Y.; Ghnaya, T.; Montemurro, F.; Abdelly, C.; Lakhdar, A. The role of humic substances in mitigating the harmful effects of soil salinity and improve plant productivity. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2014, 8, 353–374.
- Bah, C.S.F.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A.; Carne, A.; McConnell, M.A. Production of bioactive peptide hydrolysates from deer, sheep, and pig plasma using plant and fungal protease preparations. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 54–63.
- Colla, G.; Nardi, S.; Cardarelli, M.; Ertani, A.; Lucini, L.; Canaguier, R.; Rouphael, Y. Protein hydrolysates as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 28–38.
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Lin, M. Research progress of fermented functional foods and protein factory-microbial fermentation technology. Fermentation 2022, 8, 688.
- Battacharyya, D.; Babgohari, M.Z.; Rathor, P.; Prithiviraj, B. Seaweed extracts as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 39–48.
- Gupta, V.; Kumar, M.; Brahmbhatt, H.; Reddy, C.; Seth, A.; Jha, B. Simultaneous determination of different endogenetic plant growth regulators in common green seaweeds using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 49, 1259–1263.
- Sivasankari, S.; Venkatesalu, V.; Anantharaj, M.; Chandrasekaran, M. Effect of seaweed extract on the growth and biochemical constituents of Vigna sinensis. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1745–1751.
- Pizzeghello, D.; Francioso, O.; Ertani, A.; Muscolo, A.; Nardi, S. Isopentenyladenosine and cytokinin-like activity of different humic substances. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 129, 70–75.
- Puglisi, I.; Barone, V.; Sidella, S.; Coppa, M.; Broccanello, C.; Gennari, M.; Baglieri, A. Biostimulant activity of humic-like substances from agro-industrial waste on Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus quadricauda. Eur. J. Phycol. 2018, 53, 433–442.
- Vujinovic, T.; Zanin, L.; Venuti, S.; Contin, M.; Ceccon, P.; Tomasi, N.; Pinton, R.; Cesco, S.; De Nobili, M. Biostimulant action of dissolved humic substances from a conventionally and an organically managed soil on nitrate acquisition in maize plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1652.
- Olaetxea, M.; De Hita, D.; Garcia, C.A.; Fuentes, M.; Baigorri, R.; Mora, V.; Garnica, M.; Urrutia, O.; Erro, J.; Zamarreno, A.M.; et al. Hypothetical framework integrating the main mechanisms involved in the promoting action of rhizospheric humic substances on plant root- and shoot- growth. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 123, 521–537.
- Conselvan, G.B.; Fuentes, D.; Merchant, A.; Peggion, C.; Francioso, O.; Carletti, P. Effects of humic substances and indole-3-acetic acid on Arabidopsis sugar and amino acid metabolic profile. Plant Soil 2018, 426, 17–32.
- Garcia, A.C.; Olaetxea, M.; Santos, L.A.; Mora, V.; Baigorri, R.; Fuentes, M.; Zamarreno, A.M.; Berbara, R.L.; Garcia-Mina, J.M. Involvement of hormone- and ROS- signaling pathways in the beneficial action of humic substances on plants growing under normal and stressing conditions. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 3747501.
- Jindo, K.; Martim, S.A.; Navarro, E.C.; Perez-Alfocea, F.; Hernandez, T.; Garcia, C.; Aguiar, N.O.; Canellas, L.P. Root growth promotion by humic acids from composted and non-composted urban organic wastes. Plant Soil 2012, 353, 209–220.
- Goni, O.; Quille, P.; O’Connell, S. Production of chitosan oligosaccharides for inclusion in a plant biostimulant. Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 88, 881–889.
- Xu, C.; Mou, B. Chitosan as soil amendment affects lettuce growth, photochemical efficiency, and gas exchange. HortTechnology 2018, 28, 476–480.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. Survey on medicinal plants and herbs in traditional Iranian medicine with anti-oxidant, anti-viral, anti-microbial, and anti-inflammation properties. Lett. Drud Des. Discov. 2023, 20, 1707–1743.
