Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mohammad Fouad Bayan | -- | 2254 | 2023-05-23 12:00:11 | | | |
| 2 | Rita Xu | Meta information modification | 2254 | 2023-05-23 12:04:49 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Kaur, R.; Kaur, K.; Alyami, M.H.; Lang, D.K.; Saini, B.; Bayan, M.F.; Chandrasekaran, B. Metals as Antimicrobials. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/44708 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Kaur R, Kaur K, Alyami MH, Lang DK, Saini B, Bayan MF, et al. Metals as Antimicrobials. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/44708. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Kaur, Rajwinder, Kirandeep Kaur, Mohammad H. Alyami, Damanpreet Kaur Lang, Balraj Saini, Mohammad F. Bayan, Balakumar Chandrasekaran. "Metals as Antimicrobials" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/44708 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Kaur, R., Kaur, K., Alyami, M.H., Lang, D.K., Saini, B., Bayan, M.F., & Chandrasekaran, B. (2023, May 23). Metals as Antimicrobials. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/44708
Kaur, Rajwinder, et al. "Metals as Antimicrobials." Encyclopedia. Web. 23 May, 2023.
Copy Citation
The nature of microorganisms and the efficiency of antimicrobials have witnessed a huge co-dependent change in their dynamics over the last few decades. On the other side, metals and metallic compounds have gained popularity owing to their effectiveness against various microbial strains.
metals
nanoparticles
antimicrobial action
1. Introduction
Several kinds of microorganisms lead to the initiation and further development of microbial infections. Such infections primarily and solely manifest in many pathological conditions with variant degrees of severity. Their pathologies precipitate numerous mild symptoms (fever, fatigue, nausea, headache) to serious symptoms (cyanosis, tissue necrosis, lymphadenopathy, respiratory effects) [1][2]. These have also evolved to be one of the major secondary factors in various diseased conditions, while in some, they ultimately cause death [3][4]. Microbial infections and their manifestations interfere at every step of medical methodologies from concluding misleading and erroneous diagnoses to resulting in deleterious surgeries as well as unsuccessful and incomplete treatments [5]. The severity of the condition worsens when there is any kind of additional or major infection. All of this has made antimicrobials a very important and fundamental part of therapeutics and pharmacology [6][7].
The last century has seen excessive use of antibiotics for various kinds of infections. They work by targeting bacterial cell components and altering necessary processes like DNA replication, cell wall synthesis, etc. [8][9][10]. However, they do have certain drawbacks that make them insufficient and problematic in various ways:
-
Inconsistency in therapeutic security and the number of associated side-effects [15].
Along with these deficiencies, increasing antibiotic resistance has hinted at the clinical need for newer antimicrobials to tackle microbial growth and biofilm production effectively. Continuous mutations, irrational use of antibiotics, and the production of enzymes that inactivate the bacterial cells have contributed to this increasing resistance to the agents [16][17].
Barring antibiotics, metal compounds were largely in use and practice before the 1920s, after which antibiotics took over [18][19][20]. The potential of metals to conveniently restrict biofilm production make them the best possible alternative in present times [21][22]. Antimicrobial properties of metals have been used since ancient times for disinfecting food and water, managing plant diseases in agriculture, and in medical areas as well [23][24]. Certain metals are necessary for cell functioning and cell membrane formation but their presence in excess amounts can be lethal, whereas specific other metals like non-essential groups, such as mercury, silver, etc., are found to be microbicidal even at very low concentrations [25].
2. Metals as Antimicrobials
Metals are abundant in the earth’s crust and ecosphere. The Great Oxidation Event (GOE), which took place 2.3–2.4 billion years ago, exposed bacteria to a wide range of metal ions. The earth’s crust contains a variety of oxidized forms of metal compounds as a result of the atmosphere’s rising oxygen level. Enzymes used metals like copper, iron, and zinc for their redox reactions. Metals are necessary for the process of life but are toxic at high intracellular concentrations, and, thus, cells need a homeostasis mechanism to keep the intracellular concentration constant. Zinc and copper share a similar pathogen-killing mechanism in eukaryotes, where oxidative stress is used to destroy the encapsulated bacterium. Metals like gold, silver, and mercury are extremely poisonous to microorganisms at low concentrations [26].
