
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Marina S Gorbaytuk | + 4041 word(s) | 4041 | 2022-02-07 09:54:24 | | | |
| 2 | Beatrix Zheng | + 707 word(s) | 4748 | 2022-02-15 04:19:12 | | | | |
| 3 | Beatrix Zheng | Meta information modification | 4748 | 2022-02-15 04:21:09 | | |
Video Upload Options
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is an ocular complication of diabetes mellitus (DM), a metabolic disorder characterized by elevation in blood glucose level. The pathogenesis of DR includes vascular, neuronal, and inflammatory components leading to activation of complex cellular molecular signaling. If untreated, the disease can culminate in vision loss that eventually leads to blindness. Animal models mimicking different aspects of DM complications have been developed to study the development and progression of DR. Despite the significant contribution of the developed DR models to discovering the mechanisms of DR and the recent achievements in the research field, the sequence of cellular events in diabetic retinas is still under investigation. Partially, this is due to the complexity of molecular mechanisms, although the lack of availability of models that adequately mimic all the neurovascular pathobiological features observed in patients has also contributed to the delay in determining a precise molecular trigger.
1. Introduction
2. Rodent Models of Diabetic Retinopathy
2.1. Pathological Signs in Rodent Models of Diabetic Retinopathy
2.1.1. Neovascularization and Microvascular Changes in Diabetic Rodents
2.1.2. The Detection of Functional Changes of the Neural Retina in Diabetic Rodents
2.2. Cellular Signaling Changes in the Diabetic Rodent Retina
2.2.1. Insulin Signaling in the Diabetic Retina
2.2.2. Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) and Inflammation in the Diabetic Retina
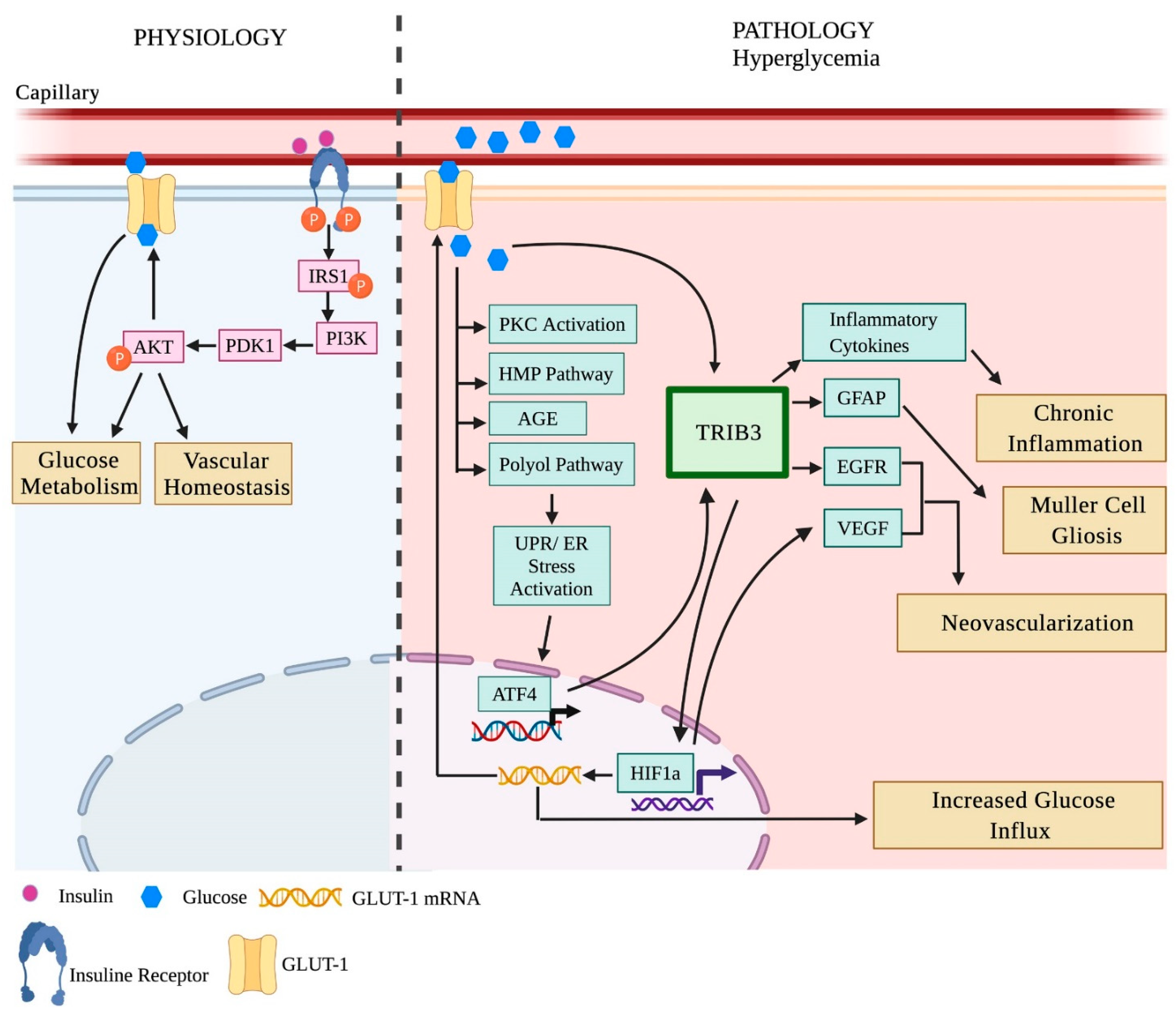 Figure 1. Tribbles homolog 3 (TRIB3) protein controls the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy. The PERK UPR marker TRIB3 is a known psuedokinase that binds and prevents AKT phosphorylation by PDK1. In addition, it controls the expression of HIF1α, EGFR, GFAP, and inflammatory cytokines in cells. In hyperglycemic retinas and retinas of mice with proliferative retinopathy, TRIB3 is significantly upregulated. This results in overexpression of HIF1α, EGFR, GFAP, and inflammatory cytokines (Icam1, Nf-kb1, Rc3h1, Zc3h12a, VEGF, COX2, and AIF1, [59]). In turn, overexpressed HIF1α leads to GLUT1 activation and, together with TRIB3, increases the influx of glucose, which affects the overall glucose metabolism in diabetic retinas. Aberrant glucose flux and hyperglycemia in diabetic retinas are responsible for the activation of PKC, HMP, AGE, and polyol pathways, which eventually leads to chronic UPR activation. TRIB3-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokine expression results in chronic inflammation, GFAP increase leads to the retinal gliosis observed in proliferative retinas, and VEGF elevation triggers neovascularization in the late stages of DR. Image created by Biorender.com, (accessed on 30 May 2021).
