Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Zhao, Y.; Tan, D.; Peng, B.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Shi, R.; Chong, C.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, S.; Liang, Q.; et al. Neuroendocrine–Immune Regulatory Network of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/24244 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Zhao Y, Tan D, Peng B, Yang L, Zhang S, Shi R, et al. Neuroendocrine–Immune Regulatory Network of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/24244. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Zhao, Yi, De-Chao Tan, Bo Peng, Lin Yang, Si-Yuan Zhang, Rui-Peng Shi, Cheong-Meng Chong, Zhang-Feng Zhong, Sheng-Peng Wang, Qiong-Lin Liang, et al. "Neuroendocrine–Immune Regulatory Network of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/24244 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Zhao, Y., Tan, D., Peng, B., Yang, L., Zhang, S., Shi, R., Chong, C., Zhong, Z., Wang, S., Liang, Q., & Wang, Y. (2022, June 21). Neuroendocrine–Immune Regulatory Network of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/24244
Zhao, Yi, et al. "Neuroendocrine–Immune Regulatory Network of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver." Encyclopedia. Web. 21 June, 2022.
Copy Citation
Eucommia ulmoides Oliver (E. ulmoides) is a popular medicinal herb and health supplement in China, Japan, and Korea, and has a variety of pharmaceutical properties. The neuroendocrine–immune (NEI) network is crucial in maintaining homeostasis and physical or psychological functions at a holistic level, consistent with the regulatory theory of natural medicine.
Eucommia ulmoides Oliver (E. ulmoides)
neuroendocrine–immune
cancer
network pharmacology
1. Introduction
Eucommia ulmoides Oliver (E. ulmoides) is a monotypic genus Eucommia, also known as tuchong in Japanese and tu-chung in Korean, and was recorded in Shen Nong Ben Cao, a classic Chinese medical book [1]. It is characterized by being resistant to cold (−40 °C) and hot (44 °C) conditions [2]. Generally, E. ulmoides is cultivated in the southern area of Qingling in China, including the Guizhou, Sichuan, Hubei, Shaanxi, Hunan, Gansu, Yunnan, Anhui, Guangxi, Henan, Zhejiang, and Jiangxi provinces (Figure 1A) [3][4][5]. E. ulmoides has been utilized for at least 2000 years according to ancient Chinese medical records [6]. In 1955, the first global conference on the pharmacological effects of E. ulmoides was organized in Leningrad, and the scientists there suggested that E. ulmoides was effective in decreasing blood pressure [7]. From then on, E. ulmoides has attracted intensive attention worldwide and a great deal of scientific research and clinical trials have been undertaken to study its biological functions and pharmacological effects (Figure 1B).
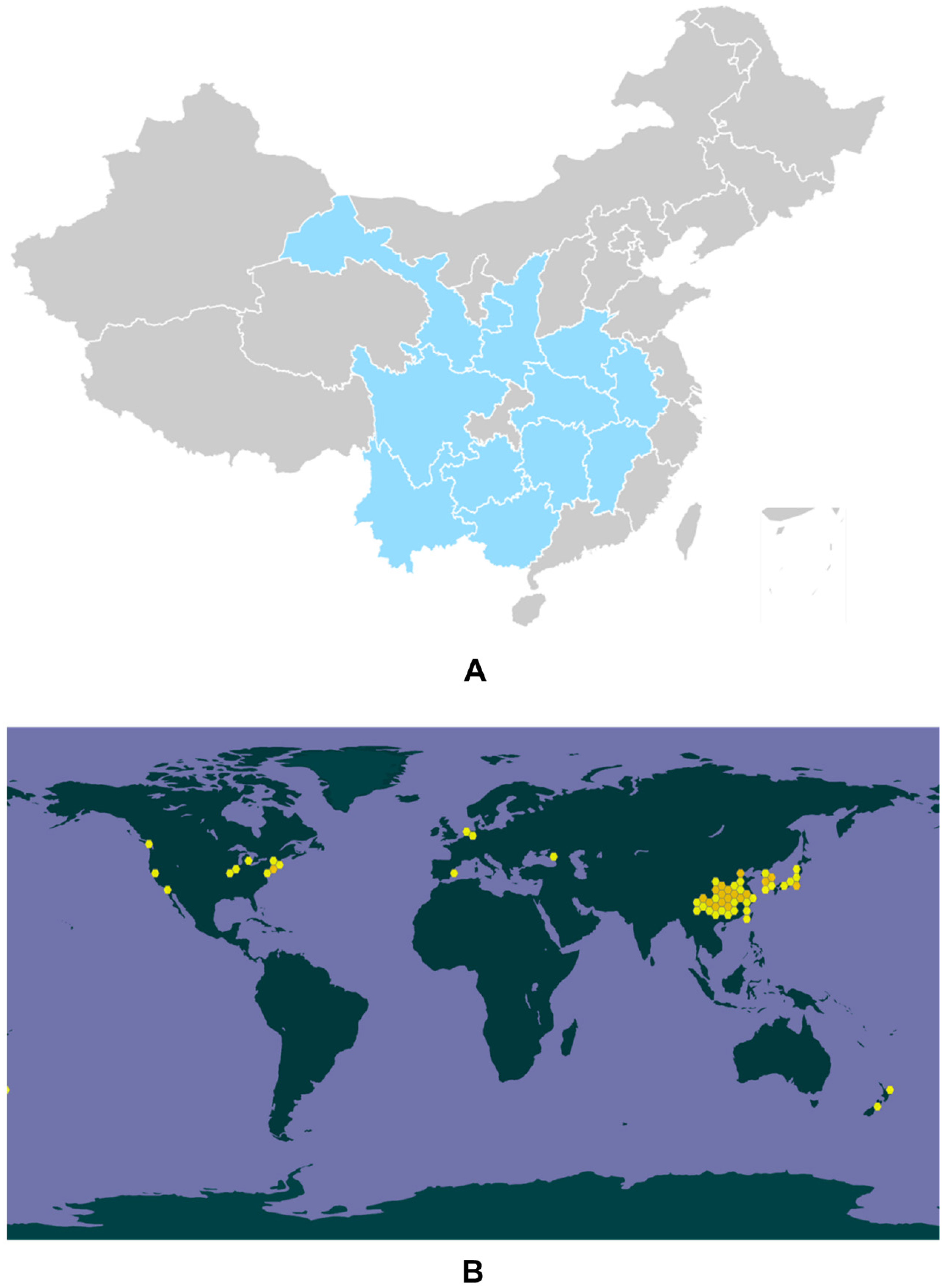
Figure 1. Genuine areas for E. ulmoides in China (A). The global biodiversity information of E. ulmoides (B).
