Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Patricia Johansson | + 2469 word(s) | 2469 | 2022-03-08 10:16:45 | | | |
| 2 | Beatrix Zheng | + 1 word(s) | 2470 | 2022-03-18 11:10:29 | | | | |
| 3 | Beatrix Zheng | + 1 word(s) | 2470 | 2022-03-18 11:20:06 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Johansson, P. Pathogenesis of Ocular Adnexal Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/20719 (accessed on 13 March 2026).
Johansson P. Pathogenesis of Ocular Adnexal Marginal Zone Lymphomas. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/20719. Accessed March 13, 2026.
Johansson, Patricia. "Pathogenesis of Ocular Adnexal Marginal Zone Lymphomas" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/20719 (accessed March 13, 2026).
Johansson, P. (2022, March 18). Pathogenesis of Ocular Adnexal Marginal Zone Lymphomas. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/20719
Johansson, Patricia. "Pathogenesis of Ocular Adnexal Marginal Zone Lymphomas." Encyclopedia. Web. 18 March, 2022.
Copy Citation
Ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphoma (OAMZL) is a distinct type of lymphoma that presents in tissues around the eyeball. The lymphoma develops from mature B lymphocytes that have been triggered by antigens for prolonged times. It seems that the B cells often recognize autoantigens. The lymphoma cells often carry specific chromosomal gains and, in some cases, chromosomal translocations. A main factor in the development of this lymphoma is the constitutive activation of the NF-κB pathway, which occurs through various types of genetic alterations. Further key pathogenetic mechanisms involve epigenetic changes, indicated by recurrent mutations in epigenetic regulators.
ocular adnexal lymphoma
extranodal marginal zone lymphoma
mucosa-associated tissue
MALT lymphoma
NF-κB
ocular adnexa
orbit
1. Precursor Lesions
Several precursor lesions potentially developing to Ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphoma (OAMZL) have been described, among them orbital pseudotumors (idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease (IOID)), reactive lymphoid hyperplasia (RLH), and IgG4-related disease [1]. Both exogenous antigens and autoantigens can trigger the abovementioned precursor lesions in the ocular adnexa. Precursor lesions as inflammatory non-malignant states have in common that they result in chronic antigenic stimulation, which may lead to activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, to chromosomal alterations, and to other genetic and epigenetic alterations. This multistep process can drive lymphoma development [2].
OAMZL arising in the context of IgG4-related disease has been repeatedly reported as OAMZL with IgG4-positive cells or infiltrated by IgG4-positive cells [3][4][5][6][7]. In some cases, the differentiation between the two entities is challenging, since OAMZL exhibits IgG4-positive plasma cells in up to 62% of cases [8]. Histopathologically, obliteration of venous vessels is specific. Plasma cells in IgG4-related disease are polytypic. In IgG4-related disease, eosinophilia, high IgE titers, polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia, and often elevated serum IgG4 levels are observed [9]. Infraorbital nerve enlargement is a unique feature on MRI scans [5]. Upregulation of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID)—the master factor for somatic hypermutation and class-switch recombination of immunoglobulin genes—was observed in IgG4-related ophthalmic disease and OAMZL, whereas AID expression was lower in IgG4-negative OAMZL [10]. AID might be a driver for oncogenesis in the development of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease to IgG4-positive OAMZL.
2. Antigen Stimulation
Chronic (auto)antigenic stimulation via chronic inflammation, infection, or autoimmune disease is supposed to be a relevant pathogenic mechanism in the development of primary MALT lymphoma in general [11]. A multistep process is supposed to promote survival and growth advantages of stimulated B cells, which may finally give rise to monoclonal B-cell populations. Various mechanisms are described causing this antigenic stimulation.
2.1. Infectious Agents
Chlamydophila psittaci
Chlamydia are human pathogenic intracellular bacteria that are typically transmitted via infected birds. Mostly, infections are asymptomatic, but they can cause pneumonia, chronic conjunctivitis, pericarditis, and hepatitis [12]. Chlamydophila psittaci can induce immune reactions cross-reacting with autoantigens, leading to insufficient elimination of the pathogen and induction of lymphoma development [13][14][15].
The prevalence of C. psittaci in OAL seems to be region-specific. In most studies involving patients from Italy or Korea, C. psittaci was repeatedly detected by PCR and other methods in OAL cases. Other Chlamydia species were predominantly observed in China (C. pneumonia) and the UK (C. trachomatis) [13][16][17]. In other countries, however—including Japan, the USA, Cuba, the UK, the Netherlands, France, and Germany—no evidence for C. psittaci in samples of OAL was observed [18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26].
- (1)Other Bacteria
Among 308 OAL patients analyzed in 11 studies, Helicobacter pylori was detected in 23% of the lymphomas [27]. However, there is the risk of contamination of OAL biopsy specimens by the rather prevalent H. pylori during sampling, so the true incidence may be substantially lower. Notably, the prevalence of OAL patients with H. pylori-positive gastric infections is overall no higher than in the general population [27], arguing against a significantly increased risk of OAL development in individuals with chronic gastric H. pylori infection. A recent study confirmed a lack of association between gastric H. pylori infection and OAL incidence [28]; none of 18 OAL cases in that study showed H. pylori DNA in the lymphoma tissue. Thus, the role of H. pylori in the development of OAL is still unresolved.
- (2)Viral Pathogens
In several studies on a potential viral etiology of OAL, no viruses were detected in the lymphomas [26][29]. For chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections, the association with marginal-zone lymphomas is especially well known [30][31]. Although there are clear indications for a role of HCV in the pathogenesis of some types of B-cell lymphoma, its role in OAMZL is less clear [32].
For human-immunodeficiency-virus-infected patients, a higher risk of developing marginal-zone lymphomas has been described, but there are no reports on higher incidences of OAMZL [33]. Regarding Epstein–Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and human papilloma virus, there are also no reports on higher infection rates in patients with OAL [29][34].
