
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Oscar Campuzano | + 6924 word(s) | 6924 | 2022-01-10 07:53:51 | | | |
| 2 | Bruce Ren | Meta information modification | 6924 | 2022-01-12 10:05:00 | | |
Video Upload Options
Sudden death is a rare event in the pediatric population but with a social shock due to its presentation as the first symptom in previously healthy children. Comprehensive autopsy in pediatric cases identify an inconclusive cause in 40–50% of cases. In such cases, a diagnosis of sudden arrhythmic death syndrome is suggested as the main potential cause of death. Molecular autopsy identifies nearly 30% of cases under 16 years of age carrying a pathogenic/potentially pathogenic alteration in genes associated with any inherited arrhythmogenic disease. In the last few years, despite the increasing rate of post-mortem genetic diagnosis, many families still remain without a conclusive genetic cause of the unexpected death.
1. Introduction
2. Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes
3. Long QT Syndrome
3.1. Genetics
| Cardiac Phenotype | Inheritance Model | Frequency | Gene Curation |
Genes | Main Type of Mutations |
Current Affected |
Non-Cardiac Phenotype |
Phenotypic Overlap (Both LOF/GOF Variants) |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LQTS | |||||||||
| LQT1 | AD | 30–35% | Definitive genes | KCNQ1 | LOF | IKs | SNHL (AR), seizures |
JLNS (AR), SQTS, AF | [10][33][34][35][36][37][38] |
| LQT2 | AD | 25–30% | KCNH2 | LOF | IKr | Seizures | SQTS, BrS, AF | [10][33][34][39] | |
| LQT3 | AD | 5–10% | SCN5A | GOF | INa | Multiple (including seizures) |
BrS, SQTS, CPVT, ERS, AF, AFL, ARVC/D, HCM, DCM, LVNC, SVT, AVB, SND, PCCD, WPW | [10][33][34][40][41][42] | |
| LQT14–16 | AD | <1% | Definitive genes with atypical characteristics | CALM1–3 | GOF | ICa | Seizures, DD | CPVT | [10][33][43][44][45] |
| LQT17 (TKOS) | AR | <1% | TRDN | LOF | ICa | Muscle weakness | CPVT | [10][33][46][47] | |
| LQT5 | AD | <1% | Genes with moderate or limited evidence, associated with multiorgan syndromes |
KCNE1 | LOF | IKs | SNHL (AR) | JLNS (AR) | [10][33][34][48] |
| LQT8 | AD | <1% | CACNA1C | GOF | ICa | Dysmorphic and neurodevelopmental features | TS, SQTS, BrS, ERS, HCM, AF, SND, CND | [10][33][49][50][51][52][53] | |
| LQT7 | AD | <1% | KCNJ2 | LOF | IK1 | Muscle weakness, dysmorphic features, DD, seizures |
ATS, SQTS, AF, CPVT, DCM |
[10][33][37][42][54][55][56][57][58] | |
| LQTS | AD | <1% each | Other genes with limited evidence | ANK2 KCNJ5 KCNE2 AKAP9 SCN4B CAV3 SNTA1 |
LOF LOF LOF LOF GOF GOF GOF |
Many IK-Ach IKr IKs INa INa INa |
Seizures | CPVT, BrS, CND AF, SND AF |
[10][33][34][42][48][59][60][61][62][63] |
| BrS | |||||||||
| BrS1 | AD | 20–30% | Definitive gene | SCN5A | LOF | INa | Multiple (including seizures) |
BrS, SQTS, CPVT, ERS, AF, AFL, ARVC, HCM, DCM, LVNC, SVT, AVB, SND, PCCD, WPW | [12][64][65][66][67][68][69][70][71][72][73][74][75][76] |
| BrS | AD | <5% | Genes with moderate or limited evidence |
ABCC9 ANK2 KCNH2 KCNJ8 KCND3 KCNE3 CACNA1C CACNB2 CACNA2D1 HCN4 PKP2 GPD1-L TRPM4 SCN1B–3B SCN10A SLMAP RANGRF |
GOF GOF GOF GOF GOF GOF LOF LOF LOF LOF LOF LOF LOF LOF LOF LOF LOF |
IK-ATP Many IKr IK-ATP Ito Ito ICa ICa ICa Ih INa INa INa INa INa INa INa |
Seizures Seizures Seizures, SCA (See LQT8) |
ERS, AF, DCM LQTS, CPVT, CND LQTS, SQTS, AF ERS, AF ERS, AF, CND AF Multiple (see LQT8) SQTS, ERS, CND SQTS, ERS, CND AF, SND ARVC, DCM, ACM, CPVT DM LQTS AF AF |
[12][33][37][64][77][78][79][80][81] |
| XD | KCNE5 | LOF | Ito | AF | |||||
| CPVT | |||||||||
| CPVT1 | AD | 55–60% | Definitive genes | RYR2 | GOF | ICa | LQTS, HCM, LVNC, CRDS | [11][48][82][83][84][85][86][87] | |
