Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pilar Pérez Romero | + 2692 word(s) | 2692 | 2022-03-11 06:52:37 | | | |
| 2 | Rita Xu | Meta information modification | 2692 | 2022-03-21 02:55:52 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Pérez Romero, P. Potential Coding of Human Cytomegalovirus. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/20744 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Pérez Romero P. Potential Coding of Human Cytomegalovirus. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/20744. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Pérez Romero, Pilar. "Potential Coding of Human Cytomegalovirus" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/20744 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Pérez Romero, P. (2022, March 18). Potential Coding of Human Cytomegalovirus. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/20744
Pérez Romero, Pilar. "Potential Coding of Human Cytomegalovirus." Encyclopedia. Web. 18 March, 2022.
Copy Citation
Human cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a large envelope worldwide prevalent betaherpesvirus, ranging from 45% to 100% in the general population based on socio-economic factors. CMV is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised individuals that will benefit from the availability of a vaccine. Despite the efforts made during the last decade, no CMV vaccine is available. An ideal CMV vaccine should elicit a broad immune response against multiple viral antigens including proteins involved in virus-cell interaction and entry. However, the therapeutic use of neutralizing antibodies targeting glycoproteins involved in viral entry achieved only partial protection against infection.
cytomegalovirus
pangenome
proteome
1. Introduction
Although CMV generally causes asymptomatic infections in immunocompetent individuals, it is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised individuals such as organ transplant recipients, AIDS, and with congenital infection [1][2][3][4][5].
The CMV genome (236 kb) consists of a unique long (UL) and a unique short (US) region flanked by inverted repeats. CMV gene expression occurs with the expression of immediate-early genes followed by early, early-late and late transcripts [6]. In addition to the 165 canonical ORFs [7][8], CMV genome encodes for other alternative transcripts in addition to have non-canonical translation initiation sites [9][10]. Furthermore, CMV encodes for a large number of genes, many of them with unknown functions that may probably be involved in key processes during host-cell interaction [11].
CMV is able to infect a high number of cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial cells, epithelial cells and myeloid lineage cells, among others [12][13]. CMV is a highly complex virus with multiple proteins embedded in the viral envelope, with at least four distinct types of covalently linked glycoprotein complexes required for CMV infectivity including gCI complex (gB dimer), gCII complex (gM, gN), gCIII complex (trimer gH, gL, gO) and pentameric complex (gH/gL/UL128-131) [14][15]. The therapeutic use of neutralizing antibodies, targeting glycoproteins mediating viral entry, have demonstrated to only achieve partial protection against CMV infection [16][17][18][19][20][21]. One possible explanation if that other proteins may be involved in viral entry that might be also necessary to target in order to elicit a complete protection against infection. An ideal vaccine against CMV infection should elicit a broad immune response, including both neutralizing antibody and T-cell response, against multiple viral antigens including proteins involved in virus-cell interaction and entry [22][23], which may increase efficacy compared with the previously tested vaccines [24][25][26][27]. In fact, despite the efforts made during the last decade, no CMV vaccine is still available [16][26][28][29]. Thus, understanding the complete repertoire of CMV proteins involved in cell entry may also help to determine the neutralizing response necessary to block infection and may provide novel candidates that could be included in new vaccines design.
2. Identification of Putative Transmembrane Proteins
To determine the transmembrane regions of the proteins encoded by the CMV genome, the genome of nine different CMV strains including both clinical and laboratory strains (Table 1) were analyzed using three different bioinformatic methods: Phobius, PureseqTM and TMHMM. A description of the methodological approach used is represented in Figure 1. CMV is known to accumulate mutations quite rapidly in cell culture during cell passaging [30]. In order to test to what level these nine selected CMV strains are representative of the 335 available CMV genomes in GenBank, the 56190 ORFs were aligned with the ORFs in their CMV dataset. Researchers obtained 100% median percentage identity and breadth coverage (overlapping distance), representing 99.95% of the total ORFs from the Human betaherpesvirus 5 in the NCBI database.
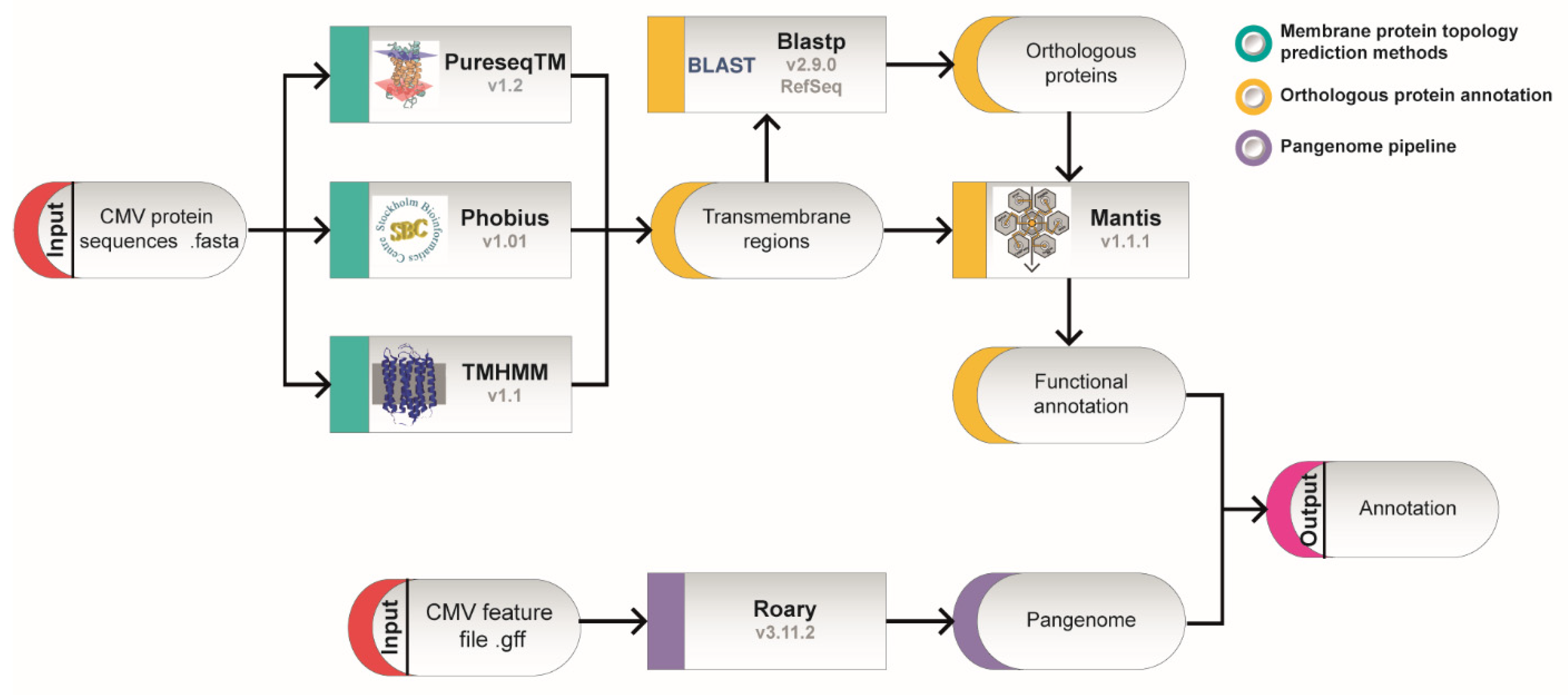
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the applied workflow. Fasta format protein sequences from nine CMV genomes were analyzed in parallel to predict transmembrane domains and to create an entire set of genes from all strains (pangenome). Transmembrane topology was studied following three different approaches: PureseqTM, Phobius and TMHMM, under default parameters. Predicted transmembrane proteins were compared with orthologous proteins identified by BLAST with the whole Mantis database for the prediction of functional annotation. Proteins that were common to all nine genome datasets formed the core protein set, and functions were annotated accordingly for each transmembrane protein.