2.2. Autoimmune Diseases
The detailed mechanisms of lymphomagenesis in the context of autoimmunity remain unclear. The occurrence of lymphomas in association with rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s syndrome, Hashimoto thyroiditis, and other autoimmune diseases is well described [35][36]. A meta-analysis of 20 studies including patients with the abovementioned autoimmune diseases revealed that lymphomas are more common in these patients than in healthy subjects [37]. The most common lymphoma subtype occurring in patients with autoimmune diseases is marginal-zone lymphoma [38]. Disease activity, the presence of rheumatoid factor, and/or cryoglobulinemia in patients with autoimmune diseases are prognostic factors for lymphoma development, reflecting a continuing immune stimulation [39]. Apoptotic resistance—mediated by high BCL2 expression, activation of NF-κB, and overexpression of B-cell activating factor (BAFF)—is increased in autoimmune diseases [40]. Figure 1 provides a proposed scenario of OAMZL pathogenesis.
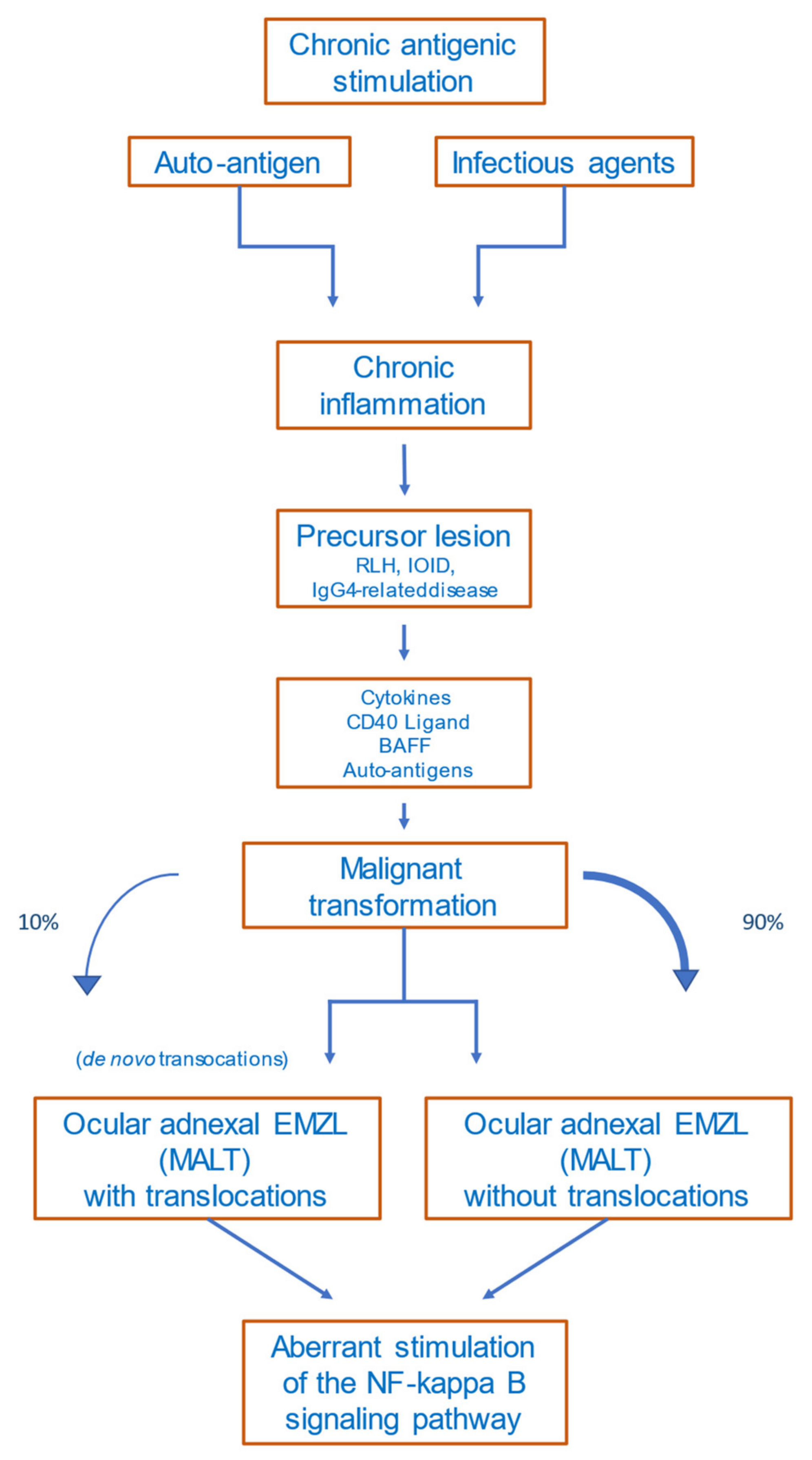
Figure 1. Proposed scheme of OAMZL pathogenesis. RLH: reactive lymphoid hyperplasia; IOID: idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease; BAFF: B-cell activating factor; EMZL: extranodal marginal-zone lymphoma; MALT: mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue.
3. Chromosomal Aberrations
3.1. Translocations
In OAMZL, chromosomal translocations leading to constitutive activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway have been described [41]; these include t(11;18)(q21;q21)/BIRC3-MALT1, often accompanied by a trisomy 3 [42], and t(14;18)(q32;q21)/IGH-MALT1 (Table 1). The t(11;18)(q21;q21) juxtaposes BIRC3 (previously also known as API2) to MALT1, resulting in a fusion gene; this translocation has been detected in 10–15% of OAL cases [43][44]. The t(14;18)(q32;q21) translocation brings the MALT1 gene under control of the IGH locus enhancers, causing constitutive expression of MALT1, and is present in around 5–10% of OAMZLs. MALT1 is a protease and an important mediator of canonical NF-κB signaling [45].