| CPVT2 | AR | 3–5% | CASQ2 | LOF | ICa | [11][48][88] | |||
| CPVT3 | AR | 1–2% | TECRL | LOF | ICa | [11][48][89][90] | |||
| CPVT4 | AD | <1% | CALM1–3 | LOF | ICa | Seizures, DD | LQTS | [11][43][44][45][48] | |
| CPVT5 | AR | 1–2% | TRDN | LOF | ICa | Muscle weakness | LQTS | [11][47][48][91] | |
| CPVT | AD | <1% | Genes with moderate or limited evidence |
SCN5A PKP2 ANK2 KCNJ2 |
LOF LOF LOF LOF |
INa INa Many IK1 |
Multiple Seizures Seizures (See LQT7) |
Multiple (see BrS1) ARVC, DCM, ACM, CPVT LQTS, BrS, CND Multiple (see LQT7) |
[11][48][92] |
| SQTS | |||||||||
| SQT1 | AD | 15% | Definitive gene | KCNH2 | GOF | IKr | Seizures | LQTS, AF, BrS | [11][33][34][93] |
| SQT2–3 | AD | <5% each | Genes with strong-moderate evidence | KCNQ1 KCNJ2 |
GOF GOF |
IKs IK1 |
(See LQT1) (See LQT7) |
JLNS (AR), SQTS, AF Multiple (see LQT7) |
[10][11][33][34][35][36][37][38] |
| SQTS | AD | <1% | Gene with moderate evidence |
SLC4A3 | LOF | AE3 | [11][94] | ||
| SQTS | AD AR |
<1% each | Genes with limited evidence |
CACNA1C CACNB2 CACNA2D1 SCN5A SLC22A5 |
LOF LOF LOF LOF LOF |
ICa ICa ICa INa INa |
(See LQT8) Multiple Metabolic decompensation, skeletal myopathy |
Multiple (see LQT8) SQTS, ERS, CND SQTS, ERS, CND Multiple (see BrS1) CDSP |
[11][33][65][95][96][97] |
3.2. Definitive Genes for LQTS
3.3. Definitive Genes for LQTS with Atypical Characteristics
3.4. Genes with Moderate or Limited Evidence for LQTS
3.5. Genetic Modifiers and Acquired LQTS
3.6. Diagnosis
3.7. Risk Stratification
3.8. Genetic Counselling
3.9. Management and Treatment
4. Brugada Syndrome
4.1. Genetics
4.2. Definitive Gene for BrS
4.3. BrS2–12 and Other Susceptibility Genes with Limited Evidence
4.4. Diagnosis
4.5. Risk Stratification
4.6. Management and Treatment
4.7. Genetic Counseling
5. Short QT Syndrome
5.1. Genetics
5.2. SQT1 Definitive Gene: KCNH2
5.3. Genes with Strong or Moderate Evidence for SQTS
5.4. Diagnosis
5.5. Risk Stratification
5.6. Management and Treatment
5.7. Genetic Counselling
6. Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
6.1. Genetics
6.2. Definitive Genes for CPVT
6.3. Diagnosis
6.4. Risk Stratification
6.5. Management and Treatment
6.6. Genetic Counseling
7. Genetic Overlap
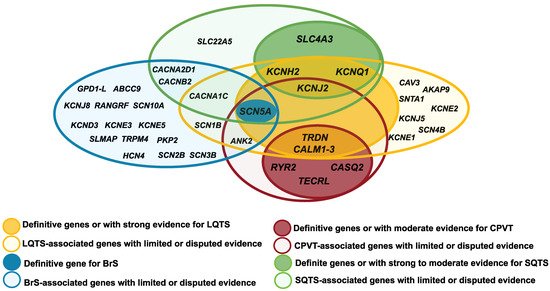
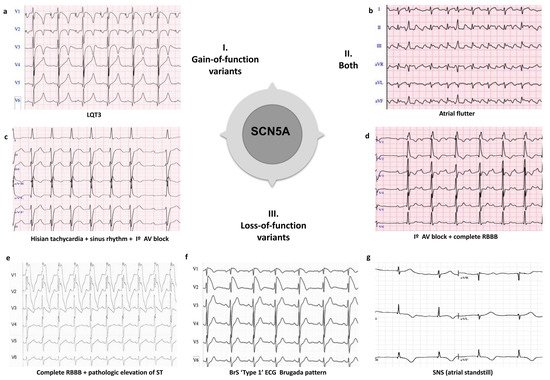
7.1. SCN5A Clinical Overlap
7.2. Genetic Overlap of Arrhythmogenic Phenotypes and Epilepsy
7.3. Non-Genetic Phenotype Overlapping
References
- Ha, F.J.; Han, H.-C.; Sanders, P.; Fendel, K.; Teh, A.W.; Kalman, J.M.; O’Donnell, D.; Leong, T.; Farouque, O.; Lim, H.S. Sudden Cardiac Death in the Young. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2020, 13, e006470.
- Couper, K.; Putt, O.; Field, R.; Poole, K.; Bradlow, W.; Clarke, A.; Perkins, G.D.; Royle, P.; Yeung, J.; Taylor-Phillips, S. Incidence of sudden cardiac death in the young: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e040815.
- Bagnall, R.D.; Singer, E.S.; Tfelt-Hansen, J. Sudden Cardiac Death in the Young. Heart Lung Circ. 2020, 29, 498–504.
- Hayashi, M.; Shimizu, W.; Albert, C.M. The Spectrum of Epidemiology Underlying Sudden Cardiac Death. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1887–1906.
- Meyer, L.; Stubbs, B.; Fahrenbruch, C.; Maeda, C.; Harmon, K.; Eisenberg, M.; Drezner, J. Incidence, causes, and survival trends from cardiovascular-related sudden cardiac arrest in children and young adults 0 to 35 years of age: A 30-year review. Circulation 2012, 126, 1363–1372.
- Goldberg, N.; Rodriguez-Prado, Y.; Tillery, R.; Chua, C. Sudden Infant Death Syndrome: A Review. Pediatr. Ann. 2018, 47, e118–e123.