Metals were once utilized as antibacterial agents, but their industrial usage can harm the ecological system, although they do have a medical use. Infections were treated with arsenic, mercury, silver, copper, zinc, and other elements. Antimony and arsenic are employed as fungicides, rodenticides, insecticides, and to treat protozoal illnesses. While zinc salts can be used to treat diarrhea, copper salts are used to make the Bordeaux and Burgundy mixture, which is used to prevent bacterial and fungal problems in plants and to promote animal growth. Burns can be relieved with silver. Organic mercury compounds are utilized to keep eye drops in good condition. Mercury was utilized as a disinfectant and a syphilis infection treatment. In dental restorations, mercury is combined with copper, silver, and tin [27].
2.1. Metal-Based Nanoparticles as Antimicrobials
Metallic NPs of sizes ranging from 1 nm to 100 nm can be synthesized by two approaches, i.e., top-down and bottom-up. The top-down approach involves beginning with the material in bulk, which is then broken down into the size of a nanoscopic scale via ball milling or attrition etc. It is an easy method to employ, but increased accommodated impurities and non-uniform sizes of particles limit its use [28][29]. On the other hand, the bottom-up nanofabrication approach includes variant techniques such as the colloidal synthesis, the sol-gel method, the chemical vapor decomposition process, and the atomic layer deposition among others. The process, though time consuming and tedious, has the benefit of uniform-sized and uniform-shaped smaller particles bearing the least number of defects and controlled surface properties [29][30][31].
The use of metal-based nanoparticles as components in the creation of antibacterial agents has been made possible by nanotechnologies. Metal-based nanoparticles (NPs) demonstrate an effective role in locating and eliminating bacteria through a variety of mechanisms, including attraction to the surface of the bacteria, disruption of the cell wall and membrane, and induction of a toxic mechanism mediated by an increase in oxidative stress (e.g., the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS)) [32][33][34][35]. The creation of oxidative stress is a valuable and effective antibacterial method to combat MDR bacteria, given the absence of new antimicrobial medicines with unique mechanisms of action. Therefore, it is important to identify and properly characterize whether NPs might cause oxidative stress in these bacteria [36][37][38]. Metal-based NPs physically interact with bacterial cell surfaces, disrupt their membrane, and, ultimately, restrict the formation of biofilms [39]. The formation of biofilms also leads to the development of resistance against antimicrobial agents, so their hindrance ultimately restricts the modulation of resistant mutants, too [40][41][42]. The shape of metal-based NPs along with their ultra-small, compliantly controllable size, and resultant greater surface area to mass ratio all contribute to the prevention of biofilm formation [43][44][45]. The target microorganisms and their mechanisms of action for a few metal-based nanoparticles are provided in Table 1.
Table 1. Antimicrobial activity mechanisms of different metal-based NPs.
| S. No. | Metal-Based Nanoparticles | Microorganism | Mechanism of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Smaller silica nanoparticles | E. coli bacteria | Cell wall rupturing | [46] |
| 2. | AgNPs | K. pneumoniae | Damage to bacterial cell wall Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) generation |
[47] |
| 3. | CuNPs | F. oxysporum | Structural and functional changes in fungi cell, affects DNA and its replication, and protein synthesis | [48] |
| 4. | AuNPs | B. subtilis | Bacterial membrane damage | [49] |
| 5. | Iron nanoparticles | P. aeruginosa, E. coli, S. aureus and B. subtilis | Bacterial cell membrane rupture ultimately led to bacteria death | [50] |
| 6. | Gallium based nanoparticles | P. aeruginosa | ROS-mediated bacterial cell wall damage | [51] |
The targeted drug delivery approach of metal-based NPs can be achieved through either active or passive targeting. Active targeting involves the modification of surfaces of metal-based NPs and processes like magnetic targeting, receptor targeting, and other approaches such as temperature-dependent cell death patterned targeting. Passive targeting, meanwhile, is generally accomplished by improving permeation and enhanced retention at the site of infection [52].
Within a single metal-based NP, multiple drugs can be accommodated to bring an elaborative action. Different drugs that have different kinds of mechanisms will exert a joint action and will subsequently result in higher efficiency. The microbe being either resistant or a multi-drug resistant mutant will probably be successfully affected via one or the other of the variant processes [53][54].
2.2. Mechanisms Involved in Antimicrobial Activity of Metal and Metal-Based NPs
Metal and metal NPs interfere with bacteria’s hemostasis in 3 major ways: disruption of the membrane, oxidative stress, and interaction with proteins and enzymes (Figure 1).