Table 1. Genetic alterations of OAMZL.
| Chromosomes or Genes Affected | Type of Genetic Alteration | Pathway or Main Function | Approximate Frequency (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromosomal alterations | ||||
| Trisomy 3 | Chromosomal gain | unclear (FOXP1?) |
30–60 | [46][47][48] |
| Trisomy 18 | Chromosomal gain | unclear | 20–55 | [46][47][48] |
| t(11;18)(q21;q21) | BIRC3-MALT1 translocation | NF-κB pathway | 10–15 | [44][49] |
| t(14;18)(q32;q21) | IGH-MALT1 translocation | NF-κB pathway | 5–10 | [43][46][50] |
| t(3;14)(p14.1;q32) | FOXP1-IGH translocation | B-cell development and survival (NF-κB pathway) | 5–15 | [51][52] |
| Gene mutations | ||||
| TNFAIP3 | Deletions, non-synonymous mutations | NF-κB pathway | 30–50 | [53][54][55][56][57] |
| MYD88 | Non-synonymous mutations (mostly p.L265P) | NF-κB pathway | 5–35 | [54][57][58][59][60] |
| NOTCH1 | Non-synonymous mutations (mostly HD and PEST domains) | NOTCH pathway | 2–10 | [54][56][61] |
| NOTCH2 | Non-synonymous mutations (mostly TAD and PEST domains) | NOTCH pathway | 5–10 | [54][62] |
| KMT2D | Non-synonymous mutations | Epigenetic regulation | 5–20 | [54][56][57][62] |
| CREBBP | Non-synonymous mutations | Epigenetic regulation | 15 | [26][56] |
| TBL1XR1 | Non-synonymous mutations (mostly WD40 domain) | Regulation of nuclear receptor activity (NF-κB and AP1 pathway) | 10–20 | [26][56][57][61] |
| JAK3 | Non-synonymous mutations | JAK/STAT signaling | 5–10 | [26][57] |
| CABIN1 | deletions, Non-synonymous mutations | NFAT signaling | 30% | [63] |
| RHOA | deletions, Non-synonymous mutations | Rho signaling | 26% | [63] |
Non-synonymous mutations: includes damaging point mutations, small insertions/deletions.
The t(3;14)(p14.1;q32)/FOXP1-IGH was observed in around 5–15% of OALs, and leads to constitutive expression of FOXP1 [51][52][64]. FOXP1 is a transcription factor that supports B-cell survival, and can cooperate with NF-κB, so that for this translocation event there is also a link to the NF-κB pathway [65].
Further translocations occur in OAMZL with lower prevalence. These include t(1;14)(p22;q34) juxtaposing BCL10 to the IGH locus, or t(5;11) with unknown translocation partners [66]. Notably, translocations are observed in OAMZL at lower frequencies than in MALT lymphomas occurring in other regions, and the various EMZLs show distinct patterns of recurrent chromosomal translocations [64].
3.2. Copy Number Variations
The most frequent copy number variations in OAMZL are trisomy 3 and trisomy 18, in approximately 30–60% and 20–55% of patients, respectively (Table 1) [46][47]. Trisomy 3 is more common in persons above 50 years of age, whereas trisomy 18 is observed mostly in younger, female patients. The cases with trisomy 18 have more lymphoproliferative lesions, less nodularity, and are associated with recurrent disease [67]. The pathogenetic effect of these trisomies in OAMZL is unknown.
4. Genetic Alterations in Particular Signaling Pathways
4.1. Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) Pathway
NF-κB is a transcription factor family that plays a critical role in B-cells’ activation, development, and survival [68]. The NF-κB pathway is normally only transiently activated in B cells by binding of various ligands to receptors, including Toll-like receptors, the TNF-α receptor, the BCR, CD40, and others. The intracellular signaling transduction is mediated via a canonical and a non-canonical pathway [64]. A major role of deregulated activation of this pathway in OAMZL is already indicated by the fact that the three most frequent chromosomal translocations of OAMZL cause, or at least contribute to, NF-κB activation, as discussed above. A further major driver for constitutive NF-κB activation in OAMZL is genetic alterations leading to functional changes of TNF-α-inducible protein 3 (TNFAIP3), previously also called A20. Somatic deletions and/or point mutations lead to inactivation of this negative regulator of the classical NF-κB pathway [55]. In OAMZL, destructive TNFAIP3 mutations and/or deletions were observed in 30–50% of cases [53][56] (Table 1). TNFAIP3 is the most frequently mutated gene detected so far in OAMZL. It has been reported that IGH/MALT1 translocations are mutually exclusive with TNFAIP3 mutations/deletions in OAMZL [55], indicating that these are alternative mechanisms for deregulated NF-κB activation in OAMZL.
To identify potential mutations in further genes of the NF-κB signaling pathway, sequencing analyses were performed by several groups. In 24 OAMZL samples, sequencing of hotspots in the genes CARD11, MYD88, and CD79B, known to be frequently mutated in other B-cell lymphomas, revealed no mutations [69]. In a targeted sequencing approach of genes involved in the NF-κB signaling pathway performed by the researchers' team with 63 patients, mutations in TNFAIP3 (27% of cases), MYD88 (19%), and BCL10 (6%) were observed [54]. Further genes, mutated to lower frequencies, were TNIP1, NFKBIA, BIRC3, CARD11, and CD79B. Only a few genes encoding components of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway were mutated (MAP3K14, BIRC3, and CYLD), whereas other mutated genes were involved in the canonical pathway [54]. A further study analyzing the frequency of MYD88 L265P mutations in primary OAL found the gene to be mutated in 36% of patients [58]. In a targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) approach to OAL including 20 samples, with 17 of them being primary OAL, 25% of cases exhibited mutations in the TIR domain of MYD88 [59]. Two of the three studies mentioned carefully excluded lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström macroglobulinemia by analyzing paraproteins and plasmacytic differentiation—especially with IgM [54][59], which is necessary when analyzing MYD88 mutations. Further NGS-based approaches using whole genomes, whole exomes, and targeted sequencing confirmed and extended these findings [26][56][62].
