
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Li Li | + 1822 word(s) | 1822 | 2022-03-02 07:37:45 | | | |
| 2 | Beatrix Zheng | Meta information modification | 1822 | 2022-03-07 02:48:25 | | | | |
| 3 | Beatrix Zheng | Meta information modification | 1822 | 2022-03-07 02:59:15 | | | | |
| 4 | Beatrix Zheng | Meta information modification | 1822 | 2022-03-07 03:03:09 | | |
Video Upload Options
The combustion of fossil fuels has led to a large amount of carbon dioxide emissions and increased greenhouse effect. Methanation of carbon dioxide can not only mitigate the greenhouse effect, but also utilize the hydrogen generated by renewable electricity such as wind, solar, tidal energy, and others, which could ameliorate the energy crisis to some extent. Highly efficient catalysts and processes are important to make CO2 methanation practical. Although noble metal catalysts exhibit higher catalytic activity and CH4 selectivity at low temperature, their large-scale industrial applications are limited by the high costs. Ni-based catalysts have attracted extensive attention due to their high activity, low cost, and abundance. At the same time, it is of great importance to study the mechanism of CO2 methanation on Ni-based catalysts in designing high-activity and stability catalysts.
1. Introduction
CO2 + 4 H2 → CH4 + 2 H2O, ΔH298K = −165.4 kJ/mol, ΔG298K = −130.8 kJ/mol, (1)
2. The Reaction Mechanism of CO2 Methanation
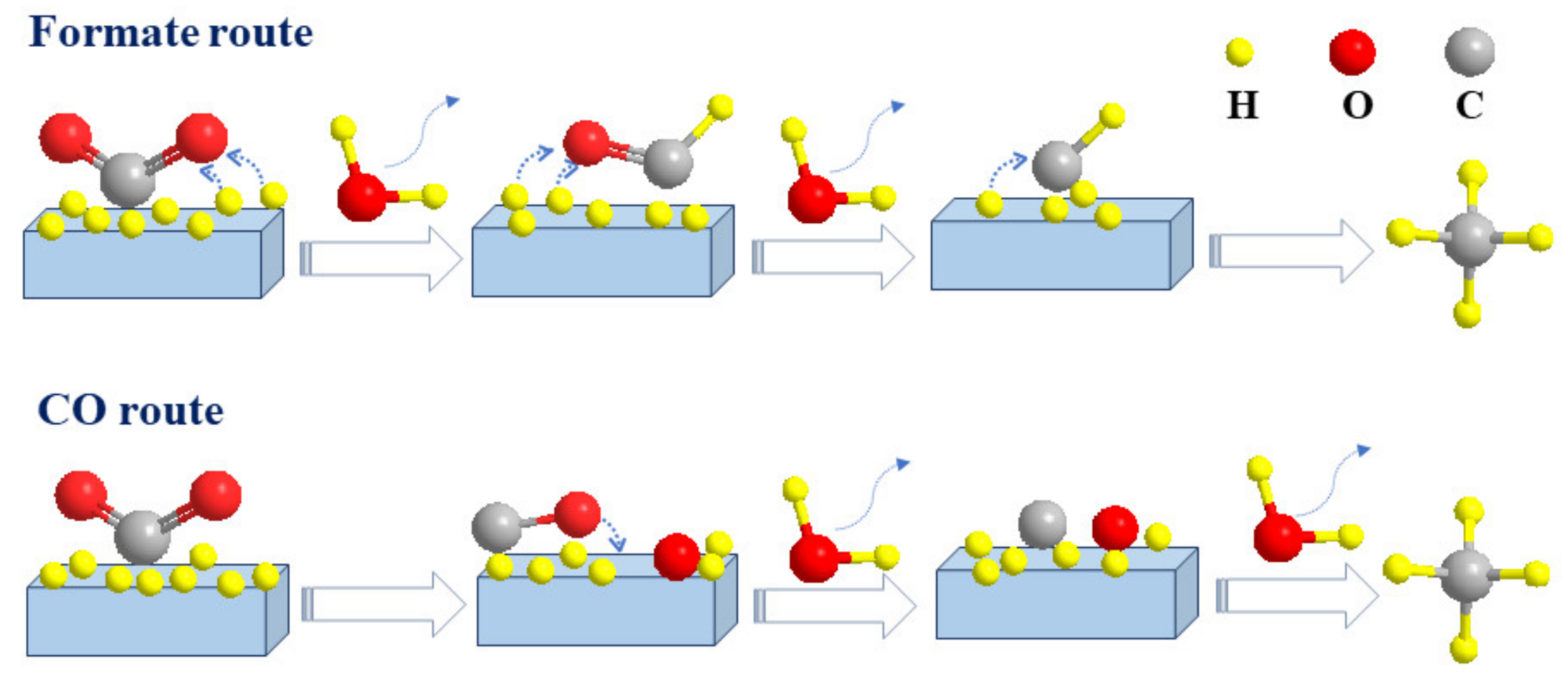
2.1. The Formate Pathway
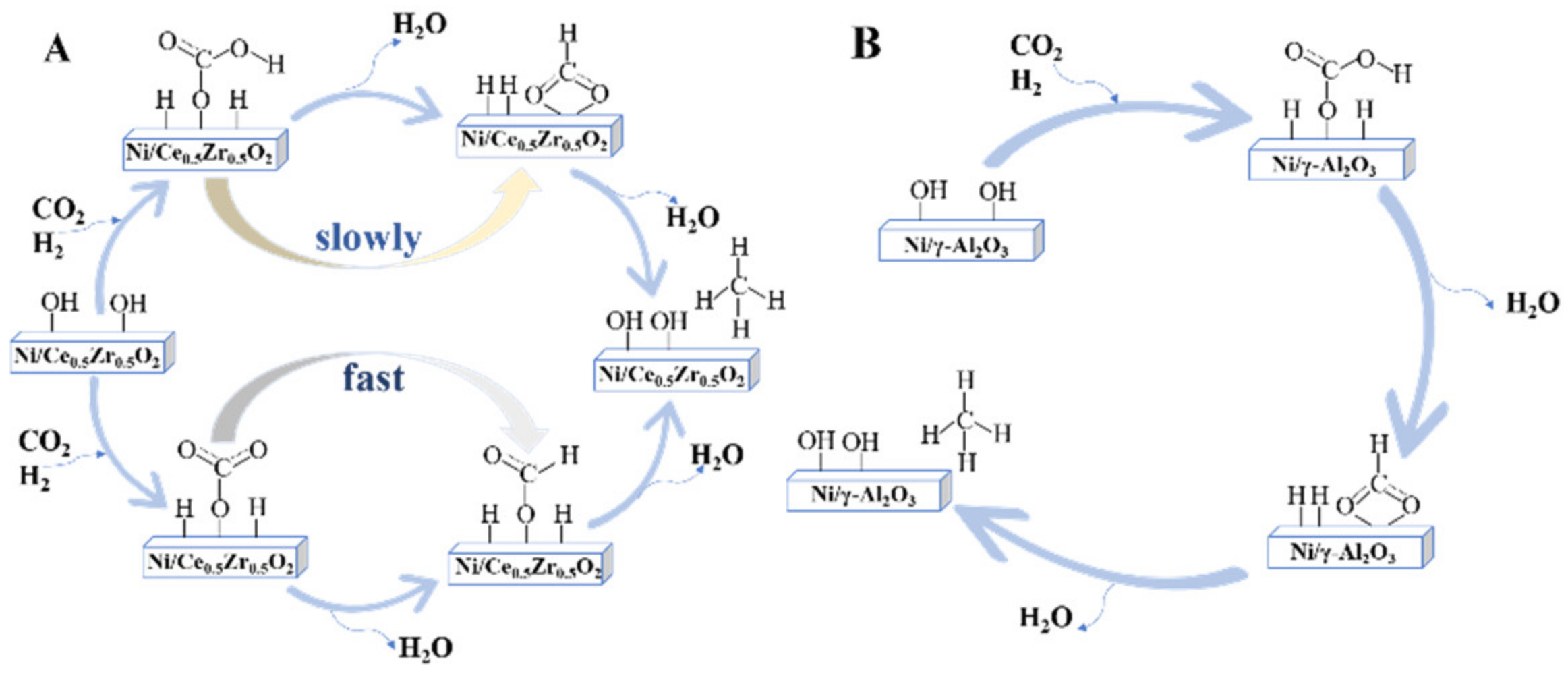
2.2. The CO Pathway
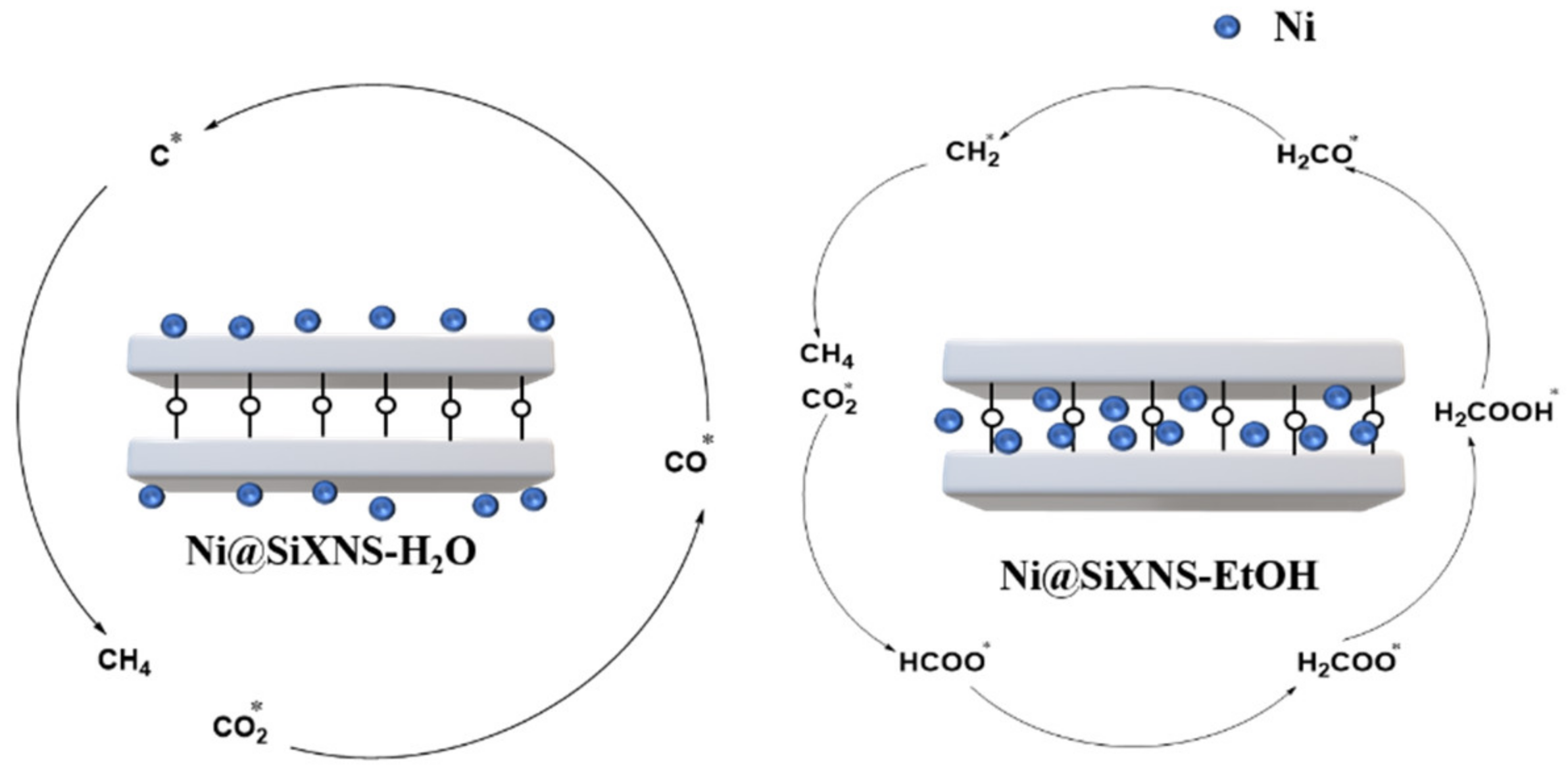
2.3. The Key Factors of CO2 Methanation Reaction Route
References
- Anwar, M.N.; Fayyaz, A.; Sohail, N.F.; Khokhar, M.F.; Baqar, M.; Yasar, A.; Rasool, K.; Nazir, A.; Raja, M.U.F.; Rehan, M.; et al. CO2 utilization: Turning greenhouse gas into fuels and valuable products. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110059.