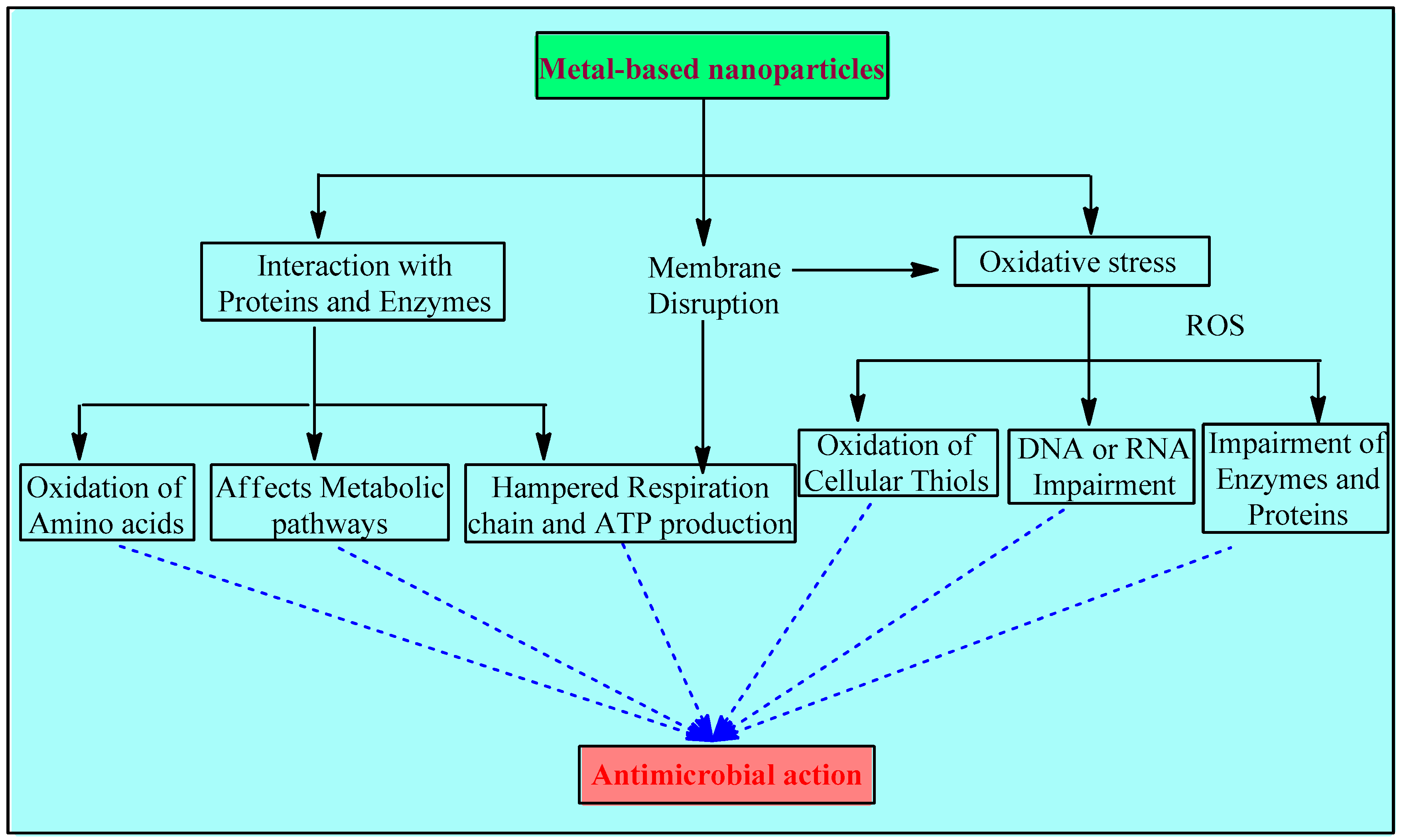
Figure 1. Mechanisms involved in the antimicrobial activity of metals and metal-based NPs.
2.2.1. Disruption of the Membrane
Associating metal nanoparticles with conducting polymers that have positive charges on their surfaces is essential for stabilizing solutions with high nanoparticle concentrations. According to the bacterial eradication mechanism, cell death is caused by electrostatic contact between the negatively charged bacteria (electronegative groups of the polysaccharides in the membrane) and the positively charged compound, such as metal and metal oxide nanoparticles with a variety of forms, roughness, and positive zeta potentials. Positively charged NPs interact with electro-negatively charged bacterial membranes, directly causing bactericidal toxicity in the membrane and targeting cell integrity The surface charge is an important factor for the antibacterial activity of the metal-based NPs. Positively charged NPs are more effective than neutral or negatively charged ones. As reported in [42], NPs with a positive charge display higher toxicity due to their electrostatic interaction with the negative charge of the bacterial cell wall. A comparative study showed that magnetic NPs with a positive charge (NP+) efficiently attracted over 90% of E. coli, while negatively charged magnetic NPs (NP−) did not show any affinities. These results suggest that NPs+ have good potential to capture bacteria via electrostatic attraction. In another study, the antibacterial efficiency of three different AgNPs that were positively, negatively, and neutrally charged were compared, and it was found that positively charged NPs showed the highest bactericidal activity, while the negative ones showed the lowest [55][56][57].
