
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Parth Patel | -- | 2444 | 2022-08-19 22:59:24 | | | |
| 2 | Lindsay Dong | Meta information modification | 2444 | 2022-08-22 05:57:48 | | |
Video Upload Options
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of irreversible vision loss in the elderly population. AMD is characterized in its late form by neovascularization (wet type) or geographic atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium cell layer (dry type). Regarding the latter type, there is growing evidence supporting an association between the pathophysiology of dry AMD and key proteins in the complement cascade. The complement cascade works as a central part of the innate immune system by defending against foreign pathogens and modified self-tissues. Through three distinct pathways, a series of plasma and membrane-associated serum proteins are activated upon identification of a foreign entity. Several of these proteins have been implicated in the development and progression of dry AMD. Potential therapeutic targets include C1q, C3, C5, complement factors (B, D, H, I), membrane attack complex, and properdin.
1. Introduction
2. General Pathogenesis of Dry AMD
3. Complement Cascade
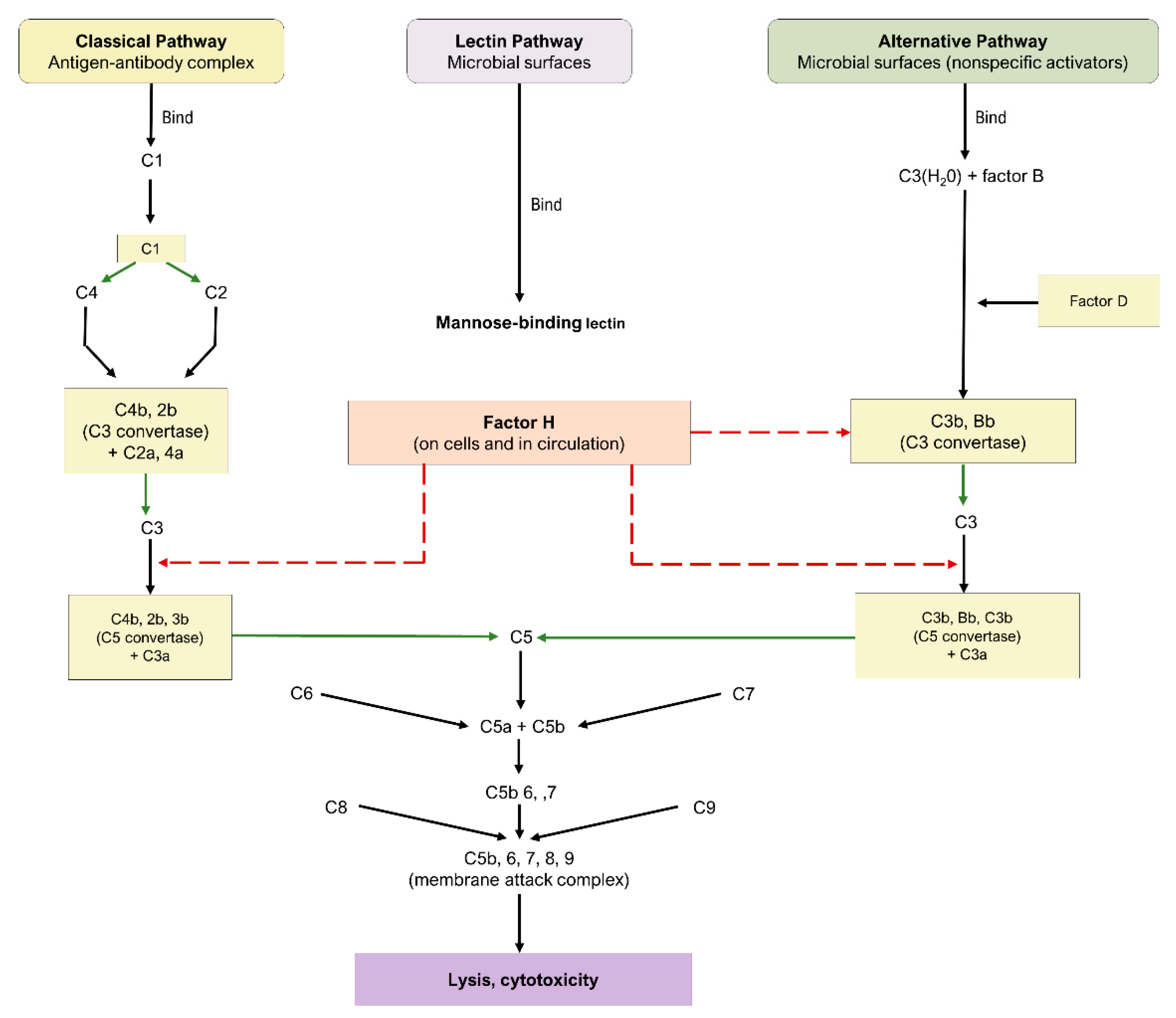
3.1. Pathways of the Complement Cascade
3.2. Complement Cascade in AMD
4. Current Therapeutic Targets
ANX007 (Annexon Inc., Brisbane, CA, USA) is a recombinant monoclonal antibody with an antigen-binding fragment that inhibits c1q. Through its action on c1q, the classical complement pathway is inhibited alongside C3 and C5 [38][39]. In a murine model of retinal photooxidative damage, ANX-M1, a monoclonal anti-C1q antibody similar to ANX007, reduced retinal atrophy [40]. Furthermore, a phase I trial (NCT04188015) using 2.5 mg and 5 mg of intravitreal (IVT) ANX007 demonstrated the safety and tolerability of both doses in 17 patients with primary open-angle glaucoma [38][39].