Table 1. Characteristics of CMV strains used in this study and their corresponding accession number at nucleotide database.
| CMV Strains | Isolation Source | Number of Culture Passages | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| AD169 | Adenoids of a 7-year-old girl | Many times in human fibroblasts | FJ527563.1 |
| Towne | Urine of a 2-month-old infant with microcephaly and hepatosplenomegaly | Many times in human fibroblasts | FJ616285.1 |
| Toledo | Urine from a congenitally infected infant | Several times in human fibroblasts | GU937742.2 |
| TR | Vitreous humor from eye of HIV-positive male | Several times in human fibroblasts | KF021605.1 |
| VR7863 | Urine samples of a congenitally infected neonate and cultured in endothelial and epithelial cells | Cultured in endothelial and epithelial cells | KX544838.1 |
| TB40-E_UNC | Throat swab of a bone marrow transplant patient | Cultured adapted | KX544839.1 |
| HANSCTR4 | Blood from stem cell transplant recipient (D-R+) | Sequenced directly from clinical material via target enrichment | KY123653.1 |
| AD169-BAC20 | - | - | MN920393.1 |
| Merlin | Urine from a congenitally infected child | 3 times in human fibroblasts | NC006273.2 |
Based on the first analysis, researchers identified 94 proteins with potential transmembrane domains (Figure 2). Seventeen of them were not considered for further analysis because of the following reasons. Proteins UL74, UL115, UL47, UL49, UL76, US22, UL77, UL105, UL122 and UL89 were previously described not to be part of membrane structures [31][32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40]. UL47, UL49, UL76 and US22 proteins are known to be part of the tegument, UL77 is located in the capsid; UL105, UL122 and UL89 are found in the nucleus of the host cells [31][32][33][34][35][36][37][38]. In addition, UL4, UL22A and UL116, which were predicted to have one transmembrane domain, were discarded because the transmembrane domain corresponded to the sequence of signal peptide [41][42][43]. In addition, RL13TRL14 and US33 (TB40-E_UNC strain) or ORFL27C and ORFL49W.IORF1 (AD169-BAC20) proteins were only found in one of the CMV studied strains and were not considered for further analysis.
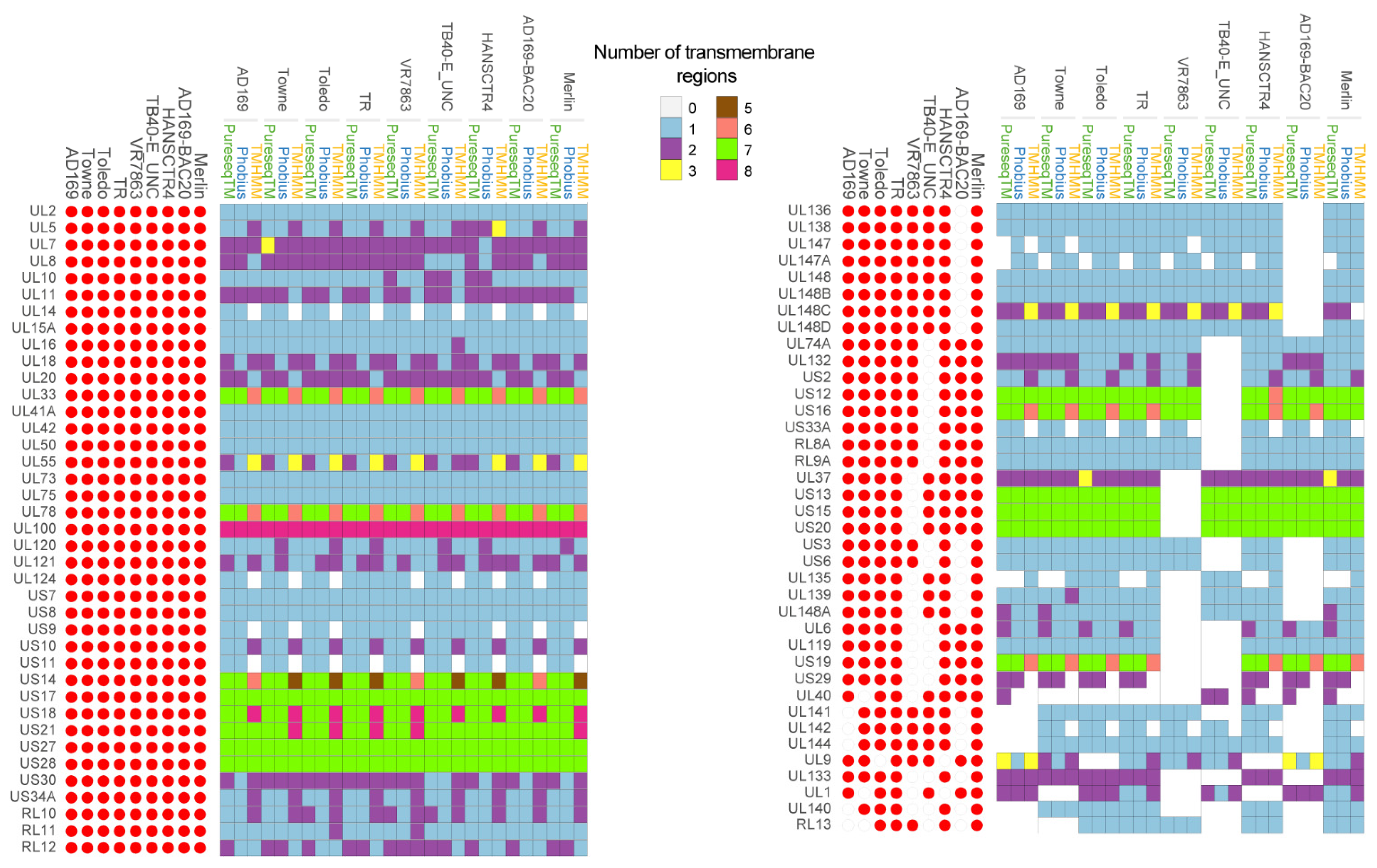
Figure 2. Predicted transmembrane proteins for the studied CMV genomes. Proteins with at least one predicted transmembrane domain with one of three tested methods were annotated as transmembrane proteins. The number of transmembrane domains for each protein was represented using the indicated chromatic scale ranging from zero to eight regions for each of the three methods used (PureseqTM, Phobius and TMHMM). For each strain, the presence of the gene was represented with the filled red circles and absent genes with empty red circles.
For further characterization of the 77 remaining proteins with predicted transmembrane (TM) domains, a systematic review was performed to search for any previous published information. A graphical representation of the number of predicted TM regions found for each ORF, in each of the nine strains with the indicated bioinformatics tool is shown in Figure 2. Of the 77 proteins analyzed, 33 (43%) proteins only had one TM domain, 23 (29.87%) had from 1 to 2 TM domains, 6 (7.7%) exhibited 1-3, while 15 proteins (19.48%) had from 5 to 8 TM domains. None of the analyzed proteins had four TM domains.
Nineteen out of the 77 proteins (UL2, UL6, UL9, UL14, UL15A, UL74A, UL120, UL121, UL140, UL148C, UL148D, US13, US15, US19, US29, US30, US33A, RL8A, RL9A and RL10) have no previously described function, 13 (UL1, UL5, UL8, UL10, UL20, UL42, UL78, UL124, UL139, UL147, US34A, RL12 and RL13) have been partially studied, 1 (UL41A) has previously been shown not to code for a protein [8] and the other 43 proteins have a previously described function (Table 2).