Recently, the barks and leaves of E. ulmoides have been listed separately in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 version), with different quality control criteria, but identical functions, including nourishing the liver and kidney, and strengthening bones and muscles [8]. Additionally, Eucommia ulmoides Oliver barks (EUE) were recorded in the European Pharmacopoeia (9th Edition), Japanese Pharmacopoeia (17th Edition, English Version), Hong Kong Chinese Materia Medica Standards (Volume 3), and Taiwan Herbal Pharmacopeia (3rd Edition). In particular, among the 200 standard formulations in the Taiwan Herbal Pharmacopeia, 5 prescriptions involve EUE [9]. Traditionally, E. ulmoides has been considered to have the properties of tonifying the kidney and liver, strengthening bones and muscles, and fixing meridians from ancient records [6]. While in modern pharmacology, 204 chemical constituents have been identified from the leaves, barks, seeds, and flowers of E. ulmoides, and these compounds are divided into phenols, iridoids, lignans, flavonoids, terpenoids, sterols, gutta-percha, polysaccharides, unsaturated fatty acids, amino acids, and mineral elements [10]. Several components display vital biological functions both in vivo and in vitro, such as hypolipidemic, antihypertensive, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, bone-metabolic, renoprotective, anti-aging, anti-fatigue, antidepressant, hypnotic-sedative, immune regulation, cognitive improvement, uterine smooth relaxation muscles, and erectile function enhancement [11][12][13][14][15]. Apart from being a medicine, E. ulmoides has also been employed as a health supplement popular in China, Japan, and Korea [16]. In short, E. ulmoides has great economic value and the potential for being used in novel drugs.
The neuroendocrine–immune (NEI) regulatory network (Figure 2) is a complex system, incorporating the nervous system, endocrine system, and immune system, to maintain homeostasis and plays a pivotal role in the treatment of complicated diseases, with the involvement of bioregulatory signals such as neurotransmitters, hormones, and cytokines/chemokines [17][18][19]. Researchers systematically summarize the chemical components, biological activities, and pharmacological effects of E. ulmoides on NEI diseases, which will provide a reference for research, development, and application of the active components of E. ulmoides.
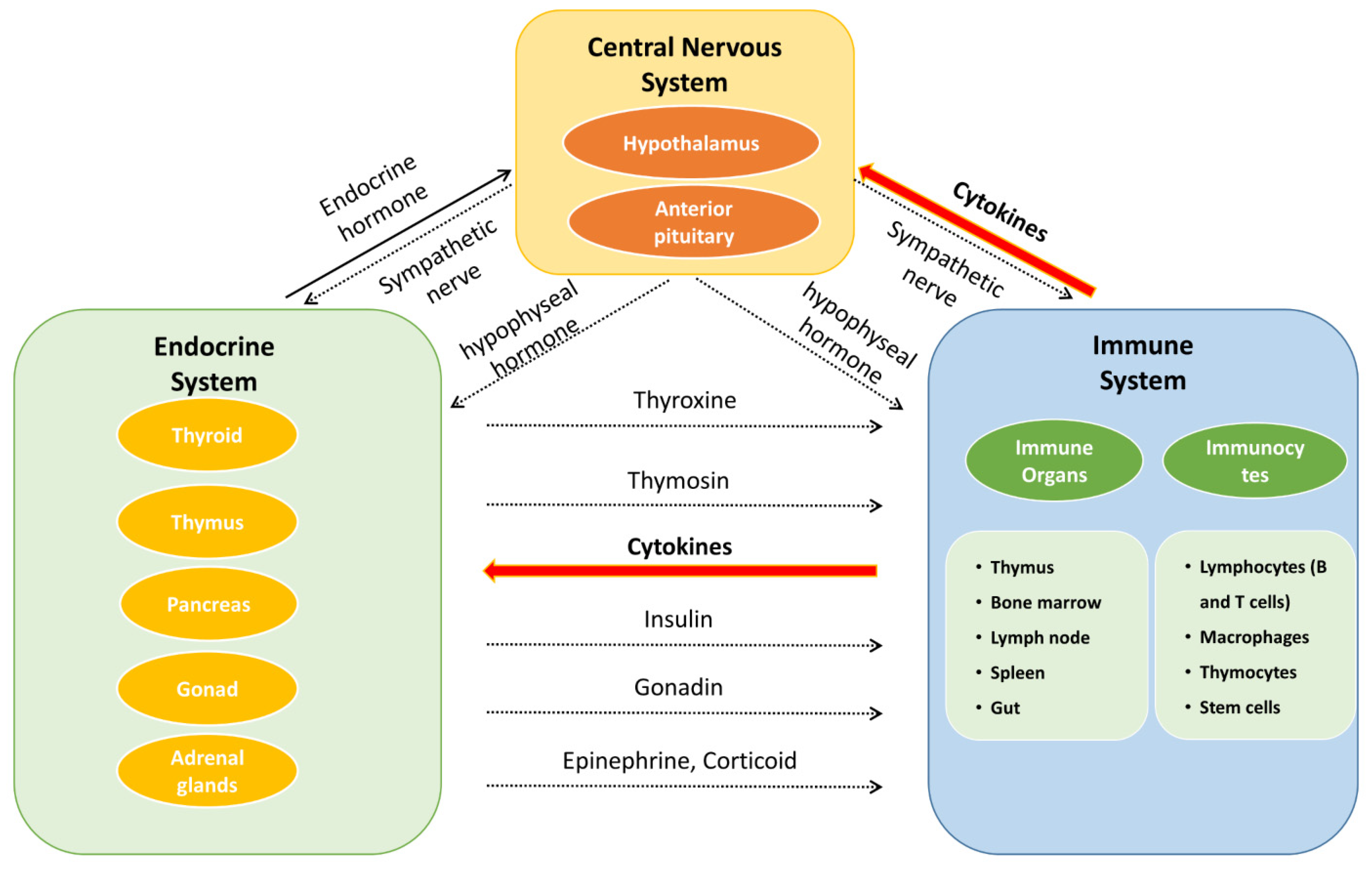
Figure 2. The interaction of neuroendocrine–immune system.