- Morentin, B.; Suárez-Mier, M.P.; Monzó, A.; Molina, P.; Lucena, J.S. Sports-related sudden cardiac death due to myocardial diseases on a population from 1–35 years: A multicentre forensic study in Spain. Forensic Sci. Res. 2019, 4, 257–266.
- Bagnall, R.D.; Weintraub, R.G.; Ingles, J.; Duflou, J.; Yeates, L.; Lam, L.; Davis, A.M.; Thompson, T.; Connell, V.; Wallace, J.; et al. A Prospective Study of Sudden Cardiac Death among Children and Young Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2441–2452.
- Tsuda, T.; Fitzgerald, K.K.; Templer, J. Sudden cardiac death in children and young adults without structural heart disease: A comprehensive review. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 21, 205–216.
- Adler, A.; Novelli, V.; Amin, A.S.; Abiusi, E.; Care, M.; Nannenberg, E.A.; Feilotter, H.; Amenta, S.; Mazza, D.; Bikker, H.; et al. An International, Multicentered, Evidence-Based Reappraisal of Genes Reported to Cause Congenital Long QT Syndrome. Circulation 2020, 141, 418–428.
- Walsh, R.; Adler, A.; Amin, A.S.; Abiusi, E.; Care, M.; Bikker, H.; Amenta, S.; Feilotter, H.; Nannenberg, E.A.; Mazzarotto, F.; et al. Evaluation of gene validity for CPVT and short QT syndrome in sudden arrhythmic death. Eur. Heart J. 2021, ehab687.
- Hosseini, S.M.; Kim, R.; Udupa, S.; Costain, G.; Jobling, R.; Liston, E.; Jamal, S.M.; Szybowska, M.; Morel, C.F.; Bowdin, S.; et al. Reappraisal of reported genes for sudden arrhythmic death: Evidence-based evaluation of gene validity for brugada syndrome. Circulation 2018, 138, 1195–1205.
- Rehm, H.L.; Berg, J.S.; Brooks, L.D.; Bustamante, C.D.; Evans, J.P.; Landrum, M.J.; Ledbetter, D.H.; Maglott, D.R.; Martin, C.L.; Nussbaum, R.L.; et al. ClinGen—The Clinical Genome Resource. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2235–2242.
- Denham, N.C.; Pearman, C.M.; Ding, W.Y.; Waktare, J.; Gupta, D.; Snowdon, R.; Hall, M.; Cooper, R.; Modi, S.; Todd, D.; et al. Systematic re-evaluation of SCN5A variants associated with Brugada syndrome. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019, 30, 118–127.
- Campuzano, O.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Fernandez-Falgueras, A.; Coll, M.; Iglesias, A.; Ferrer-Costa, C.; Cesar, S.; Arbelo, E.; García-Álvarez, A.; Jordà, P.; et al. Reanalysis and reclassification of rare genetic variants associated with inherited arrhythmogenic syndromes. EBioMedicine 2020, 54, 102732.
- Grassi, S.; Campuzano, O.; Coll, M.; Brión, M.; Arena, V.; Iglesias, A.; Carracedo, A.; Brugada, R.; Oliva, A. Genetic variants of uncertain significance: How to match scientific rigour and standard of proof in sudden cardiac death? Leg. Med. 2020, 45, 101712.
- Campuzano, O.; Sanchez-Molero, O.; Fernandez, A.; Mademont-Soler, I.; Coll, M.; Perez-Serra, A.; Mates, J.; del Olmo, B.; Pico, F.; Nogue-Navarro, L.; et al. Sudden Arrhythmic Death During Exercise: A Post-Mortem Genetic Analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2101–2115.
- Walsh, R.; Lahrouchi, N.; Tadros, R.; Kyndt, F.; Glinge, C.; Postema, P.G.; Amin, A.S.; Nannenberg, E.A.; Ware, J.S.; Whiffin, N.; et al. Enhancing rare variant interpretation in inherited arrhythmias through quantitative analysis of consortium disease cohorts and population controls. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 47–58.
- Kline, J.; Costantini, O. Inherited Cardiac Arrhythmias and Channelopathies. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 809–820.
- Tse, G.; Chan, Y.W.F.; Keung, W.; Yan, B.P. Electrophysiological mechanisms of long and short QT syndromes. IJC Heart Vasc. 2017, 14, 8–13.
- Campuzano, O.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Cesar, S.; Iglesias, A.; Arbelo, E.; Brugada, J.; Brugada, R. Genetics of inherited arrhythmias in pediatrics. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2015, 27, 665–674.
- Coll, M.; Pérez-Serra, A.; Mates, J.; Del Olmo, B.; Puigmulé, M.; Fernandez-Falgueras, A.; Iglesias, A.; Picó, F.; Lopez, L.; Brugada, R.; et al. Incomplete Penetrance and Variable Expressivity: Hallmarks in Channelopathies Associated with Sudden Cardiac Death. Biology 2017, 7, 3.
- Ackerman, M.J.; Priori, S.G.; Willems, S.; Berul, C.; Brugada, R.; Calkins, H.; Camm, A.J.; Ellinor, P.T.; Gollob, M.; Hamilton, R.; et al. HRS/EHRA expert consensus statement on the state of genetic testing for the channelopathies and cardiomyopathies: This document was developed as a partnership between the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) and the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA). Heart Rhythm 2011, 8, 1308–1339.