Table 2. CMV predicted transmembrane proteins indicating the cellular localization based on biotool Uniprop, the ascribed functions based on a bibliographic search and the number of predicted domains using the three different tools. (*) indicates unknown or non-verified function.
| Gene | Localization | Function | Number of TM Domains | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UL1 * | VM | Unknown. pUL1 could modulate CMV host cell tropism. | 1–2 | [44] |
| UL2 * | HM | Unknown. | 1 | - |
| UL5 * | V | Unknown. It is suggested to be involved in efficient viral assembly, propagation and replication. | 1–3 | [45][46] |
| UL6 * | HM | Unknown. | 1–2 | - |
| UL7 | UL7 is involved in immunomodulation. | 2–3 | [47][48][49] | |
| UL8 * | HM | UL8 decreases the release of a large number of pro-inflammatory factors later after infection of THP-1 myeloid cells. UL8 may exert an immunosuppressive role key for CMV survival in the host. | 1–2 | [50] |
| UL9 * | HM | Unknown function. Its deletion mutation cause enhanced growth in HFFs cells. |
1–3 | [7] |
| UL10 * | M | Unknown. Potential role in immunomodulation. | 1–2 | [51] |
| UL11 | HM, ERM | pUL11 interacts with CD45 phosphatase on T cells, inducing the IL-10 secretion. | 1–2 | [52] |
| UL14 * | HM | Unknown. | 0–1 | - |
| UL15A * | HM | Unknown. | 1 | - |
| UL16 | HM | Immunoevasion and inhibition of the activation of NK cells. | 1 | [53] |
| UL18 | HM | Immunomodulation and immunoevasion. | 1–2 | [54] |
| UL20 * | ERM | Unknown. UL20 could be destined to sequester cellular proteinases not known to date for degradation in lysosomes. | 1–2 | [55] |
| UL33 | HM | UL33 has homology with GPCR which activates different ligand-independent signalling pathways and also involved in virus dissemination. | 6–7 | [56][57][58] |
| UL37 | ERM, GM, MM | Viral replication. | 2–3 | [59][60] |
| UL40 | HM | Immunomodulation. | 0–2 | [61] |
| UL41A * | VM | Unknown. UL41A not to code for proteins. | 1 | [8] |
| UL42 * | HM, C | Unknown. Potential role in immunoevasion. | 1 | [62][63] |
| UL50 | HNM | Assembly, maturation and egress of virions. | 1 | [64] |
| UL55 | VM, HM, GM | Glycoprotein B participates in viral entry. | 1–3 | [65] |
| UL73 | VM, HM, GM | Glycoprotein N is involved in the binding of the virus to the host cell, viral spread and virion morphogenesis. | 1 | [66] |
| UL74A * | VM | Unknown | 1 | - |
| UL75 | HM, VM | Glycoprotein H participates in viral entry. It is part of the trimeric and pentameric complexes. |
1 | [67] |
| UL78 * | HM, ERM | Unknown. UL78 is a G protein-coupled receptor. | 6–7 | [68][69] |
| UL100 | HM, VM | Envelope glycoprotein M participates in viral entry. | 8 | [70][71] |
| UL119 | VM | Immunoevasion. | 1 | [72] |
| UL120 * | HM | Unknown. | 1–2 | - |
| UL121 * | HM | Unknown. | 1–2 | - |
| UL124 * | HM | Potential role in latency. | 0–1 | [73] |
| UL132 | VM | Essential for CMV assembly compartment formation and the efficient production of infectious particles. | 1–2 | [74] |
| UL133 | GM | UL133 forms a complex with UL138 and UL136. It is involved in the establishment of CMV latency. | 2 | [75] |
| UL135 | HM, GM | Immunomodulation. Post entry Tropism in Endothelial Cells. | 0–1 | [76][77] |
| UL136 | HM | Replication, latency, and dissemination. Post entry Tropism in Endothelial Cells. | 1 | [75][77][78][79] |
| UL138 | GM | Latency and DNA replication. | 1 | [80][81] |
| UL139 * | HM | Unknown. Potential role in immunomodulation. | 1–2 | [82] |
| UL140 * | HM | Unknown. | 1 | - |
| UL141 | ERM | Immunomodulation and DNA replication. | 1 | [83][84][85] |
| UL142 | ERM | Immunomodulation. | 0–1 | [86] |
| UL144 | HM | Inhibition of T-cell activation and latency. | 1 | [87][88] |
| UL147 * | EXR | Unknown. Potential role in immunomodulation. | 0–1 | [89] |
| UL147A | HM | Immunomodulation. | 0–1 | [90] |
| UL148 | ERM | Viral ER-resident glycoprotein that interacts with UL116 promoting the incorporation of gH/gL complexes into virions. | 1 | [91] |
| UL148A | HM | Immunoevasion of NK cells. | 1–2 | [92] |
| UL148B * | HM | Unknown. | 1 | [93] |
| UL148C * | HM | Unknown. | 0–3 | [93] |
| UL148D * | HM | Unknown. | 1 | [93] |
| US2 | ERM | Immunomodulation. | 1–2 | [94] |
| US3 | ERM | Immunoevasion. | 1 | [95] |
| US6 | ERM | Immunomodulation. | 1 | [96] |
| US7 | ERM | Immunoevasion. | 1 | [97] |
| US8 | ERM, GM | Immunomodulation. | 1 | [97] |
| US9 | ERM, GM, CK | Glycoprotein US9 is an antagonist of IFN signalling to persistently evade host innate antiviral responses. | 0–1 | [98] |
| US10 | ERM | Inhibition of the host immune response. | 1–2 | [99] |
| US11 | ERM | Inhibition of the host immune response. | 0–1 | [100] |
| US12 | HM | Inmunomodulation of NK cells activation. | 6–7 | [101] |
| US13 * | HM | Unknown. | 7 | - |
| US14 | HM | Inmunomodulation of NK cells activation. Potential role in virions maturation and egress. | 5–7 | [101][102] |
| US15 * | HM | Unknown. | 7 | - |
| US16 | HM, C | Tropism in endothelial and epithelial cells. | 6–7 | [103] |
| US17 | HM | Immunomodulation. | 7 | [104] |
| US18 | HM. | Immunoevasion of NK cell. | 7–8 | [105] |
| US19 * | HM | Unknown. Its delection affect NK cell activation. | 6–7 | [101] |
| US20 | M | Inhibition NK cell activation. Also participates in the viral replication process in endothelial cells. | 7 | [105][106] |
| US21 | HM | Viroporin that modulates calcium homeostasis and protects cells against apoptosis. | 7–8 | [107] |
| US27 | V, HM | Immunomodulation. Also is required for efficient viral spread by the extracellular route. | 7 | [108][109][110] |
| US28 | HM | Immunomodulation. Lytic and latent CMV infection. Possible role in regulation of the actin cytoskeleton or cytoskeletal remodelling. | 7 | [111][112] |
| US29 * | HM | Unknown. | 0–2 | - |
| US30 * | HM | Unknown. | 1–2 | - |
| US33A * | - | Unknown. | 0–1 | [113] |
| US34A * | HM. | Unknown. Potential target of SUMO complex. | 1–2 | [114] |
| RL8A * | HM | Unknown. | 1 | - |
| RL9A * | HM | Unknown. | 1 | - |
| RL10 * | VM | Unknown. | 1–2 | - |
| RL11 | HM | Immunomodulation. RL11 is a type I transmembrane glycoproteins which bind immunoglobulin G Fc. I | 1–2 | [115] |
| RL12 * | VM | Unknown. RL12 is a Fc binding protein. | 1–2 | [116] |
| RL13 * | VM | Unknown. Potential role in replication, immunoevasión and viral spread by cell-free or cell-to-cell mechanisms. | 1 | [117][118][119] |
* indicates unknown or non-verified function. CK: Cytoskeleton C: Cytoplasm, ERM: Host endoplasmic reticulum membrane, EXR: Extracellular region, GM: Golgi reticulum membrane, HM: host membrane, HMN: Host nucleus membrane, M: Membrane, MM: Mitochondrion membrane, V: Virion, VM: Virion membrane.
