Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wenshuo Tang | -- | 1825 | 2023-09-12 14:40:09 | | | |
| 2 | Catherine Yang | Meta information modification | 1825 | 2023-09-13 03:00:46 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Tang, W.; Brown, K.; Mitchell, D.; Blanche, J.; Flynn, D. Subsea Power Cable Health Management. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/49078 (accessed on 14 January 2026).
Tang W, Brown K, Mitchell D, Blanche J, Flynn D. Subsea Power Cable Health Management. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/49078. Accessed January 14, 2026.
Tang, Wenshuo, Keith Brown, Daniel Mitchell, Jamie Blanche, David Flynn. "Subsea Power Cable Health Management" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/49078 (accessed January 14, 2026).
Tang, W., Brown, K., Mitchell, D., Blanche, J., & Flynn, D. (2023, September 12). Subsea Power Cable Health Management. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/49078
Tang, Wenshuo, et al. "Subsea Power Cable Health Management." Encyclopedia. Web. 12 September, 2023.
Copy Citation
Subsea power cables are critical assets for electrical transmission and distribution networks, and highly relevant to regional, national, and international energy security and decarbonization given the growth in offshore renewable energy generation. Existing condition monitoring techniques are restricted to highly constrained online monitoring systems that only prioritize internal failure modes, representing only 30% of cable failure mechanisms, and has limited capacity to provide precursor indicators of such failures or damages.
subsea power cable
machine learning
sensing
condition monitoring
1. Introduction
There is a growing trend of increased investment in offshore renewable energy [1]. The United Kingdom presents a well-established and expanding market opportunity with 29 operational offshore wind farms, currently providing a total installed capacity of 5.1 GW. The UK plans involve generating 20–40 GW of power from its offshore wind farms, necessitating an investment of approximately GBP 80–160 billion [2]. These offshore installations heavily depend on crucial infrastructure assets like subsea power cables, responsible for exporting and transmitting power to the mainland. The demand for this vital asset is projected to increase significantly, reaching an estimated total of 24,103 km between 2017 and 2021, driven by the continuous expansion of offshore wind power capacities [3][4].
The sustainability and economic feasibility of offshore wind farms hinge on the reliability of subsea cables for asset owners. Failures in these cables can lead to disruptions in power supply, resulting in substantial revenue losses for utility companies and asset owners. To illustrate, a 300 MW wind farm could face losses of approximately GBP 5.4 million per month in revenue due to a power outage caused by a fault in one of its subsea cables [5].
In 2015, insurance claims related to subsea power cables in the offshore sector amounted to EUR 60 million, as reported by underwriter GCube [6]. The cost for locating and replacing a damaged section of a subsea cable can vary from GBP 0.6 million to GBP 1.2 million [7], while any delay in repair and replacement may cost more than EUR 20,000 per extra hour [8]. Prior to deployment, cable manufacturers undertake rigorous tests to ensure cables meet specific pre-set standards related to the electrical and thermal behaviour of cables and their mechanical strength during operation [9]. However, once cables are deployed underwater, this becomes more difficult to monitor due to the long distance between onshore substations and offshore wind farms and dynamic subsea environment.
2. Subsea Power Cables
There are two widely utilized types of high-voltage subsea cables: high-voltage alternating current (HVAC) cables and high-voltage direct current (HVDC) cables. HVAC cables are known as “three-phase” cables that employ solid insulation materials, such as ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) or crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) [10]. These cables consist of three conductors enclosed by conductor screenings and insulation systems made of EPR or XLPE. The primary purpose of these insulation systems is to prevent partial discharges and overheating [11]. Additionally, binder tapes are used to bind the conductors together, and the entire assembly is protected by a single or double steel armor layer. The steel armor provides stability against tension, compression, and mechanical damage during the installation process and protects the cable from abrasion caused by the seabed and rocks [12].
To protect subsea cables from external threats like fishing equipment or ship anchors that could cause damage, one of the most effective approaches is cable burial. This process can be carried out in suitable seabed conditions [13]. Single-armored cables are typically buried to provide overall protection, especially in areas where external threats can compromise the cable’s integrity [10]. On the other hand, double-armored cables, although heavier and less flexible, offer enhanced protection and are better suited for achieving the desired burial depth. These cables are considered preferable alternatives to single-armored cables in regions with a higher risk of damage due to trawling, heavy ship traffic, and other third-party activities [10].