- Heying, R.; Albert, D.C.; Voges, I.; Sendzikaite, S.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Pluchinotta, F.; Brzezinska-Rajszys, G.; Stein, J.I.; Milanesi, O. Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology recommendations for basic training in paediatric and congenital cardiology 2020. Cardiol. Young 2020, 30, 1572–1587.
- Offerhaus, J.A.; Bezzina, C.R.; Wilde, A.A.M. Epidemiology of inherited arrhythmias. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 205–215.
- Schwartz, P.J.; Stramba-Badiale, M.; Crotti, L.; Pedrazzini, M.; Besana, A.; Bosi, G.; Gabbarini, F.; Goulene, K.; Insolia, R.; Mannarino, S.; et al. Prevalence of the congenital long-qt syndrome. Circulation 2009, 120, 1761–1767.
- Sarquella-Brugada, G.; García-Algar, O.; Zambrano, M.D.; Fernández-Falgueres, A.; Sailer, S.; Cesar, S.; Sebastiani, G.; Martí-Almor, J.; Aurensanz, E.; Cruzalegui, J.C.; et al. Early Identification of Prolonged QT Interval for Prevention of Sudden Infant Death. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 704580.
- Goldenberg, I.; Moss, A.J. Long QT Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 2291–2300.
- Waddell-Smith, K.E.; Skinner, J.R. Update on the Diagnosis and Management of Familial Long QT Syndrome. Heart Lung Circ. 2016, 25, 769–776.
- Skinner, J.R.; Winbo, A.; Abrams, D.; Vohra, J.; Wilde, A.A. Channelopathies That Lead to Sudden Cardiac Death: Clinical and Genetic Aspects. Heart Lung Circ. 2019, 28, 22–30.
- Krishnan, M.N.; Pavithran, K. Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30725985/ (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Fernandez-Falgueras, A.; Cesar, S.; Arbelo, E.; Jordà, P.; García-Álvarez, A.; Cruzalegui, J.C.; Merchan, E.F.; Fiol, V.; Brugada, J.; et al. Pediatric Malignant Arrhythmias Caused by Rare Homozygous Genetic Variants in TRDN: A Comprehensive Interpretation. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 8, 754.
- Nakajima, T.; Tamura, S.; Kurabayashi, M.; Kaneko, Y. Towards Mutation-Specific Precision Medicine in Atypical Clinical Phenotypes of Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3930.
- Wallace, E.; Howard, L.; Liu, M.; O’Brien, T.; Ward, D.; Shen, S.; Prendiville, T. Long QT Syndrome: Genetics and Future Perspective. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2019, 40, 1419–1430.
- Neyroud, N.; Tesson, F.; Denjoy, I.; Leibovici, M.; Donger, C.; Barhanin, J.; Fauré, S.; Gary, F.; Coumel, P.; Petit, C.; et al. A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome. Nat. Genet. 1997, 15, 186–189.
- Bellocq, C.; Van Ginneken, A.C.G.; Bezzina, C.R.; Alders, M.; Escande, D.; Mannens, M.M.A.M.; Baró, I.; Wilde, A.A.M. Mutation in the KCNQ1 gene leading to the short QT-interval syndrome. Circulation 2004, 109, 2394–2397.
- Feghaly, J.; Zakka, P.; London, B.; MacRae, C.A.; Refaat, M.M. Genetics of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009884.
- González, A.; Aurlien, D.; Haugaa, K.H.; Taubøll, E. Epilepsy in patients with long QT syndrome type 1: A Norwegian family. Epilepsy Behav. Case Rep. 2018, 10, 118–121.
- Zamorano-León, J.J.; Yañez, R.; Jaime, G.; Rodriguez-Sierra, P.; Calatrava-Ledrado, L.; Alvarez-Granada, R.R.; Mateos-Cáceres, P.J.; MacAya, C.; López-Farré, A.J. KCNH2 gene mutation: A potential link between epilepsy and long QT-2 syndrome. J. Neurogenet. 2012, 26, 382–386.
- McNair, W.P.; Ku, L.; Taylor, M.R.G.; Fain, P.R.; Dao, D.; Wolfel, E.; Mestroni, L. SCN5A mutation associated with dilated cardiomyopathy, conduction disorder, and arrhythmia. Circulation 2004, 110, 2163–2167.
- García-Cisneros, S.; Sánchez-Alemán, M.; Conde-Glez, C.J.; Lara-Zaragoza, S.J.; Herrera-Ortiz, A.; Plett-Torres, T.; Olamendi-Portugal, M. Performance of ELISA and Western blot to detect antibodies against HSV-2 using dried blood spots. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 224–228.
- Kallas, D.; Lamba, A.; Roston, T.M.; Arslanova, A.; Franciosi, S.; Tibbits, G.F.; Sanatani, S. Pediatric Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia: A Translational Perspective for the Clinician-Scientist. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9293.
- Badone, B.; Ronchi, C.; Kotta, M.-C.; Sala, L.; Ghidoni, A.; Crotti, L.; Zaza, A. Calmodulinopathy: Functional Effects of CALM Mutations and Their Relationship With Clinical Phenotypes. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 5.
- Makita, N.; Yagihara, N.; Crotti, L.; Johnson, C.N.; Beckmann, B.M.; Roh, M.S.; Shigemizu, D.; Lichtner, P.; Ishikawa, T.; Aiba, T.; et al. Novel calmodulin mutations associated with congenital arrhythmia susceptibility. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 466–474.