The number of predicted domains differed in some of the studied proteins when using different methods. The results obtained TMHMM method were the most divergent of the three tested methods. On the contrary, a group of proteins encoded by the genes UL33, UL78 and the genes from the unique short (US) region US12-US21, US27 and US28 proteins were predicted to have more than five TM regions by all three methods. In fact, TM regions of these genes, such as the members of US12 family and the proteins with homology to the chemokine receptor family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): US27 and US28, have been previously described supporting the results [107][108][120].
A validation experiment was carried out using as an example UL2 and UL124, two of the identified proteins with unknown function. The ORF encoding for these two proteins were cloned into a eukaryotic expression plasmid that included a Myc tag sequence in the 5´end of the clone products. After transfecting the HEK 293T mammalian cell line, plasma membrane proteins were extracted and the cytoplasmic (C) and plasma membrane (PM) protein fractions were tested by Western Blot using an anti Myc antibody.
3. Homology Analysis of thePredicted Transmembrane Proteins
In addition to the exhaustive systematic review of the literature, further analysis of sequence homology with known proteins from other organisms was performed using Mantis software. Based on this analysis, researchers found homologies for two of the proteins with unknown function. UL139 had some level of homology (e-value = 5.1 × 10−28) with proteins involved in cell adhesion, while UL15A had some homology (e value = 1.53 × 10−4) with a biotin permease protein. UL15A ORF was identified in all 9 CMV strains analyzed, while UL139 that was only present in the TR strain.
In addition, Mantis analysis shed an association of UL1 with a carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule, which is a cell adhesion receptor of the immunoglobulin-like superfamily. UL78 was also identified by Mantis as seven transmembrane receptor from the rhodopsin family. UL147 has been proposed by Mantis to be involved in immune response and chemokine activity and US33A seems to have a von Willebrand A (VWA) domain. However, US33A was present exclusively in Towne, Toledo, TR and VR7863 strains.
4. Sequence Differences among Strains
The analysis of the generated pangenome (Figure 2 and Figure 3), revealed wide differences among strains [11]. Clinical isolate VR7863 and TB40-E_UNC strains lacked a large number of genes compared to the other strains. The VR7863 strain lacked some genes with unknown functions such as UL1, UL6, UL139, UL140, US13, US15, US19 and US29 and other genes involved in immunoevasion, DNA packaging, latency or viral replication such as UL37, UL40, UL119, UL133, UL135, UL148A and US20 [38][59][60][61][72][75][76][92][105]. The TB40-E_UNC strain lacked some genes with unknown function such as UL6, UL74A, UL140, US12, US19, US29, US33A, RL8A, RL9A and RL13 and other genes involved in host immune response evasion, CMV assembly, tropism, or latency such as UL119, UL132, UL133, US2, US3 and US16 [72][74][94][95][101][103][117][118].
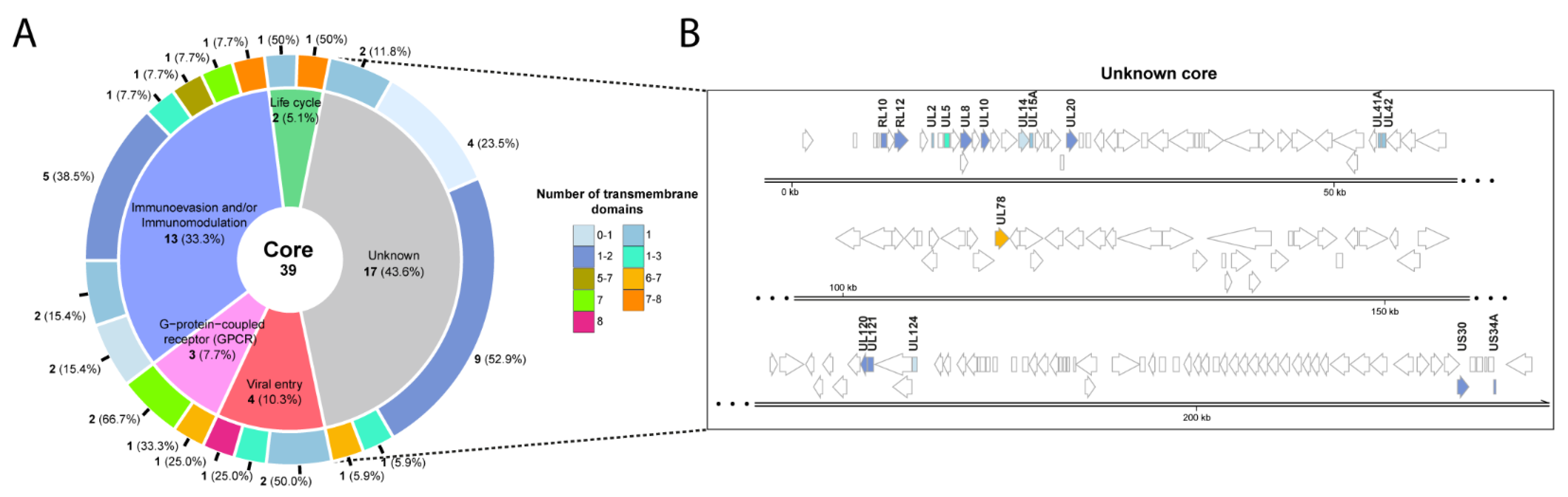
Figure 3. Functional analysis of the 39 core proteins. (A) Pie chart of the proteins found in all the studied strains were grouped based on their functions. For each group, the number of predicted transmembrane domains is also indicated. When the number of transmembrane domains predicted was different using the three methods, a range of values is shown. The number of proteins in each section is marked in blue and the percentage between brackets. (B) Genomic location of the 17 proteins with non-described function.
AD169 strain have a deletion of a genomic region that included UL140, UL141, UL142, UL144 genes and RL13 gene (known to have TM domains) [116]. All of them have functions related to the evasion of the host’s immune system [83][84][85][86][87]. In addition, the AD169 BACmid (Table 1) widely used for research, lacked several genes encoding TM proteins [116]. Some of them such as UL140, UL141, UL142, UL144 and RL13 were also deleted in AD169 strain. While the AD169 BACmid also lacked other genes such as UL135, UL136, UL138, UL148 and US3-US6 genes, involved in DNA replication, latency, virulence, tropism, evasion of the immune response and other genes such as UL139, UL147, UL148B, UL148C and UL148D with uncharacterized function [76][78][80][91][95][96][116]. The Toledo strain lacked RL13, UL9 and UL128 genes, while the Towne strain lacked RL13, UL1 and UL40 genes. The TR and Merlin strains, widely used in research included all the analyzed genes.
References
- Murphy, E.; Shenk, T.E. Human Cytomegalovirus Genome; Shenk, T.E., Stinski, M.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 325, ISBN 9783540773481.
- Emery, V.C. Investigation of CMV disease in immunocompromised patients. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 84–88.
- Boeckh, M.; Geballe, A.P. Science in medicine Cytomegalovirus: Pathogen, paradigm, and puzzle. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1673–1680.
- Seitz, R. Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV)-Revised. Transfus. Med. Hemotherapy 2010, 37, 365–375.
- Griffiths, P.; Baraniak, I.; Reeves, M. The pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 288–297.
- Stenberg, R.M.; Witte, P.R.; Stinski, M.F. Multiple spliced and unspliced transcripts from human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 and evidence for a common initiation site within immediate-early region 1. J. Virol. 1985, 56, 665–675.