4.2. NOTCH Pathway
The NOTCH signaling pathway is important in cell differentiation; it is active in many cell types regulating cell development, differentiation, and homeostasis, and is involved in many malignant diseases, including lymphomas [70][71][72]. The NOTCH signaling pathway cross-interacts with the NF-κB signaling pathway as its upstream regulator [73][74][75]. Non-synonymous NOTCH1 or NOTCH2 mutations were observed in up to 10% of OAMZLs, with a similar pattern as described for other B-cell lymphomas. There is a clustering of the mutations in the HD and PEST domains of NOTCH1, as well as downstream of the ankyrin repeats in the intracellular domain of NOTCH2 [54][56]. For both genes, these types of mutations cause a gain of function, as the inhibitory C-terminal PEST domains are removed or otherwise inactivated. Copy number gains in the NOTCH target HES4 may be a further mechanism of enforced NOTCH pathway activity in OAMZL [26][76].
4.3. NFAT Signaling
A recent exome sequencing study provided the first evidence for recurrent alterations in the NFAT signaling pathway in OAMZL. Frequent deletions and destructive mutations were detected in the gene encoding the negative NFAT signaling regulator CABIN1 (30% of cases with mutations), as well as rarer mutations in NFAT members themselves and other NFAT signaling pathway components.
5. Epigenetic Regulators
Alterations in epigenetic modifiers occur in several types of lymphoma [77]; additionally, in OAMZL, genes encoding epigenetic regulators are mutated. Among these genes are KMT2D (approximately 5–20% of cases) and CREBBP (ca. 15%). In individual studies, mutations in the epigenetic regulators KMT2C and EP300 have been detected, such that a clear determination of the overall frequency of such alterations needs further investigation [54][56][62]. KMT2C and KMT2D, belonging to the mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) family of histone methyltransferases, methylate Lys-4 of histone H3. Mutations leading to inactivation of these genes lead to diminished global H3K4 methylation in follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [78]. Conditional deletion of Kmt2d in different developmental stages of B cells in mice resulted in an increased number of germinal-center B cells end enhanced proliferation. From these results, the authors suggested the KMT2D acts as tumor suppressor gene. KMT2C, which functions very similarly to KMT2D, and can partially replace a loss of KMT2D, is therefore also supposed to be tumorigenic in case of a loss [79]. CREBBP and EP300 are related histone and non-histone acetyltransferases, which regulate transcriptional activity in several signaling pathways via chromatin remodeling. In follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, monoallelic deletions/mutations result in defects of acetylation of the oncoprotein BCL6 and the tumor suppressor p53.
6. Additional Mutated Genes
In addition to the genes in major signaling pathways or involving epigenetic regulators already mentioned, further genes recurrently mutated in OAMZL include TBL1XR1 [57]. TBL1XR1 is an essential regulator of transcriptional repression, and contributes to canonical NF-κB activation [80]. This gene can activate the transcription of transcription factors such as NF-κB and JUN [81], and may therefore contribute to the strong NF-κB activity in OAML. TBL1XR1 is mutated in various tumors and lymphomas, promoting tumor cell survival. In OAMZL, mutations were consistently detected in 10–20% of cases, so TBL1XR1 is one of the most frequently mutated genes in this type of lymphoma (Table 1). TBL1XR1 mutations have been linked to a poor prognosis in aggressive lymphomas [82][83]. In a small cohort of patients with OAL of the MALT subtype, TBL1XR1 mutations were associated with unique morphometric phenotypes [84]; the cells exhibited significantly lower circularity and solidity as analyzed via computational digital image analysis.
The JAK/STAT signaling pathway is necessary for cytokine signaling and immune regulation, and plays an important role in various types of lymphoma [85]. Activating mutations in JAK3, known to cause constitutive activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, were observed in up to 10% of patients with OAMZL [26]. Interestingly, patients with mutant JAK3 exhibited a shorter progression-free survival [26].
In a recent study, deletions and non-synonymous mutations in the RHOA gene were detected in 26% of OAMZL studies [63]; this points to a potential role of altered Rho signaling in OAMZL, but further studies are needed in order to clarify the consequences of the mutations detected in RHOA.
References
- Das, D.; Deka, P.; Bhattacharjee, K.; Das, J.K.; Kuri, G.C.; Bhattaacharjee, H.; Deori, N.; Deshmukh, S.; Paidi, R.; Deka, A. Idiopathic inflammatory diseases of orbit and ocular adnexa: Histopathological and immunochemical analysis. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 67, 1993–1995.
- Ferreri, A.J.; Dolcetti, R.; Du, M.Q.; Doglioni, C.; Resti, A.G.; Politi, L.S.; De Conciliis, C.; Radford, J.; Bertoni, F.; Zucca, E.; et al. Ocular adnexal MALT lymphoma: An intriguing model for antigen-driven lymphomagenesis and microbial-targeted therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 835–846.
- Go, H.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, Y.A.; Chung, H.K.; Khwarg, S.I.; Kim, C.W.; Jeon, Y.K. Ocular adnexal IgG4-related disease: Comparative analysis with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma and other chronic inflammatory conditions. Histopathology 2012, 60, 296–312.
- Kubota, T.; Moritani, S.; Yoshino, T.; Nagai, H.; Terasaki, H. Ocular adnexal marginal zone B cell lymphoma infiltrated by IgG4-positive plasma cells. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 63, 1059–1065.