To further shield the armor layer from corrosion, an exterior layer is added, typically comprising Hessian tape, bituminous compound, and yarn or polypropylene strings. This outer serving layer prevents penetration by seawater, maintaining a dry environment for the inner steel armor.
3. Subsea Power Cable Failures
Subsea cables play a critical role in undersea power transmission, but repairing them is a challenging and costly process. Cable failures can result in power outages, loss of revenue, and can be mainly classified into four categories, internal, early-stage, external, or environmental damage, as well as third-party damage [13]; however, data on cable failures are limited because cable operators are often reluctant to report it.
Internal failures can be caused by overvoltage and overheating, while early-stage failures may result from manufacturing defects, installation stresses, or damage during installation. External failures are often due to environmental conditions, such as corrosion, abrasion, and third-party damage from fishing activities or installation mishaps. Environmental factors like ocean currents, waves, and natural disasters can also contribute to cable damage.
Previous studies [13][14][15] have indicated that the primary causes of subsea cable failures are related to environmental conditions (48%) and third-party damage (27%), as shown in Figure 1. Failures of cable armor and sheath are due to wear-out mechanisms, such as corrosion and abrasion, while third-party-inflicted failures result from random events caused by shipping practices, such as anchoring and trawling. Several reports from Cigré have shown that commercial fishing is also a major cause of offshore cable failures, which is supported by the SSE report [13]. When subsea cables become exposed and float above the burial seabed, fishing activities can endanger cable health.
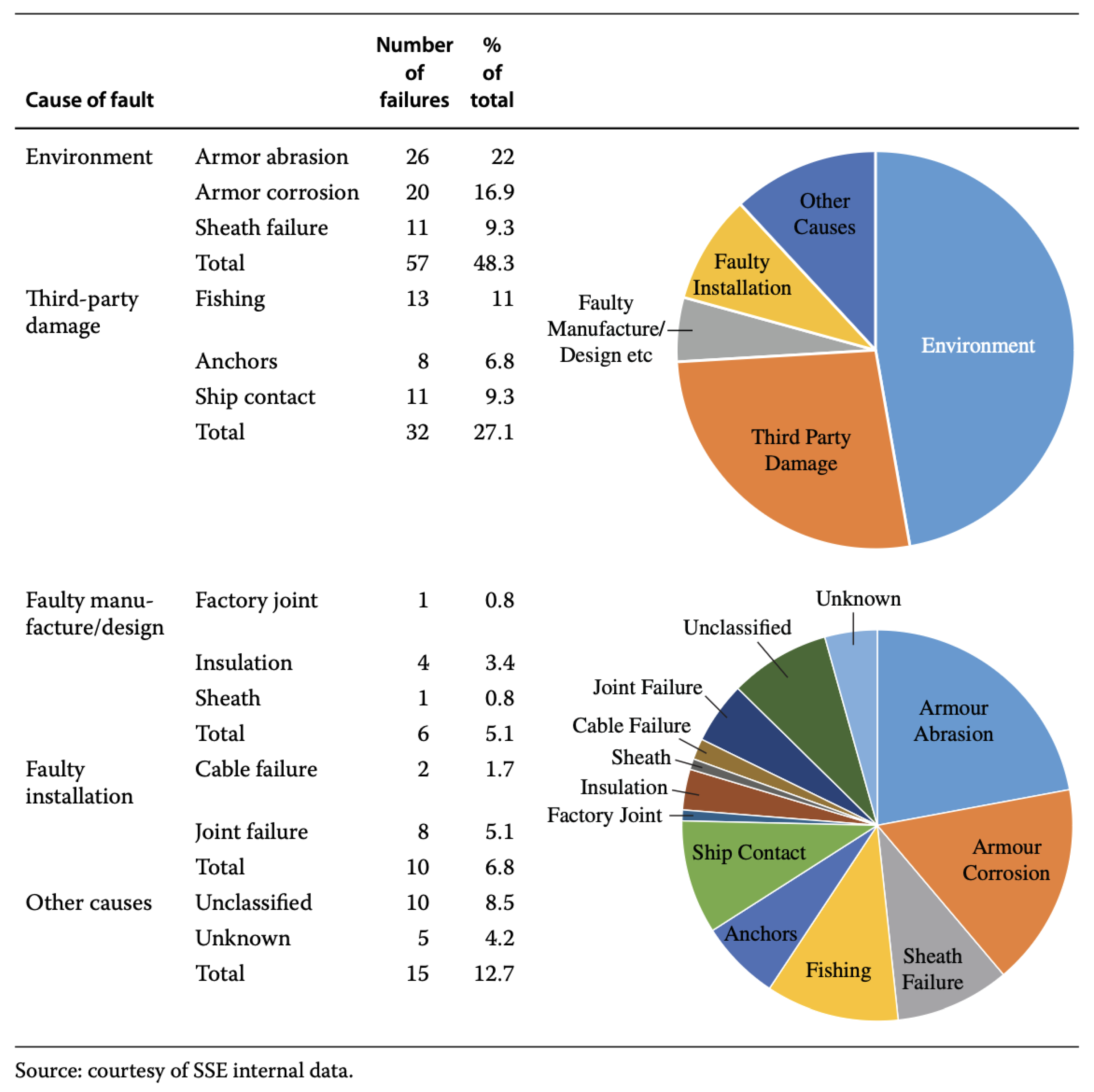
Figure 1. Subsea cable faults over a 15-year period (up to 2006) [16].