Electron microscopic studies over S. aureus and E. coli also indicate the compromised cytoplasmic membrane’s integrity due to toxic doses of certain metals such as aluminum and silver. A few agents, especially silver, impede the electron transport chain [ETC] [58][59]. Cell wall synthesis is also interrupted due to the interaction between the sulfur-containing constituents of the membrane and the silver nanomaterials. Apart from this, toxic doses of copper and cadmium have also been thought to cause lipid peroxidation [57][60][61].
All such disruptions lead to oxidative stress and, subsequently, to further damage, such as interrupted energy homeostasis, impeded respiration, and, ultimately, cell death [62].
2.2.2. Oxidative Stress
The metal-based NP system provides the benefit of controlling the particle specifications, including its shape, size, and even the charge on the surface, and it also provides the option to manage the release of metal ions [63]. The mode of their action is generally linked with the disruption of the membrane initially and the generation of ROS in large amounts gradually. The driving force of their action is associated with the controlled release of metal ions, while some research suggests that this release is through the leaching of metal complexes with amino acids of bacteria [64]. Metal ions in solution, ROS, and ROS-mediated machinery may all play a role in the toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. The potential of CuO NPs for toxicity may be related to problems with DNA synthesis and repair as well as an increase in the production of reactive oxygen species [65][66]. Higher antimicrobial activity of smaller metallic NPs is reported compared to larger NPs, and this is due to their larger surface area to volume ratio, which increases the production of ROS [67].
The introduction of metal-based NPs initiates intracellular ROS production, which has been confirmed by the electron paramagnetic resonance technique [38]. Such oxidation reactions are catalyzed by numerous metal ions, such as copper, iron, chromium, arsenic, etc., which upregulate genes and also cause other damage [68]. Iron brings in auto-oxidation through aerobic respiration, which leads to the production of oxygen radicals and hydrogen peroxide [69].
Moreover, the consumption of cellular anti-oxidants may also begin during this redox cycling phase of metals. Oxidative imbalance causes oxidation of cellular thiols as well, which, in turn, develops covalent bonds with sulfur. Ultimately, this results in the formation of protein disulfides and the reduction of anti-oxidant sources [67][70][71][72]. Oxidative stress led by ROS impairs the DNA or RNA, attacks enzymes and proteins, and thereby damages macromolecules [73].
2.2.3. Interaction with Proteins and Enzymes
Metallic NPs initiate an antimicrobial response by binding to cytosolic proteins. The interaction of these NPs with enzymes and DNA hampers the whole homeostasis. Since metabolic pathways are affected, the respiratory chain, ATP production, and replication processes are impaired and ultimately inhibited [74][75].
2.3. Bio-Medical Antimicrobial Applications of Metal-Based NPs
Multi-drug resistant organisms are often resistant to commonly used antibiotics. The lack of and the great need for effective antimicrobial agents have led to the development of novel strategies to address this growing public health issue. A growing number of drug-resistant mutants and the inability to cure infective conditions completely has fueled the production of NPs, and this has now found several applications:
Dental products—Microbes tend to settle on teeth, leading to the development of plaque, thereby increasing the chance of mouth infections. NPs not only potently restrict the growth of bacteria but nano-crystallization also improves their performance and inhibits the formation of biofilms as well [76].
Coating of implantable devices—Coating of implantable devices like heart valves prevents adhesion and further growth of bacteria like E. coli, reducing the risk of inflammation and infections [77][78]. Devices that are commonly prone to the colonization of bacteria, such as dental implants, catheters, etc., are generally subjected to NP coatings [53][59].
Wound dressings—Several microbes like Streptococcus, E. coli, and Staphylococcus, among others, can cause wound infections, inflammation, and other complications that can be precipitated. To significantly prevent this, broad-spectrum antimicrobial NPs are an option [79][80].