- Nishida, K.; Sogabe, Y.; Makihara, A.; Senoo, A.; Morimoto, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Gion, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Sato, Y. Ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphoma arising in a patient with IgG4-related ophthalmic disease. Mod. Rheumatol. 2019, 29, 383–387.
- Ohno, K.; Sato, Y.; Ohshima, K.; Takata, K.; Miyata-Takata, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Gion, Y.; Tachibana, T.; Orita, Y.; Ito, T.; et al. A subset of ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphomas may arise in association with IgG4-related disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13539.
- Sohn, E.J.; Ahn, H.B.; Roh, M.S.; Jung, W.J.; Ryu, W.Y.; Kwon, Y.H. Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-Positive Ocular Adnexal Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma and Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 34, 313–319.
- Li, K.M.; Xu, M.H.; Wu, X.; He, W.M. The Expression of IgG and IgG4 in Orbital MALT Lymphoma: The Similarities and Differences of IgG4-Related Diseases. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5755–5761.
- Karadeniz, H.; Vaglio, A. IgG4-related disease: A contemporary review. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 1616–1631.
- Nishikori, A.; Nishimura, Y.; Shibata, R.; Ohshima, K.I.; Gion, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Nishimura, M.F.; Yoshino, T.; Sato, Y. Upregulated Expression of Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase in Ocular Adnexal Marginal Zone Lymphoma with IgG4-Positive Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4083.
- Du, M.Q. MALT lymphoma: A paradigm of NF-kappaB dysregulation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 39, 49–60.
- Melenotte, C.; Mezouar, S.; Mege, J.L.; Gorvel, J.P.; Kroemer, G.; Raoult, D. Bacterial infection and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 46, 270–287.
- Sassone, M.; Ponzoni, M.; Ferreri, A.J. Ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphoma: Clinical presentation, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2017, 30, 118–130.
- Biernat, M.M.; Wrobel, T. Bacterial Infection and Non-Hodgkin B-Cell Lymphoma: Interactions between Pathogen, Host and the Tumor Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7372.
- Collina, F.; De Chiara, A.; De Renzo, A.; De Rosa, G.; Botti, G.; Franco, R. Chlamydia psittaci in ocular adnexa MALT lymphoma: A possible role in lymphomagenesis and a different geographical distribution. Infect. Agents Cancer 2012, 7, 8.
- Ferreri, A.J.; Guidoboni, M.; Ponzoni, M.; De Conciliis, C.; Dell’Oro, S.; Fleischhauer, K.; Caggiari, L.; Lettini, A.A.; Dal Cin, E.; Ieri, R.; et al. Evidence for an association between Chlamydia psittaci and ocular adnexal lymphomas. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 586–594.
- Yoo, C.; Ryu, M.H.; Huh, J.; Park, J.H.; Kang, H.J.; Ahn, H.S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, T.W.; et al. Chlamydia psittaci infection and clinicopathologic analysis of ocular adnexal lymphomas in Korea. Am. J. Hematol. 2007, 82, 821–823.
- Daibata, M.; Nemoto, Y.; Togitani, K.; Fukushima, A.; Ueno, H.; Ouchi, K.; Fukushi, H.; Imai, S.; Taguchi, H. Absence of Chlamydia psittaci in ocular adnexal lymphoma from Japanese patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 132, 651–652.
- De Cremoux, P.; Subtil, A.; Ferreri, A.J.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Ponzoni, M.; Chaoui, D.; Arnaud, P.; Lumbroso-Le Rouic, L.; Sacchetti, F.; Dendale, R.; et al. Re: Evidence for an association between Chlamydia psittaci and ocular adnexal lymphomas. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 365–366.
- Mulder, M.M.; Heddema, E.R.; Pannekoek, Y.; Faridpooya, K.; Oud, M.E.; Schilder-Tol, E.; Saeed, P.; Pals, S.T. No evidence for an association of ocular adnexal lymphoma with Chlamydia psittaci in a cohort of patients from the Netherlands. Leuk. Res. 2006, 30, 1305–1307.
- Rosado, M.F.; Byrne, G.E., Jr.; Ding, F.; Fields, K.A.; Ruiz, P.; Dubovy, S.R.; Walker, G.R.; Markoe, A.; Lossos, I.S. Ocular adnexal lymphoma: A clinicopathologic study of a large cohort of patients with no evidence for an association with Chlamydia psittaci. Blood 2006, 107, 467–472.
- Vargas, R.L.; Fallone, E.; Felgar, R.E.; Friedberg, J.W.; Arbini, A.A.; Andersen, A.A.; Rothberg, P.G. Is there an association between ocular adnexal lymphoma and infection with Chlamydia psittaci? The University of Rochester experience. Leuk. Res. 2006, 30, 547–551.
- Zhang, G.S.; Winter, J.N.; Variakojis, D.; Reich, S.; Lissner, G.S.; Bryar, P.; Regner, M.; Mangold, K.; Kaul, K. Lack of an association between Chlamydia psittaci and ocular adnexal lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2007, 48, 577–583.
- Gracia, E.; Froesch, P.; Mazzucchelli, L.; Martin, V.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Jimenez, J.; Melgares, M.; Santos, D.; Capo, V.; Cavalli, F.; et al. Low prevalence of Chlamydia psittaci in ocular adnexal lymphomas from Cuban patients. Leuk. Lymphoma 2007, 48, 104–108.
- Matthews, J.M.; Moreno, L.I.; Dennis, J.; Byrne, G.E., Jr.; Ruiz, P.; Dubovy, S.R.; Lossos, I.S. Ocular Adnexal Lymphoma: No evidence for bacterial DNA associated with lymphoma pathogenesis. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 246–249.
- Johansson, P.; Klein-Hitpass, L.; Budeus, B.; Kuhn, M.; Lauber, C.; Seifert, M.; Roeder, I.; Pfortner, R.; Stuschke, M.; Dührsen, U.; et al. Identifying Genetic Lesions in Ocular Adnexal Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphomas of the MALT Subtype by Whole Genome, Whole Exome and Targeted Sequencing. Cancers 2020, 12, 986.