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Wu, D. Reaction mechanism of CO2 methanation over Rh/TiO2 catalyst. Fuel 2020, 276, 118093.
- Burger, T.; Koschany, F.; Thomys, O.; Köhler, K.; Hinrichsen, O. CO2 methanation over Fe- and Mn-promoted co-precipitated Ni-Al catalysts: Synthesis, characterization and catalysis study. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 558, 44–54.
- Ahadzi, E.; Ramyashree, M.; Priya, S.S.; Sudhakar, K.; Tahir, M. CO2 to green fuel: Photocatalytic process optimization study. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 24, 100533.
- Silva, T.C.D.; Isha, A.; Chandra, R.; Vijay, V.K.; Subbarao, P.M.V.; Kumar, R.; Chaudhary, V.P.; Singh, H.; Khan, A.A.; Tyagi, V.K.; et al. Enhancing methane production in anaerobic digestion through hydrogen assisted pathways—A state-of-the-art review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 151, 111536.
- Hussain, M.; Akhter, P.; Russo, N.; Saracco, G. Novel Ti-KIT-6 material for the photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to methane. Catal. Commun. 2013, 36, 58–62.
- Li, S.; Guo, S.; Gong, D.; Kang, N.; Fang, K.-G.; Liu, Y. Nano composite composed of MoOx-La2O3-Ni on SiO2 for storing hydrogen into CH4 via CO2 methanation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 1597–1609.
- Alarcón, A.; Guilera, J.; Díaz-López, J.A.; Andreu, T. Optimization of nickel and ceria catalyst content for synthetic natural gas production through CO2 methanation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 193, 114–122.
- Xing, Y.; Ma, Z.; Su, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Analysis of Research Status of CO2 Conversion Technology Based on Bibliometrics. Catalysts 2020, 10, 370.
- Panagiotopoulou, P. Methanation of CO2 over alkali-promoted Ru/TiO2 catalysts: II. Effect of alkali additives on the reaction pathway. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 236, 162–170.
- Rasheed, T.; Shafi, S.; Anwar, M.T.; Rizwan, K.; Ahmad, T.; Bilal, M. Revisiting Photo and Electro-catalytic Modalities for Sustainable Conversion of CO2. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 623, 118248.
- Aldana, P.U.; Ocampo, F.; Kobl, K.; Louis, B.; Thibault-Starzyk, F.; Daturi, M.; Bazin, P.; Thomas, S.; Roger, A. Catalytic CO2 valorization into CH4 on Ni-based ceria-zirconia. Reaction mechanism by operando IR spectroscopy. Catal. Today 2013, 215, 201–207.
- Aziz, M.; Jalil, A.; Triwahyono, S.; Sidik, S. Methanation of carbon dioxide on metal-promoted mesostructured silica nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 486, 115–122.
- Budi, C.S.; Wu, H.-C.; Chen, C.-S.; Saikia, D.; Kao, H.-M. Ni Nanoparticles Supported on Cage-Type Mesoporous Silica for CO2 Hydrogenation with High CH4 Selectivity. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 2326–2331.
- Chen, H.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Zhou, S. Mechanochemical in-situ incorporation of Ni on MgO/MgH2 surface for the selective O-/C-terminal catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 to CH4. J. Catal. 2021, 394, 397–405.
- Baysal, Z.; Kureti, S. CO2 methanation on Mg-promoted Fe catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 262, 118300.
- Dębek, R.; Azzolina-Jury, F.; Travert, A.; Maugé, F. A review on plasma-catalytic methanation of carbon dioxide—Looking for an efficient catalyst. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 116, 109427.