2. Neuroendocrine–Immune Regulatory Network
Besedobsky first proposed the NEI network in 1997. The interactions among the NEI system represent a complete communication circuit by sharing common signaling ligands and their receptors. In general, the nervous system regulates the immune system in two ways. One is through the release of neurotransmitters or neuropeptides such as acetylcholine, 5-HT, and opioid peptides from the endings of autonomic nerves, which act on immune cells and organs (bone marrow, thymus, lymph nodes, and gut) [20]. The second regulatory mechanism is through the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical (HPA), hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid (HPT), hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG), and hypothalamic–pituitary–somatotropic (HPS) axes to regulate the immune system. The release of neurohormones such as corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus can stimulate the anterior pituitary gland to secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH acts on the adrenal cortex and promotes the secretion of glandular hormones (e.g., glucocorticoids) to mediate the immune response [21]. On the other hand, immune cells can generate various immune mediators to trigger the activation of the nervous system in response to inflammatory and invasive stimuli. For example, IL-1 can upregulate the secretion of CRH [22], IL-1β, and TNF-α, which are regarded as potential neurotoxic substances [23], while the proinflammatory cytokine induction of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) provides neuroprotection during acute neuroinflammation by inducing the secretion of IL-6 [24].
The secretion of hormones also has a role in the nervous system. For example, thyroxine is important for the development of the brain [25], oxytocin can improve the learning and memory of mice by regulating the hippocampus [26], and vasopressin can also enhance memory [27]. As for the immune system, hormones such as glucocorticoids secreted by the adrenal cortex have both anti-inflammatory and proinflammatory effects [28]. As gonadal hormones, both androgens and estrogens can improve immunity [29][30]. In particular, estrogen can alter the immune response by binding to specific receptors on immune cells, resulting in their proliferation, and they play a feedback regulatory role on the hypothalamic–pituitary axis [29][31].
The NEI network is involved in multidirectional functions and multiple systems. Once the imbalance or alteration of the NEI network occurs, various diseases may follow, such as multiple sclerosis, fatigue, inflammation, psoriatic arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, depression, anxiety, cancer, and obesity [32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40][41]. From a holistic perspective, E. ulmoides has a “multi-components, multi-targets” profile for the treatment of various diseases. Hence, it is valuable to understand the pharmacological effects of E. ulmoides in the NEI network and fill this research gap.
3. Pharmacological Effects of E. ulmoides on NEI Network-Associated Diseases
The NEI network mediators and their end products have widespread effects at the systemic and cellular levels. They are responsible for disease behavior, such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD) which are explained in Figure 3A), metabolic disorders including obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and dyslipidemia, as well as osteoporosis, fatigue, depression, and anxiety [32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40][41][42][43][44] (Figure 3B). Thus, maintaining the balance of the NEI network may bring benefits for the treatment of these diseases. Through reviewing the literature on E. ulmoides, researchers found that the herb does affect these diseases, as discussed in the following sections and summarized in Table 1.
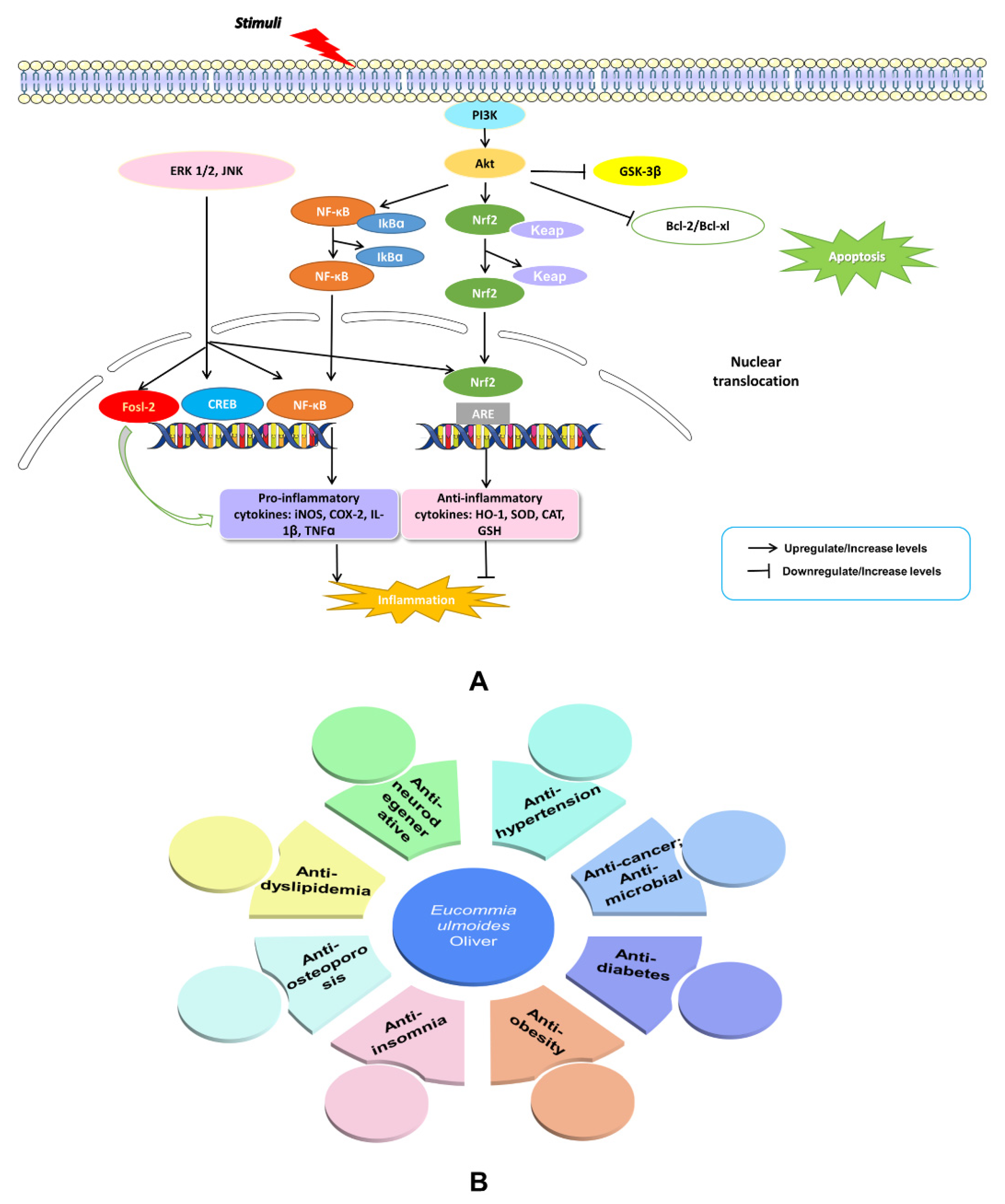
Figure 3. An illustration of NF-kB and PI3K-Akt signaling and their effects on AD and PD (A). Summary of published therapeutic properties of E. ulmoides (B).