- Reed, G.J.; Boczek, N.J.; Etheridge, S.P.; Ackerman, M.J. CALM3 mutation associated with long QT syndrome. Hear. Rhythm 2015, 12, 419–422.
- Rabbani, B.; Khorgami, M.; Dalili, M.; Zamani, N.; Mahdieh, N.; Gollob, M.H. Novel cases of pediatric sudden cardiac death secondary to TRDN mutations presenting as long QT syndrome at rest and catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia during exercise: The TRDN arrhythmia syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2021, 185, 3433–3445.
- Altmann, H.M.; Tester, D.J.; Will, M.L.; Middha, S.; Evans, J.M.; Eckloff, B.W.; Ackerman, M.J. Homozygous/compound heterozygous triadin mutations associated with autosomal-recessive long-QT syndrome and pediatric sudden cardiac arrest: Elucidation of the triadin knockout syndrome. Circulation 2015, 131, 2051–2060.
- Song, J.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, Y.; He, J. Advances in the Molecular Genetics of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 2148.
- Gakenheimer-Smith, L.; Meyers, L.; Lundahl, D.; Menon, S.C.; Bunch, T.J.; Sawyer, B.L.; Tristani-Firouzi, M.; Etheridge, S.P. Expanding the phenotype of CACNA1C mutation disorders. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2021, 9, e1673.
- Endres, D.; Decher, N.; Röhr, I.; Vowinkel, K.; Domschke, K.; Komlosi, K.; Tzschach, A.; Gläser, B.; Schiele, M.A.; Runge, K.; et al. New CaV1.2 channelopathy with high-functioning autism, affective disorder, severe dental enamel defects, a short QT interval, and a novel cacna1c loss-of-function mutation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8611.
- Di Mauro, V.; Ceriotti, P.; Lodola, F.; Salvarani, N.; Modica, J.; Bang, M.L.; Mazzanti, A.; Napolitano, C.; Priori, S.G.; Catalucci, D. Peptide-Based Targeting of the L-Type Calcium Channel Corrects the Loss-of-Function Phenotype of Two Novel Mutations of the CACNA1 Gene Associated With Brugada Syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 1741.
- Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Xie, J.; Bao, H.; Cao, Q.; Wan, R.; Xu, X.; Zhou, H.; Huang, L.; Xu, Z.; et al. A mutation in the CACNA1C gene leads to early repolarization syndrome with incomplete penetrance: A Chinese family study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177532.
- Splawski, I.; Timothy, K.W.; Sharpe, L.M.; Decher, N.; Kumar, P.; Bloise, R.; Napolitano, C.; Schwartz, P.J.; Joseph, R.M.; Condouris, K.; et al. CaV1.2 calcium channel dysfunction causes a multisystem disorder including arrhythmia and autism. Cell 2004, 119, 19–31.
- Mazzanti, A.; Guz, D.; Trancuccio, A.; Pagan, E.; Kukavica, D.; Chargeishvili, T.; Olivetti, N.; Biernacka, E.K.; Sacilotto, L.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; et al. Natural History and Risk Stratification in Andersen-Tawil Syndrome Type 1. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1772–1784.
- Kalscheur, M.M.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Orland, K.M.; Abozeid, S.; Fabry, N.; Maginot, K.R.; January, C.T.; Makielski, J.C.; Eckhardt, L.L. KCNJ2 mutation causes an adrenergic-dependent rectification abnormality with calcium sensitivity and ventricular arrhythmia. Heart Rhythm 2014, 11, 885–894.
- Kimura, H.; Zhou, J.; Kawamura, M.; Itoh, H.; Mizusawa, Y.; Ding, W.G.; Wu, J.; Ohno, S.; Makiyama, T.; Miyamoto, A.; et al. Phenotype variability in patients carrying KCNJ2 mutations. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2012, 5, 344–353.
- Rezazadeh, S.; Guo, J.; Duff, H.J.; Ferrier, R.A.; Gerull, B. Reversible Dilated Cardiomyopathy Caused by a High Burden of Ventricular Arrhythmias in Andersen-Tawil Syndrome. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 1576.e15–1576.e18.
- Priori, S.G.; Pandit, S.V.; Rivolta, I.; Berenfeld, O.; Ronchetti, E.; Dhamoon, A.; Napolitano, C.; Anumonwo, J.; Di Barletta, M.R.; Gudapakkam, S.; et al. A novel form of short QT syndrome (SQT3) is caused by a mutation in the KCNJ2 gene. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 800–807.
- Mohler, P.J.; Splawski, I.; Napolitano, C.; Bottelli, G.; Sharpe, L.; Timothy, K.; Priori, S.G.; Keating, M.T.; Bennett, V. A cardiac arrhythmia syndrome caused by loss of ankyrin-B function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9137–9142.
- Mohler, P.J.; Rivolta, I.; Napolitano, C.; LeMaillet, G.; Lambert, S.; Priori, S.G.; Bennett, V. Nav1.5 E1053K mutation causing Brugada syndrome blocks binding to ankyrin-G and expression of Nav1.5 on the of cardiomyocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17533–17538.
- Giudicessi, J.R.; Ackerman, M.J. Established Loss-of-Function Variants in ANK2 -Encoded Ankyrin-B Rarely Cause a concerning Cardiac Phenotype in Humans. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2020, 13, 80–82.
- Yang, R.; Walder-Christensen, K.K.; Kim, N.; Wu, D.; Lorenzo, D.N.; Badea, A.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yin, H.H.; Wetsel, W.C.; Bennett, V. ANK2 autism mutation targeting giant ankyrin-B promotes axon branching and ectopic connectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15262–15271.
