
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jarred Cain Lloyd | -- | 1068 | 2022-04-16 06:49:04 | | | |
| 2 | Jarred Cain Lloyd | Meta information modification | 1068 | 2022-04-16 06:50:19 | | | | |
| 3 | Lindsay Dong | Meta information modification | 1068 | 2022-04-18 03:01:02 | | |
Video Upload Options
The Adelaide Superbasin is a series of geologically related rift to passive margin sedimentary basins formed during the Neoproterozoic to Cambrian. They are located at the south-eastern margin of Proterozoic Australia.
1. Introduction
2. Geologic History
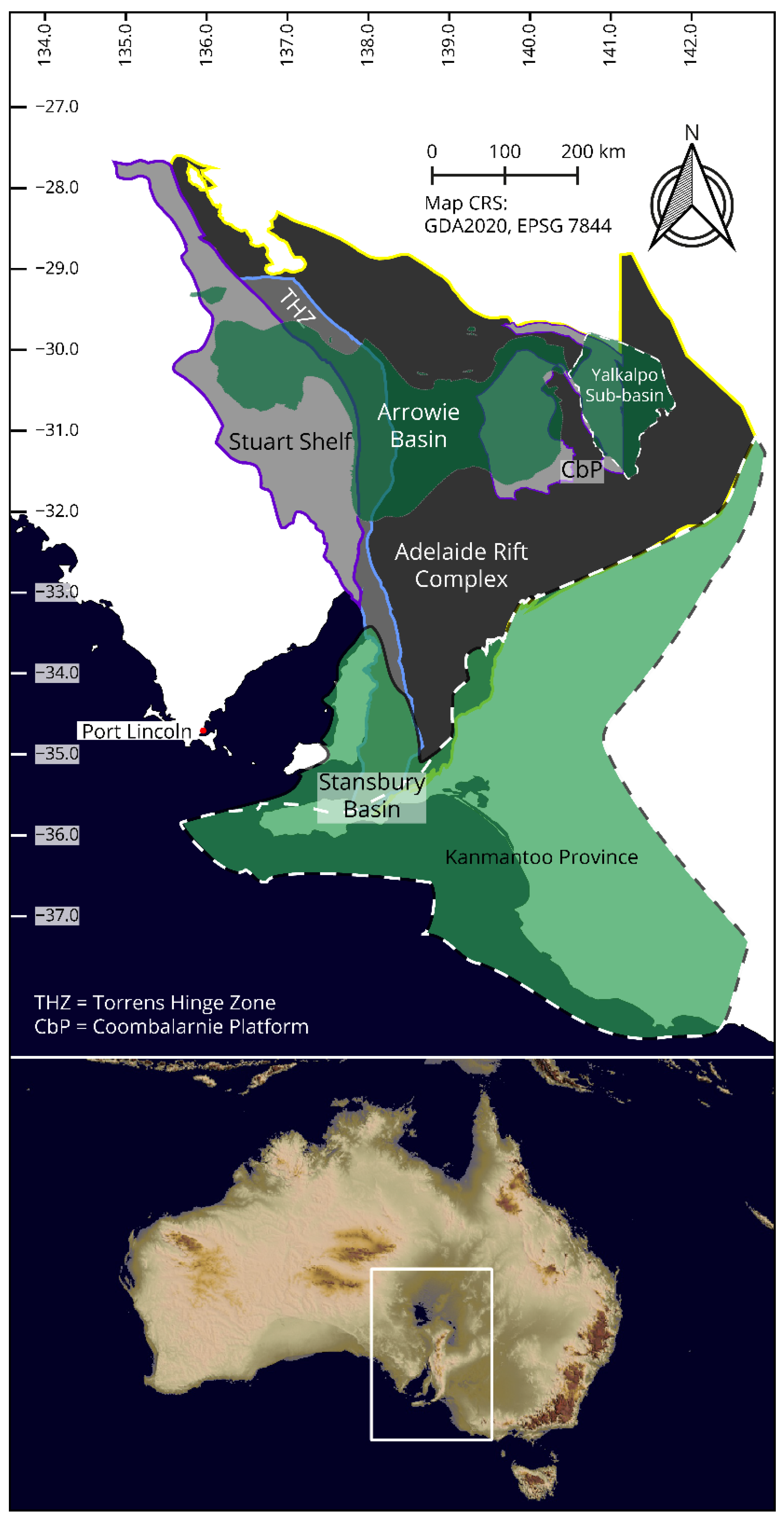
3. Basin Hierarchy
3.1. Adelaide Rift Complex
The Adelaide Rift Complex is the oldest and most central part of the Adelaide Superbasin. It is a series of rift troughs and passive margin depocentres that have a protracted development from c. 890 Ma to c. 550 Ma. The Warrina and Hesyen Supergroups form the rocks of this part of the basin, being separated from the Cambrian Moralana Supergoup by a basin wide unconformity.