Table 1. Summary of pharmacological effects for Eucommia ulmoides Oliver.
| Disease | Compound | Model | Dosage | Effect | Mechanism | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vitro | In Vivo | ||||||
| Cancer | Chlorogenic acid | AGS cells | 0–2 mg/mL | Cytotoxicity | [45] | ||
| Total flavonoids | GBMs cells lines U251, U87, HS683 and A172 and human normal cell HA | H22 tumor-bearing mice | 50–200 mg/kg | Inhibit tumor growth Radiosensitization Induce apoptosis |
Increase Bax expression and decrease in Bcl-2 expression; Decrease the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax and downregulate the expression of HIF-1α, MMP-2 as well as Wee1. |
[46][47] | |
| Eucommicin A | iCSCL-10A-1, iCSCL-10A-2, MCF7, MDA-MB231 cells | 0–100 μM | Cytotoxicity, suppressed tumor sphere formation | [48] | |||
| Pentacyclic triterpenoids (betulinic acid, lupeol, and 3-O-laurylbetulinic acid) | Hela, MDA-MB-231, and T47D cells | 3–80 μM | Inhibit tumor cell growth and induce apoptosis | Induce mitochondrial fragmentation and suppress lysosome production in Hela cells. | [49] | ||
| Chlorogenic acid | HCT-116, LOVO | 600–1600 µg/mL | Inhibit proliferation and promote apoptosis | [50] | |||
| Eucommia ulmoides Oliver leaf (EUL) extract | A549, SNU-C4, HeLa, | 25–200 µg/mL | Inhibit proliferation | [51] | |||
| Total Polysaccharides | LLC, KMB-17 | 0.5–8.0 µg/mL | Induce apoptosis and inhibit proliferation | Activate Caspase-3 pathway. | [52] | ||
| E. ulmoides extract | HCT116 | 500–800 mg/L | Cytotoxicity | [53] | |||
| EUL extract and chlorogenic acid | HCT116, LOVO | 1600 µg/mL | Inhibit invasion and migration | [54] | |||
| Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD) | Eucommia ulmoides Oliver bark (EUE) extract | Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated BV-2 microglia 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced SH-SY5Y cells |
2.5–100 μg/mL | Anti-inflammatory Anti-oxidative stress |
Inhibit phosphorylation of MAPKs, PI3K/Akt, and GSK-3β, suppress NF-κB activation and induce Nrf2-dependent HO-1 activation; Inhibit reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, mitochondrial dysfunction, and phosphorylation of JNK, PI3K/Akt and GSK-3β, thereby blocking NF-κB nuclear translocation. |
[55][56] | |
| EUE extract | H2O2 -induced SH-SY5Y cells | Scopolamine-induced ICR mice | 5–20 μg/mL, 5–20 mg/kg |
Anti-cytotoxicity Enhance cholinergic signaling |
Inhibit cytotoxicity, reduce ROS accumulation, DNA condensation, MMP stabilization, regulate Bcl-2 family proteins, inhibit MAPKs and PI3K/Akt phosphorylation; Decrease the activity of AChE and TBARS, protect BDNF and activate CREB expression. |
[57][58] | |
| EUE extract | MPTP-induced male C57BL/6J mice | 2.5–10 g/kg, 150–600 mg/kg |
Anti-neuroinflammationAnti-PD | Downregulate expression of p38, JNK, and Fosl2, reduce pro-inflammatory factors; Antagonize loss of striatal neurotransmitters and alleviate associated ambulatory motor abnormalities. |
[59][60] | ||
| Betulin, wogonin, oroxylin A, geniposidic, aucubin |
MPP+-induced SH-SY5Y cells | 10 μM | Anti-PD | Ameliorate the ubiquitin-proteasome system. | [60] | ||
| Geniposidic acid (GPA) | APP/PS1 mice and C57BL/6J mice | 25, 75 mg/kg | Anti-neuroinflammatory | Inhibit the activation of astrocytes and microglia, down-regulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and iNOS, upregulate the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines and Arg-1, and block the TLR4/2-MyD88 signaling pathway by reducing the expression of HMGB-1. | [61] | ||
| Macranthoin G | Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced PC12 cells | 6.25–50 μM | Anti-oxidative stress-mediated cellular injury Anti-PD and anti-AD |
Decrease MDA production and ROS levels, increase MMP, restore CAT, GSH-Px and SOD activity, and inhibit NF-κB pathway and activation of IκBα, p38 and ERK. | [62] | ||
| Dsylipidemia | EUL extract | High-fat diet (HFD)-induced male Sprague-Dawley | 200 mg/kg | Hepatoprotective | Inhibit ER stress, enhance lysosomal function, and increase autophagic flux associated with inhibition of the mTOR-ER stress pathway. | [63] | |
| EUE extract, aucubin and geniposide | Palmitate-induced HepG2 cells HFD-induced female Sprague-Dawley rats |
100 μg/mL extracts, 10 μg/mL aucubin or geniposide | Anti-hepatic dyslipidemia | Inhibit ER stress by increasing V-ATPase activity, reduce hepatic lipid accumulation through secretion of apolipoprotein B and associated triglycerides and cholesterol; Enhance lysosomal activity and to regulate ER stress. |
[64] | ||
| EUE extract | CCl4-induced Sprague-Dawley rats | 0.25–1 g/kg | Anti-hepatic dyslipidemia | Increase lysosomal enzyme activity, reduce ER stress by improving Apo B secretion, then inhibit ROS accumulation. | [65] | ||
| EUE extract, aucubin, geniposide | BAX-induced HepG2 cells; | HFD-induced female Sprague-Dawley | 100 μg/mL extracts, 10 μg/mL aucubin or geniposide; 0.25–1 g/kg; |
Anti-hepatic dyslipidemia | Inhibit cell death through enhancement of lysosome activity; Enhance lysosomal activity to the regulate lysosomal BAX activation and cell death. |
[66] | |
| CGA enriched-EUL extract | HepG2 cells | 10–80 mg/L; 0.3–600 μM; | Lipid-lowering | Activate AMPK and inhibit SREBP2 and HMGCR to reduce TC synthesis and TG levels, increase ABCA1 and CYP7A1, and enhance TC excretion and bile acid transport, synthesis and excretion. | [67] | ||
| Total flavonoid | HFD-induced male Wistar rats | 10–90 mg/kg/day | Anti-hyperlipidemia | Lower serum cholesterol, triglyceride, lipoprotein, apolipoprotein, and density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, increase HDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein A. | [68] | ||
| Osteoporosis | Total lignans | Primary cultures of rat osteoblasts | Ovariectomy rat model | 20, 40, or 80 mg/kg/day; 300 μg/mL |
Anti-osteoporosis, prevent OVX-induced decrease of bone mass and deterioration of trabecular microarchitecture | Induce primary osteoblastic cell proliferation and differentiation; Increase osteoprotegrin expression and decrease NF-κB ligand expression. |
[69] |
| EUE extract | Adolescent female rats | 30, 100 mg/kg | Increase longitudinal bone growth rate and enhance osteoblastogenesis | Promote chondrogenesis in the growth plate and increase BMP-2 and IGF-1. | [70] | ||
| 5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furaldehyde (5-HMF) | Rat bone mesenchymal stem cells (bMSCs) | 0.05, 0.10, and 0.20 mg/mL | Anti-osteoporosis; inhibit adipogenesis and enhance osteoblastogenesis | Increase ALP, COL1alpha1 (7 days only), OCN and OPN expression, decrease PPARgamma, FABP4, C/EBPalpha and LPL expression. | [71] | ||