Figure 1. Tribbles homolog 3 (TRIB3) protein controls the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy. The PERK UPR marker TRIB3 is a known psuedokinase that binds and prevents AKT phosphorylation by PDK1. In addition, it controls the expression of HIF1α, EGFR, GFAP, and inflammatory cytokines in cells. In hyperglycemic retinas and retinas of mice with proliferative retinopathy, TRIB3 is significantly upregulated. This results in overexpression of HIF1α, EGFR, GFAP, and inflammatory cytokines (Icam1, Nf-kb1, Rc3h1, Zc3h12a, VEGF, COX2, and AIF1, [59]). In turn, overexpressed HIF1α leads to GLUT1 activation and, together with TRIB3, increases the influx of glucose, which affects the overall glucose metabolism in diabetic retinas. Aberrant glucose flux and hyperglycemia in diabetic retinas are responsible for the activation of PKC, HMP, AGE, and polyol pathways, which eventually leads to chronic UPR activation. TRIB3-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokine expression results in chronic inflammation, GFAP increase leads to the retinal gliosis observed in proliferative retinas, and VEGF elevation triggers neovascularization in the late stages of DR. Image created by Biorender.com, (accessed on 30 May 2021).| Molecular Signaling | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Changes | Duration of Hyperglycemia | References | |
| 1. | STZ Rat | Elevated CHOP, Caspase 12, MAPK retinal cytokines | 8 weeks | [57][80][87][97] |
| Reduced IR kinase activity | 8 weeks | |||
| Elevated retinal cytokines | 3 months | |||
| Reduced IR kinase activity and autophosphorylation and downregulation of IRS-2 & PI3K | 3 months | |||
| Upregulation of HIF-A, ATF-6, XBP1 | 4 months | |||
| 2. | ZFD Rat | Elevated Bax, TNF-α and NF-kappaB | 6 weeks | [89] |
| 3. | OIR Rat | Elevated VEGF, PDEG and TNF-α | P16 | [36][37] |
| 4. | STZ Mouse | Upregulation of GRP78, pPERK, CHOP, VEGF, pEIF2α, retinal cytokine and TNF-α | 4 weeks | [59][81][82][90][91][92][93] |
| Elevated IR expression and tyrosine phosphorylation; upregulated IRS-2 and reduced PDK1/ AKT protein levels and phosphorylation | 1 week | |||
| Reduced IR phosphorylation | 1 week | |||
| Upregulation of TRIB3 and inflammatory cytokines (Icam1, Nf-kb1, Rc3h1, Zc3h12a, VEGF, COX2, and AIF1) | 4 weeks | |||
| 5. | Ins2Akita Mouse |
VEGF and TNF-α elevation, increased mRNA expression; protein expression of GRP78 and elevated peIF2α and ATF4 and reduced IR kinase activity | 12 weeks | [26][92][93] |
| 6. | Leprdb (db/db) Mouse |
Increased IRS-2 expression and reduced PDK1/ AKT protein levels and phosphorylation | 10 weeks | [92][95] |
| GFAP activation, increased expression of HIF-A, VEGF, GRP78, p-IRE-1, CHOP, Casapase-3 and ATF4 | 15 months | |||
| Microangiopathy | ||||
| Model | Changes | Duration of Hyperglycemia |
References | |
| 1. | STZ Rat | Blood retinal barrier disruption | 2 weeks | [8][46][48] |
| Adherent leukocytes | 8 weeks | |||
| Thickened Basement Membrane (BM) | 12 weeks | |||
| Neovascularization | 3–4 months | |||
| 2. | Alloxan Rat | Leukocytosis | 2 months | [49][50] |
| Neovascularization | 9 months | |||
| Pericyte loss, acellular capillaries, and BM thickening | 12 months | |||
| 3. | BB Rat | Basement membrane thickening | 4 months | [18][19][51] |
| Blood retinal barrier breakdown | 6 months | |||
| Pericyte loss | 8 months | |||
| 4. | ZDF Rat | BM thickening, pericyte loss and acellular capillaries | 6 months | [21][22] |
| 5. | OLETF Rat | BM thickening, pericyte loss and acellular capillaries | 9 months | [23][52] |
| 6. | OIR SD Rat | Increased extra retinal neovascularization and impaired pericyte distribution | P18 | [40] |
| 7. | STZ Mouse | Increased vascular permeability | 8 days | [44][43][45][59] |
| Decreased arteriolar diameter and velocity | 8 weeks | |||
| BM thickening | 4–15 months | |||
| Pericyte loss, acellular capillaries and pericyte ghost | 6–9 months | |||