- Renda, S.; Ricca, A.; Palma, V. Precursor salts influence in Ruthenium catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to methane. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115767.
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, C. The Effect of Si on CO2 Methanation over Ni-xSi/ZrO2 Catalysts at Low Temperature. Catalysts 2021, 11, 67.
- Martínez, J.; Hernández, E.; Alfaro, S.; Medina, R.L.; Aguilar, G.V.; Albiter, E.; Valenzuela, M.A. High Selectivity and Stability of Nickel Catalysts for CO2 Methanation: Support Effects. Catalysts 2018, 9, 24.
- Tu, J.; Wu, H.; Qian, Q.; Han, S.; Chu, M.; Jia, S.; Feng, R.; Zhai, J.; He, M.; Han, B. Low temperature methanation of CO2 over an amorphous cobalt-based catalyst. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3937–3943.
- Mateo, D.; Albero, J.; García, H. Titanium-Perovskite-Supported RuO2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic CO2 Methanation. Joule 2019, 3, 1949–1962.
- Falbo, L.; Martinelli, M.; Visconti, C.G.; Lietti, L.; Bassano, C.; Deiana, P. Kinetics of CO2 methanation on a Ru-based catalyst at process conditions relevant for Power-to-Gas applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 225, 354–363.
- Liu, Q.; Bian, B.; Fan, J.; Yang, J. Cobalt doped Ni based ordered mesoporous catalysts for CO2 methanation with enhanced catalytic performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 4893–4901.
- Karelovic, A.; Ruiz, P. Mechanistic study of low temperature CO2 methanation over Rh/TiO2 catalysts. J. Catal. 2013, 301, 141–153.
- Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Tong, Y.; Fang, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, D.-E.; Wang, X. Facile Cr3+-Doping Strategy Dramatically Promoting Ru/CeO2 for Low-Temperature CO2 Methanation: Unraveling the Roles of Surface Oxygen Vacancies and Hydroxyl Groups. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 5762–5775.
- Dreyer, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Beh, G.K.; Zhang, R.; Sit, P.; Teoh, W.Y. Influence of the oxide support reducibility on the CO2 methanation over Ru-based catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 219, 715–726.
- Iqbal, M.M.A.; Abu Bakar, W.A.W.; Toemen, S.; Razak, F.I.A.; Azelee, N.I.W. Optimization study by Box-Behnken design (BBD) and mechanistic insight of CO2 methanation over Ru-Fe-Ce/γ-Al2O3 catalyst by in-situ FTIR technique. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4170–4179.
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.M.; Park, J.-N. Bifunctional Mechanism of CO2 Methanation on Pd-MgO/SiO2 Catalyst: Independent Roles of MgO and Pd on CO2 Methanation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 7128–7131.
- Jiang, H.; Gao, Q.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M. The synergistic effect of Pd NPs and UiO-66 for enhanced activity of carbon dioxide methanation. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 31, 167–172.
- Ashok, J.; Pati, S.; Hongmanorom, P.; Tianxi, Z.; Junmei, C.; Kawi, S. A review of recent catalyst advances in CO2 methanation processes. Catal. Today 2020, 356, 471–489.
- Quindimil, A.; Bacariza, M.C.; González-Marcos, J.A.; Henriques, C.; González-Velasco, J.R. Enhancing the CO2 methanation activity of γ-Al2O3 supported mono- and bi-metallic catalysts prepared by glycerol assisted impregnation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 296, 120322.
- Yan, X.; Sun, W.; Fan, L.; Duchesne, P.N.; Wang, W.; Kübel, C.; Wang, D.; Kumar, S.G.H.; Li, Y.F.; Tavasoli, A.; et al. catalytic nanosheets for high-performance CO2 methanation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2608–2618.
- Pan, Q.; Peng, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. In situ FTIR spectroscopic study of the CO2 methanation mechanism on Ni/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 502–509.
- Xu, X.; Tong, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, J.; Fang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Insights into CO2 methanation mechanism on cubic ZrO2 supported Ni catalyst via a combination of experiments and DFT calculations. Fuel 2020, 283, 118867.
