
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kelly Godbout | -- | 4201 | 2023-02-18 00:15:16 | | | |
| 2 | Dean Liu | Meta information modification | 4170 | 2023-02-21 01:46:20 | | | | |
| 3 | Dean Liu | Meta information modification | 4170 | 2023-02-21 01:47:42 | | | | |
| 4 | Dean Liu | Meta information modification | 4170 | 2023-02-21 01:49:56 | | |
Video Upload Options
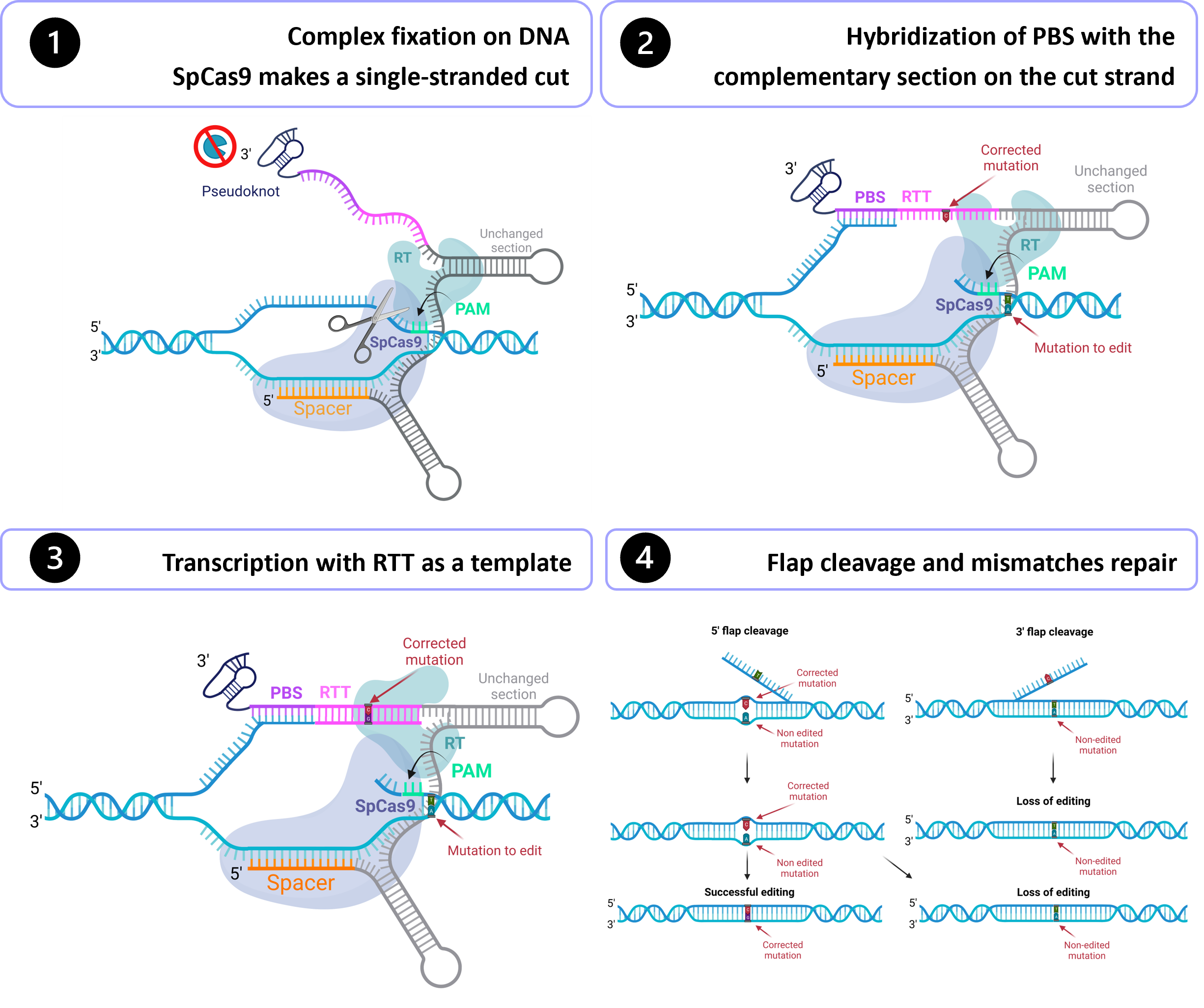
Gene therapy holds tremendous potential in the treatment of inherited diseases. Unlike traditional medicines, which only treat the symptoms, gene therapy has the potential to cure the disease by addressing the root of the problem: genetic mutations. The discovery of CRISPR/Cas9 in 2012 paved the way for the development of those therapies. Improvement of this system led to the recent development of an outstanding technology called prime editing. This system can introduce targeted insertions, deletions, and all 12 possible base-to-base conversions in the human genome. Since the first publication on prime editing in 2019, groups all around the world have worked on this promising technology to develop a treatment for genetic diseases. Liver diseases are currently the most studied field for human gene therapy by prime editing. To date, prime editing has been attempted in preclinical studies for tyrosinemia type 1, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, phenylketonuria, DGAT1-deficiency, bile salt export pump deficiency, liver cancer, and for a liver disease caused by a mutation in the DNMT1 gene.