| 8. | Ins2Akita Mouse |
Leukocytosis | 8 weeks | [26][42] |
| Increased vascular permeability | 12 weeks | |||
| Blood vessels in the outer plexiform layer (OPL) and microaneurysms | 6 months | |||
| Acellular capillaries, BM thickening and neovascularization. | 9 months | |||
| 9. | Kimba Mouse | Abnormal blood vessel development around photoreceptor | P28 | [29][41] |
| Increased vascular permeability and adherent leukocytes | 6 weeks | |||
| Loss of retinal capillaries, neovascularization, increased avascular area and alteration in the vessel length | 9 weeks | |||
| Pericyte loss | 24 weeks | |||
| 10. | Akimba Mouse | Microaneurysms, neovascularization, blood vessel constriction, beading, vessel edema, capillary dropout, and new vessel formation it the ONL | 8 weeks | [30] |
| 11. | OIR Mouse | Irregular blood vessel development and reduced inner retinal plexus and deep plexus | P18 | [39] |
| 12. | Db/db Mouse | Increased vascular permeability and BM thickening | 13–14 weeks | [53][54] |
| Pericyte loss | 18 weeks | |||
| Acellular capillaries | 26 weeks | |||
| 13. | High-fat diet Mouse |
Pericyte loss, blood retinal barrier disruption and vascular leakage | 12 months | [55] |
| Retinal Integrity | ||||
| Model | Changes | Duration of Hyperglycemia | References | |
| 1. | STZ Rat | Decreased pre- and post-synaptic photoreceptor ribbon synapses | 4 weeks | [56][57][58] |
| Increased GFAP reactivity | 6–7 weeks | |||
| Loss of ONL, INL, GCL | 12–16 weeks | |||
| Severe photoreceptor cell loss | 24 weeks | |||
| 2. | WBN/Kob Rat | Photoreceptor degeneration | 4 weeks | [20] |
| Severe OS and ONL degeneration | 5–14 months | |||
| 3. | BB Rat | RPE degeneration | 4 months | [61] |
| 4. | ZDF Rat | Decreased OS, damage to amacrine cells and RPE with gliosis | 32 weeks | [62] |
| 5. | OLETF Rat | Decreased INL and photoreceptor cells | 9 months | [23] |
| 6. | OIR Rat | Reduction in OS, INL, IPL, total retinal thickness, astrocytes and increased muller activity | P18 | [40][63] |
| 7. | High galactose Rat |
Increased gliosis and reduced INL and OPL |
28 months | [61] |
| 8. | STZ Mouse | GFAP hyperactivity | 5 weeks | [45][59][65][67][70] |
| Reduced ONL, INL thickness | 6–14 weeks | |||
| Total retinal thickness reduced | 20 weeks | |||
| No retinal cell loss and gliosis | 8–12 months | |||
| Reduced RGCs | 8 months | |||
| 9. | Ins2Akita Mouse |
GFAP hyperactivity | 8 weeks | [26][68] |
| Reduced IPL, INL and cone photoreceptors | 3 months | |||
| Reduced RGCs | 22 weeks | |||
| Decreased presynaptic and post-synaptic photoreceptor ribbons | 36 weeks | |||
| 10. | db/db Mouse | Reduced NFL and RGCs | 16-28 weeks | [67][69] |
| Reduced total retinal thickness | 28 weeks | |||
| 11. | Akimba Mouse | Photoreceptor cell death | 28 weeks | [30] |
| 12. | OIR Mouse | Total retinal thickness reduction, distorted photoreceptor OS, neuronal loss, hyperactivity of Müller cells, microglial activation and disrupted INL and IPL | P17-188 | [39][59] |
| Retinal Electrophysiology | ||||
| Model | Changes | Duration of Hyperglycemia |
References | |
| 1. | STZ Rat | Decrease in OP amplitude | 2–7 weeks | [56][74][75] |
| Decrease in OP implicit time | 7 weeks | |||
| Decreased a- and b-wave amplitude | 10–12 weeks and at 44 weeks | |||
| 2. | OIR Rat | Decreased a- and b-wave amplitude | P18 | [40][63][64] |
| 3. | STZ Mouse | Reduced OP amplitude and implicit time | 4–6 weeks | [59][76][77][78] |
| Reduced a- and b-wave amplitude | 6 months | |||
