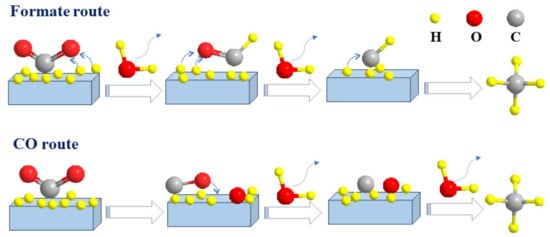
Many studies have reported that CO
2 methanation follows the formate route on different nickel catalysts such as Ni/MgO
[37][198], Ni-Mn/Al@Al
2O
3 [38][199], Ni/Y
2O
3 [39][200], Ni/ZrO
2 [35][40][196,201], Ni/ultra-stable Y (USY) zeolite
[41][139], and Ni@C
[42][102]. For example, Xu and coworkers
[35][196] discussed the formation and evolution of CO
2 adsorbed species on Ni/c-ZrO
2 by in situ FTIR and DFT calculations. CO
2 methanation on Ni/c-ZrO
2 was dominated by the formate pathway as follows: CO
2*→ HCOO* → H
2COO* → H
2COOH* → H
2CO* → CH
2*→ CH
4*, which is the same as that shown in
Figure 14. CO was a by-product instead of a reaction intermediate, which could not further form CH
4, and the DFT calculations also confirmed the formate pathway, which was highly consistent with the in situ FTIR results. Solis-Garcia et al.
[40][201] also found that CO
2 methanation follows the formate pathway over Ni/ZrO
2 and no CO species were observed during the reaction. The possible reaction pathway of the CO
2 methanation over Ni@C was also investigated by CO
2-TPD measurements and in situ FTIR characterization. All results demonstrated that CO
2 methanation over Ni@C catalyst proceeded via the formate route without involving CO as an intermediate
[42][102]. Aldana et al.
[12][41] also found that the main CO
2 methanation mechanism on Ni-CZ
sol–gel was the formate pathway, which does not require CO as reaction intermediate. They also found that H
2 was dissociated on Ni
0 sites while CO
2 was activated on the ceria–zirconia support to form carbonates and then further into CH
4, suggesting that a stable metal–support interface is beneficial for the adsorption of CO
2.
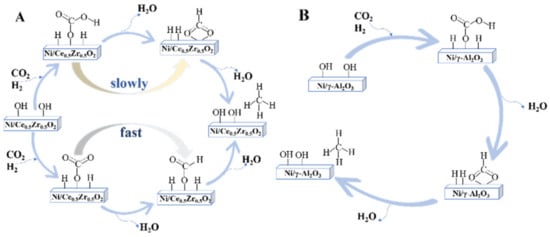
In another study, Pan et al.
[43][202] found that the reaction pathway on Ni/γ-Al
2O
3 and Ni/Ce
0.5Zr
0.5O
2 all followed the formate pathway, only differing in reactive basic sites. On the Ni/Ce
0.5Zr
0.5O
2 catalyst, CO
2 adsorption on medium basic sites formed bidentate formate, whereas CO
2 adsorption on surface oxygen resulted in the monodentate formate. Due to the faster hydrogenation of monodentate formate, it was assumed to be the main reaction route on the Ni/Ce
0.5Zr
0.5O
2 catalyst. For CO
2 methanation on Ni/γ-Al
2O
3, hydrogenation of bidentate formate was the main reaction route as bidentate formate was the main adsorption and intermediate species and CO
2 adsorbed on strong basic sites of Ni/γ-Al
2O
3 will not participate in the CO
2 methanation reaction. It was assumed that medium basic sites are responsible for promoting the formation of monodentate formate species, thus enhancing CO
2 methanation activity. CO
2 methanation reaction pathways on Ni/Ce
0.5Zr
0.5O
2 and Ni/γ-Al
2O
3 are shown in
Figure 25.