AMY-106, derived from Cp40-KKK, a fourth-generation compstatin analog, is a novel C3 inhibitor in development by Amyndas Pharmaceuticals [41][42]. This therapeutic maintained intraocular residence for more than 90 days after one 0.5 mg IVT injection in an investigation involving cynomolgus monkeys. Moreover, AMY-106 exhibited notable retinal tissue penetrance, as it localized with C3 in the choriocapillaris [41]. Provided its promise for dry AMD treatment, a phase I trial of AMY-106 is in development [42].
Pegcetacoplan, additionally denoted as APL-2, is a PEGylated peptide inhibitor of C3 formulated by Apellis Pharmaceuticals that is administered intravitreally [43]. The agent was evaluated in the FILLY trial (NCT02503332) [43], a multicenter, randomized phase II trial encompassing 246 patients with GA. Subjects were randomized in a 2:2:1:1 ratio to injections of 15 mg pegcetacoplan monthly or EOM, or sham injections monthly or EOM for 12 months. Follow-up was conducted at 15 and 18 months. Pegcetacoplan treatment produced statistically significant reductions in GA growth rates.
POT-4 (AL-78898A) is a compstatin analog originally developed by Potentia Pharmaceuticals that functions as a C3 inhibitor and was the first complement inhibitor tested in humans with AMD [38][44]. Phase I trial (NCT00473928) results revealed no adverse drug events (ADEs) or serious adverse events (SAEs) with doses of up to 450 mg for patients with wet AMD [44]. Based on the tolerability of POT-4, a multicenter, randomized phase II trial (NCT01603043) with 10 patients was conducted to assess its efficacy in reducing GA lesion growth among individuals with dry AMD. However, the study was terminated prematurely, as four of seven participants (57.14%) in the POT-4 group developed drug product deposits in the eye.
NGM621 (NGM Biopharmaceuticals, San Francisco, CA, USA) is a humanized immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody formulated as a C3 inhibitor. A phase I trial (NCT04014777) included 15 patients with GA secondary to dry AMD [45]. Participants were treated with either single-ascending doses (2 mg, 7.5 mg, 15 mg) of NGM621 or two doses of 15 mg delivered 4 weeks apart. Monitoring occurred for 12 weeks within all cohorts, and results indicated an appropriate safety profile, with no SAEs, ADEs, or new-onset CNV reported.
Eculizumab (Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc) is a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against C5 [46][47]. Systemic eculizumab is currently approved for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Thus, considering the evidence for the relationship of the complement cascade with AMD, the COMPLETE study (NCT00935883) was designed [46][47].
Avacincaptad pegol (Zimura®), by Iveric Bio (Cranbury, NJ, USA), is a PEGylated RNA aptamer that operates as a C5 cleavage inhibitor, thereby impeding the complement cascade irrespective of the initial activation pathway. This agent was evaluated in the phase II/III GATHER1 trial (NCT02686658), a multicenter, randomized investigation. Randomization was conducted in two stages. In total, 77 part I participants were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to injections of 1 mg of avacincaptad pegol, 2 mg of avacincaptad pegol, and sham. Then, 209 part II participants were randomized in a 1:2:2 ratio to 2 mg of avacincaptad pegol, 4 mg of avacincaptad pegol, and sham. Relative to sham, subjects receiving 2 mg of avacincaptad pegol and 4 mg of avacincaptad pegol experienced a 27.4% (p = 0.0072) and 27.8% (p = 0.0051) reduction, respectively, in the mean rate of GA growth [48].