- Yamada, N.; Asano, Y.; Fujita, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Inanobe, A.; Matsuura, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Ohno, S.; Ebana, Y.; Tsukamoto, O.; et al. Mutant KCNJ3 and KCNJ5 Potassium Channels as Novel Molecular Targets in Bradyarrhythmias and Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2019, 139, 2157–2169.
- Antzelevitch, C.; Yan, G.X.; Ackerman, M.J.; Borggrefe, M.; Corrado, D.; Guo, J.; Gussak, I.; Hasdemir, C.; Horie, M.; Huikuri, H.; et al. J-Wave syndromes expert consensus conference report: Emerging concepts and gaps in knowledge. Europace 2017, 19, 665–694.
- D’Imperio, S.; Monasky, M.M.; Micaglio, E.; Ciconte, G.; Anastasia, L.; Pappone, C. Brugada Syndrome: Warning of a Systemic Condition? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 1386.
- Boukens, B.J.; Potse, M.; Coronel, R. Fibrosis and conduction abnormalities as basis for overlap of brugada syndrome and early repolarization syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1570.
- Moncayo-Arlandi, J.; Brugada, R. Unmasking the molecular link between arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy and Brugada syndrome. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 744–756.
- Erdoğan, O. Coexistence of Wolff-Parkinson-White and Brugada ECG. Turk Kardiyol. Dern. Ars. 2018, 46, 433–434.
- Hothi, S.S.; Ara, F.; Timperley, J. p.Y1449C SCN5A mutation associated with overlap disorder comprising conduction disease, Brugada syndrome, and atrial flutter. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2015, 26, 93–97.
- Vlachos, K.; Mascia, G.; Martin, C.A.; Bazoukis, G.; Frontera, A.; Cheniti, G.; Letsas, K.P.; Efremidis, M.; Georgopoulos, S.; Gkalapis, C.; et al. Atrial fibrillation in Brugada syndrome: Current perspectives. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 975–984.
- Kewcharoen, J.; Rattanawong, P.; Kanitsoraphan, C.; Mekritthikrai, R.; Prasitlumkum, N.; Putthapiban, P.; Mekraksakit, P.; Pattison, R.J.; Vutthikraivit, W. Atrial fibrillation and risk of major arrhythmic events in Brugada syndrome: A meta-analysis. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019, 24, e12676.
- Abdelghani, M.; Chapra, A.; Asaad, N.; Hayat, S. Epilepsy and Brugada Syndrome: Association or Uncommon Presentation? Heart Views 2020, 21, 114.
- Parisi, P.; Oliva, A.; Coll Vidal, M.; Partemi, S.; Campuzano, O.; Iglesias, A.; Pisani, D.; Pascali, V.L.; Paolino, M.C.; Villa, M.P.; et al. Coexistence of epilepsy and Brugada syndrome in a family with SCN5A mutation. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 105, 415–418.
- Sandorfi, G.; Clemens, B.; Csanadi, Z. Electrical storm in the brain and in the heart: Epilepsy and Brugada syndrome. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 1167–1173.
- Camacho Velásquez, J.L.; Rivero Sanz, E.; Velazquez Benito, A.; Mauri Llerda, J.A. Epilepsia y síndrome de Brugada. Neurologia 2017, 32, 58–60.
- Sasaki, T.; Ikeda, K.; Nakajima, T.; Kawabata-Iwakawa, R.; Iizuka, T.; Dharmawan, T.; Tamura, S.; Niwamae, N.; Tange, S.; Nishiyama, M.; et al. Multiple arrhythmic and cardiomyopathic phenotypes associated with an SCN5A A735E mutation. J. Electrocardiol. 2021, 65, 122–127.
- Amarouch, M.Y.; El Hilaly, J. Inherited Cardiac Arrhythmia Syndromes: Focus on Molecular Mechanisms Underlying TRPM4 Channelopathies. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2020, 2020, 1–10.
- Bienengraeber, M.; Olson, T.M.; Selivanov, V.A.; Kathmann, E.C.; O’Cochlain, F.; Gao, F.; Karger, A.B.; Ballew, J.D.; Hodgson, D.M.; Zingman, L.V.; et al. ABCC9 mutations identified in human dilated cardiomyopathy disrupt catalytic KATP channel gating. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 382–387.
- Gerull, B.; Heuser, A.; Wichter, T.; Paul, M.; Basson, C.T.; McDermott, D.A.; Lerman, B.B.; Markowitz, S.M.; Ellinor, P.T.; MacRae, C.A.; et al. Mutations in the desmosomal protein plakophilin-2 are common in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1162–1164.
- Elliott, P.; O’Mahony, C.; Syrris, P.; Evans, A.; Sorensen, C.R.; Sheppard, M.N.; Carr-White, G.; Pantazis, A.; McKenna, W.J. Prevalence of desmosomal protein gene mutations in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2010, 3, 314–322.
- James, C.A.; Jongbloed, J.D.H.; Hershberger, R.E.; Morales, A.; Judge, D.P.; Syrris, P.; Pilichou, K.; Domingo, A.M.; Murray, B.; Cadrin-Tourigny, J.; et al. International Evidence Based Reappraisal of Genes Associated with Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Using the Clinical Genome Resource Framework. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2021, 14, 273–284.
- Bottillo, I.; D’Angelantonio, D.; Caputo, V.; Paiardini, A.; Lipari, M.; De Bernardo, C.; Giannarelli, D.; Pizzuti, A.; Majore, S.; Castori, M.; et al. Molecular analysis of sarcomeric and non-sarcomeric genes in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Gene 2016, 577, 227–235.