- Oosten, M.J.V.; Pepe, O.; Pascale, S.D.; Silletti, S.; Maggio, A. The role of biostimulants and bioeffectors as alleviators of abiotic stress in crop plants. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2017, 4, 5.
- Rai, V.K. Role of amino acids in plant responses to stresses. Biol. Plant. 2002, 45, 481–487.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. Sustainable approaches to boost yield and chemical constituents of aromatic and medicinal plants by application of biostimulants. Recent Adv. Food Nutr. Agric. 2022, 13, 72–92.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. Mechanism of action of collagen and epidermal growth factor: A review on theory and research methods. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2023, 23.
- Popko, M.; Michalak, I.; Wilk, R.; Gramza, M.; Chojnacka, K.; Gorecki, H. Effect of the new plant growth biostimulants based on amino acids on yield and grain quality of winter wheat. Molecules 2018, 23, 470.
- Sadak, S.H.; Abdelhamid, M.T.; Schmidhalter, U. Effect of foliar application of amino acids on plant yield and physiological parameters in bean plants irrigated with seawater. Acta. Biol. Colomb. 2015, 20, 141–152.
- Ozyigit, I.I.; Kahraman, M.V.; Ercan, O. Relation between explants age, total phenol and regeneration response in tissue cultured cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6, 3–8.
- Sharma, A.; Shahzad, B.; Rehman, A.; Bhardwaj, R.; Landi, M.; Zheng, B. Response of phenylpropanoid pathway and the role of polyphenols in plants under abiotic stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 2452.
- Schaafsma, G. Safety of protein hydrolysates, fractions thereof and bioactive peptides in human nutrition. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, 1161–1168.
- Albertsen, A.; Ravnskov, S.; Green, H.; Jensen, D.F.; Larsen, J. Interactions between the external mycelium of the Mycorrhizal fungus, Glomus intraradices and other soil microorganisms as affected by organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1008–1014.
- Scervino, J.M.; Ponce, M.A.; Erra-Bassells, R.; Vierheilig, H.; Ocampo, J.A.; Godeas, A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization of tomato by Gigaspora and Glomus species in the presence of root flavonoids. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 625–633.
- Porcel, R.; Aroca, R.; Cano, C.; Bago, A.; Ruiz-Lozano, J.M. A gene from the Arbuscular mycorrhical fungus Glomus intraradices encoding a binding protein is up-regulated by drought stress in some mycorrhizal plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 60, 251–256.
- Schubert, M.; Mourad, S.; Fink, S.; Schwarze, F.W.M.R. Ecophysiological responses of the biocontrol agent Trichoderma atroviride (T-15603.1) to combined environmental parameters. Biol. Control 2005, 49, 84–90.
- Reiter, B.; Sessitsch, A. Bacterial endophytes of the wildflower Crocus albiflorus analyzed by characterization of isolates and by a cultivation-independent approach. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 140–149.
- Niznansky, L.; Varecka, L.; Kyrstofova, S. Disruption of GABA shunt affects Trichoderma atroviride response to nutritional and environmental stimuli. Acta Chim. Solv. 2016, 9, 109–113.
- Blaszczyk, L.; Siwulski, M.; Sobieralski, K.; Lisiecka, J.; Jedryczka, M. Trichoderma spp.—Application and prospects for use in organic farming and industry. J. Plant. Prot. Res. 2014, 54, 309–317.
- Wuczkowski, M.; Druzhinina, I.; Gherbawy, Y.; Klug, B.; Prillinger, H.; Kubicek, C.P. Species pattern and genetic diversity of trichoderma in a mid-European, primeval floodplain-forest. Microbiol. Res. 2003, 158, 125–133.
- Katenkamp, U.; Jacob, H.-E.; Kerns, G.; Dalchow, E. Hybridization of Trichoderma reesei protoplasts by electrofusion. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1989, 22, 57–67.
- Keshavarz, B.; Khalesi, M. Trichoderma reesi, a superior cellulose source for industrial applications. Biofuels 2016, 7, 713–721.