Tesidolumab (LFG316), a monoclonal C5 inhibitor developed by Novartis Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland), was investigated in a multicenter, randomized phase II clinical trial (NCT01527500). In the study, 158 patients were enrolled and separated into two groups. Part A examined the safety and efficacy of multiple 5 mg IVT injections of LFG316 relative to sham every 28 days over the course of 505 days. Part B examined the safety and pharmacokinetic properties of a single 10 mg IVT injection. Results revealed a relatively benign safety profile, with no demonstrable improvement in the primary outcome of GA lesion growth or the secondary outcome of BCVA.
IONIS-FB-lrx (Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Carlsbad, CA, USA) is a novel anti-sense oligonucleotide (ASO) targeting the gene encoding complement factor B (CFB), a moiety of the alternative complement pathway. When delivered subcutaneously, IONIS-FB-lrx reduced circulating levels of CFB in a dose-dependent manner among 54 healthy participants of a phase I trial [49]. No notable adverse effects were reported. Given these results, the multicenter, randomized phase II GOLDEN trial (NCT03815825) has been initiated to evaluate the influence of IONIS-FB-lrx administration on the progression of GA lesion size [49].
5. Conclusions
References
- Bourne, R.R.; Jonas, J.B.; Bron, A.M.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Flaxman, S.R.; Friedman, D.S.; Keeffe, J.E.; Kempen, J.H.; Leasher, J. Prevalence and causes of vision loss in high-income countries and in Eastern and Central Europe in 2015: Magnitude, temporal trends and projections. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 575–585.
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e106–e116.
- Kim, S.; Park, S.J.; Byun, S.J.; Park, K.H.; Suh, H.S. Incremental economic burden associated with exudative age-related macular degeneration: A population-based study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2019, 19, 828.
- Sadda, S.R.; Guymer, R.; Holz, F.G.; Schmitz-Valckenberg, S.; Curcio, C.A.; Bird, A.C.; Blodi, B.A.; Bottoni, F.; Chakravarthy, U.; Chew, E.Y.; et al. Consensus Definition for Atrophy Associated with Age-Related Macular Degeneration on OCT: Classification of Atrophy Report 3. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 537–548.
- Bird, A.C.; Bressler, N.M.; Bressler, S.B.; Chisholm, I.H.; Coscas, G.; Davis, M.D.; de Jong, P.T.; Klaver, C.C.; Klein, B.E.; Klein, R.; et al. An international classification and grading system for age-related maculopathy and age-related macular degeneration. The International ARM Epidemiological Study Group. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1995, 39, 367–374.
- Ferris, F.L.; Davis, M.D.; Clemons, T.E.; Lee, L.Y.; Chew, E.Y.; Lindblad, A.S.; Milton, R.C.; Bressler, S.B.; Klein, R. A simplified severity scale for age-related macular degeneration: AREDS Report No. 18. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2005, 123, 1570–1574.
- Ferris, F.L., 3rd; Wilkinson, C.P.; Bird, A.; Chakravarthy, U.; Chew, E.; Csaky, K.; Sadda, S.R. Clinical classification of age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 844–851.
- Keane, P.A.; Liakopoulos, S.; Ongchin, S.C.; Heussen, F.M.; Msutta, S.; Chang, K.T.; Walsh, A.C.; Sadda, S.R. Quantitative subanalysis of optical coherence tomography after treatment with ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3115–3120.
- Horner, F.; Lip, P.L.; Mohammed, B.R.; Fusi-Rubiano, W.; Gokhale, E.; Mushtaq, B.; Chavan, R. Comparing Effectiveness of Three Different Anti-VEGF Treatment Regimens for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Two Years’ Real-World Clinical Outcomes. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 1703–1713.
- Arrigo, A.; Saladino, A.; Aragona, E.; Mercuri, S.; Introini, U.; Bandello, F.; Parodi, M.B. Different Outcomes of Anti-VEGF Treatment for Neovascular AMD according to Neovascular Sutypes and Baseline Features: 2-Year Real-Life Clinical Outcomes. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5516981.
- Brown, G.C.; Brown, M.M.; Rapuano, S.; Boyer, D. Cost-Utility Analysis of VEGF Inhibitors for Treating Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 218, 225–241.