- Taniguchi, Y.; Miyazaki, A.; Sakaguchi, H.; Hayama, Y.; Ebishima, N.; Negishi, J.; Noritake, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Shimizu, W.; Aiba, T.; et al. Prominent QTc prolongation in a patient with a rare variant in the cardiac ryanodine receptor gene. Heart Vessels 2017, 32, 229–233.
- Hirose, S.; Murayama, T.; Tetsuo, N.; Hoshiai, M.; Kise, H.; Yoshinaga, M.; Aoki, H.; Fukuyama, M.; Wuriyanghai, Y.; Wada, Y.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in cardiac ryanodine receptor channel cause various types of arrhythmias including long QT syndrome. Europace 2021, euab250.
- Roston, T.M.; Guo, W.; Krahn, A.D.; Wang, R.; Van Petegem, F.; Sanatani, S.; Chen, S.R.W.; Lehman, A. A novel RYR2 loss-of-function mutation (I4855M) is associated with left ventricular non-compaction and atypical catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. J. Electrocardiol. 2017, 50, 227–233.
- Roston, T.M.; Wei, J.; Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Zhong, X.; Wang, R.; Estillore, J.P.; Peltenburg, P.J.; Noguer, F.R.I.; Till, J.; et al. Clinical and Functional Characterization of Ryanodine Receptor 2 Variants Implicated in Calcium-Release Deficiency Syndrome. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, e214458.
- Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Guo, W.; Sun, B.; Estillore, J.P.; Wang, R.; Yoruk, A.; Roston, T.M.; Sanatani, S.; Wilde, A.A.M.; et al. Human RyR2 (Ryanodine Receptor 2) Loss-of-Function Mutations: Clinical Phenotypes and In Vitro Characterization. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2021, 14, 874–885.
- Lahat, H.; Pras, E.; Olender, T.; Avidan, N.; Ben-Asher, E.; Man, O.; Levy-Nissenbaum, E.; Khoury, A.; Lorber, A.; Goldman, B.; et al. A missense mutation in a highly conserved region of CASQ2 is associated with autosomal recessive catecholamine-induced polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in Bedouin families from Israel. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 1378–1384.
- Devalla, H.D.; Gélinas, R.; Aburawi, E.H.; Beqqali, A.; Goyette, P.; Freund, C.; Chaix, M.; Tadros, R.; Jiang, H.; Le Béchec, A.; et al. TECRL, a new life-threatening inherited arrhythmia gene associated with overlapping clinical features of both LQTS and CPVT. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 1390–1408.
- Jalloul, Y.; Refaat, M.M. Novel variants in TECRL cause catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 1536–1538.
- Roux-buisson, N.; Cacheux, M.; Fourest-lieuvin, A.; Fauconnier, J.; Brocard, J.; Denjoy, I.; Durand, P.; Guicheney, P.; Kyndt, F.; Leenhardt, A.; et al. Absence of triadin, a protein of the calcium release complex, is responsible for cardiac arrhythmia with sudden death in human. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 2759–2767.
- Imberti, J.F.; Underwood, K.; Mazzanti, A.; Priori, S.G. Clinical Challenges in Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia. Heart Lung Circ. 2016, 25, 777–783.
- Campuzano, O.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Cesar, S.; Arbelo, E.; Brugada, J.; Brugada, R. Recent Advances in Short QT Syndrome. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5.
- Thorsen, K.; Dam, V.S.; Kjaer-Sorensen, K.; Pedersen, L.N.; Skeberdis, V.A.; Jurevičius, J.; Treinys, R.; Petersen, I.M.B.S.; Nielsen, M.S.; Oxvig, C.; et al. Loss-of-activity-mutation in the cardiac chloride-bicarbonate exchanger AE3 causes short QT syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8.
- Roussel, J.; Labarthe, F.; Thireau, J.; Ferro, F.; Farah, C.; Roy, J.; Horiuchi, M.; Tardieu, M.; Lefort, B.; François Benoist, J.; et al. Carnitine deficiency induces a short QT syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13, 165–174.
- Gélinas, R.; Leach, E.; Horvath, G.; Laksman, Z. Molecular Autopsy Implicates Primary Carnitine Deficiency in Sudden Unexplained Death and Reversible Short QT Syndrome. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 1256.e1–1256.e2.
- Kessi, M.; Chen, B.; Peng, J.; Yan, F.; Yang, L.; Yin, F. Calcium channelopathies and intellectual disability: A systematic review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16.
- Schwartz, P.J.; Ackerman, M.J.; Antzelevitch, C.; Bezzina, C.R.; Borggrefe, M.; Cuneo, B.F.; Wilde, A.A.M. Inherited cardiac arrhythmias. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 1–22.
- Mizusawa, Y. Recent advances in genetic testing and counseling for inherited arrhythmias. J. Arrhythm. 2016, 32, 389–397.
- Tester, D.J.; Will, M.L.; Haglund, C.M.; Ackerman, M.J. Compendium of cardiac channel mutations in 541 consecutive unrelated patients referred for long QT syndrome genetic testing. Heart Rhythm 2005, 2, 507–517.
- Schwartz, P.J.; Priori, S.G.; Spazzolini, C.; Moss, A.J.; Michael Vincent, G.; Napolitano, C.; Denjoy, I.; Guicheney, P.; Breithardt, G.; Keating, M.T.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation in the long-QT syndrome: Gene-specific triggers for life-threatening arrhythmias. Circulation 2001, 103, 89–95.