| Reduced PhNR amplitude | 8 months | |||
| 4. | Ins2Akita Mouse |
Decreased OP amplitude, delay in the OP and decreased b-wave | 9 months | [26][68] |
| 5. | Db/db Mouse | Delay in the b-wave, delay in the OP implicit time and decreased amplitude of both photopic and scotopic b-wave | 16–24 weeks | [69][79] |
| 6. | OIR Mouse | Significant decrease in the amplitude of a- and b-wave | P18 | [39] |
| 7. | High-fat diet Mouse |
Decreased OP amplitude | 12 months | [55] |
References
- Vujosevic, S.; Midena, E. Retinal layers changes in human preclinical and early clinical diabetic retinopathy support early retinal neuronal and Muller cells alterations. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 905058.
- Baget-Bernaldiz, M.; Romero-Aroca, P.; Bautista-Perez, A.; Mercado, J. Multifocal electroretinography changes at the 1-year follow-up in a cohort of diabetic macular edema patients treated with ranibizumab. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 85–96.
- Tehrani, N.M.; Riazi-Esfahani, H.; Jafarzadehpur, E.; Mirzajani, A.; Talebi, H.; Amini, A.; Mazloumi, M.; Roohipoor, R.; Riazi-Esfahani, M. Multifocal Electroretinogram in Diabetic Macular Edema; Correlation with Visual Acuity and Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Ophthalmic. Vis. Res. 2015, 10, 165–171.
- Grunwald, J.E.; DuPont, J.; Riva, C.E. Retinal haemodynamics in patients with early diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 80, 327–331.
- Sinclair, S.H.; Schwartz, S.S. Diabetic Retinopathy-An Underdiagnosed and Undertreated Inflammatory, Neuro-Vascular Complication of Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 843.
- Nork, T.M.; Wallow, I.H.; Sramek, S.J.; Anderson, G. Muller’s cell involvement in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1987, 105, 1424–1429.
- Mizutani, M.; Gerhardinger, C.; Lorenzi, M. Muller cell changes in human diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 1998, 47, 445–449.
- Rungger-Brandle, E.; Dosso, A.A.; Leuenberger, P.M. Glial reactivity, an early feature of diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1971–1980.
- Barber, A.J.; Antonetti, D.A.; Gardner, T.W. Altered expression of retinal occludin and glial fibrillary acidic protein in experimental diabetes. The Penn State Retina Research Group. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 3561–3568.
- Abu-El-Asrar, A.M.; Dralands, L.; Missotten, L.; Al-Jadaan, I.A.; Geboes, K. Expression of apoptosis markers in the retinas of human subjects with diabetes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 2760–2766.
- Muramatsu, D.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Usui, Y.; Okunuki, Y.; Kezuka, T.; Goto, H. Correlation of complement fragment C5a with inflammatory cytokines in the vitreous of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2013, 251, 15–17.
- Abu El-Asrar, A.M.; Struyf, S.; Kangave, D.; Geboes, K.; Van Damme, J. Chemokines in proliferative diabetic retinopathy and proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2006, 17, 155–165.
- Freyberger, H.; Brocker, M.; Yakut, H.; Hammer, J.; Effert, R.; Schifferdecker, E.; Schatz, H.; Derwahl, M. Increased levels of platelet-derived growth factor in vitreous fluid of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2000, 108, 106–109.
- Elner, S.G.; Elner, V.M.; Jaffe, G.J.; Stuart, A.; Kunkel, S.L.; Strieter, R.M. Cytokines in proliferative diabetic retinopathy and proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Curr. Eye Res. 1995, 14, 1045–1053.