4. Subsea Power Cable Standards and Condition Monitoring
To ensure cables meet specific pre-set standards, cable manufacturers conduct rigorous tests that focus on the electrical and thermal behavior of cables, as well as their mechanical strength during operation, as detailed in the IEC standard 60229 [17]. However, these tests, such as the abrasion wear test, which involves subjecting a cable to a mechanical rug test where a steel angle is dragged horizontally along the cable, are not always applicable to cables’ actual operating conditions. For example, these tests may not capture the mechanical strength of cables when subjected to sliding on the seabed due to tidal flows. Therefore, test results may not reflect actual abrasion behavior during cable operation. Once cables are in operation, they become more challenging to monitor due to the long distance between onshore substations and offshore wind farms.
Billions of dollars have been invested in international subsea cable projects recently. However, the monitoring systems currently in use for subsea power cables lack the capability to monitor or predict the RUL concerning significant subsea cable failure mechanisms. Most of these failures result from environmental factors. Traditional condition monitoring technologies for subsea cables are centered around internal failure modes, including partial discharge monitoring and distributed temperature sensing (DTS) monitoring, to detect cable overheating and electrical overload using embedded fibre optics [18][19][20]. However, these methods does not offer precursor indicators to cable failures, and does not monitor operating environment induced failures, such as abrasion and corrosion due to interactions between subsea cable, seabed, and tidal flows.
Recent developments on providing more dynamic condition monitoring capabilities can be found in [21] where embedded optic fibre is shown to be useful for monitoring damage related to tidal flows under experimental conditions, but not verified using operational cable data. In addition, combined with temperature and stress sensors, fibre Bragg sensors (FBG) can also help detect stress and strain along subsea cable as in [22]. Compared to prescribed cable capacity, the robustness level obtained using this hybrid-sensor method can help warn asset operators about potential external failures. However, sensors need to be embedded into subsea power cables pre-installation, thus subject to higher costs for asset owners. In addition, when defects are detected, verification is required through inspections. Current commercial inspection programs that involve expensive and challenging visual inspection with diver and/or ROV supported video footage are subject to requiring good visibility, challenges in locating the cable and inability to identify failure modes at the interface of the seabed.
There exists limited studies on condition monitoring of subsea cables due to abrasion and corrosion. Larsen-Basse et al. [23] use a localized abrasion wear model for a specific section of the cable route but does not include corrosion and scouring. In Wu’s [24], modeling abrasion and corrosion requires cable movement information to be readily available as input data. As discussed earlier, abrasion and corrosion are likely to result from external and environmental factors. In addition, existing methods outlined previously have limited capacity to provide precursor indicators for cable integrity status, and are developed mostly under controlled, static experiment conditions.
Currently, there are limited options available for assessing the RUL of subsea cables through effective monitoring and prediction. While mechanical, chemical, and electrical failures are well-documented, environmental and third-party damages, which are the most common failure modes, have not been fully examined. To achieve effective subsea power cable health management, more dynamic condition monitoring techniques are required, along with advanced sensing technologies to obtain data for damages, such as abrasion and corrosion.
In situ measurements are necessary to predict external cable failure modes due to the sensitivity of degradation rates to local ambient conditions. However, inspection is limited to diver inspection and video footage, which has various limitations, such as requiring good visibility, access to the cable, challenges in locating the cable, and limited data.