3.2. Stuart Shelf
The Stuart Shelf is a region of platform deposits in the western portion of the Adelaide Superbasin that overlie the Gawler Craton. Limited deposition occured during the early development of the Adelaide Superbasin, with a significant hiatus until the late Neoproterzoic when a period of marine transgression occured. The rocks of the Stuart Shelf remain relatively undeformed to this day.
3.3. Coombalarnie Platform
The Coombalarnie Platform is a second region of platformal deposits that lie in the north-east of the Adelaide Superbasin, overlying the Curnamona Province. This region only experienced deposition after a transgression ocurring in the late Neoproterozoic.
3.4. Stansbury Basin
The Stansbury Basin is one of the two known Cambrian basins of the Adelaide Superbasin. It is exposed in the south of the superbasin, extending from Kangaroo Island and the Mount Lofty Ranges toward Victoria underneath the Murray Basin. The true eastward extent of this basin is not well understood and is a focus of current geological research in South Australia. It is likely that deposition was continuous with the Arrowie Basin to the north [17]. The Kanmantoo Province is a subdivision of the Stansbury Basin forming it's southern and eastern areas.
3.5. Arrowie Basin
The Arrowie Basin is the second of the two known Cambrian basins of the Adelaide Superbasin. It extends from the Stuart Shelf in the west of the superbasin, across the Flinders Ranges to western New South Wales. The Yalkalpo Sub-basin is in the easternmost areas of the Arrowie Basin, bound to it's west by the Benagerie Ridge of the Curnamona Province.
4. Lithostratigraphic Division
The lithostratigraphy of the Adelaide Superbasin is divided into three supergroups, with numerous group and subgroup level divisions. The lowermost and oldest supergroup is the Warrina Supergroup [19], this is further divided into the Callanna Group and Burra Group which have numerous subgroup divisions. The rocks of the Callanna Group are mostly mostly coarse siliclastic rocks to cyclic, evaporitic mixed carbonate and siliclastic rocks with pulses of mafic igneous rocks, and minor bidmodal igneous rocks. The Burra Group is made of mostly siliciclastic and carbonate rocks with minor bimodal igneous rocks in the lower portions of the group. The Heysen Supergroup [19] overlies the Warrina Supergroup, and is separated by a basin wide erosional unconformity caused by the Sturtian glaciation. The Heysen Supergroup is divided into the Umberatana Group and Wilpena Group, with numerous subgroup divisions. The Umberatana Group is mostly made of siliciclastic rocks, with several carbonate rocks as well. These rocks represent two glacial periods and a corresponding interglacial period. The overlying WIlpena Group is primarily made of siliciclastic rocks with and overall regressive base level trend. The Moralana Supergroup [19] is the uppermost high-level stratigraphic division of the Adelaide Superbasin and is comprised of all the Cambrian rocks within the superbasin.
References
- Lloyd, J.C.; Blades, M.L.; Counts, J.W.; Collins, A.S.; Amos, K.J.; Wade, B.P.; Hall, J.W.; Hore, S.; Ball, A.L.; Shahin, S.; et al. Neoproterozoic geochronology and provenance of the Adelaide Superbasin. Precambrian Res. 2020, 350, 105849.
- Bogdanova, S.V.; Pisarevsky, S.A.; Li, Z.-X. Assembly and Breakup of Rodinia (Some results of IGCP project 440). Stratigr. Geol. Correl. 2009, 17, 259–274.
- Cawood, P.A.; Strachan, R.A.; Pisarevsky, S.A.; Gladkochub, D.P.; Murphy, J.B. Linking collisional and accretionary orogens during Rodinia assembly and breakup: Implications for models of supercontinent cycles. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 449, 118–126.