- Travaglino, A.; Pace, M.; Varricchio, S.; Russo, D.; Pugliese, N.; Severino, A.; Picardi, M.; Pane, F.; Insabato, L.; Staibano, S.; et al. Involvement of Helicobacter Pylori in Ocular Adnexa Lymphoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 2075–2081.
- Kalin-Hajdu, E.; Bernier-Turmel, F.; Frost, E.; Labbe, A.C.; Couture, S.; Wong, J.; Boulos, P.R.; Codere, F.; Hardy, I. Helicobacter pylori Infection of the Gastric Mucosa and Ocular Adnexa-Lack of Association with Ocular Adnexal Lymphoma. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 37, S1–S5.
- Mollerup, S.; Mikkelsen, L.H.; Hansen, A.J.; Heegaard, S. High-throughput sequencing reveals no viral pathogens in eight cases of ocular adnexal extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 185, 107677.
- De Sanjose, S.; Benavente, Y.; Vajdic, C.M.; Engels, E.A.; Morton, L.M.; Bracci, P.M.; Spinelli, J.J.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Franceschi, S.; et al. Hepatitis C and non-Hodgkin lymphoma among 4784 cases and 6269 controls from the International Lymphoma Epidemiology Consortium. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 451–458.
- Tang, A.; Hallouch, O.; Chernyak, V.; Kamaya, A.; Sirlin, C.B. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Target population for surveillance and diagnosis. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 13–25.
- Couronne, L.; Bachy, E.; Roulland, S.; Nadel, B.; Davi, F.; Armand, M.; Canioni, D.; Michot, J.M.; Visco, C.; Arcaini, L.; et al. From hepatitis C virus infection to B-cell lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 92–100.
- Gibson, T.M.; Morton, L.M.; Shiels, M.S.; Clarke, C.A.; Engels, E.A. Risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes in HIV-infected people during the HAART era: A population-based study. AIDS 2014, 28, 2313–2318.
- Verma, V.; Shen, D.; Sieving, P.C.; Chan, C.C. The role of infectious agents in the etiology of ocular adnexal neoplasia. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2008, 53, 312–331.
- Wohrer, S.; Troch, M.; Streubel, B.; Zwerina, J.; Skrabs, C.; Formanek, M.; Hauff, W.; Hoffmann, M.; Mullauer, L.; Chott, A.; et al. MALT lymphoma in patients with autoimmune diseases: A comparative analysis of characteristics and clinical course. Leukemia 2007, 21, 1812–1818.
- Smedby, K.E.; Vajdic, C.M.; Falster, M.; Engels, E.A.; Martinez-Maza, O.; Turner, J.; Hjalgrim, H.; Vineis, P.; Costantini, A.S.; Bracci, P.M.; et al. Autoimmune disorders and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes: A pooled analysis within the InterLymph Consortium. Blood 2008, 111, 4029–4038.
- Zintzaras, E.; Voulgarelis, M.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. The risk of lymphoma development in autoimmune diseases: A meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 2337–2344.
- Royer, B.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Sibilia, J.; Agbalika, F.; Cayuela, J.M.; Soussi, T.; Maloisel, F.; Clauvel, J.P.; Brouet, J.C.; Mariette, X. Lymphomas in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome are marginal zone B-cell neoplasms, arise in diverse extranodal and nodal sites, and are not associated with viruses. Blood 1997, 90, 766–775.
- Nocturne, G.; Virone, A.; Ng, W.F.; Le Guern, V.; Hachulla, E.; Cornec, D.; Daien, C.; Vittecoq, O.; Bienvenu, B.; Marcelli, C.; et al. Rheumatoid Factor and Disease Activity Are Independent Predictors of Lymphoma in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 977–985.
- Mackay, F.; Woodcock, S.A.; Lawton, P.; Ambrose, C.; Baetscher, M.; Schneider, P.; Tschopp, J.; Browning, J.L. Mice transgenic for BAFF develop lymphocytic disorders along with autoimmune manifestations. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1697–1710.
- Isaacson, P.G.; Du, M.Q. MALT lymphoma: From morphology to molecules. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 644–653.
- Wotherspoon, A.C.; Pan, L.X.; Diss, T.C.; Isaacson, P.G. Cytogenetic study of B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1992, 58, 35–38.
- Streubel, B.; Simonitsch-Klupp, I.; Mullauer, L.; Lamprecht, A.; Huber, D.; Siebert, R.; Stolte, M.; Trautinger, F.; Lukas, J.; Puspok, A.; et al. Variable frequencies of MALT lymphoma-associated genetic aberrations in MALT lymphomas of different sites. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1722–1726.
- Ye, H.; Liu, H.; Attygalle, A.; Wotherspoon, A.C.; Nicholson, A.G.; Charlotte, F.; Leblond, V.; Speight, P.; Goodlad, J.; Lavergne-Slove, A.; et al. Variable frequencies of t(11;18)(q21;q21) in MALT lymphomas of different sites: Significant association with CagA strains of H pylori in gastric MALT lymphoma. Blood 2003, 102, 1012–1018.
- Hamoudi, R.A.; Appert, A.; Ye, H.; Ruskone-Fourmestraux, A.; Streubel, B.; Chott, A.; Raderer, M.; Gong, L.; Wlodarska, I.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; et al. Differential expression of NF-kappaB target genes in MALT lymphoma with and without chromosome translocation: Insights into molecular mechanism. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1487–1497.
- Tanimoto, K.; Sekiguchi, N.; Yokota, Y.; Kaneko, A.; Watanabe, T.; Maeshima, A.M.; Matsuno, Y.; Harada, M.; Tobinai, K.; Kobayashi, Y. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis of primary ocular adnexal MALT lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 249.