- Bhattarai, N.; Hytti, M.; Reinisalo, M.; Kaarniranta, K.; Mysore, Y.; Kauppinen, A. Hydroquinone predisposes for retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cell degeneration in inflammatory conditions. Immunol. Res. 2022.
- Chang, Y.-Y.; Lee, Y.-J.; Hsu, M.-Y.; Wang, M.; Tsou, S.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Lin, J.-A.; Hsiao, Y.-P.; Lin, H.-W. Protective Effect of Quercetin on Sodium Iodate-Induced Retinal Apoptosis through the Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mitochondrion-Dependent Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4056.
- Soundara Pandi, S.P.; Ratnayaka, J.A.; Lotery, A.J.; Teeling, J.L. Progress in developing rodent models of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 203, 108404.
- Nagata, K.; Hishikawa, D.; Sagara, H.; Saito, M.; Watanabe, S.; Shimizu, T.; Shindou, H. Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 1 controls mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation and survival of retinal photoreceptor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101958.
- Hsu, M.-Y.; Hsiao, Y.-P.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chen, C.; Lee, C.-M.; Liao, W.-C.; Tsou, S.-C.; Lin, H.-W.; Chang, Y.-Y. Quercetin Alleviates the Accumulation of Superoxide in Sodium Iodate-Induced Retinal Autophagy by Regulating Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Homeostasis through Enhanced Deacetyl-SOD2 via the Nrf2-PGC-1α-Sirt1 Pathway. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1125.
- Eells, J.T. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Aging Retina. Biology 2019, 8, 31.
- Lazzarini, R.; Nicolai, M.; Lucarini, G.; Pirani, V.; Mariotti, C.; Bracci, M.; Mattioli-Belmonte, M. Oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelium impairs stem cells: A vicious cycle in age-related macular degeneration. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 477, 67–77.
- Anderson, D.H.; Mullins, R.F.; Hageman, G.S.; Johnson, L.V. A role for local inflammation in the formation of drusen in the aging eye. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 134, 411–431.
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ji, J.; Wang, L.; Lv, W.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Feng, G.; Chen, K. A histological study of atherosclerotic characteristics in age-related macular degeneration. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08973.
- van Lookeren Campagne, M.; LeCouter, J.; Yaspan, B.L.; Ye, W. Mechanisms of age-related macular degeneration and therapeutic opportunities. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 151–164.
- Handa, J.T.; Bowes Rickman, C.; Dick, A.D.; Gorin, M.B.; Miller, J.W.; Toth, C.A.; Ueffing, M.; Zarbin, M.; Farrer, L.A. A systems biology approach towards understanding and treating non-neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3347.
- Kim, S.-Y.; Kambhampati, S.P.; Bhutto, I.A.; McLeod, D.S.; Lutty, G.A.; Kannan, R.M. Evolution of oxidative stress, inflammation and neovascularization in the choroid and retina in a subretinal lipid induced age-related macular degeneration model. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 203, 108391.
- Garcia-Garcia, J.; Usategui-Martin, R.; Sanabria, M.R.; Fernandez-Perez, E.; Telleria, J.J.; Coco-Martin, R.M. Pathophysiology of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Implications for Treatment. Ophthalmic Res. 2022.
- Fleckenstein, M.; Mitchell, P.; Freund, K.B.; Sadda, S.; Holz, F.G.; Brittain, C.; Henry, E.C.; Ferrara, D. The Progression of Geographic Atrophy Secondary to Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 369–390.
- Schmitz-Valckenberg, S.; Sadda, S.; Staurenghi, G.; Chew, E.Y.; Fleckenstein, M.; Holz, F.G. Geographic Atrophy: Semantic Considerations and Literature Review. Retina 2016, 36, 2250–2264.
- Lorthiois, E.; Anderson, K.; Vulpetti, A.; Rogel, O.; Cumin, F.; Ostermann, N.; Steinbacher, S.; Mac Sweeney, A.; Delgado, O.; Liao, S.-M. Discovery of highly potent and selective small-molecule reversible factor D inhibitors demonstrating alternative complement pathway inhibition in vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 5717–5735.
- Desai, D.; Dugel, P.U. Complement cascade inhibition in geographic atrophy: A review. Eye 2022, 36, 294–302.