1. Introduction
| CRISPR/Cas9 | Base Editing | Prime Editing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Off-target effects |
Significant off-target effects | Little or no off-target effects | Little or no off-target effects |
|
|
|
|
| Flexibility |
|
|
|
| Programmability 1 | Only if a DNA donor template is given | Yes | Yes |
| Efficient in vivo delivery |
Currently possible | Currently possible (but more difficult than CRISPR/Cas9 because of its larger size) |
Need to be improved (too big for conventional vehicles) |
2. Application of Prime Editing to Liver Hereditary Diseases
| Disease | Gene | Mutation | Goal 1 | Prime Editor |
% of Editing |
Cells or Animal Models | Length (nt) | Edit Position from the Nick |
Delivery Method | Prime Editor Form | Comments | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spacer | PBS | RTT | |||||||||||||
| Liver cancer | CTNNB1 | 6 nt deletion | I | PE3 | 30 | Liver organoid | 20 | 12 | 17 | +1 | Electroporation | Plasmid | Schene 2020 [24] | ||
| Bile salt export pump deficiency | ABCB11 | D482G | A > G | 20 | 20 | +7 | The PAM is also mutated (+5 G > A silent mutation) | ||||||||
| DGAT1-deficiency | DGAT1 | S210del | Del CCT |
C | 21 | Patient-derived intestinal cells | 20 | ||||||||
| Bile salt export pump deficiency | ABCB11 | R1153H | G > A | 0 | Patient-derived liver organoids | ||||||||||
| Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency | SERPINA1 | E342K | G > A | I | PE2 | 1.9 | HEK293T cells | 20 | 13 | 27 | Lipo 2000 | Plasmid | Liu 2021 [25] | ||
| PE3 | 9.9 | ||||||||||||||
| PE2* | 6.4 | ||||||||||||||
| PE3* | 15.8 | ||||||||||||||
| C | PE2 | 2.1 | PiZ mice | Hydrodynamic TVI | |||||||||||
| PE2* | 6.7 | ||||||||||||||
| PE3 | 3.1 | AAV8 | |||||||||||||
| PE3 | 0.83 | hPSCs | 20 | 9 | 13 | +3 | Electroporation | Plasmid | Habib 2022 [26] | ||||||
| PE2-NGA | 2.0–3.0 | HEK293T cells | 20 | 13 | 20 | Lipo 2000 | Plasmid | Lung 2021 [27] | |||||||
| PE3-NGA | 3.0–5.0 | ||||||||||||||
| PE2-NGA | 1.99 | Human primary fibroblasts | |||||||||||||
| Liver disease | dnmt1 | G > C | I | Intein-split PE2∆RnH | 15 | C57BL/6J pups | 21 | AAV8 | Plasmid | Böck 2022 [28] | |||||
| PE2∆RnH | 35.9 | C57BL/6J adult mice | AdV | ||||||||||||
| 58.2 | C57BL/6J pups | ||||||||||||||
| Phenylketonuria | Pahenu2 | F263S | T > C | C | Intein-split PE2∆RnH | <1% | Pahenu2 mice | 20 | 13 | 19 | AAV8 | Plasmid | |||
| PE2∆RnH | 2.0 | Adult Pahenu2 mice | AdV | ||||||||||||
| 6.9 | Neonates Pahenu2 mice | ||||||||||||||
| PE3∆RnH | 11.1 | ||||||||||||||
| PE3 | 19.6 | HEK293T cells | 16 | Lipo 2000 | |||||||||||
| PE3 | 19.7 | 19 | |||||||||||||
| Tyrosinemia type 1 | fah | C | PEDAR | 0.76 | FahΔExon5 mice | Hydrodynamic injection | Plasmid | Jiang 2022 [29] | |||||||
| G > A | PE3 | 2.3 | HT1-mCdHs | 20 | 11 | 15 | Electroporation | Plasmid | sgRNA of PE3 nick in position -4 | Kim 2021 [30] | |||||
| 34.3 | HT1 mice | Transplantation | |||||||||||||
| c.706G > A | PE3 | 61 | Fahmut/mut mice | 20 | +10 | Hydrodynamic TVI | Plasmid | Jang 2022 [31] | |||||||
| PE2 | 33 | ||||||||||||||
| FAH | 18.7 | HEK293T cells | Lentiviral vector | ||||||||||||
References
- Sherkow, J.S.; Zettler, P.J.; Greely, H.T. Is it “gene therapy”? J. Law Biosci. 2018, 5, 786–793.