- Takahashi, H.; Usui, Y.; Ueda, S.; Yamakawa, N.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Sato, Y.; Ogawa, S.; Goto, H. Genome-Wide Analysis of Ocular Adnexal Lymphoproliferative Disorders Using High-Resolution Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Array. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 4156–4165.
- Schiby, G.; Polak-Charcon, S.; Mardoukh, C.; Rosenblatt, K.; Goldberg, I.; Kneller, A.; Rosner, M.; Kopolovic, J. Orbital marginal zone lymphomas: An immunohistochemical, polymerase chain reaction, and fluorescence in situ hybridization study. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 435–442.
- Takada, S.; Yoshino, T.; Taniwaki, M.; Nakamura, N.; Nakamine, H.; Oshima, K.; Sadahira, Y.; Inagaki, H.; Oshima, K.; Tadaatsu, A. Involvement of the chromosomal translocation t(11;18) in some mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the ocular adnexa: Evidence from multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and fluorescence in situ hybridization on using formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens. Mod. Pathol. 2003, 16, 445–452.
- Zhu, D.; Ikpatt, O.F.; Dubovy, S.R.; Lossos, C.; Natkunam, Y.; Chapman-Fredricks, J.R.; Fan, Y.S.; Lossos, I.S. Molecular and genomic aberrations in Chlamydophila psittaci negative ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphomas. Am. J. Hematol. 2013, 88, 730–735.
- Streubel, B.; Vinatzer, U.; Lamprecht, A.; Raderer, M.; Chott, A. T(3;14)(p14.1;q32) involving IGH and FOXP1 is a novel recurrent chromosomal aberration in MALT lymphoma. Leukemia 2005, 19, 652–658.
- Adam, P.; Haralambieva, E.; Hartmann, M.; Mao, Z.; Ott, G.; Rosenwald, A. Rare occurrence of IgVH gene translocations and restricted IgVH gene repertoire in ocular MALT-type lymphoma. Haematologica 2008, 93, 319–320.
- Bi, Y.; Zeng, N.; Chanudet, E.; Huang, Y.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Liu, H.; Dong, G.; Watkins, A.J.; Ley, S.C.; Zou, L.; et al. A20 inactivation in ocular adnexal MALT lymphoma. Haematologica 2012, 97, 926–930.
- Johansson, P.; Klein-Hitpass, L.; Grabellus, F.; Arnold, G.; Klapper, W.; Pfortner, R.; Dührsen, U.; Eckstein, A.; Dürig, J.; Küppers, R. Recurrent mutations in NF-kappaB pathway components, KMT2D, and NOTCH1/2 in ocular adnexal MALT-type marginal zone lymphomas. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62627–62639.
- Chanudet, E.; Huang, Y.; Ichimura, K.; Dong, G.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Radford, J.; Wotherspoon, A.C.; Isaacson, P.G.; Ferry, J.; Du, M.Q. A20 is targeted by promoter methylation, deletion and inactivating mutation in MALT lymphoma. Leukemia 2010, 24, 483–487.
- Jung, H.; Yoo, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, S.; Joung, J.G.; Nam, J.Y.; Ryu, D.; Yun, J.W.; et al. The mutational landscape of ocular marginal zone lymphoma identifies frequent alterations in TNFAIP3 followed by mutations in TBL1XR1 and CREBBP. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17038–17049.
- Vela, V.; Juskevicius, D.; Dirnhofer, S.; Menter, T.; Tzankov, A. Mutational landscape of marginal zone B-cell lymphomas of various origin: Organotypic alterations and diagnostic potential for assignment of organ origin. Virchows Arch. 2021.
- Behdad, A.; Zhou, X.Y.; Gao, J.; Raparia, K.; Dittman, D.; Green, S.J.; Qi, C.; Betz, B.; Bryar, P.; Chen, Q.; et al. High Frequency of MYD88 L265P Mutation in Primary Ocular Adnexal Marginal Zone Lymphoma and Its Clinicopathologic Correlation: A Study From a Single Institution. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 483–493.
- Cani, A.K.; Soliman, M.; Hovelson, D.H.; Liu, C.J.; McDaniel, A.S.; Haller, M.J.; Bratley, J.V.; Rahrig, S.E.; Li, Q.; Briceno, C.A.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiling of orbital and ocular adnexal lymphomas identifies frequent alterations in MYD88 and chromatin modifiers: New routes to targeted therapies. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 685–697.
- Yan, Q.; Wang, M.; Moody, S.; Xue, X.; Huang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Du, M.Q. Distinct involvement of NF-kappaB regulators by somatic mutation in ocular adnexal malt lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 160, 851–854.
- Moody, S.; Thompson, J.S.; Chuang, S.S.; Liu, H.; Raderer, M.; Vassiliou, G.; Wlodarska, I.; Wu, F.; Cogliatti, S.; Robson, A.; et al. Novel GPR34 and CCR6 mutation and distinct genetic profiles in MALT lymphomas of different sites. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1329–1336.
- Cascione, L.; Rinaldi, A.; Bruscaggin, A.; Tarantelli, C.; Arribas, A.J.; Kwee, I.; Pecciarini, L.; Mensah, A.A.; Spina, V.; Chung, E.Y.L.; et al. Novel insights into the genetics and epigenetics of MALT lymphoma unveiled by next generation sequencing analyses. Haematologica 2019, 104, e558–e561.
- Magistri, M.; Happ, L.E.; Ramdial, J.; Lu, X.; Stathias, V.; Kunkalla, K.; Agarwal, N.; Jiang, X.; Schürer, S.C.; Dubovy, S.R.; et al. The Genetic Landscape of Ocular Adnexa MALT Lymphoma Reveals Frequent Aberrations in NFAT and MEF2B Signaling Pathways. Cancer Res. Commun. 2021, 1, 1–16.