- Bora, P.S.; Sohn, J.H.; Cruz, J.M.; Jha, P.; Nishihori, H.; Wang, Y.; Kaliappan, S.; Kaplan, H.J.; Bora, N.S. Role of complement and complement membrane attack complex in laser-induced choroidal neovascularization. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 491–497.
- Natoli, R.; Fernando, N.; Jiao, H.; Racic, T.; Madigan, M.; Barnett, N.L.; Chu-Tan, J.A.; Valter, K.; Provis, J.; Rutar, M. Retinal Macrophages Synthesize C3 and Activate Complement in AMD and in Models of Focal Retinal Degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 2977–2990.
- Wu, J.; Sun, X. Complement system and age-related macular degeneration: Drugs and challenges. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 2413–2425.
- Lechner, J.; Chen, M.; Hogg, R.E.; Toth, L.; Silvestri, G.; Chakravarthy, U.; Xu, H. Higher plasma levels of complement C3a, C4a and C5a increase the risk of subretinal fibrosis in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Immun. Ageing 2016, 13, 4.
- Katschke, K.J., Jr.; Xi, H.; Cox, C.; Truong, T.; Malato, Y.; Lee, W.P.; McKenzie, B.; Arceo, R.; Tao, J.; Rangell, L.; et al. Classical and alternative complement activation on photoreceptor outer segments drives monocyte-dependent retinal atrophy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7348.
- Udsen, M.; Tagmose, C.; Garred, P.; Nissen, M.H.; Faber, C. Complement activation by RPE cells preexposed to TNFα and IFNγ. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 218, 108982.
- Khandhadia, S.; Cipriani, V.; Yates, J.R.; Lotery, A.J. Age-related macular degeneration and the complement system. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 127–146.
- Nishiguchi, K.M.; Yasuma, T.R.; Tomida, D.; Nakamura, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Kikuchi, M.; Ohmi, Y.; Niwa, T.; Hamajima, N.; Furukawa, K.; et al. C9-R95X polymorphism in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 508–512.
- Rohrer, B.; Guo, Y.; Kunchithapautham, K.; Gilkeson, G.S. Eliminating complement factor D reduces photoreceptor susceptibility to light-induced damage. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 5282–5289.
- Qin, S.; Dong, N.; Yang, M.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y. Complement Inhibitors in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Potential Therapeutic Option. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 9945725.
- Fong, D. Spotlight on ANX007—Inhibition of C1q for GA. In Proceedings of the 2nd Dry AMD Therapeutic Development Summit, Online, 19–20 October 2021.
- Jiao, H.; Rutar, M.; Fernando, N.; Yednock, T.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Aggio-Bruce, R.; Provis, J.; Natoli, R. Subretinal macrophages produce classical complement activator C1q leading to the progression of focal retinal degeneration. Mol. Neurodegener 2018, 13, 45.
- Hughes, S.; Gumas, J.; Lee, R.; Rumano, M.; Berger, N.; Gautam, A.K.; Sfyroera, G.; Chan, A.L.; Gnanaguru, G.; Connor, K.M.; et al. Prolonged intraocular residence and retinal tissue distribution of a fourth-generation compstatin-based C3 inhibitor in non-human primates. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 214, 108391.
- Kim, B.J.; Hughes, S.; Gumas, J.; Rumano, M.; Yancopoulou, D.; Mastellos, D.; Lambris, J.D. Prolonged Intraocular residence of a fourth generation compstatin complement C3 inhibitor supports its clinical development for geographic atrophy. In Proceedings of the Retina Society, Virtual, 25 August–22 September 2020.
- Liao, D.S.; Grossi, F.V.; El Mehdi, D.; Gerber, M.R.; Brown, D.M.; Heier, J.S.; Wykoff, C.C.; Singerman, L.J.; Abraham, P.; Grassmann, F.; et al. Complement C3 Inhibitor Pegcetacoplan for Geographic Atrophy Secondary to Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Randomized Phase 2 Trial. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 186–195.
- Kaushal, S.; Grossi, F.; Francois, C.; Slakter, J.; Group, A.S. Complement C3 inhibitor POT-4: Clinical Safety of Intravitreal Administration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 5010.
- Wykoff, C.C.; Hershberger, V.; Eichenbaum, D.; Henry, E.; Younis, H.S.; Chandra, P.; Yuan, N.; Solloway, M.; DePaoli, A. Inhibition of Complement Factor 3 in Geographic Atrophy with NGM621: Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Study Results. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 235, 131–142.