- Hashiba, T.; Narisawa, K. The development and endophytic nature of the fungus Heteroconium chaetrospira. FEMS. Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 252, 191–196.
- Ohki, T.; Yonezawa, M.; Hashiba, T.; Masuya, H.; Usuki, F.; Narisawa, K.; Narisawa, K. Colonization process of the root endophytic fungus Heteroconium chaetospira in roots of Chinese cabbage. Mycoscience 2002, 43, 191–194.
- Orlandini, V.; Maida, I.; Fondi, M.; Perrin, E.; Papaleo, M.C.; Bosi, E.; Pascale, D.D.; Tutino, M.L.; Michaud, L.; Giudice, A.L.; et al. Genomic analysis of three sponge-associated Arthrobacter antarcitic strains, inhibiting the growth of Burkholderia cepacia complex bacteria by synthesizing volatile organic compounds. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 593–601.
- Mukhia, S.; Khatri, A.; Acharya, V.; Kumar, R. Comparative genomics and molecular adaptational analysis of Arthrobacter from Sikkim Himalaya provided insights into its survivability under multiple high-altitude stress. Genomics 2021, 113, 151–158.
- Cacciari, I.; Lippi, D. Arthrobacters: Successful arid soil bacteria: A review. Arid. Soil. Res. Rehabil. 1987, 1, 1–30.
- Wu, H.-G.; Liu, W.-S.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.-X. Research and analysis of 74 bloodstream infection cases of Acinetobacter baumannii and drug resistance. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 1782–1786.
- Khaksar, G.; Treesubsuntorn, C.; Thiravetyan, P. Impact of endophytic colonization patterns on Zamioculcas amiifolia stress response and in regulating ROS, tryptophan and IAA levels under airbone formaldehyde and formaldehyde-contaminated soil conditions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 1–9.
- Lin, H.-R.; Shu, H.-Y.; Lin, G.-H. Biological roles of indole-3-acetic acid in Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 216, 30–39.
- Joe, M.M.; Devaraj, S.; Benson, A.; Sa, T. Isolation of phosphate solubilizing endophytic bacteria from Phyllanthus amarus schum & thonn: Evaluation of plant growth promotion an antioxidant activity under salt stress. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2016, 3, 71–77.
- Abraham, J.; Silambarasan, S. Biodegradation of carbendazim by Rhodococcus erythropolis and its plant growth-promoting traits. Biol. Environ. 2018, 118, 69–80.
- Hashem, A.; Tabassum, B.; Fathi Abd Allah, E. Bacillus subtilis: A plant-growth promoting rhizobacterium that also impacts biotic stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1291–1297.
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q. Anise (Pimpinella anisum L.), a dominant spice and traditional medicinal herb for both food and medicinal purposes. Cogent Biol. 2019, 5, 1673688.
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q. Natural dietary and medicinal plants with anti-obesity therapeutics activities for treatment and prevention of obesity during lock down and in post-COVID-19 era. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7889.
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q. Fenugreek cultivation with emphasis on historical aspects and its uses in traditional medicine and modern pharmaceutical science. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 724–730.
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q. Nitrogen fixation and diazotrophs—A review. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 26, 2834–2845.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q. Traditional herbal medicine for the prevention and treatment of Cold and Flu in the autumn of 2020, overlapped with COVID-19. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20951431.
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Soleymani, A.; Cheng, Q. Traditional herbal medicines to overcome stress, anxiety and improve mental health in outbreaks of human coronaviruses. Phytother. Res. 2020, 35, 1237–1247.
- Francis, P.B.; Earnest, L.D.; Bryant, K. Maize growth and yield response to a biostimulant amendment. J. Crop Improv. 2016, 6, 632–640.
- Marmitt, D.; Shahrajabian, M.H. Plant species used in Brazil and Asia regions with toxic properties. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 4703–4726.
More
Information
Subjects:
Agriculture, Dairy & Animal Science
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
2.0K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
18 Sep 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