- Li, Z.-X.; Bogdanova, S.V.; Collins, A.S.; Davidson, A.; De Waele, B.; Ernst, R.E.; Fitzsimons, I.C.W.; Fuck, R.A.; Gladkochub, D.P.; Jacobs, J.; et al. Assembly, configuration, and break-up history of Rodinia: A synthesis. Precambrian Res. 2008, 160, 179–210.
- Merdith, A.S.; Williams, S.E.; Müller, R.D.; Collins, A.S. Kinematic constraints on the Rodinia to Gondwana transition. Precambrian Res. 2017, 299, 132–150.
- Brookfield, M.E. Neoproterozoic Laurentia-Australia fit. Geology 1993, 21, 683–686.
- Dalziel, I.W.D. OVERVIEW: Neoproterozoic-Paleozoic geography and tectonics: Review, hypothesis, environmental speculation. GSA Bull. 1997, 109, 16–42.
- Hoffman, P.F. Did the Breakout of Laurentia Turn Gondwanaland Inside-Out? Science 1991, 252, 1409–1412.
- Karlstrom, K.E.; Harlan, S.S.; Williams, M.L.; McLelland, J.; Geissman, J.W.; Ahäll, K.-I. Refining Rodinia: Geologic evidence for the Australia-western US connection in the Proterozoic. GSA Today 1999, 9, 1–7.
- Moores, E.M. Southwest U.S.-East Antarctic (SWEAT) connection: A hypothesis. Geology 1991, 19, 425–428.
- Wingate, M.T.D.; Pisarevsky, S.A.; Evans, D.A.D. Rodinia connections between Australia and Laurentia: No SWEAT, no AUSWUS? Terra Nova 2002, 14, 121–128.
- Li, Z.-X.; Zhang, L.; Powell, C.M. South China in Rodinia: Part of the missing link between Australia–East Antarctica and Laurentia? Geology 1995, 23, 407–410.
- Wen, B.; Evans, D.A.D.; Li, Y.-X. Neoproterozoic paleogeography of the Tarim Block: An extended or alternative “missing-link” model for Rodinia? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 458, 92–106.
- Wen, B.; Evans, D.A.D.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.-X.; Jing, X. A positive test for the Greater Tarim Block at the heart of Rodinia: Mega-dextral suturing of supercontinent assembly. Geology 2018, 46, 687–690.
- Sprigg, R.C. Sedimentation in the Adelaide Geosyncline and the formation of the continental terrace. In Sir Douglas Mawson Anniversary Volume; Glaessner, M.F., Sprigg, R.C., Eds.; The University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 1952; pp. 153–159.
- Callen, R.A. Curnamona; Department of Mines and Energy: Adelaide, Australia, 1990; p. 56.
- Preiss, W.V.; Alexander, E.M.; Cowley, W.M.; Schwarz, M.P. Towards defining South Australia’s geological provinces and sedimentary basins. MESA J. 2002, 27, 39–52.
- Mulder, J.A.; Berry, R.F.; Halpin, J.A.; Meffre, S.; Everard, J.L. Depositional age and correlation of the Oonah Formation: Refining the timing of Neoproterozoic basin formation in Tasmania. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 65, 391–407.
- Preiss, W.V. The Adelaide Geosyncline of South Australia and its significance in Neoproterozoic continental reconstruction. Precambrian Res. 2000, 100, 21–63.
- Drexel, J.F.; Preiss, W.V. (Eds.) The Geology of South Australia; Geological Survey of South Australia: Adelaide, Australia, 1995; Volume 2.
- Foden, J.D.; Elburg, M.A.; Dougherty-Page, J.; Burtt, A. The timing and duration of the Delamerian orogeny: Correlation with the Ross Orogen and implications for Gondwana assembly. J. Geol. 2006, 114, 189–210.
- Foden, J.D.; Elburg, M.A.; Turner, S.; Clark, C.; Blades, M.L.; Cox, G.; Collins, A.S.; Wolff, K.; George, C. Cambro-Ordovician magmatism in the Delamerian orogeny: Implications for tectonic development of the southern Gondwanan margin. Gondwana Res. 2020, 81, 490–521.