| Pinoresinol 4′-O-β-d-glucopyranoside, pinoresinol di-O-β-d-glucopyranoside, aucubin, wogonin, baicalein, and α-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-4,2′,4′-trihydroxydihydrochalcone | MCF-7 cells; MDA-MB-231 cells; Hela cells | 10−6 M, 10−5 M, and 10−4 M | Prevent estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis | Activate ER-dependent transcription of estrogen target genes; Exhibit significant difference in ER subtype (α vs. β) selectivity; Proliferation effect on breast cancer cells mediated by the genomic action of Erα. Stimulation of endogenous estrogen-responsive genes (pS2). |
[72] | ||
| EUL extracts | Rat osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells | 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, and 100 µg/mL | Anti-osteoporosis, restrain cell oxidative damage and increase cell survival rate in a dose-dependent manner | Decrease the expression of caspases 3, 6, 7, and 9. | [73] | ||
| Insomnia | Astragalin; Eucommiol | KM mice | 5, 10 and 20 mg/kg; 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg |
Reduce spontaneous activity, increase sleep ratio, shorten sleep latency and lengthen sleep time; Reduce the convulsion rate and prolong convulsion latency. |
[74][75] | ||
| Hypertension | Total flavonoid | Human glioblastoma cells (U251, U87, HS683 and A172) | 0.5–32 μg/mL | Enhance the radiotherapy effect, decrease the cell viability, inhibit migration and invasion, | HIF-α/MMP-2 pathway and intrinsic apoptosis pathway. | [46] | |
| Male flower extract | Male spontaneously hypertensive rats, Sprague Dawley rats | 0.05, 0.10, 0.20 g/mL | Reduce blood pressure, promote the expression of ACE2 | Activate the ACE2-Ang-(1–7)-Mas signaling pathways. | [76] | ||
| EUL extract | Wistar-Kyoto rats | 5% (w/w, extract/high-fat diet) | Reduce blood pressure, prevent aortic media hypertrophy | [11] | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | EUE extract | Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rat model | 1.4 g/kg | Reduce the level of plasma glucose | Prohibit the reduction of superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity; Suppress the elevation of malondialdehyde (MDA). |
[77] | |
| EUL extract and EUL powder | HFD-induced male SD rats | 3%, 9% EUL 3%, 9% EGLP |
Improve insulin resistance and decrease plasma glucose level, reduce the production of ATP and the level of triacylglyceride, and regulate fatty acid oxidation | Enhance the use of circulating blood glucose in skeletal muscles. | [78] | ||
| Asperuloside | HFD-induced male SD rats | 0.03, 0.1, 0.3 ASP; 5% ELE | Reduce body weight, visceral fat, food intake, and circulating levels of glucose, insulin, triacylglyceride and nonesterified fatty acid | Increase mRNA levels of Cs, Idh3α, Ogdh, Sdha, Comp I, Comp IV, and Comp V in skeletal muscles; Reduce ATP production in WAT; Increase mRNA level of FA transport protein, Cpt1α and Acadvl, suppress Fas mRNA, and activate FA β-oxidation. | [79] | ||
| 5% chlorogenic acids contained in ELE | HepG2 cells | 200, 400, 500 μg/mL | Promote glucose uptake | Inhibit glucose-6-phosphate displacement enzyme and α-glucosidase. | [80] | ||
| E. ulmoides | STZ induced- type 1-like DM rats | 1 g/kg/day oral administration | Decrease the level of blood urea nitrogen and creatinine, improve renal fibrosis, without influencing blood glucose level | Inhibit TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway and suppress expression of TGF-β/connective tissue growth factor. | [81] | ||
| EUE extract | STZ-induced mice | 200 mg/kg oral administration | Inhibit production of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and AGEs receptors | Increase the Glo1 expression and activity; Elevate Nrf2 protein expression and reduce RAGE expression. |
[82] | ||
| Isoquercetin, 6″-O-acetyl-astragalin, kaempferol, quercetin, rutin, kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside, astragalin | Ribose-gelatin | 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100 μg/mL | Inhibit the formation of AGEs | Block the formation of CML and CMA. | [83] | ||
| Lignans | RF/6A cells | STZ-induced male C57BL/6 mice | 25, 50, 75, and 100 μg/mL | Protect endothelial function from AGEs injury and oxidative stress | Regulate Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. | [16] | |
| Lignans | RMCs (HBZY-1 cells) | 20, 40, and 80 mg/L | Inhibit the proliferation of mesangial cells | Reduce the mRNA expression of Col I, Col III, Col IV, and fibronectin; Reverse the elevation of aldose reductase. |
[84] | ||
| Obesity | Asperuloside | Male C57BL/6J mice | 0.25% (w/w) | Reduce liver, epididymal, and mesenteric white adipose tissue, decrease serum triglyceride level |
Increase Akkermansia, Parabacteroides, Bacteroides, Sutterella, Anaerostipes, Roseburia, and Coprobacillus abundance Change metabolic level of cecum, Inhibit GLP-1; Reduce the level of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1), and collagen type 1 alpha1 (Col1a1) Increase lipoprotein lipase (Lpl) and carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 (Cpt1). |
[85] | |
| EUL extract Asperuloside |
HFD-induced male SD rats | 0.03, 0.1, 0.3 ASP; 5% ELE | ASP reduce the body weight, visceral fat, food take, triacylglyceride and nonestesterified fatty acid | Diminish dehydrogenase;Increase Glut4, succinyl CoA synthase; Increase mRNA levels of Cs, Idh3α, Ogdh, Sdha, Comp I, Comp IV and Comp V in skeletal muscles; Increase uncoupling protein 1 in brown adipose tissue mRNA;Reduce ATP production in WAT; Increase mRNA level of FA transport protein, Cpt1α and Acadvl, suppress Fas mRNA, and activate FA β-oxidation. |
[79] | ||
| Quercetin | Reduce fat accumulation in liver | Decrease the level of plasma lipid. | [86] | ||||
| ELE, ELE aroma | Male SD rats | 5% ELE | Promote metabolism of lipid | Elevate the level of Cpt2, Acad, complex II and V mRNA in liver; Increase expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, protein kinase, and phospholipase Cγ in hypothalamus. |
[87] | ||
| ELE extract | Male Wistar-Kyoto rats | 5% ELE | Reduce the body weight gain, visceral and perirenal fat | [11] | |||
| CGA-enriched extract from EUE | HepG2 cells | 10, 20, 25, 40, 60, and 80 mg/L | Reduce the lipid in HepG2 cells | Elevate the expression of ABCA1, CYP7A1, and AMPKα2; Reduce the level of SREBP2 and inhibit mRNA and expression of HMGCR. |
[67] | ||
References
- Anderson, W.R.; Cronquist, A. An integrated system of classification of flowering plants. Brittonia 1982, 34, 268–270.