- Du, M.Q. MALT lymphoma: Many roads lead to nuclear factor-kappab activation. Histopathology 2011, 58, 26–38.
- Van Keimpema, M.; Gruneberg, L.J.; Mokry, M.; van Boxtel, R.; Koster, J.; Coffer, P.J.; Pals, S.T.; Spaargaren, M. FOXP1 directly represses transcription of proapoptotic genes and cooperates with NF-kappaB to promote survival of human B cells. Blood 2014, 124, 3431–3440.
- Clement, C.G.; Potluri, V.R.; Gonzales, J.; Qian, Y.W. Translocation (5; 11) in a conjunctival MALT lymphoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2011, 4, 722–726.
- Kim, W.S.; Honma, K.; Karnan, S.; Tagawa, H.; Kim, Y.D.; Oh, Y.L.; Seto, M.; Ko, Y.H. Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization of ocular marginal zone B cell lymphoma: Comparison with pulmonary and nodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2007, 46, 776–783.
- Sasaki, Y.; Iwai, K. Roles of the NF-kappaB Pathway in B-Lymphocyte Biology. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 393, 177–209.
- Liu, F.; Karube, K.; Kato, H.; Arita, K.; Yoshida, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Tsuzuki, S.; Kim, W.; Ko, Y.H.; Seto, M. Mutation analysis of NF-kappaB signal pathway-related genes in ocular MALT lymphoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2012, 5, 436–441.
- Fabbri, G.; Rasi, S.; Rossi, D.; Trifonov, V.; Khiabanian, H.; Ma, J.; Grunn, A.; Fangazio, M.; Capello, D.; Monti, S.; et al. Analysis of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia coding genome: Role of NOTCH1 mutational activation. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1389–1401.
- Kiel, M.J.; Velusamy, T.; Betz, B.L.; Zhao, L.; Weigelin, H.G.; Chiang, M.Y.; Huebner-Chan, D.R.; Bailey, N.G.; Yang, D.T.; Bhagat, G.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent somatic NOTCH2 mutations in splenic marginal zone lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1553–1565.
- Rossi, D.; Trifonov, V.; Fangazio, M.; Bruscaggin, A.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Monti, S.; Vaisitti, T.; Arruga, F.; Fama, R.; et al. The coding genome of splenic marginal zone lymphoma: Activation of NOTCH2 and other pathways regulating marginal zone development. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1537–1551.
- Osipo, C.; Golde, T.E.; Osborne, B.A.; Miele, L.A. Off the beaten pathway: The complex cross talk between Notch and NF-kappaB. Lab. Investig. 2008, 88, 11–17.
- Schwarzer, R.; Dorken, B.; Jundt, F. Notch is an essential upstream regulator of NF-kappaB and is relevant for survival of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Leukemia 2012, 26, 806–813.
- Wang, J.; Shelly, L.; Miele, L.; Boykins, R.; Norcross, M.A.; Guan, E. Human Notch-1 inhibits NF-kappa B activity in the nucleus through a direct interaction involving a novel domain. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 289–295.
- De Decker, M.; Lavaert, M.; Roels, J.; Tilleman, L.; Vandekerckhove, B.; Leclercq, G.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; Taghon, T. HES1 and HES4 have non-redundant roles downstream of Notch during early human T-cell development. Haematologica 2021, 106, 130–141.
- Morin, R.D.; Mendez-Lago, M.; Mungall, A.J.; Goya, R.; Mungall, K.L.; Corbett, R.D.; Johnson, N.A.; Severson, T.M.; Chiu, R.; Field, M.; et al. Frequent mutation of histone-modifying genes in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Nature 2011, 476, 298–303.
- Zhang, J.; Dominguez-Sola, D.; Hussein, S.; Lee, J.E.; Holmes, A.B.; Bansal, M.; Vlasevska, S.; Mo, T.; Tang, H.; Basso, K.; et al. Disruption of KMT2D perturbs germinal center B cell development and promotes lymphomagenesis. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1190–1198.
- Fagan, R.J.; Dingwall, A.K. COMPASS Ascending: Emerging clues regarding the roles of MLL3/KMT2C and MLL2/KMT2D proteins in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 458, 56–65.
- Perissi, V.; Aggarwal, A.; Glass, C.K.; Rose, D.W.; Rosenfeld, M.G. A corepressor/coactivator exchange complex required for transcriptional activation by nuclear receptors and other regulated transcription factors. Cell 2004, 116, 511–526.
- Li, J.Y.; Daniels, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. TBL1XR1 in physiological and pathological states. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2015, 3, 13–23.
- Venturutti, L.; Teater, M.; Zhai, A.; Chadburn, A.; Babiker, L.; Kim, D.; Beguelin, W.; Lee, T.C.; Kim, Y.; Chin, C.R.; et al. TBL1XR1 Mutations Drive Extranodal Lymphoma by Inducing a Pro-tumorigenic Memory Fate. Cell 2020, 182, 297–316.e227.
- Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Cai, W.; Bao, H.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Ruan, C.; Wu, D.; Shen, H.; et al. TBL1XR1 mutation predicts poor outcome in primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 10.
- Jangam, D.; Sridhar, K.; Butzmann, A.; Samghabadi, P.; Plowey, E.D.; Ohgami, R.S. TBL1XR1 Mutations in Primary Marginal Zone Lymphomas of Ocular Adnexa are Associated with Unique Morphometric Phenotypes. Curr. Eye Res. 2020, 45, 1583–1589.
- O’Shea, J.J.; Holland, S.M.; Staudt, L.M. JAKs and STATs in immunity, immunodeficiency, and cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 161–170.
More
Information
Subjects:
Hematology
Contributor
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
833
Revisions:
3 times
(View History)
Update Date:
18 Mar 2022
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No