- Dunn, W.; Chou, C.; Li, H.; Hai, R.; Patterson, D.; Stolc, V.; Zhu, H.; Liu, F. Functional profiling of a human cytomegalovirus genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14223–14228.
- Van Damme, E.; Van Loock, M. Functional annotation of human cytomegalovirus gene products: An update. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 218.
- Balázs, Z.; Tombácz, D.; Szucs, A.; Csabai, Z.; Megyeri, K.; Petrov, A.N.; Snyder, M.; Boldogkoi, Z. Long-Read Sequencing of Human Cytomegalovirus Transcriptome Reveals RNA Isoforms Carrying Distinct Coding Potentials. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15989.
- Stern-Ginossar, N.; Weisburd, B.; Michalski, A.; Le, V.T.K.; Hein, M.Y.; Huang, S.X.; Ma, M.; Shen, B.; Qian, S.B.; Hengel, H.; et al. Decoding human cytomegalovirus. Science 2012, 338, 1088–1093.
- Galitska, G.; Coscia, A.; Forni, D.; Steinbrueck, L.; De Meo, S.; Biolatti, M.; De Andrea, M.; Cagliani, R.; Leone, A.; Bertino, E.; et al. Genetic Variability of Human Cytomegalovirus Clinical Isolates Correlates with Altered Expression of Natural Killer Cell-Activating Ligands and IFN-γ. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 15989.
- Li, G.; Kamil, J.P. Viral Regulation of Cell Tropism in Human Cytomegalovirus. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 626–629.
- Gerna, G.; Kabanova, A.; Lilleri, D. Human Cytomegalovirus Cell Tropism and Host Cell Receptors. Vaccines 2019, 7, 70.
- Tandon, R.; Mocarski, E.S. Viral and host control of cytomegalovirus maturation. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 392–401.
- Das, S.; Ortiz, D.A.; Gurczynski, S.J.; Khan, F.; Pellett, P.E. Identification of Human Cytomegalovirus Genes Important for Biogenesis of the Cytoplasmic Virion Assembly Complex. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9086–9099.
- Bernstein, D.I.; Munoz, F.M.; Callahan, S.T.; Rupp, R.; Wootton, S.H.; Edwards, K.M.; Turley, C.B.; Stanberry, L.R.; Patel, S.M.; Mcneal, M.M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of a cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B (gB) vaccine in adolescent girls: A randomized clinical trial. Vaccine 2016, 34, 313–319.
- Pass, R.F. Development and evidence for efficacy of CMV glycoprotein B vaccine with MF59 adjuvant. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, S73–S76.
- Nelson, C.S.; Herold, B.C.; Permar, S.R. A new era in cytomegalovirus vaccinology: Considerations for rational design of next-generation vaccines to prevent congenital cytomegalovirus infection. NPJ Vaccines 2018, 3, 38.
- Baraniak, I.; Kropff, B.; Ambrose, L.; McIntosh, M.; McLean, G.R.; Pichon, S.; Atkinson, C.; Milne, R.S.B.; Mach, M.; Griffiths, P.D.; et al. Protection from cytomegalovirus viremia following glycoprotein B vaccination is not dependent on neutralizing antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6273–6278.
- Nelson, C.S.; Huffman, T.; Jenks, J.A.; De La Rosa, E.C.; Xie, G.; Vandergrift, N.; Pass, R.F.; Pollara, J.; Permar, S.R. HCMV glycoprotein B subunit vaccine efficacy mediated by nonneutralizing antibody effector functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6267–6272.
- Vincenti, F.; Budde, K.; Merville, P.; Shihab, F.; Ram Peddi, V.; Shah, M.; Wyburn, K.; Cassuto-Viguier, E.; Weidemann, A.; Lee, M.; et al. A randomized, phase 2 study of ASP0113, a DNA-based vaccine, for the prevention of CMV in CMV-seronegative kidney transplant recipients receiving a kidney from a CMV-seropositive donor. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 2945–2954.
- Sandonís, V.; García-Ríos, E.; McConnell, M.J.; Pérez-Romero, P. Role of Neutralizing Antibodies in CMV Infection: Implications for New Therapeutic Approaches. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 900–912.
- Pérez-Romero, P.; Blanco, P.; Giménez, E.; Solano, C.; Navarro, D. An update on the treatment of cytomegalovirus infection after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2015, 12, 937–945.
- Plotkin, S.A.; Boppana, S.B. Vaccination against the human cytomegalovirus. Vaccine 2019, 37, 7437–7442.
- Krause, P.R.; Bialek, S.R.; Boppana, S.B.; Griffiths, P.D.; Laughlin, C.A.; Ljungdahl, P.O.; Mocarski, E.S.; Pass, R.F.; Read, J.S.; Schleiss, M.R.; et al. Priorities for CMV vaccine development. Vaccine 2013, 32, 4–10.
- Gomes, A.C.; Griffiths, P.D.; Reeves, M.B. The Humoral Immune Response Against the gB Vaccine: Lessons Learnt from Protection in Solid Organ Transplantation. Vaccines 2019, 7, 67.
- Caposio, P.; van den Worm, S.; Crawford, L.; Perez, W.; Kreklywich, C.; Gilbride, R.M.; Hughes, C.M.; Ventura, A.B.; Ratts, R.; Marshall, E.E.; et al. Characterization of a live-attenuated HCMV-based vaccine platform. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19236.
- Schleiss, M.R. Cytomegalovirus vaccines under clinical development. J. Virus Erad. 2016, 2, 198–207.
- Cui, X.; Cao, Z.; Wang, S.; Lee, R.B.; Wang, X.; Murata, H.; Adler, S.P.; McVoy, M.A.; Snapper, C.M. Novel trimeric human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B elicits a high-titer neutralizing antibody response. Vaccine 2018, 36, 5580–5590.
- Dargan, D.J.; Douglas, E.; Cunningham, C.; Jamieson, F.; Stanton, R.J.; Baluchova, K.; McSharry, B.P.; Tomasec, P.; Emery, V.C.; Percivalle, E.; et al. Sequential mutations associated with adaptation of human cytomegalovirus to growth in cell culture. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1535–1546.
- Cappadona, I.; Villinger, C.; Schutzius, G.; Mertens, T.; von Einem, J. Human Cytomegalovirus pUL47 Modulates Tegumentation and Capsid Accumulation at the Viral Assembly Complex. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7314–7328.
- Zhu, F.; Yuan, J.; Li, H.J.; Zeng, Z.F.; Luo, Z.W.; Li, S.Q.; He, C.Q.; Jia, X.F.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, H.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus UL49 encodes an early, virion-associated protein essential for virus growth in human foreskin fibroblasts. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 1273–1284.
- Zhang, W.; Yao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, M. Unconserved C terminal of human cytomegalovirus tegument protein pUL76 elicits nuclear aggresome formation and induces DNA damage in transfected cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 95.
- Köppen-Rung, P.; Dittmer, A.; Bogner, E. Intracellular Distribution of Capsid-Associated pUL77 of Human Cytomegalovirus and Interactions with Packaging Proteins and pUL93. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5876–5885.
- Adair, R.; Douglas, E.R.; MacLean, J.B.; Graham, S.Y.; Aitken, J.D.; Jamieson, F.E.; Dargan, D.J. The products of human cytomegalovirus genes UL23, UL24, UL43 and US22 are tegument components. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1315–1324.
- Luo, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, E.; Shen, A.; Gong, H.; Pei, Z.; Xiao, G.; Lu, S.; Liu, F. Modulation of the Cellular Distribution of Human Cytomegalovirus Helicase by Cellular Factor Snapin. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10628–10640.
- Pizzorno, M.C.; Mullen, M.A.; Chang, Y.N.; Hayward, G.S. The functionally active IE2 immediate-early regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus is an 80-kilodalton polypeptide that contains two distinct activator domains and a duplicated nuclear localization signal. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 3839–3852.