- Ishikawa, K.; Yoshida, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Nakama, T.; Nakao, S.; Sassa, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Niiro, H.; Akashi, K.; et al. Microarray analysis of gene expression in fibrovascular membranes excised from patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 932–946.
- Lutty, G.A.; McLeod, D.S.; Merges, C.; Diggs, A.; Plouet, J. Localization of vascular endothelial growth factor in human retina and choroid. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1996, 114, 971–977.
- Mizutani, M.; Kern, T.S.; Lorenzi, M. Accelerated death of retinal microvascular cells in human and experimental diabetic retinopathy. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2883–2890.
- Sima, A.A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Garcia-Salinas, R.; Basu, P.K. The BB-rat—An authentic model of human diabetic retinopathy. Curr. Eye Res. 1985, 4, 1087–1092.
- Sima, A.A.; Garcia-Salinas, R.; Basu, P.K. The BB Wistar rat: An experimental model for the study of diabetic retinopathy. Metabolism 1983, 32, 136–140.
- Miyamura, N.; Amemiya, T. Lens and retinal changes in the WBN/Kob rat (spontaneously diabetic strain). Electron-microscopic study. Ophthalmic. Res. 1998, 30, 221–232.
- Yokoi, N.; Hoshino, M.; Hidaka, S.; Yoshida, E.; Beppu, M.; Hoshikawa, R.; Sudo, K.; Kawada, A.; Takagi, S.; Seino, S. A Novel Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes: The Zucker Fatty Diabetes Mellitus ZFDM Rat. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 103731.
- Peterson, R.G.; Shaw, W.N.; Neel, M.A.; Little, L.A.; Eichberg, J. Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rat as a Model for Non-insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus. ILAR J. 1990, 32, 16–19.
- Lu, Z.Y.; Bhutto, I.A.; Amemiya, T. Retinal changes in Otsuka long-evans Tokushima Fatty rats (spontaneously diabetic rat)—Possibility of a new experimental model for diabetic retinopathy. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 47, 28–35.
- Shinohara, M.; Masuyama, T.; Shoda, T.; Takahashi, T.; Katsuda, Y.; Komeda, K.; Kuroki, M.; Kakehashi, A.; Kanazawa, Y. A new spontaneously diabetic non-obese Torii rat strain with severe ocular complications. Int. J. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2000, 1, 89–100.
- Yoshioka, M.; Kayo, T.; Ikeda, T.; Koizumi, A. A novel locus, Mody4, distal to D7Mit189 on chromosome 7 determines early-onset NIDDM in nonobese C57BL/6 (Akita) mutant mice. Diabetes 1997, 46, 887–894.
- Barber, A.J.; Antonetti, D.A.; Kern, T.S.; Reiter, C.E.; Soans, R.S.; Krady, J.K.; Levison, S.W.; Gardner, T.W.; Bronson, S.K. The Ins2Akita mouse as a model of early retinal complications in diabetes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 2210–2218.
- Wicker, L.S.; Todd, J.A.; Peterson, L.B. Genetic control of autoimmune diabetes in the NOD mouse. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1995, 13, 179–200.
- Makino, S.; Kunimoto, K.; Muraoka, Y.; Mizushima, Y.; Katagiri, K.; Tochino, Y. Breeding of a non-obese, diabetic strain of mice. Jikken Dobutsu 1980, 29, 1–13.
- van Eeden, P.E.; Tee, L.B.; Lukehurst, S.; Lai, C.M.; Rakoczy, E.P.; Beazley, L.D.; Dunlop, S.A. Early vascular and neuronal changes in a VEGF transgenic mouse model of retinal neovascularization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 4638–4645.
- Rakoczy, E.P.; Ali Rahman, I.S.; Binz, N.; Li, C.R.; Vagaja, N.N.; de Pinho, M.; Lai, C.M. Characterization of a mouse model of hyperglycemia and retinal neovascularization. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2659–2670.
- Hummel, K.P.; Dickie, M.M.; Coleman, D.L. Diabetes, a new mutation in the mouse. Science 1966, 153, 1127–1128.
- Fong, D.S.; Aiello, L.P.; Ferris, F.L., 3rd; Klein, R. Diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2540–2553.
- Smith, L.E.; Wesolowski, E.; McLellan, A.; Kostyk, S.K.; D’Amato, R.; Sullivan, R.; D’Amore, P.A. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the mouse. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 101–111.
- Patz, A.; Eastham, A.; Higginbotham, D.H.; Kleh, T. Oxygen studies in retrolental fibroplasia. II. The production of the microscopic changes of retrolental fibroplasia in experimental animals. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1953, 36, 1511–1522.