- Miao, B.; Ma, S.S.K.; Wang, X.; Su, H.; Chan, S.H. Catalysis mechanisms of CO2 and CO methanation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 4048–4058.
- Huang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, X. New insights into CO2 methanation mechanisms on Ni/MgO catalysts by DFT calculations: Elucidating Ni and MgO roles and support effects. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 33, 55–63.
- Le, T.A.; Kim, J.; Kang, J.K.; Park, E.D. CO and CO2 methanation over M (M Mn, Ce, Zr, Mg, K, Zn, or V)-promoted Ni/2O3 catalysts. Catal. Today 2019, 348, 80–88.
- Hasan, M.; Asakoshi, T.; Muroyama, H.; Matsui, T.; Eguchi, K. CO2 methanation mechanism over Ni/Y2O3: An in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopic study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 5551–5558.
- Solis-Garcia, A.; Hernandez, J.F.; Almendarez-Camarillo, A.; Fierro-Gonzalez, J. Participation of surface bicarbonate, formate and methoxy species in the carbon dioxide methanation catalyzed by ZrO2-supported Ni. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 218, 611–620.
- Westermann, A.; Azambre, B.; Bacariza, M.C.; Graça, I.; Ribeiro, M.F.; Lopes, J.M.; Henriques, C. Insight into CO2 methanation mechanism over NiUSY zeolites: An operando IR study. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 174–175, 120–125.
- Lin, X.; Wang, S.; Tu, W.; Hu, Z.; Ding, Z.; Hou, Y.; Xu, R.; Dai, W. MOF-derived hierarchical hollow spheres composed of carbon-confined Ni nanoparticles for efficient CO2 methanation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 731–738.
- Pan, Q.; Peng, J.; Sun, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. Insight into the reaction route of CO2 methanation: Promotion effect of medium basic sites. Catal. Commun. 2013, 45, 74–78.
- Younas, M.; Kong, L.L.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Nadeem, H.; Shehzad, A.; Sethupathi, S. Recent Advancements, Fundamental Challenges, and Opportunities in Catalytic Methanation of CO2. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 8815–8831.
- Su, X.; Xu, J.; Liang, B.; Duan, H.; Hou, B.; Huang, Y. Catalytic carbon dioxide hydrogenation to methane: A review of recent studies. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 553–565.
- Jacquemin, M.; Beuls, A.; Ruiz, P. Catalytic production of methane from CO2 and H2 at low temperature: Insight on the reaction mechanism. Catal. Today 2010, 157, 462–466.
- Italiano, C.; Llorca, J.; Pino, L.; Ferraro, M.; Antonucci, V.; Vita, A. CO and CO2 methanation over Ni catalysts supported on CeO2, Al2O3 and Y2O3 oxides. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 264, 118494.
- Zhou, G.; Liu, H.; Cui, K.; Jia, A.; Hu, G.; Jiao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Role of surface Ni and Ce species of Ni/CeO2 catalyst in CO2 methanation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 383, 248–252.
- Bukhari, S.N.; Chong, C.C.; Setiabudi, H.D.; Cheng, Y.W.; Teh, L.P.; Jalil, A.A. Ni/Fibrous type SBA-15: Highly active and coke resistant catalyst for CO2 methanation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 229, 116141.
- Cerdá-Moreno, C.; Chica, A.; Keller, S.; Rautenberg, C.; Bentrup, U. Ni-sepiolite and Ni-todorokite as efficient CO2 methanation catalysts: Mechanistic insight by operando DRIFTS. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 264, 118546.
- Liang, C.; Hu, X.; Wei, T.; Jia, P.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, D.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Hu, G. Methanation of CO2 over Ni/Al2O3 modified with alkaline earth metals: Impacts of oxygen vacancies on catalytic activity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 8197–8213.
- Zhou, R.; Rui, N.; Fan, Z.; Liu, C.-J. Effect of the structure of Ni/TiO2 catalyst on CO2 methanation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 22017–22025.
- Jia, X.; Zhang, X.; Rui, N.; Hu, X.; Liu, C.-J. Structural effect of Ni/ZrO2 catalyst on CO2 methanation with enhanced activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 244, 159–169.