- Wang, Y.; Mao, L.; Kankanala, J.; Wang, Z.; Geraghty, R.J. Inhibition of Human Cytomegalovirus pUL89 Terminase Subunit Blocks Virus Replication and Genome Cleavage. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02152-16.
- Connolly, S.A.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. The structural basis of herpesvirus entry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 110–121.
- Nguyen, C.C.; Kamil, J.P. Pathogen at the gates: Human cytomegalovirus entry and cell tropism. Viruses 2018, 10, 704.
- Gao, S.; Ruan, S.; Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Zheng, B.; Qi, Y.; Sun, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ruan, Q. Newly identified transcripts of UL4 and UL5 genes of human cytomegalovirus. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 97–101.
- Chang, C.P.; Vesole, D.H.; Nelson, J.; Oldstone, M.B.; Stinski, M.F. Identification and expression of a human cytomegalovirus early glycoprotein. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 3330–3337.
- Vezzani, G.; Amendola, D.; Yu, D.; Chandramouli, S.; Frigimelica, E.; Maione, D.; Merola, M. The Human Cytomegalovirus UL116 Glycoprotein Is a Chaperone to Control gH-Based Complexes Levels on Virions. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 630121.
- Shikhagaie, M.; Mercé-Maldonado, E.; Isern, E.; Muntasell, A.; Albà, M.M.; López-Botet, M.; Hengel, H.; Angulo, A. The Human Cytomegalovirus-Specific UL1 Gene Encodes a Late-Phase Glycoprotein Incorporated in the Virion Envelope. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4091–4101.
- Anselmi, G.; Giuliani, M.; Vezzani, G.; Ferranti, R.; Gentile, M.; Cortese, M.; Amendola, D.; Pacchiani, N.; D’Aurizio, R.; Bruno, L.; et al. Characterization of pUL5, an HCMV protein interacting with the cellular protein IQGAP1. Virology 2020, 540, 57–65.
- Gonzalez-Perez, A.C.; Stempel, M.; Wyler, E.; Urban, C.; Piras, A.; Hennig, T.; Ganskih, S.; Wei, Y.; Heim, A.; Landthaler, M.; et al. The Zinc Finger Antiviral Protein ZAP Restricts Human Cytomegalovirus and Selectively Binds and Destabilizes Viral UL4/UL5 Transcripts. MBio 2021, 12, e02683-20.
- Engel, P.; Pérez-Carmona, N.; Albà, M.M.; Robertson, K.; Ghazal, P.; Angulo, A. Human cytomegalovirus UL7, a homologue of the SLAM-family receptor CD229, impairs cytokine production. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 753–766.
- MacManiman, J.D.; Meuser, A.; Botto, S.; Smith, P.P.; Liu, F.; Jarvis, M.A.; Nelson, J.A.; Caposio, P. Human Cytomegalovirus-Encoded pUL7 Is a Novel CEACAM1-Like Molecule Responsible for Promotion of Angiogenesis. MBio 2014, 5, e02035.
- Crawford, L.B.; Kim, J.H.; Collins-McMillen, D.; Lee, B.J.; Landais, I.; Held, C.; Nelson, J.A.; Yurochko, A.D.; Caposio, P. Human cytomegalovirus encodes a novel FLT3 receptor ligand necessary for hematopoietic cell differentiation and viral reactivation. MBio 2018, 9, e00682-18.
- Pérez-Carmona, N.; Martínez-Vicente, P.; Farré, D.; Gabaev, I.; Messerle, M.; Engel, P.; Angulo, A. A Prominent Role of the Human Cytomegalovirus UL8 Glycoprotein in Restraining Proinflammatory Cytokine Production by Myeloid Cells at Late Times during Infection. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02229-17.
- Bruno, L.; Cortese, M.; Monda, G.; Gentile, M.; Caló, S.; Schiavetti, F.; Zedda, L.; Cattaneo, E.; Piccioli, D.; Schaefer, M.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus pUL10 interacts with leukocytes and impairs TCR-mediated T-cell activation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 849–860.
- Zischke, J.; Mamareli, P.; Pokoyski, C.; Gabaev, I.; Buyny, S.; Jacobs, R.; Falk, C.S.; Lochner, M.; Sparwasser, T.; Schulz, T.F.; et al. The human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein pUL11 acts via CD45 to induce T cell IL-10 secretion. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006454.
- Rölle, A.; Mousavi-Jazi, M.; Eriksson, M.; Odeberg, J.; Söderberg-Nauclér, C.; Cosman, D.; Kärre, K.; Cerboni, C. Effects of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection on Ligands for the Activating NKG2D Receptor of NK Cells: Up-Regulation of UL16-Binding Protein (ULBP)1 and ULBP2 Is Counteracted by the Viral UL16 Protein. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 902–908.
- Kim, Y.; Park, B.; Cho, S.; Shin, J.; Cho, K.; Jun, Y.; Ahn, K. Human cytomegalovirus UL18 utilizes US6 for evading the NK and T-cell responses. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, 1000123.
- Jelcic, I.; Reichel, J.; Schlude, C.; Treutler, E.; Sinzger, C.; Steinle, A. The polymorphic HCMV glycoprotein UL20 is targeted for lysosomal degradation by multiple cytoplasmic dileucine motifs. Traffic 2011, 12, 1444–1456.
- Casarosa, P.; Gruijthuijsen, Y.K.; Michel, D.; Beisser, P.S.; Holl, J.; Fitzsimons, C.P.; Verzijl, D.; Bruggeman, C.A.; Mertens, T.; Leurs, R.; et al. Constitutive Signaling of the Human Cytomegalovirus-encoded Receptor UL33 Differs from That of Its Rat Cytomegalovirus Homolog R33 by Promiscuous Activation of G Proteins of the Gq, Gi, and Gs Classes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50010–50023.
- Van Senten, J.R.; Bebelman, M.P.; Fan, T.S.; Heukers, R.; Bergkamp, N.D.; Van Gasselt, P.; Langemeijer, E.V.; Slinger, E.; Lagerweij, T.; Rahbar, A.; et al. The human cytomegalovirus-encoded G protein- coupled receptor UL33 exhibits oncomodulatory properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 16297–16308.
- van Senten, J.R.; Bebelman, M.P.; van Gasselt, P.; Bergkamp, N.D.; van den Bor, J.; Siderius, M.; Smit, M.J. Human cytomegalovirus-encoded G protein-coupled receptor UL33 facilitates virus dissemination via the extracellular and cell-to-cell route. Viruses 2020, 12, 594.
- Xi, Y.; Harwood, S.; Wise, L.M.; Purdy, J.G. Human Cytomegalovirus pUL37x1 Is Important for Remodeling of Host Lipid Metabolism. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00843-19.
- Brune, W.; Andoniou, C.E. Die another day: Inhibition of cell death pathways by cytomegalovirus. Viruses 2017, 9, 249.
- Prod’homme, V.; Tomasec, P.; Cunningham, C.; Lemberg, M.K.; Stanton, R.J.; McSharry, B.P.; Wang, E.C.Y.; Cuff, S.; Martoglio, B.; Davison, A.J.; et al. Human Cytomegalovirus UL40 Signal Peptide Regulates Cell Surface Expression of the NK Cell Ligands HLA-E and gpUL18. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2794–2804.
- Koshizuka, T.; Inoue, N. Activation of c-Jun by human cytomegalovirus UL42 through JNK activation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232635.
- Fu, Y.Z.; Guo, Y.; Zou, H.M.; Su, S.; Wang, S.Y.; Yang, Q.; Luo, M.H.; Wang, Y.Y. Human cytomegalovirus protein UL42 antagonizes cGAS/MITA-mediated innate antiviral response. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007691.