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Bai, X.; Wang, N.; Liu, S. Study advancement about chemical composition and pharmacological effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2012, 33, 378–382.
- Wang, J.J.; Qin, X.M.; Gao, X.X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, P.Y.; Hao, J.Q.; Du, G.H. Research progress on chemical compounds, pharmacological action, and quality status of Eucommia ulmoides. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2019, 48, 3228–3237.
- Du, H.Y. Green Book of Eucommia Industry: Report on Development of China’s Eucommia Rubber Resources and Industry; Social Sciences Academic Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Nakazawa, Y.; Toda, Y. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.(Eucommiaceae): In vitro culture and the production of iridoids, lignans, and other secondary metabolites. In Medicinal and Aromatic Plants VIII; Bajaj, Y.P.S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; Volume 33, pp. 215–231.
- He, X.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Hao, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; He, R.; Tao, R. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.: Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 78–92.
- Feng, H.; Zhou, H.H.; Ouyang, D.S. Chemical constituents and pharmacology of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 20, 713–720.
- National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 1.
- Ministry of Health and Welfare. Taiwan Herbal Pharmacopeia, 3rd ed.; Ministry of Health and Welfare: Taipei, Taiwan, 2018.
- Wang, C.Y.; Tang, L.; He, J.W.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.Z. Ethnobotany, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Properties of Eucommia ulmoides: A Review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 259–300.
- Hosoo, S.; Koyama, M.; Watanabe, A.; Ishida, R.; Hirata, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yamasaki, H.; Wada, K.; Higashi, Y.; Nakamura, K. Preventive effect of Eucommia leaf extract on aortic media hypertrophy in Wistar-Kyoto rats fed a high-fat diet. Hypertens. Res. 2017, 40, 546–551.
- Bai, M.M.; Shi, W.; Tian, J.M.; Lei, M.; Kim, J.H.; Sun, Y.N.; Kim, Y.H.; Gao, J.M. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory components from the leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver (duzhong). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2198–2205.
- Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; He, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Dong, L.; Wang, C. Post-screening characterisation and in vivo evaluation of an anti-inflammatory polysaccharide fraction from Eucommia ulmoides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 169, 304–314.
- Cho, S.; Hong, R.; Yim, P.; Yeom, M.; Lee, B.; Yang, W.M.; Hong, J.; Lee, H.S.; Hahm, D.H. An herbal formula consisting of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill, Lycium chinense Mill and Eucommia ulmoides Oliv alleviates disuse muscle atrophy in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 213, 328–339.
- Luo, D.; Or, T.C.; Yang, C.L.; Lau, A.S. Anti-inflammatory activity of iridoid and catechol derivatives from Eucommia ulmoides Oliver. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 855–866.
- Liu, B.; Li, C.P.; Wang, W.Q.; Song, S.G.; Liu, X.M. Lignans Extracted from Eucommia Ulmoides Oliv. Protects Against AGEs-Induced Retinal Endothelial Cell Injury. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2044–2054.
- Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Hou, Z.; Gao, D.; Gao, Q.; Song, L. The simple neuroendocrine-immune regulatory network in oyster Crassostrea gigas mediates complex functions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26396.
- Ashley, N.T.; Demas, G.E. Neuroendocrine-immune circuits, phenotypes, and interactions. Horm. Behav. 2017, 87, 25–34.
- Verburg-van Kemenade, B.M.L.; Cohen, N.; Chadzinska, M. Neuroendocrine-immune interaction: Evolutionarily conserved mechanisms that maintain allostasis in an ever-changing environment. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 66, 2–23.
- Kerage, D.; Sloan, E.K.; Mattarollo, S.R.; McCombe, P.A. Interaction of neurotransmitters and neurochemicals with lymphocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 332, 99–111.
- Allen, M.J.; Sharma, S. Physiology, Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022.
- Procaccini, C.; Pucino, V.; De Rosa, V.; Marone, G.; Matarese, G. Neuro-endocrine networks controlling immune system in health and disease. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 143.
- Ye, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, G.; Zheng, J.C. IL-1beta and TNF-alpha induce neurotoxicity through glutamate production: A potential role for neuronal glutaminase. J. Neurochem. 2013, 125, 897–908.
- Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Hu, M.; Tian, L.; Yang, J.; Xing, W.; Zhang, W.; et al. Neuroprotection by IFN-gamma via astrocyte-secreted IL-6 in acute neuroinflammation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 40065–40078.
- Rovet, J.F. The role of thyroid hormones for brain development and cognitive function. In Paediatric Thyroidology; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 26, pp. 26–43.
- Hayashi, R.; Kasahara, Y.; Hidema, S.; Fukumitsu, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Nishimori, K. Oxytocin ameliorates impaired behaviors of high fat diet-induced obese mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 379.
- Geng, C.H.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Ma, R.Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.H. Arginine vasopressin improves the memory deficits in Han Chinese patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Peptides 2017, 97, 8–15.
- Cruz-Topete, D.; Cidlowski, J.A. One hormone, two actions: Anti- and pro-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. Neuroimmunomodulation 2015, 22, 20–32.
- Villa, A.; Rizzi, N.; Vegeto, E.; Ciana, P.; Maggi, A. Estrogen accelerates the resolution of inflammation in macrophagic cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15224.
- Maseroli, E.; Cellai, I.; Filippi, S.; Comeglio, P.; Cipriani, S.; Rastrelli, G.; Rosi, M.; Sorbi, F.; Fambrini, M.; Petraglia, F.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of androgens in the human vagina. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2020, 65, 109–124.