Other than these, NPs can often be used along with bone cement and also in certain drug delivery systems [81]. It has been stated that researchers are on the verge of the ‘post-antibiotic era’ by the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The prediction of more deaths due to antimicrobial resistance than cancers by 2050 has also been made by many, and all of these predictions and statistics have led to the desire for newer molecule options and drug delivery methods as well as post-numerous research and studies, and the use of metal-based nanoparticles seems to be an effective lead here [82]. Indeed, the latter have been spotted to target resistance and biofilms via different mechanisms and pathways, depending on the metal and its potential.
References
- Azimi, S.; Lewin, G.R.; Whiteley, M. The biogeography of infection revisited. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 579–592.
- El-Radhi, A.S. Fever in Common Infectious Diseases. In Clinical Manual of Fever in Children; El-Radhi, A.S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 85–140.
- Hilton, B.; Wilson, D.J.; O’Connell, A.-M.; Ironmonger, D.; Rudkin, J.K.; Allen, N.; Oliver, I.; Wyllie, D.H. Laboratory diagnosed microbial infection in English UK Biobank participants in comparison to the general population. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 496.
- Frei, A.; Verderosa, A.D.; Elliott, A.G.; Zuegg, J.; Blaskovich, M.A. Metals to combat antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2023, 7, 202–224.
- Taebnia, N.; Römling, U.; Lauschke, V.M. In vitro and ex vivo modeling of enteric bacterial infections. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2158034.
- Patil, S.A.; Nesaragi, A.R.; Rodríguez-Berrios, R.R.; Hampton, S.M.; Bugarin, A.; Patil, S.A. Coumarin Triazoles as Potential Antimicrobial Agents. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 160.
- Abe, T.; Tokuda, Y.; Shiraishi, A.; Fujishima, S.; Mayumi, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Deshpande, G.A.; Shiino, Y.; Hifumi, T.; Otomo, Y. In-hospital mortality associated with the misdiagnosis or unidentified site of infection at admission. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 202.
- Rosas, N.C.; Lithgow, T. Targeting bacterial outer-membrane remodelling to impact antimicrobial drug resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 544–552.
- Kohanski, M.A.; Dwyer, D.J.; Collins, J.J. How antibiotics kill bacteria: From targets to networks. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 423–435.
- Thomas, S.P.; Denizer, E.; Zuffa, S.; Best, B.M.; Bode, L.; Chambers, C.D.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Liu, G.Y.; Momper, J.D.; Nizet, V. Transfer of antibiotics and their metabolites in human milk: Implications for infant health and microbiota. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2022.
- Mmbando, G.S. Recent Advances in Antibiotic-Free Markers; Novel Technologies to Enhance Safe Human Food Production in the World. Mol. Biotechnol. 2022, 1–12.
- Madhav, A.; Will, R.C.; Mutreja, A. The Evolution of Microbial Defence Systems Against Antimicrobial Agents. Antimicrob. Resist. Glob. Chall. Future Interv. 2020, 1–31.
- Gopal, A.; Yan, L.; Kashif, S.; Munshi, T.; Roy, V.A.; Voelcker, N.H.; Chen, X. Biosensors and Point-of-Care Devices for Bacterial Detection: Rapid Diagnostics Informing Antibiotic Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2101546.
- Mendes, A.I.; Rebelo, R.; Aroso, I.; Correlo, V.M.; Fraga, A.G.; Pedrosa, J.; Marques, A.P. Development of an antibiotics delivery system for topical treatment of the neglected tropical disease Buruli ulcer. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 623, 121954.
- Dubey, A.; Ghosh, N.; Saxena, G.K.; Purohit, D.; Patel, S.; Singh, S. Management implications for neurotoxic effects associated with antibiotic use. Neuro-Quantology 2022, 20, 304–328.
- Xu, J.; Xie, S.; Chi, S.; Zhang, S.; Cao, J.; Tan, B. Short-term dietary antibiotics altered the intestinal microbiota and improved the lipid metabolism in hybrid grouper fed medium and high-lipid diets. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737453.
- Mboya, E.A.; Sanga, L.A.; Ngocho, J.S. Irrational use of antibiotics in the Moshi Municipality Northern Tanzania: A cross sectional study. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2018, 31, 165.
- Vala, A.K.; Andhariya, N.; Chudasama, B.K. Silver and gold nanoparticles: Promising candidates as antimicrobial nanomedicines. In Gold and Silver Nanoparticles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 329–354.
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384.
- Seena, S.; Rai, A. Nanoengineering Approaches to Fight Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. In Non-Traditional Approaches to Combat Antimicrobial Drug Resistance; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 221–248.