- September 14, 1990: The Beginning. Hum. Gene Ther. 1990, 1, 371–372.
- Tamura, R.; Toda, M. Historic Overview of Genetic Engineering Technologies for Human Gene Therapy. Neurol. Med.-Chir. 2020, 60, 483–491.
- Urnov, F.D.; Rebar, E.J.; Holmes, M.C.; Zhang, H.S.; Gregory, P.D. Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 636–646.
- Sun, N.; Zhao, H. Transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs): A highly efficient and versatile tool for genome editing. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 1811–1821.
- Sander, J.D.; Joung, J.K. CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 347–355.
- Zhang, F.; Wen, Y.; Guo, X. CRISPR/Cas9 for genome editing: Progress, implications and challenges. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, R40–R46.
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A Programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821.
- Wu, X.; Kriz, A.J.; Sharp, P.A. Target specificity of the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Quant. Biol. 2014, 2, 59–70.
- Miyaoka, Y.; Berman, J.R.; Cooper, S.B.; Mayerl, S.J.; Chan, A.H.; Zhang, B.; Karlin-Neumann, G.A.; Conklin, B.R. Systematic quantification of HDR and NHEJ reveals effects of locus, nuclease, and cell type on genome-editing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23549.
- Sfeir, A.; Symington, L.S. Microhomology-Mediated End Joining: A Back-up Survival Mechanism or Dedicated Pathway? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 701–714.
- Sakuma, T.; Nakade, S.; Sakane, Y.; Suzuki, K.-I.T.; Yamamoto, T. MMEJ-assisted gene knock-in using TALENs and CRISPR-Cas9 with the PITCh systems. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 11, 118–133.
- Zhang, C.; Meng, X.; Wei, X.; Lu, L. Highly efficient CRISPR mutagenesis by microhomology-mediated end joining in Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2016, 86, 47–57.
- Komor, A.C.; Kim, Y.B.; Packer, M.S.; Zuris, J.A.; Liu, D.R. Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature 2016, 533, 420–424.
- Gaudelli, N.M.; Komor, A.C.; Rees, H.A.; Packer, M.S.; Badran, A.H.; Bryson, D.I.; Liu, D.R. Programmable base editing of A•T to G•C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage. Nature 2017, 551, 464–471.
- Kurt, I.C.; Zhou, R.; Iyer, S.; Garcia, S.P.; Miller, B.R.; Langner, L.M.; Grünewald, J.; Joung, J.K. CRISPR C-to-G base editors for inducing targeted DNA transversions in human cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 39, 41–46.
- Porto, E.M.; Komor, A.C.; Slaymaker, I.M.; Yeo, G.W. Base editing: Advances and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 839–859.
- Cao, T.; Liu, S.; Qiu, Y.; Gao, M.; Wu, J.; Wu, G.; Liang, P.; Huang, J. Generation of C-to-G transversion in mouse embryos via CG editors. Transgenic Res. 2022, 31, 445–455.
- Anzalone, A.V.; Koblan, L.; Liu, D.R. Genome editing with CRISPR–Cas nucleases, base editors, transposases and prime editors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 824–844.