5. Low-Frequency Wide-Band Sonar
There has been extensive research into dolphin echolocation, or bio-sonar systems, which allows the animal to detect objects, and evaluate size, shape, and other object characteristics, such as material and thickness [23][25][26][27][28]. In essence, dolphins emit short acoustic pulses, also known as clicks towards objects, and then evaluate the returned echo for object characterisation. Sound scattering from the object creates return echos, which were found to contain information on size and structure of target objects [29]. Gaunaurd et al. [30] showed that echo responses returned by recorded wideband dolphin pulses can be processed to obtain features that identifies radius and thickness, as well as material of a cylindrical beeswax-filled shell. Development of bio-inspired systems include dolphin-based sonar that emits and receives biometric dolphin-like pulses designed by the Bio-sonar Program office at the SPAWAR Systems Center, San Diego, and Applied Research Laboratories, University of Texas (ARL-UT) [31]. The application of bio-inspired wide-band sonar for cable inspection builds upon the research conducted by [32], which focused on underwater target detection and tracking. In their work, they developed a compact bio-inspired sensing system capable of being fitted onto an autonomous underwater vehicle. This system enabled autonomous tracking of underwater cables. The wideband sonar proved to be exceptionally effective in classifying and recognizing mid-water and bottom set targets. Moreover, Ref. [33] conducted a study that demonstrated the use of sonar for object classification. They represented the echo responses from sonar scans of underwater objects in the Time-Frequency Domain (TFD) and input these data into a Convolution Neural Network system for classification. The accuracy of using sonar echo responses for object classification reached an impressive 98.44%. These findings suggest the potential of utilizing bio-sonar in real-time monitoring of subsea cables. Implementing this technology could offer in situ status updates for critical aspects of these cables, such as their integrity and any changes in degradation over time.
References
- European Subsea Cable Association. Submarine Power Cables, Ensuring the Lights Stay On! 2017. Available online: http://www.escaeu.org/articles/submarine-power-cables/ (accessed on 1 January 2017).
- The Crown Estate. Transmission Infrastructure Associated with Connecting Offshore Generation. 2013. Available online: https://knowledge.energyinst.org/search/record?id=87359 (accessed on 4 January 2013).
- Douglas-Westwood. Offshore Wind Driving 2017–2021 Subsea Cable Market Growth. 2013. Available online: http://www.offshorewind.biz/2017/02/24/offshore-wind-driving-2017-2021-subsea-cable-demand/ (accessed on 24 February 2017).
- The Crown Estate. Offshore Wind Operational Report. 2017. Available online: https://www.thecrownestate.co.uk/media/2082/offshore-wind-operational-report-2017.pdf/ (accessed on 1 April 2018).
- Warnock, J.; McMillan, D.; Pilgrim, J.A.; Shenton, S. Review of offshore cable reliability metrics. In Proceedings of the 13th IET International Conference on AC and DC Power Transmission (ACDC 2017), Manchester, UK, 14–16 February 2017; pp. 1–6.
- Clark, D. Down to the Wire: An Insurance Buyer’s Guide to Subsea Cabling Incidents; Technical Report; GCube Renewable Energy Insurance: Newport Beach, CA, USA, 2016.
- Beale, J. Transmission cable protection and stabilisation for the wave and tidal energy industries. In Proceedings of the 9th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference (EWTEC), University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 5–9 September 2011.
- Electrical Review. Reliable Offshore Power Connection. 2015. Available online: https://uk.megger.com/electrical-tester/march-2015/reliable-offshore-power-connections (accessed on 1 March 2015).
- PFOW Enabling Actions Project: Sub-Sea Cable Lifecycle Study; Technical Report; European Marine Energy Centre Ltd. (EMEC): Stromness, UK; The Crown Estate and UK Government: London, UK, 2015.
- Department for Business Enterprise & Regulatory Reform. Review of Cabling Techniques and Environmental Effects Applicable to the Offshore Wind Farm Industry, Technical Report. 2008. Available online: http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/+/http:/www.berr.gov.uk/files/file43527.pdf/ (accessed on 10 January 2008).
- Worzyk, T. Submarine Power Cables: Design, Installation, Repair, Environmental Aspects; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009.
- Ardelean, M.; Minnebo, P. HVDC Submarine Power Cables in the World, Joint Research Centre Technical Reports, European Union. 2015. Available online: http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC97720/ld-na-27527-en-n.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2016).
- Flynn, D.; Bailey, C.; Rajaguru, P.; Tang, W.; Yin, C. PHM of Subsea Cables. In Prognostics and Health Management of Electronics, 1st ed.; Pecht, M., Kang, M., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 451–478.