- McLeod, D.S.; Lutty, G.A. Targeting VEGF in canine oxygen-induced retinopathy—A model for human retinopathy of prematurity. Eye Brain 2016, 8, 55–65.
- Zhang, S.X.; Ma, J.X.; Sima, J.; Chen, Y.; Hu, M.S.; Ottlecz, A.; Lambrou, G.N. Genetic difference in susceptibility to the blood-retina barrier breakdown in diabetes and oxygen-induced retinopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 313–321.
- Zhang, S.X.; Wang, J.J.; Gao, G.; Shao, C.; Mott, R.; Ma, J.X. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is an endogenous antiinflammatory factor. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 323–325.
- Kim, C.B.; D’Amore, P.A.; Connor, K.M. Revisiting the mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Eye Brain 2016, 8, 67–79.
- Vessey, K.A.; Wilkinson-Berka, J.L.; Fletcher, E.L. Characterization of retinal function and glial cell response in a mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 506–527.
- Downie, L.E.; Pianta, M.J.; Vingrys, A.J.; Wilkinson-Berka, J.L.; Fletcher, E.L. AT1 receptor inhibition prevents astrocyte degeneration and restores vascular growth in oxygen-induced retinopathy. Glia 2008, 56, 1076–1090.
- Shen, W.Y.; Lai, C.M.; Graham, C.E.; Binz, N.; Lai, Y.K.; Eade, J.; Guidolin, D.; Ribatti, D.; Dunlop, S.A.; Rakoczy, P.E. Long-term global retinal microvascular changes in a transgenic vascular endothelial growth factor mouse model. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1690–1701.
- Han, Z.; Guo, J.; Conley, S.M.; Naash, M.I. Retinal angiogenesis in the Ins2(Akita) mouse model of diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 574–584.
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, Y.S.; Cho, C.S.; Kim, K.W. Blockade of angiotensin II attenuates VEGF-mediated blood-retinal barrier breakdown in diabetic retinopathy. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 621–628.
- Wright, W.S.; Harris, N.R. Ozagrel attenuates early streptozotocin-induced constriction of arterioles in the mouse retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2008, 86, 528–536.
- Feit-Leichman, R.A.; Kinouchi, R.; Takeda, M.; Fan, Z.; Mohr, S.; Kern, T.S.; Chen, D.F. Vascular damage in a mouse model of diabetic retinopathy: Relation to neuronal and glial changes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 4281–4287.
- Jariyapongskul, A.; Rungjaroen, T.; Kasetsuwan, N.; Patumraj, S.; Seki, J.; Niimi, H. Long-term effects of oral vitamin C supplementation on the endothelial dysfunction in the iris microvessels of diabetic rats. Microvasc. Res. 2007, 74, 32–38.
- Anderson, H.R.; Stitt, A.W.; Gardiner, T.A.; Archer, D.B. Diabetic retinopathy: Morphometric analysis of basement membrane thickening of capillaries in different retinal layers within arterial and venous environments. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1995, 79, 1120–1123.
- Gong, C.Y.; Lu, B.; Hu, Q.W.; Ji, L.L. Streptozotocin induced diabetic retinopathy in rat and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 6, 573–577.
- Schroder, S.; Palinski, W.; Schmid-Schonbein, G.W. Activated monocytes and granulocytes, capillary nonperfusion, and neovascularization in diabetic retinopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 1991, 139, 81–100.
- Kowluru, R.A.; Tang, J.; Kern, T.S. Abnormalities of retinal metabolism in diabetes and experimental galactosemia. VII. Effect of long-term administration of antioxidants on the development of retinopathy. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1938–1942.
- Blair, N.P.; Tso, M.O.; Dodge, J.T. Pathologic studies of the blood—Retinal barrier in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1984, 25, 302–311.
- Behl, Y.; Krothapalli, P.; Desta, T.; DiPiazza, A.; Roy, S.; Graves, D.T. Diabetes-enhanced tumor necrosis factor-alpha production promotes apoptosis and the loss of retinal microvascular cells in type 1 and type 2 models of diabetic retinopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 1411–1418.
- Cheung, A.K.; Fung, M.K.; Lo, A.C.; Lam, T.T.; So, K.F.; Chung, S.S.; Chung, S.K. Aldose reductase deficiency prevents diabetes-induced blood-retinal barrier breakdown, apoptosis, and glial reactivation in the retina of db/db mice. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3119–3125.
- Clements, R.S., Jr.; Robison, W.G., Jr.; Cohen, M.P. Anti-glycated albumin therapy ameliorates early retinal microvascular pathology in db/db mice. J. Diabetes Complicat. 1998, 12, 28–33.
- Rajagopal, R.; Bligard, G.W.; Zhang, S.; Yin, L.; Lukasiewicz, P.; Semenkovich, C.F. Functional Deficits Precede Structural Lesions in Mice with High-Fat Diet-Induced Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1072–1084.