- Sharma, M.; Bassi, H.; Chauhan, P.; Thakur, P.; Chauhan, A.; Kumar, R.; Kollarigowda, R.H.; Thakur, N.K. Inhibition of the bacterial growth as a consequence of synergism of Ag and ZnO: Calendula officinalis mediated green approach for nanoparticles and impact of altitude. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 136, 109131.
- Marji, S.M.; Bayan, M.F.; Jaradat, A. Facile Fabrication of Methyl Gallate Encapsulated Folate ZIF-L Nanoframeworks as a pH Responsive Drug Delivery System for Anti-Biofilm and Anticancer Therapy. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 242.
- Manzoor, A.; Khan, S.; Dar, A.H.; Pandey, V.K.; Shams, R.; Ahmad, S.; Jeevarathinam, G.; Kumar, M.; Singh, P.; Pandiselvam, R. Recent insights into green antimicrobial packaging towards food safety reinforcement: A review. J. Food Saf. 2023, e13046.
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic use in agriculture and its consequential resistance in environmental sources: Potential public health implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795.
- Subramaniyam, R.; Manickaraj, S.; Anusuyadevi, P.R. Bioinspired Metal Nanoparticles for Microbicidal Activity. Bioinspired Nanomater. Synth. Emerg. Appl. 2021, 111, 36–62.
- Ameen, F.; Alsamhary, K.; Alabdullatif, J.A.; Alnadhari, S. A review on metal-based nanoparticles and their toxicity to beneficial soil bacteria and fungi. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112027.
- Mittapally, S.; Taranum, R.; Parveen, S. Metal ions as antibacterial agents. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2018, 8, 411–419.
- Abid, N.; Khan, A.M.; Shujait, S.; Chaudhary, K.; Ikram, M.; Imran, M.; Haider, J.; Khan, M.; Khan, Q.; Maqbool, M. Synthesis of nanomaterials using various top-down and bottom-up approaches, influencing factors, advantages, and disadvantages: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 300, 102597.
- Arora, N.; Thangavelu, K.; Karanikolos, G.N. Bimetallic Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications. Front Chem 2020, 8, 412.
- Andreo, J.; Ettlinger, R.; Zaremba, O.; Pena, Q.; Lächelt, U.; de Luis, R.F.; Freund, R.; Canossa, S.; Ploetz, E.; Zhu, W. Reticular nanoscience: Bottom-up assembly nanotechnology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 7531–7550.
- Indiarto, R.; Indriana, L.P.A.; Andoyo, R.; Subroto, E.; Nurhadi, B. Bottom–up nanoparticle synthesis: A review of techniques, polyphenol-based core materials, and their properties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 1–24.
- Chellathurai, B.J.; Anburose, R.; Alyami, M.H.; Sellappan, M.; Bayan, M.F.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Chidambaram, K.; Rahamathulla, M. Development of a Polyherbal Topical Gel for the Treatment of Acne. Gels 2023, 9, 163.
- Paesa, M.; de Ganuza, C.R.; Alejo, T.; Yus, C.; Irusta, S.; Arruebo, M.; Sebastian, V.; Mendoza, G. Elucidating the mechanisms of action of antibiotic-like ionic gold and biogenic gold nanoparticles against bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 633, 786–799.
- Ayipo, Y.O.; Osunniran, W.A.; Babamale, H.F.; Ayinde, M.O.; Mordi, M.N. Metalloenzyme mimicry and modulation strategies to conquer antimicrobial resistance: Metal-ligand coordination perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 453, 214317.
- Salazar-Alemán, D.A.; Turner, R.J. Metal Based Antimicrobials: Uses and Challenges. In Microbial Metabolism of Metals and Metalloids; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 77–106.
- Mammari, N.; Lamouroux, E.; Boudier, A.; Duval, R.E. Current Knowledge on the Oxidative-Stress-Mediated Antimicrobial Properties of Metal-Based Nanoparticles. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 437.
- Klębowski, B.; Depciuch, J.; Parlińska-Wojtan, M.; Baran, J. Applications of Noble Metal-Based Nanoparticles in Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4031.
- Abdal Dayem, A.; Hossain, M.K.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, K.; Saha, S.K.; Yang, G.M.; Choi, H.Y.; Cho, S.G. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the Biological Activities of Metallic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 120.
- Ozdal, M.; Gurkok, S. Recent advances in nanoparticles as antibacterial agent. ADMET DMPK 2022, 10, 115–129.
- Abebe, G.M. The role of bacterial biofilm in antibiotic resistance and food contamination. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1705814.