- Priyanka, H.P.; Nair, R.S. Strategies to overcome neuroendocrine immune deficits in aging: Role of neuroendocrine-immune modulators and bioactive plant extracts. Turk. J. Immunol. 2019, 7, S99–S107.
- Jiang, S.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Hu, L.P.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, J.; Gu, J.R.; Zhang, Z.G. Systemic regulation of cancer development by neuro-endocrine-immune signaling network at multiple levels. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 586757.
- Silverman, M.N.; Heim, C.M.; Nater, U.M.; Marques, A.H.; Sternberg, E.M. Neuroendocrine and immune contributors to fatigue. PM R 2010, 2, 338–346.
- Padro, C.J.; Sanders, V.M. Neuroendocrine regulation of inflammation. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 357–368.
- Syzon, O.; Voznyak, I.; Dashko, M. Features of some clinical examination parameters in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Wiad. Lek. 2017, 70, 205–207.
- Jara, L.J.; Medina, G.; Saavedra, M.A.; Vera-Lastra, O.; Torres-Aguilar, H.; Navarro, C.; del Mercado, M.V.; Espinoza, L.R. Prolactin has a pathogenic role in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 512–523.
- Bellavance, M.A.; Rivest, S. The neuroendocrine control of the innate immune system in health and brain diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 248, 36–55.
- Oglodek, E.; Szota, A.; Just, M.; Mos, D.; Araszkiewicz, A. The role of the neuroendocrine and immune systems in the pathogenesis of depression. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 776–781.
- Bilbo, S.D.; Klein, S.L. Special Issue: The neuroendocrine-immune axis in health and disease. Horm. Behav. 2012, 62, 187–190.
- Procaccini, C.; La Rocca, C.; Carbone, F.; De Rosa, V.; Galgani, M.; Matarese, G. Leptin as immune mediator: Interaction between neuroendocrine and immune system. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 66, 120–129.
- Deckx, N.; Lee, W.P.; Berneman, Z.N.; Cools, N. Neuroendocrine immunoregulation in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 705232.
- Sturmberg, J.P.; Bennett, J.M.; Martin, C.M.; Picard, M. ‘Multimorbidity’ as the manifestation of network disturbances. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2017, 23, 199–208.
- Straub, R.H.; Cutolo, M.; Buttgereit, F.; Pongratz, G. Energy regulation and neuroendocrine-immune control in chronic inflammatory diseases. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 267, 543–560.
- Fisher, R.E.; Steele, M.; Karrow, N.A. Fetal programming of the neuroendocrine-immune system and metabolic disease. J. Pregnancy 2012, 2012, 792934.
- Shao, P.; Zhang, J.F.; Chen, X.X.; Sun, P.L. Microwave-assisted extraction and purification of chlorogenic acid from by-products of Eucommia Ulmoides Oliver and its potential anti-tumor activity. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4925–4934.
- Wang, Y.; Tan, X.; Li, S.; Yang, S. The total flavonoid of Eucommia ulmoides sensitizes human glioblastoma cells to radiotherapy via HIF-alpha/MMP-2 pathway and activates intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 5515–5524.
- Yuan, D.; Shu, L.; Huang, R. Antitumor effects of total flavonoids of Eucommia ulmoides in tumorbearing mice. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 19, 1332–1336.
- Fujiwara, A.; Nishi, M.; Yoshida, S.; Hasegawa, M.; Yasuma, C.; Ryo, A.; Suzuki, Y. Eucommicin A, a beta-truxinate lignan from Eucommia ulmoides, is a selective inhibitor of cancer stem cells. Phytochemistry 2016, 122, 139–145.
- Qian, W.; Tan, A.; Lv, S.; Chen, B.; Du, A.; Wang, S. Pentacyclic triterpenoids from Eucommia ulmoides and their antitumor activities. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2019, 41, 1059–1065.
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q. Effect of Active Components of Eucommia Ulmoides Leaves on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 36, 284–287.
- In, M.-J.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, D.C. In vitro anticancer and antioxidant effects of acetone extract of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver leaves. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2018, 61, 119–124.
- Li, H.; Luo, Z.G. The mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides total polysaccharides EOP inhibit tumor cell proliferation through upregulating caspase3 expression in lung cancer cell line. Pract. J. Cancer 2018, 33, 1045–1048, 1060.
- Zeng, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D. Characterization of Nano Bamboo Charcoal Drug Delivery System for Eucommia ulmoides Extract and Its Anticancer Effect In vitro. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, 498–503.
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.L.; Lyu, L.; Dong, X.T. Effect of Eucommia ulmoides leaves extract on invasion and migration of colon cancer cells. Liaoning J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 45, 1019–1022, 1118.
- Kwon, S.H.; Ma, S.X.; Hwang, J.Y.; Ko, Y.H.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, B.R.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. The anti-inflammatory activity of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. bark. involves NF-kappaB suppression and Nrf2-dependent HO-1 induction in BV-2 microglial cells. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 268–282.
- Kwon, S.H.; Ma, S.X.; Hong, S.I.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. bark. attenuates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal cell death through inhibition of oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 173–182.
- Kwon, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ma, S.X.; You, I.J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Bark. protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced neuronal cell death in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 337–345.
- Kwon, S.H.; Ma, S.X.; Joo, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Inhibitory effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. bark on scopolamine-induced learning and memory deficits in mice. Biomol. Ther. 2013, 21, 462–469.
- Fan, S.; Yin, Q.; Li, D.; Ma, J.; Li, L.; Chai, S.; Guo, H.; Yang, Z. Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. In a Parkinson’s mouse model through the regulation of p38/JNK-Fosl2 gene expression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 260, 113016.
- Guo, H.; Shi, F.; Li, M.; Liu, Q.; Yu, B.; Hu, L. Neuroprotective effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. and its bioactive constituent work via ameliorating the ubiquitin-proteasome system. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 151.
- Zhou, Z.; Hou, J.; Mo, Y.; Ren, M.; Yang, G.; Qu, Z.; Hu, Y. Geniposidic acid ameliorates spatial learning and memory deficits and alleviates neuroinflammation via inhibiting HMGB-1 and downregulating TLR4/2 signaling pathway in APP/PS1 mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 869, 172857.
- Hu, W.; Wang, G.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Si, C.L.; He, J.; Long, W.; Bai, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X. Neuroprotective effects of macranthoin G from Eucommia ulmoides against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells via inhibiting NF-kappaB activation. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 108–116.