- Tang, W.; Flynn, D.; Brown, K.; Valentin, R.; Zhao, X. The Application of Machine Learning and Low Frequency Sonar for Subsea Power Cable Integrity Evaluation. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2019 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE, Seattle, WA, USA, 27–31 October 2019; pp. 1–6.
- Tang, W.; Flynn, D.; Brown, K.; Valentin, R.; Zhao, X. The Design of a Fusion Prognostic Model and Health Management System for Subsea Power Cables. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2019 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE, Seattle, WA, USA, 27–31 October 2019; pp. 1–6.
- Dinmohammadi, F.; Flynn, D.; Bailey, C.; Pecht, M.; Yin, C.; Rajaguru, P.; Robu, V. Predicting Damage and Life Expectancy of Subsea Power Cables in Offshore Renewable Energy Applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54658–54669.
- Tests on Cable Oversheaths Which Have a Special Protective Function and Are Applied by Extrusion; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 1982.
- Tang, W.; Flynn, D.; Robu, V. Sensing Technologies and Artificial Intelligence for Subsea Power Cable Asset Management. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management (ICPHM), Detroit, MI, USA, 7–9 June 2021; pp. 1–6.
- Zaeni, A.; Khayam, U.; Viviantoro, D. Methods for Remaining Life Prediction of Power Cable based on Partial Discharge and Cable Failure History Data. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI), Bandung, Indonesia, 9–10 July 2019; pp. 662–665.
- Bao, X.; Dhliwayo, J.; Heron, N.; Webb, D.J.; Jackson, D.A. Experimental and theoretical studies on a distributed temperature sensor based on Brillouin scattering. J. Lightwave Technol. 1995, 13, 1340–1348.
- Masoudi, A.; Pilgrim, J.A.; Newson, T.P.; Brambilla, G. Subsea Cable Condition Monitoring With Distributed Optical Fiber Vibration Sensor. J. Lightwave Technol. 2019, 37, 1352–1358.
- Srikanth, N.; Rao, S.S. Subsea Cable Health Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 2017 Asian Conference on Energy, Power and Transportation Electrification (ACEPT), Singapore, 24–26 October 2017; pp. 1–9.
- Au, W. The Sonar of Dolphins; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004.
- Wu, P. Undersea lightguide cable reliability analyses. In Proceedings of the Annual Proceedings on Reliability and Maintainability Symposium, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 23–25 January 1990; pp. 157–159.
- Leighton, T.; White, P. Dolphin-inspired target detection for sonar and radar. Arch. Acoust. 2014, 39, 319–332.
- Avital, E.; Bholah, N.D.; Giovanelli, G.; Miloh, T. Sound Scattering by an Elastic Spherical Shell and its Cancellation using a Multi-pole Approach. Arch. Acoust. 2017, 42, 697–705.
- Pailhas, Y.; Capus, C.; Brown, K.; Petillot, Y. Chapter 22—BioSonar: A Bio-Mimetic Approach to Sonar Systems Concepts and Applications. In On Biomimetics; Pramatarova, A.L.D., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011.
- Au, W.W.; Simmons, J.A. Echolocation in dolphins and bats. Phys. Today 2007, 60, 40.
- Kaduchak, G.; Marston, P.L. Backscattering of chirped bursts by a thin spherical shell near the coincidence frequency. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 2700–2706.
- Gaunaurd, G.C.; Brill, D.; Huang, H.; Moore, P.W.B.; Strifors, H.C. Signal processing of the echo signatures returned by submerged shells insonified by dolphin “clicks”: Active classification. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 103, 1547–1557.
- Houser, D.; Martin, S.; Phillips, M.; Bauer, E.; Herrin, T.; Moore, P. Signal processing applied to the dolphin-based sonar system. In Proceedings of the Oceans 2003. Celebrating the Past… Teaming Toward the Future (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37492), San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 September 2003; Volume 1, pp. 297–303.
- Capus, C.; Pailhas, Y.; Brown, K.; Lane, D. Detection of buried and partially buried objects using a bio-inspired wideband sonar. In Proceedings of the IEEE Oceans, Sydney, Australia, 24–27 May 2010; pp. 1–6.
- Dmitrieva, M.; Valdenegro-Toro, M.; Brown, K.; Heald, G.; Lane, D. Object classification with convolution neural network based on the time-frequency representation of their echo. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 27th International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), Tokyo, Japan, 25–28 September 2017; pp. 1–6.
More
Information
Subjects:
Engineering, Ocean
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.7K
Entry Collection:
Remote Sensing Data Fusion
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
13 Sep 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