- Rojo-Molinero, E.; Macià, M.D.; Oliver, A. Social behavior of antibiotic resistant mutants within Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm communities. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 570.
- Franco, D.; Calabrese, G.; Guglielmino, S.P.P.; Conoci, S. Metal-Based Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Mechanisms and Biomedical Application. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1778.
- Lv, X.; Wang, L.; Mei, A.; Xu, Y.; Ruan, X.; Wang, W.; Shao, J.; Yang, D.; Dong, X. Recent Nanotechnologies to Overcome the Bacterial Biofilm Matrix Barriers. Small 2023, 19, 2206220.
- Lee, N.-Y.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Nanoparticles in the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant organisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1153.
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931.
- Stauber, R.H.; Siemer, S.; Becker, S.; Ding, G.-B.; Strieth, S.; Knauer, S.K. Small meets smaller: Effects of nanomaterials on microbial biology, pathology, and ecology. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6351–6359.
- Alotaibi, A.M.; Alsaleh, N.B.; Aljasham, A.T.; Tawfik, E.A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Assiri, M.A.; Alkholief, M.; Almutairi, M.M. Silver Nanoparticle-Based Combinations with Antimicrobial Agents against Antimicrobial-Resistant Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1219.
- Mali, S.C.; Dhaka, A.; Githala, C.K.; Trivedi, R. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Celastrus paniculatus Willd. leaf extract and their photocatalytic and antifungal properties. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 27, e00518.
- Sarker, S.R.; Polash, S.A.; Karim, M.N.; Saha, T.; Dekiwadia, C.; Bansal, V.; Sabri, Y.; Kandjani, A.E.; Bhargava, S.K. Functionalized concave cube gold nanoparticles as potent antimicrobial agents against pathogenic bacteria. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 492–503.
- Vitta, Y.; Figueroa, M.; Calderon, M.; Ciangherotti, C. Synthesis of iron nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Eucalyptus robusta Sm and evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 97–103.
- Qu, C.-C.; Liang, Y.-T.; Wang, X.-Q.; Gao, S.; He, Z.-Z.; Sun, X.-Y. Gallium-Based Liquid Metal Materials for Antimicrobial Applications. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 416.
- Varier, K.M.; Gudeppu, M.; Chinnasamy, A.; Thangarajan, S.; Balasubramanian, J.; Li, Y.; Gajendran, B. Nanoparticles: Antimicrobial applications and its prospects. Adv. Nanostruct. Mater. Environ. Remediat. 2019, 25, 321–355.
- Liu, J.-Q.; Li, M.; Yin, S.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Pan, Y.; Peng, Y.; Sun, J.; Kumar, A. Current status and prospects of metal-organic frameworks for bone therapy and bone repair. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 5105–5128.
- Sharma, N.; Jandaik, S.; Kumar, S.; Chitkara, M.; Sandhu, I.S. Synthesis, characterisation and antimicrobial activity of manganese-and iron-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2016, 11, 54–71.
- Maruthapandi, M.; Saravanan, A.; Gupta, A.; Luong, J.H.T.; Gedanken, A. Antimicrobial Activities of Conducting Polymers and Their Composites. Macromol 2022, 2, 78–99.
- Hemeg, H.A. Nanomaterials for alternative antibacterial therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 8211–8225.
- Slavin, Y.N.; Asnis, J.; Häfeli, U.O.; Bach, H. Metal nanoparticles: Understanding the mechanisms behind antibacterial activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 65.
- Abdelghany, T.M.; Al-Rajhi, A.M.; Yahya, R.; Bakri, M.M.; Al Abboud, M.A.; Yahya, R.; Qanash, H.; Bazaid, A.S.; Salem, S.S. Phytofabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles with advanced characterization and its antioxidant, anticancer, and antimicrobial activity against pathogenic microorganisms. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 13, 417–430.
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249.
- Carrapiço, A.; Martins, M.R.; Caldeira, A.T.; Mirão, J.; Dias, L. Biosynthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles Using Microbial Cultures: Mechanisms, Antimicrobial Activity and Applications to Cultural Heritage. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 378.
- Vellingiri, B.; Suriyanarayanan, A.; Selvaraj, P.; Abraham, K.S.; Pasha, M.Y.; Winster, H.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Singaravelu, G.; Reddy, J.K.; Ayyadurai, N. Role of heavy metals (copper (Cu), arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), iron (Fe) and lithium (Li)) induced neurotoxicity. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134625.
- Shabatina, T.I.; Vernaya, O.I.; Melnikov, M.Y. Hybrid Nanosystems of Antibiotics with Metal Nanoparticles—Novel Antibacterial Agents. Molecules 2023, 28, 1603.