- Li, Q.; Zemel, E.; Miller, B.; Perlman, I. Early retinal damage in experimental diabetes: Electroretinographical and morphological observations. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 74, 615–625.
- Shruthi, K.; Reddy, S.S.; Reddy, G.B. Ubiquitin-proteasome system and ER stress in the retina of diabetic rats. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 627, 10–20.
- Park, S.H.; Park, J.W.; Park, S.J.; Kim, K.Y.; Chung, J.W.; Chun, M.H.; Oh, S.J. Apoptotic death of photoreceptors in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat retina. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1260–1268.
- Pitale, P.M.; Saltykova, I.V.; Adu-Agyeiwaah, Y.; Calzi, S.L.; Satoh, T.; Akira, S.; Gorbatyuk, O.; Boulton, M.E.; Pardue, M.T.; Garvey, W.T.; et al. Tribbles Homolog 3 Mediates the Development and Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes 2021, 70, 1738–1753.
- Gorbatyuk, O.S.; Pitale, P.M.; Saltykova, I.V.; Dorofeeva, I.B.; Zhylkibayev, A.A.; Athar, M.; Fuchs, P.A.; Samuels, B.C.; Gorbatyuk, M.S. A Novel Tree Shrew Model of Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 799711.
- Robison, W.G., Jr.; Tillis, T.N.; Laver, N.; Kinoshita, J.H. Diabetes-related histopathologies of the rat retina prevented with an aldose reductase inhibitor. Exp. Eye Res. 1990, 50, 355–366.
- Szabo, K.; Enzsoly, A.; Dekany, B.; Szabo, A.; Hajdu, R.I.; Radovits, T.; Matyas, C.; Olah, A.; Laurik, L.K.; Somfai, G.M.; et al. Histological Evaluation of Diabetic Neurodegeneration in the Retina of Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8891.
- Downie, L.E.; Pianta, M.J.; Vingrys, A.J.; Wilkinson-Berka, J.L.; Fletcher, E.L. Neuronal and glial cell changes are determined by retinal vascularization in retinopathy of prematurity. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 504, 404–417.
- Liu, K.; Akula, J.D.; Falk, C.; Hansen, R.M.; Fulton, A.B. The retinal vasculature and function of the neural retina in a rat model of retinopathy of prematurity. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 2639–2647.
- Yang, Y.; Mao, D.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Tian, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhou, B.L. Decrease in retinal neuronal cells in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 1411–1420.
- Martin, P.M.; Roon, P.; Van Ells, T.K.; Ganapathy, V.; Smith, S.B. Death of retinal neurons in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 3330–3336.
- Sohn, E.H.; van Dijk, H.W.; Jiao, C.; Kok, P.H.; Jeong, W.; Demirkaya, N.; Garmager, A.; Wit, F.; Kucukevcilioglu, M.; van Velthoven, M.E.; et al. Retinal neurodegeneration may precede microvascular changes characteristic of diabetic retinopathy in diabetes mellitus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2655–E2664.
- Hombrebueno, J.R.; Chen, M.; Penalva, R.G.; Xu, H. Loss of synaptic connectivity, particularly in second order neurons is a key feature of diabetic retinal neuropathy in the Ins2Akita mouse. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97970.
- Yang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xie, P.; Cheng, H.; Song, Q.; Su, T.; Yuan, S.; Liu, Q. Retinal Neurodegeneration in db/db Mice at the Early Period of Diabetes. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 757412.
- Kumar, S.; Zhuo, L. Longitudinal in vivo imaging of retinal gliosis in a diabetic mouse model. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 91, 530–536.
- Pardue, M.T.; Barnes, C.S.; Kim, M.K.; Aung, M.H.; Amarnath, R.; Olson, D.E.; Thule, P.M. Rodent Hyperglycemia-Induced Inner Retinal Deficits are Mirrored in Human Diabetes. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 6.
- Aung, M.H.; Kim, M.K.; Olson, D.E.; Thule, P.M.; Pardue, M.T. Early visual deficits in streptozotocin-induced diabetic long evans rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 1370–1377.
- Hancock, H.A.; Kraft, T.W. Oscillatory potential analysis and ERGs of normal and diabetic rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 1002–1008.
- Okuno, T.; Oku, H.; Sugiyama, T.; Ikeda, T. Electroretinographic study of spontaneously diabetic Torii rats. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2008, 117, 191–196.
- Sasase, T.; Ohta, T.; Masuyama, T.; Yokoi, N.; Kakehashi, A.; Shinohara, M. The spontaneously diabetic torii rat: An animal model of nonobese type 2 diabetes with severe diabetic complications. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 976209.