- Häge, S.; Sonntag, E.; Svrlanska, A.; Borst, E.M.; Stilp, A.C.; Horsch, D.; Müller, R.; Kropff, B.; Milbradt, J.; Stamminger, T.; et al. Phenotypical characterization of the nuclear egress of recombinant cytomegaloviruses reveals defective replication upon orf-ul50 deletion but not pul50 phosphosite mutation. Viruses 2021, 13, 165.
- Weiler, N.; Paal, C.; Adams, K.; Calcaterra, C.; Fischer, D.; Stanton, R.J.; Stöhr, D.; Sampaio, K.L.; Sinzger, C. Role of envelope glycoprotein complexes in cell-associated spread of human cytomegalovirus. Viruses 2021, 13, 614.
- Mach, M.; Osinski, K.; Kropff, B.; Schloetzer-Schrehardt, U.; Krzyzaniak, M.; Britt, W. The Carboxy-Terminal Domain of Glycoprotein N of Human Cytomegalovirus Is Required for Virion Morphogenesis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5212–5224.
- Wu, Y.; Prager, A.; Boos, S.; Resch, M.; Brizic, I.; Mach, M.; Wildner, S.; Scrivano, L.; Adler, B. Human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein complex gH/gL/gO uses PDGFR-α as a key for entry. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006281.
- van Senten, J.R.; Fan, T.S.; Siderius, M.; Smit, M.J. Viral G protein-coupled receptors as modulators of cancer hallmarks. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 156, 104804.
- O’Connor, C.M.; Shenk, T. Human Cytomegalovirus pUL78 G Protein-Coupled Receptor Homologue Is Required for Timely Cell Entry in Epithelial Cells but Not Fibroblasts. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11425–11433.
- Krzyzaniak, M.A.; Mach, M.; Britt, W.J. HCMV-encoded glycoprotein M (UL100) interacts with rab11 effector protein FIP4. Traffic 2009, 10, 1439–1457.
- Krzyzaniak, M.; Mach, M.; Britt, W.J. The Cytoplasmic Tail of Glycoprotein M (gpUL100) Expresses Trafficking Signals Required for Human Cytomegalovirus Assembly and Replication. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10316–10328.
- Pandey, J.P.; Namboodiri, A.M.; Radwan, F.F.; Nietert, P.J. The decoy Fcγ receptor encoded by the cytomegalovirus UL119-UL118 gene has differential affinity to IgG proteins expressing different GM allotypes. Hum. Immunol. 2015, 76, 591–594.
- Landini, M.P.; Lazzarotto, T.; Xu, J.; Geballe, A.P.; Mocarski, E.S. Humoral Immune Response to Proteins of Human Cytomegalovirus Latency-Associated Transcripts. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2000, 6, 100–108.
- Wu, H.; Kropff, B.; Mach, M.; Britt, W.J. Human cytomegalovirus envelope protein gpul132 regulates infectious virus production through formation of the viral assembly compartment. MBio 2020, 11, e02044-20.
- Mlera, L.; Moy, M.; Maness, K.; Tran, L.N.; Goodrum, F.D. The Role of the Human Cytomegalovirus UL133-UL138 Gene Locus in Latency and Reactivation. Viruses 2020, 12, 714.
- Stanton, R.J.; Prod’Homme, V.; Purbhoo, M.A.; Moore, M.; Aicheler, R.J.; Heinzmann, M.; Bailer, S.M.; Haas, J.; Antrobus, R.; Weekes, M.P.; et al. HCMV pUL135 remodels the actin cytoskeleton to impair immune recognition of infected cells. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 201–214.
- Bughio, F.; Umashankar, M.; Wilson, J.; Goodrum, F. Human Cytomegalovirus UL135 and UL136 Genes Are Required for Postentry Tropism in Endothelial Cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6536–6550.
- Caviness, K.; Bughio, F.; Crawford, L.B.; Streblow, D.N.; Nelson, J.A.; Caposio, P.; Goodrum, F. Complex interplay of the UL136 isoforms balances cytomegalovirus replication and Latency. MBio 2016, 7, e01986.
- Bughio, F.; Elliott, D.A.; Goodrum, F. An Endothelial Cell-Specific Requirement for the UL133-UL138 Locus of Human Cytomegalovirus for Efficient Virus Maturation. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3062–3075.
- Han, L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ruan, Q. Transcriptional regulation and influence on replication of the human cytomegalovirus UL1381.4 kb transcript. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5649–5658.
- Gelbmann, C.B.; Kalejta, R.F. The Golgi sorting motifs of human cytomegalovirus UL138 are not required for latency maintenance. Virus Res. 2019, 270, 197646.
- Qi, Y.; Mao, Z.Q.; Ruan, Q.; He, R.; Ma, Y.P.; Sun, Z.R.; Ji, Y.H.; Huang, Y. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) UL139 open reading frame: Sequence variants are clustered into three major genotypes. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 517–522.
- Zou, F.; Lu, Z.T.; Wang, S.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Sun, Z.R. Human cytomegalovirus UL141 protein interacts with CELF5 and affects viral DNA replication. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4657–4664.
- Tomasec, P.; Wang, E.C.Y.; Davison, A.J.; Vojtesek, B.; Armstrong, M.; Griffin, C.; McSharry, B.P.; Morris, R.J.; Llewellyn-Lacey, S.; Rickards, C.; et al. Downregulation of natural killer cell-activating ligang CD155 by human cytomegalovirus UL141. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 181–188.
- Nemčovičová, I.; Benedict, C.A.; Zajonc, D.M. Structure of Human Cytomegalovirus UL141 Binding to TRAIL-R2 Reveals Novel, Non-canonical Death Receptor Interactions. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003224.
- Ashiru, O.; Bennett, N.J.; Boyle, L.H.; Thomas, M.; Trowsdale, J.; Wills, M.R. NKG2D Ligand MICA Is Retained in the cis -Golgi Apparatus by Human Cytomegalovirus Protein UL142. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12345–12354.
- Bitra, A.; Nemčovičová, I.; Picarda, G.; Doukov, T.; Wang, J.; Benedict, C.A.; Zajonc, D.M. Structure of human cytomegalovirus UL144, an HVEM orthologue, bound to the B and T cell lymphocyte attenuator. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10519–10529.
- Poole, E.; Walther, A.; Raven, K.; Benedict, C.A.; Mason, G.M.; Sinclair, J. The Myeloid Transcription Factor GATA-2 Regulates the Viral UL144 Gene during Human Cytomegalovirus Latency in an Isolate-Specific Manner. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4261–4271.
- Lüttichau, H.R. The cytomegalovirus UL146 gene product vCXCL1 targets both CXCR1 and CXCR2 as an agonist. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 9137–9146.
- Seidel, E.; Dassa, L.; Schuler, C.; Oiknine-Djian, E.; Wolf, D.G.; Le-Trilling, V.T.K.; Mandelboim, O. The human cytomegalovirus protein UL147A downregulates the most prevalent MICA allele: MICA*008, to evade NK cell-mediated killing. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1008807.
- Siddiquey, M.N.A.; Schultz, E.P.; Yu, Q.; Amendola, D.; Vezzani, G.; Yu, D.; Maione, D.; Lanchy, J.-M.; Ryckman, B.J.; Merola, M.; et al. The human cytomegalovirus protein UL116 interacts with the viral ER resident glycoprotein UL148 and promotes the incorporation of gH/gL complexes into virions. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0220720.
- Dassa, L.; Seidel, E.; Oiknine-Djian, E.; Yamin, R.; Wolf, D.G.; Le-Trilling, V.T.K.; Mandelboim, O. The Human Cytomegalovirus Protein UL148A Downregulates the NK Cell-Activating Ligand MICA to Avoid NK Cell Attack. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00162-18.