- Falfushynska, H.; Sokolova, I.; Stoika, R. Uptake, biodistribution, and mechanisms of toxicity of metal-containing nanoparticles in aquatic invertebrates and vertebrates. In Biomedical Nanomaterials: From Design and Synthesis to Imaging, Application and Environmental Impact; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 227–263.
- Sengul, A.B.; Asmatulu, E. Toxicity of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1659–1683.
- El-Khatib, A.M.; Doma, A.S.; Abo-Zaid, G.A.; Badawi, M.S.; Mohamed, M.M.; Mohamed, A.S. Antibacterial activity of some nanoparticles prepared by double arc discharge method. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2020, 23, 100473.
- Xiong, P.; Huang, X.; Ye, N.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Peng, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Cytotoxicity of Metal-Based Nanoparticles: From Mechanisms and Methods of Evaluation to Pathological Manifestations. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2106049.
- Chopra, H.; Bibi, S.; Singh, I.; Hasan, M.M.; Khan, M.S.; Yousafi, Q.; Baig, A.A.; Rahman, M.; Islam, F.; Emran, T.B.; et al. Green metallic nanoparticles: Biosynthesis to applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 548.
- Mang, C.; Li, G.; Rao, M.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Jiang, T. Transition metal ions-modified birnessite toward highly efficiency photocatalytic formaldehyde oxidation under visible light irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 49739–49751.
- Van Mieghem, T.; Delvaux, F.; Dekleermaeker, S.; Britton, S.J. Top of the Ferrous Wheel–The Influence of Iron Ions on Flavor Deterioration in Beer. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2022, 1–11.
- Baba, S.P.; Bhatnagar, A. Role of thiols in oxidative stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 133–139.
- Ulrich, K.; Jakob, U. The role of thiols in antioxidant systems. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 140, 14–27.
- Metryka, O.; Wasilkowski, D.; Adamczyk-Habrajska, M.; Mrozik, A. Undesirable consequences of the metallic nanoparticles action on the properties and functioning of Escherichia coli, Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus epidermidis membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130728.
- Seixas, A.F.; Quendera, A.P.; Sousa, J.P.; Silva, A.F.; Arraiano, C.M.; Andrade, J.M. Bacterial response to oxidative stress and RNA oxidation. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 821535.
- Busi, S.; Rajkumari, J. Chapter 15—Microbially synthesized nanoparticles as next generation antimicrobials: Scope and applications. In Nanoparticles in Pharmacotherapy; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 485–524.
- Sánchez-López, E.; Gomes, D.; Esteruelas, G.; Bonilla, L.; Lopez-Machado, A.L.; Galindo, R.; Cano, A.; Espina, M.; Ettcheto, M.; Camins, A.; et al. Metal-Based Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agents: An Overview. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 292.
- Zhang, S.; Lin, L.; Huang, X.; Lu, Y.-G.; Zheng, D.-L.; Feng, Y. Antimicrobial properties of metal nanoparticles and their oxide materials and their applications in oral biology. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 2063265.
- Billings, C.; Anderson, D.E. Role of implantable drug delivery devices with dual platform capabilities in the prevention and treatment of bacterial osteomyelitis. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 65.
- Khatoon, Z.; McTiernan, C.D.; Suuronen, E.J.; Mah, T.F.; Alarcon, E.I. Bacterial biofilm formation on implantable devices and approaches to its treatment and prevention. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01067.
- Sharifiaghdam, M.; Shaabani, E.; Asghari, F.; Faridi-Majidi, R. Chitosan coated metallic nanoparticles with stability, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties: Potential for wound healing application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51766.
- Bagheri, M.; Validi, M.; Gholipour, A.; Makvandi, P.; Sharifi, E. Chitosan nanofiber biocomposites for potential wound healing applications: Antioxidant activity with synergic antibacterial effect. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10254.
- Qiu, Y.; Sun, X.; Lin, X.; Yi, W.; Jiang, J. An injectable metal nanoparticle containing cellulose derivative-based hydrogels: Evaluation of antibacterial and in vitro-vivo wound healing activity in children with burn injuries. Int. Wound J. 2022, 19, 666–678.
- Gupta, A.; Mumtaz, S.; Li, C.H.; Hussain, I.; Rotello, V.M. Combatting antibiotic-resistant bacteria using nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 415–427.
More
Information
Subjects:
Medicine, Research & Experimental
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
739
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
23 May 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