- Lee, G.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, S.A.; Shin, T.S.; Chae, H.J. Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract ameliorates steatosis induced by high-fat diet in rats by increasing lysosomal function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 426.
- Lee, H.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, M.R.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. Eucommia ulmoides Oliver extract, aucubin, and geniposide enhance lysosomal activity to regulate ER stress and hepatic lipid accumulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81349.
- Jin, C.F.; Li, B.; Lin, S.M.; Yadav, R.K.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. Mechanism of the inhibitory effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. cortex extracts (EUCE) in the CCl 4 -induced acute liver lipid accumulation in rats. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 751854.
- Lee, G.H.; Lee, M.R.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. Eucommia ulmoides cortex, geniposide and aucubin regulate lipotoxicity through the inhibition of lysosomal BAX. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88017.
- Hao, S.; Xiao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Mo, Z.T.; Chen, Y.; Peng, X.F.; Xiang, C.H.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, W.N. Chlorogenic acid-enriched extract from Eucommia ulmoides leaves inhibits hepatic lipid accumulation through regulation of cholesterol metabolism in HepG2 cells. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 251–259.
- Lei, Y.N.; Zhang, X.B. The total flavonoids from Eucommia ulmoides leaves on lowering blood lipid. J. Northwest Univ. 2015, 45, 777–780, 786.
- Zhang, R.; Pan, Y.L.; Hu, S.J.; Kong, X.H.; Juan, W.; Mei, Q.B. Effects of total lignans from Eucommia ulmoides barks prevent bone loss in vivo and in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 104–112.
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.I.; Song, M.; Lee, D.; Song, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.; Choi, H.Y.; Kim, H. Effects of Eucommia ulmoides extract on longitudinal bone growth rate in adolescent female rats. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 148–153.
- Tan, X.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Cai, J.P.; Zhu, L.H.; Ge, W.J.; Zhang, X. 5-(Hydroxymethyl)-2-furaldehyde inhibits adipogenic and enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat bone mesenchymal stem cells. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 529–532.
- Wang, H.; Li, M.C.; Yang, J.; Yang, D.; Su, Y.F.; Fan, G.W.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.M.; Paoletti, R. Estrogenic properties of six compounds derived from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. and their differing biological activity through estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 408–416.
- Lin, J.; Fan, Y.J.; Mehl, C.; Zhu, J.J.; Chen, H.; Jin, L.Y.; Xu, J.H.; Wang, H.M. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. antagonizes H2O2-induced rat osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 apoptosis by inhibiting expressions of caspases 3, 6, 7, and 9. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2011, 12, 47–54.
- Li, X.; Zhu, W.; Yang, L.; Fei, D.; Fan, J.; Du, L.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of the sedative and hypnotic effects of Eucommiol in Eucommia. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 1657–1659.
- Li, X.; Tang, Z.; Fei, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, S. Evaluation of the sedative and hypnotic effects of astragalin isolated from Eucommia ulmoides leaves in mice. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2072–2076.
- Ding, Z.J.; Liang, C.; Wang, X.; Yao, X.; Yang, R.H.; Zhang, Z.S.; He, J.J.; Du, H.Y.; Fang, D.; Li, Q. Antihypertensive Activity of Eucommia Ulmoides Oliv: Male Flower Extract in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 6432173.
- He, K.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Huang, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, P.; Deng, Y.; Jin, Q.; Shi, Q.; et al. Evaluation of antidiabetic potential of selected traditional Chinese medicines in STZ-induced diabetic mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1135–1142.
- Fujikawa, T.; Hirata, T.; Wada, A.; Kawamura, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Fujimura, K.; Ueda, T.; Yurugi, Y.; Soya, H.; Nishibe, S. Chronic administration of Eucommia leaf stimulates metabolic function of rats across several organs. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1868–1877.
- Fujikawa, T.; Hirata, T.; Hosoo, S.; Nakajima, K.; Wada, A.; Yurugi, Y.; Soya, H.; Matsui, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Ogata, M.; et al. Asperuloside stimulates metabolic function in rats across several organs under high-fat diet conditions, acting like the major ingredient of Eucommia leaves with anti-obesity activity. J. Nutr. Sci. 2012, 1, e10.
- Li, X.Z.; Zhang, S. Effervescent Granules Prepared Using Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. and Moso Bamboo Leaves: Hypoglycemic Activity in HepG2 Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 6362094.
- Niu, H.S.; Liu, I.M.; Niu, C.S.; Ku, P.M.; Hsu, C.T.; Cheng, J.T. Eucommia bark (Du-Zhong) improves diabetic nephropathy without altering blood glucose in type 1-like diabetic rats. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 971–978.
- Do, M.H.; Hur, J.; Choi, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.; Ha, S.K. Eucommia ulmoides ameliorates glucotoxicity by suppressing advanced glycation end-products in diabetic mice kidney. Nutrients 2018, 10, 265.
- Sugawa, H.; Ohno, R.; Shirakawa, J.; Nakajima, A.; Kanagawa, A.; Hirata, T.; Ikeda, T.; Moroishi, N.; Nagai, M.; Nagai, R. Eucommia ulmoides extracts prevent the formation of advanced glycation end products. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2566–2573.
- Li, Z.Y.; Deng, X.L.; Huang, W.H.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Jing, X.; Tian, Y.Y.; Lv, P.Y.; Yang, T.L.; Zhou, H.H.; et al. Lignans from the bark of Eucommia ulmoides inhibited Ang II-stimulated extracellular matrix biosynthesis in mesangial cells. Chin. Med. 2014, 9, 8.
- Nakamura, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Benegiamo, G.; Hirayama, A.; Zhu, Q.; Kitamura, N.; Sugizaki, T.; Morimoto, K.; Itoh, H.; et al. Asperuloside Improves Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes through Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Signaling. iScience 2020, 23, 101522.
- Lai, L.L.; Lu, H.Q.; Li, W.N.; Huang, H.P.; Zhou, H.Y.; Leng, E.N.; Zhang, Y.Y. Protective effects of quercetin and crocin in the kidneys and liver of obese Sprague-Dawley rats with type 2 diabetes: Effects of quercetin and crocin on T2DM rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 661–672.
- Oikawa, H.; Miyazaki, S.; Kurata, R.; Hattori, M.; Hayashi, N.; Kawaguchi, N.; Hirata, T.; Ueda, T.; Fujikawa, T. Eucommia leaf extract induces BDNF production in rat hypothalamus and enhances Lipid metabolism and aerobic glycolysis in rat liver. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 234–244.
More
Information
Subjects:
Pharmacology & Pharmacy
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
824
Entry Collection:
Neurodegeneration
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
22 Jun 2022
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