- Anzalone, A.V.; Randolph, P.B.; Davis, J.R.; Sousa, A.A.; Koblan, L.W.; Levy, J.M.; Chen, P.J.; Wilson, C.; Newby, G.A.; Raguram, A.; et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature 2019, 576, 149–157.
- Merkle, F.T.; Neuhausser, W.M.; Santos, D.; Valen, E.; Gagnon, J.A.; Maas, K.; Sandoe, J.; Schier, A.F.; Eggan, K. Efficient CRISPR-Cas9-Mediated Generation of Knockin Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Lacking Undesired Mutations at the Targeted Locus. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 875–883.
- Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhong, Z.; Vanegas, J.A.; Gao, X.; Kolomeisky, A.B. A general theoretical framework to design base editors with reduced bystander effects. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6529.
- Kantor, A.; McClements, M.E.; MacLaren, R.E. CRISPR-Cas9 DNA Base-Editing and Prime-Editing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6240.
- Schene, I.F.; Joore, I.P.; Oka, R.; Mokry, M.; van Vugt, A.H.M.; van Boxtel, R.; van der Doef, H.P.J.; van der Laan, L.J.W.; Verstegen, M.M.A.; van Hasselt, P.M.; et al. Prime editing for functional repair in patient-derived disease models. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5352.
- Liu, P.; Liang, S.-Q.; Zheng, C.; Mintzer, E.; Zhao, Y.G.; Ponnienselvan, K.; Mir, A.; Sontheimer, E.J.; Gao, G.; Flotte, T.R.; et al. Improved prime editors enable pathogenic allele correction and cancer modelling in adult mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2121.
- Habib, O.; Habib, G.; Hwang, G.-H.; Bae, S. Comprehensive analysis of prime editing outcomes in human embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 1187–1197.
- Lung, G. Precise Correction of A1AT E342K by Modified NGA PAM Prime Editing and Determination of Prime Editing Inhibition by TREX2. Master’s Thesis, Harvard University Division of Continuing Education, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021.
- Böck, D.; Rothgangl, T.; Villiger, L.; Schmidheini, L.; Matsushita, M.; Mathis, N.; Ioannidi, E.; Rimann, N.; Man Grisch-Chan, H.; Kreutzer, S.; et al. In Vivo Prime Editing of a Metabolic Liver Disease in Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabl9238.
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, X.-O.; Weng, Z.; Xue, W. Deletion and replacement of long genomic sequences using prime editing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 40, 227–234.
- Kim, Y.; Hong, S.-A.; Yu, J.; Eom, J.; Jang, K.; Yoon, S.; Hong, D.H.; Seo, D.; Lee, S.-N.; Woo, J.-S.; et al. Adenine base editing and prime editing of chemically derived hepatic progenitors rescue genetic liver disease. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 1614–1624.e5.
- Jang, H.; Jo, D.H.; Cho, C.S.; Shin, J.H.; Seo, J.H.; Yu, G.; Gopalappa, R.; Kim, D.; Cho, S.-R.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Application of prime editing to the correction of mutations and phenotypes in adult mice with liver and eye diseases. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 6, 181–194.
- Godbout, K.; Tremblay, J.P. Delivery of RNAs to Specific Organs by Lipid Nanoparticles for Gene Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2129.
- Li, H.; Busquets, O.; Verma, Y.; Syed, K.M.; Kutnowski, N.; Pangilinan, G.R.; Gilbert, A.L.; Bateup, H.S.; Rio, D.C.; Hockemeyer, D.; et al. Highly efficient generation of isogenic pluripotent stem cell models using prime editing. Elife 2022, 11, e79208.
- Bothmer, A.; Phadke, T.; Barrera, L.A.; Margulies, C.M.; Lee, C.S.; Buquicchio, F.; Moss, S.; Abdulkerim, H.S.; Selleck, W.; Jayaram, H.; et al. Characterization of the interplay between DNA repair and CRISPR/Cas9-induced DNA lesions at an endogenous locus. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13905.
- Wilkinson, P.D.; Delgado, E.R.; Alencastro, F.; Leek, M.P.; Roy, N.; Weirich, M.P.; Stahl, E.C.; Otero, P.A.; Chen, M.I.; Brown, W.K.; et al. The Polyploid State Restricts Hepatocyte Proliferation and Liver Regeneration in Mice. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1242–1258.