- Yehoshua, Z.; de Amorim Garcia Filho, C.A.; Nunes, R.P.; Gregori, G.; Penha, F.M.; Moshfeghi, A.A.; Zhang, K.; Sadda, S.; Feuer, W.; Rosenfeld, P.J. Systemic complement inhibition with eculizumab for geographic atrophy in age-related macular degeneration: The COMPLETE study. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 693–701.
- Filho, C.A.d.A.G.; Yehoshua, Z.; Gregori, G.; Nunes, R.P.; Penha, F.M.; Moshfeghi, A.A.; Zhang, K.; Feuer, W.; Rosenfeld, P.J. Change in Drusen Volume as a Novel Clinical Trial Endpoint for the Study of Complement Inhibition in Age-related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2014, 45, 18–31.
- Jaffe, G.J.; Westby, K.; Csaky, K.G.; Mones, J.; Pearlman, J.A.; Patel, S.S.; Joondeph, B.C.; Randolph, J.; Masonson, H.; Rezaei, K.A. C5 Inhibitor Avacincaptad Pegol for Geographic Atrophy Due to Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Randomized Pivotal Phase 2/3 Trial. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 576–586.
- Jaffe, G.J.; Sahni, J.; Fauser, S.; Geary, R.S.; Schneider, E.; McCaleb, M. Development of IONIS-FB-LRx to Treat Geographic Atrophy Associated with AMD. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 4305.
- Katschke, K.J., Jr.; Wu, P.; Ganesan, R.; Kelley, R.F.; Mathieu, M.A.; Hass, P.E.; Murray, J.; Kirchhofer, D.; Wiesmann, C.; van Lookeren Campagne, M. Inhibiting alternative pathway complement activation by targeting the factor D exosite. J. Biol. Chem 2012, 287, 12886–12892.
- Yaspan, B.L.; Williams, D.F.; Holz, F.G.; Regillo, C.D.; Li, Z.; Dressen, A.; van Lookeren Campagne, M.; Le, K.N.; Graham, R.R.; Beres, T.; et al. Targeting factor D of the alternative complement pathway reduces geographic atrophy progression secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaf1443.
- Cashman, S.M.; Gracias, J.; Adhi, M.; Kumar-Singh, R. Adenovirus-mediated delivery of Factor H attenuates complement C3 induced pathology in the murine retina: A potential gene therapy for age-related macular degeneration. J. Gene Med. 2015, 17, 229–243.
- Cabral de Guimaraes, T.A.; Daich Varela, M.; Georgiou, M.; Michaelides, M. Treatments for dry age-related macular degeneration: Therapeutic avenues, clinical trials and future directions. Br J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 297–304.
- Khanani, A.M.; Maturi, R.K.; Bagheri, N.; Bakall, B.; Boyer, D.S.; Couvillion, S.S.; Dhoot, D.S.; Holekamp, N.M.; Jamal, K.N.; Marcus, D.M.; et al. A Phase I, Single Ascending Dose Study of GEM103 (Recombinant Human Complement Factor H) in Patients with Geographic Atrophy. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2022, 2, 100154.
- Wykoff, C.C.; Rosenfeld, P.J.; Waheed, N.K.; Singh, R.P.; Ronca, N.; Slakter, J.S.; Staurenghi, G.; Mones, J.; Baumal, C.R.; Saroj, N.; et al. Characterizing New-Onset Exudation in the Randomized Phase 2 FILLY Trial of Complement Inhibitor Pegcetacoplan for Geographic Atrophy. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 1325–1336.
- Kumar-Singh, R. The role of complement membrane attack complex in dry and wet AMD—From hypothesis to clinical trials. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 184, 266–277.
- Cashman, S.M.; Ramo, K.; Kumar-Singh, R. A non membrane-targeted human soluble CD59 attenuates choroidal neovascularization in a model of age related macular degeneration. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19078.
- Johnson, L.; Splawski, I.; Baker, L.; Carrion, A.; Nguyen, A.; Twarog, M.; Wang, Y.; Jager, U.; Keating, M.; Dryja, T.P.; et al. Generation and characterization of CLG561: A fully-human, anti-properdin Fab for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1116.
- Glazer, L.C.; Williams, J.G.; Gordon, C.M.; Dugel, P.U.; Milton, M.; Valencia, T.; Klein, U.; Kretz, S.; Gedif, K.; Grosskreutz, C.L.; et al. A first in human study of Intravitreal (IVT) CLG561 in Subjects with Advanced Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD). Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 2672.