- Ji, Y.H.; Rong Sun, Z.; Ruan, Q.; Guo, J.J.; He, R.; Qi, Y.; Ma, Y.P.; Mao, Z.Q.; Huang, Y.J. Polymorphisms of human cytomegalovirus UL148A, UL148B, UL148C, UL148D genes in clinical strains. J. Clin. Virol. 2006, 37, 252–257.
- Gabor, F.; Jahn, G.; Sedmak, D.D.; Sinzger, C. In vivo Downregulation of MHC Class I Molecules by HCMV Occurs during All Phases of Viral Replication but Is Not Always Complete. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 283.
- Park, B.; Kim, Y.; Shin, J.; Lee, S.; Cho, K.; Früh, K.; Lee, S.; Ahn, K. Human Cytomegalovirus Inhibits Tapasin-Dependent Peptide Loading and Optimization of the MHC Class I Peptide Cargo for Immune Evasion. Immunity 2004, 20, 71–85.
- Dugan, G.E.; Hewitt, E.W. Structural and Functional Dissection of the Human Cytomegalovirus Immune Evasion Protein US6. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3271–3282.
- Park, A.; Ra, E.A.; Lee, T.A.; Choi, H.; Lee, E.; Kang, S.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Park, B. HCMV-encoded US7 and US8 act as antagonists of innate immunity by distinctively targeting TLR-signaling pathways. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4670.
- Choi, H.J.; Park, A.; Kang, S.; Lee, E.; Lee, T.A.; Ra, E.A.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Park, B. Human cytomegalovirus-encoded US9 targets MAVS and STING signaling to evade type i interferon immune responses. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 125.
- Park, B.; Spooner, E.; Houser, B.L.; Strominger, J.L.; Ploegh, H.L. The HCMV membrane glycoprotein US10 selectively targets HLA-G for degradation. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2033–2041.
- Zimmermann, C.; Kowalewski, D.; Bauersfeld, L.; Hildenbrand, A.; Gerke, C.; Schwarzmüller, M.; Le-Trilling, V.T.K.; Stevanovic, S.; Hengel, H.; Momburg, F.; et al. HLA-B locus products resist degradation by the human cytomegalovirus immunoevasin US11. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008040.
- Fielding, C.A.; Weekes, M.P.; Nobre, L.V.; Ruckova, E.; Wilkie, G.S.; Paulo, J.A.; Chang, C.; Suárez, N.M.; Davies, J.A.; Antrobus, R.; et al. Control of immune ligands by members of a cytomegalovirus gene expansion suppresses natural killer cell activation. Elife 2017, 6, e22206.
- Das, S.; Pellett, P.E. Members of the HCMV US12 family of predicted heptaspanning membrane proteins have unique intracellular distributions, including association with the cytoplasmic virion assembly complex. Virology 2007, 361, 263–273.
- Luganini, A.; Cavaletto, N.; Raimondo, S.; Geuna, S.; Gribaudo, G. Loss of the Human Cytomegalovirus US16 Protein Abrogates Virus Entry into Endothelial and Epithelial Cells by Reducing the Virion Content of the Pentamer. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 205–222.
- Gurczynski, S.J.; Das, S.; Pellett, P.E. Deletion of the Human Cytomegalovirus US17 Gene Increases the Ratio of Genomes per Infectious Unit and Alters Regulation of Immune and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response Genes at Early and Late Times after Infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2168–2182.
- Charpak-Amikam, Y.; Kubsch, T.; Seidel, E.; Oiknine-Djian, E.; Cavaletto, N.; Yamin, R.; Schmiedel, D.; Wolf, D.; Gribaudo, G.; Messerle, M.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus escapes immune recognition by NK cells through the downregulation of B7-H6 by the viral genes US18 and US20. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8661.
- Cavaletto, N.; Luganini, A.; Gribaudo, G. Inactivation of the Human Cytomegalovirus US20 Gene Hampers Productive Viral Replication in Endothelial Cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11092–11106.
- Luganini, A.; Di Nardo, G.; Munaron, L.; Gilardi, G.; Pla, A.F.; Gribaudo, G. Human cytomegalovirus US21 protein is a viroporin that modulates calcium homeostasis and protects cells against apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E12370–E12377.
- Boeck, J.M.; Stowell, G.A.; O’Connor, C.M.; Spencer, J.V. The Human Cytomegalovirus US27 Gene Product Constitutively Activates Antioxidant Response Element-Mediated Transcription through G β γ, Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase, and Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00644-18.
- Tu, C.C.; O’Connor, C.M.; Spencer, J.V. Identification of a novel signaling complex containing host chemokine receptor CXCR4, Interleukin-10 receptor, and human cytomegalovirus US27. Virology 2020, 548, 49–58.
- O’Connor, C.M.; Shenk, T. Human Cytomegalovirus pUS27 G Protein-Coupled Receptor Homologue Is Required for Efficient Spread by the Extracellular Route but Not for Direct Cell-to-Cell Spread. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3700–3707.
- Nobre, L.; Nightingale, K.; Ravenhill, B.J.; Antrobus, R.; Soday, L.; Nichols, J.; Davies, J.; Seirafian, S.; Wang, E.C.Y.; Davison, A.J.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus interactome analysis identifies degradation hubs, domain associations and viral protein functions. Elife 2019, 8, e49894.
- Krishna, B.A.; Miller, W.E.; O’Connor, C.M. US28: HCMV’s swiss army knife. Viruses 2018, 10, 445.
- Gatherer, D.; Seirafian, S.; Cunningham, C.; Holton, M.; Dargan, D.J.; Baluchova, K.; Hector, R.D.; Galbraith, J.; Herzyk, P.; Wilkinson, G.W.G.; et al. High-resolution human cytomegalovirus transcriptome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19755–19760.
- Kim, E.T.; Kim, Y.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, M.K.; Hayward, G.S.; Ahn, J.H. Analysis of human cytomegalovirus-encoded SUMO targets and temporal regulation of SUMOylation of the immediate-early proteins IE1 and IE2 during infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 103308.
- Lilley, B.N.; Ploegh, H.L.; Tirabassi, R.S. Human Cytomegalovirus Open Reading Frame TRL11/IRL11 Encodes an Immunoglobulin G Fc-Binding Protein. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11218–11221.
- Wilkinson, G.W.G.; Davison, A.J.; Tomasec, P.; Fielding, C.A.; Aicheler, R.; Murrell, I.; Seirafian, S.; Wang, E.C.Y.; Weekes, M.; Lehner, P.J.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus: Taking the strain. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 204, 273–284.
- Cortese, M.; Calò, S.; D’Aurizio, R.; Lilja, A.; Pacchiani, N.; Merola, M. Recombinant Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) RL13 Binds Human Immunoglobulin G Fc. PLoS ONE 2012, 7.
- Wang, G.; Ren, G.; Cui, X.; Lu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Qi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Ruan, Q. Human cytomegalovirus RL13 protein interacts with host NUDT14 protein affecting viral DNA replication. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2167–2174.
- Schultz, E.P.; Lanchy, J.-M.; Day, L.Z.; Yu, Q.; Peterson, C.; Preece, J.; Ryckman, B.J. Specialization for Cell-Free or Cell-to-Cell Spread of BAC-Cloned Human Cytomegalovirus Strains Is Determined by Factors beyond the UL128-131 and RL13 Loci. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00034-20.
- Lesniewski, M.; Das, S.; Skomorovska-Prokvolit, Y.; Wang, F.Z.; Pellett, P.E. Primate cytomegalovirus US12 gene family: A distinct and diverse clade of seven-transmembrane proteins. Virology 2006, 354, 286–298.
More
Information
Subjects:
Virology
Contributor
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.0K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
21 Mar 2022
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