- Sasaki, M.; Ozawa, Y.; Kurihara, T.; Kubota, S.; Yuki, K.; Noda, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Ishida, S.; Tsubota, K. Neurodegenerative influence of oxidative stress in the retina of a murine model of diabetes. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 971–979.
- Moore-Dotson, J.M.; Beckman, J.J.; Mazade, R.E.; Hoon, M.; Bernstein, A.S.; Romero-Aleshire, M.J.; Brooks, H.L.; Eggers, E.D. Early Retinal Neuronal Dysfunction in Diabetic Mice: Reduced Light-Evoked Inhibition Increases Rod Pathway Signaling. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1418–1430.
- Zheng, L.; Du, Y.; Miller, C.; Gubitosi-Klug, R.A.; Kern, T.S.; Ball, S.; Berkowitz, B.A. Critical role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in degeneration of retinal capillaries in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1987–1996.
- Bogdanov, P.; Corraliza, L.; Villena, J.A.; Carvalho, A.R.; Garcia-Arumi, J.; Ramos, D.; Ruberte, J.; Simo, R.; Hernandez, C. The db/db mouse: A useful model for the study of diabetic retinal neurodegeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97302.
- Reiter, C.E.; Wu, X.; Sandirasegarane, L.; Nakamura, M.; Gilbert, K.A.; Singh, R.S.; Fort, P.E.; Antonetti, D.A.; Gardner, T.W. Diabetes reduces basal retinal insulin receptor signaling: Reversal with systemic and local insulin. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1148–1156.
- Rajala, A.; Tanito, M.; Le, Y.Z.; Kahn, C.R.; Rajala, R.V. Loss of neuroprotective survival signal in mice lacking insulin receptor gene in rod photoreceptor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 19781–19792.
- Rajala, R.V.; Wiskur, B.; Tanito, M.; Callegan, M.; Rajala, A. Diabetes reduces autophosphorylation of retinal insulin receptor and increases protein-tyrosine phosphatase-1B activity. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 1033–1040.
- He, K.; Lv, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tao, L.; Liu, D. Gene set enrichment analysis of pathways and transcription factors associated with diabetic retinopathy using a microarray dataset. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 103–112.
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Wang, J.M.; Steinle, J.J. Insulin Signal Transduction is Impaired in the Type 2 Diabetic Retina. J. Diabetes Clin. Res. 2020, 2, 12–15.
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Shu, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, X.; Ying, Y. GSK3beta-mediated tau hyperphosphorylation triggers diabetic retinal neurodegeneration by disrupting synaptic and mitochondrial functions. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 62.
- Ma, J.H.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, S.X. The unfolded protein response and diabetic retinopathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2014, 2014, 160140.
- Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Dou, H.; Tso, M.O.; Ma, Z. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the loss of retinal ganglion cells in diabetic retinopathy. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 3148–3158.
- Li, B.; Wang, H.S.; Li, G.G.; Zhao, M.J.; Zhao, M.H. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the early stage of diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2011, 48, 103–111.
- Kim, J.; Kim, C.S.; Sohn, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Jo, K.; Kim, J.S. KIOM-79 protects AGE-induced retinal pericyte apoptosis via inhibition of NF-kappaB activation in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43591.
- Chung, Y.R.; Choi, J.A.; Koh, J.Y.; Yoon, Y.H. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Attenuates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Related Retinal Pericyte Loss in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1763292.
- Zhong, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.J.; Ratan, R.; Zhang, S.X. Activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress by hyperglycemia is essential for Muller cell-derived inflammatory cytokine production in diabetes. Diabetes 2012, 61, 492–504.
- Kondo, T.; Kahn, C.R. Altered insulin signaling in retinal tissue in diabetic states. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37997–38006.
- Li, J.; Wang, J.J.; Yu, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.X. Endoplasmic reticulum stress is implicated in retinal inflammation and diabetic retinopathy. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1521–1527.
- Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Kunte, M.; Shinde, V.; Gorbatyuk, M. Modulation of angiogenesis by genetic manipulation of ATF4 in mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy . Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 5995–6002.
- Bhatta, M.; Ma, J.H.; Wang, J.J.; Sakowski, J.; Zhang, S.X. Enhanced endoplasmic reticulum stress in bone marrow angiogenic progenitor cells in a mouse model of long-term experimental type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2181–2190.
- Rana, T.; Shinde, V.M.; Starr, C.R.; Kruglov, A.A.; Boitet, E.R.; Kotla, P.; Zolotukhin, S.; Gross, A.K.; Gorbatyuk, M.S. An activated unfolded protein response promotes retinal degeneration and triggers an inflammatory response in the mouse retina. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1578.
- Kirwin, S.J.; Kanaly, S.T.; Linke, N.A.; Edelman, J.L. Strain-dependent increases in retinal inflammatory proteins and photoreceptor FGF-2 expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 5396–5404.