- Bohnen, M.S.; Peng, G.; Robey, S.H.; Terrenoire, C.; Iyer, V.; Sampson, K.J.; Kass, R.S. Molecular pathophysiology of congenital long QT syndrome. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 89–134.
- Crotti, L.; Johnson, C.N.; Graf, E.; De Ferrari, G.M.; Cuneo, B.F.; Ovadia, M.; Papagiannis, J.; Feldkamp, M.D.; Rathi, S.G.; Kunic, J.D.; et al. Calmodulin mutations associated with recurrent cardiac arrest in infants. Circulation 2013, 127, 1009–1017.
- Crotti, L.; Johnson, C.N.; Graf, E.; De Ferrari, G.M.; Cuneo, B.F.; Ovadia, M.; Papagiannis, J.; Feldkamp, M.D.; Rathi, S.G.; Kunic, J.D.; et al. Calmodulin mutations and life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias: Insights from the International Calmodulinopathy Registry. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 2964–2975.
- Clemens, D.J.; Gray, B.; Bagnall, R.D.; Tester, D.J.; Dotzler, S.M.; Giudicessi, J.R.; Matthews, E.; Semsarian, C.; Behr, E.R.; Ackerman, M.J. Triadin Knockout Syndrome Is Absent in a Multi-Center Molecular Autopsy Cohort of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome and Sudden Unexplained Death in the Young and Is Extremely Rare in the General Population. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2020, 13, 52–58.
- Korkosh, V.S.; Kiselev, A.M.; Mikhaylov, E.N.; Kostareva, A.A.; Zhorov, B.S. Atomic mechanisms of Timothy syndrome-associated mutations in calcium channel Cav1.2. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10.
- Matsuda, S.; Ohnuki, Y.; Okami, M.; Ochiai, E.; Yamada, S.; Takahashi, K.; Osawa, M.; Okami, K.; Iida, M.; Mochizuki, H. Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome with novel KCNQ1 and additional gene mutations. Hum. Genome Var. 2020, 7.
- Lahrouchi, N.; Tadros, R.; Crotti, L.; Mizusawa, Y.; Postema, P.G.; Beekman, L.; Walsh, R.; Hasegawa, K.; Barc, J.; Ernsting, M.; et al. Transethnic genome-wide association study provides insights in the genetic architecture and heritability of long QT syndrome. Circulation 2020, 142, 324–338.
- Napolitano, C.; Mazzanti, A.; Priori, S.G. Genetic risk stratification in cardiac arrhythmias. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2018, 33, 298–303.
- Ronchi, C.; Bernardi, J.; Mura, M.; Stefanello, M.; Badone, B.; Rocchetti, M.; Crotti, L.; Brink, P.; Schwartz, P.J.; Gnecchi, M.; et al. NOS1AP polymorphisms reduce NOS1 activity and interact with prolonged repolarization in arrhythmogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 472–483.
- Kääb, S.; Crawford, D.C.; Sinner, M.F.; Behr, E.R.; Kannankeril, P.J.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Bezzina, C.R.; Schulze-Bahr, E.; Guicheney, P.; Bishopric, N.H.; et al. A large candidate gene survey identifies the KCNE1D85N polymorphism as a possible modulator of drug-induced torsades de pointes. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2012, 5, 91–99.
- Sesti, F.; Abbott, G.W.; Wei, J.; Murray, K.T.; Saksena, S.; Schwartz, P.J.; Priori, S.G.; Roden, D.M.; George, A.L.; Goldstein, S.A.N. A common polymorphism associated with antibiotic-induced cardiac arrhythmia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10613–10618.
- Cheng, J.; Tester, D.J.; Tan, B.H.; Valdivia, C.R.; Kroboth, S.; Ye, B.; January, C.T.; Ackerman, M.J.; Makielski, J.C. The common African American polymorphism SCN5A-S1103Y interacts with mutation SCN5A-R680h to increase late Na current. Physiol. Genom. 2011, 43, 461–466.
- Roberts, J.D.; Krahn, A.D.; Ackerman, M.J.; Rohatgi, R.K.; Moss, A.J.; Nazer, B.; Tadros, R.; Gerull, B.; Sanatani, S.; Wijeyeratne, Y.D.; et al. Loss-of-Function KCNE2 Variants: True Monogenic Culprits of Long-QT Syndrome or Proarrhythmic Variants Requiring Secondary Provocation? Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2017, 10.
- El-Sherif, N.; Turitto, G.; Boutjdir, M. Acquired long QT syndrome and torsade de pointes. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 414–421.
- Priori, S.G.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Mazzanti, A.; Bloma, N.; Borggrefe, M.; Camm, J.; Elliott, P.M.; Fitzsimons, D.; Hatala, R.; Hindricks, G.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: The Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the Europe. Europace 2015, 17, 1601–1687.
- Schwartz, P.J.; Moss, A.J.; Vincent, G.M.; Crampton, R.S. Diagnostic criteria for the long QT syndrome. An update. Circulation 1993, 88, 782–784.
- Goldenberg, I.; Horr, S.; Moss, A.J.; Lopes, C.M.; Barsheshet, A.; McNitt, S.; Zareba, W.; Andrews, M.L.; Robinson, J.L.; Locati, E.H.; et al. Risk for life-threatening cardiac events in patients with genotype-confirmed long-QT syndrome and normal-range corrected QT intervals. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 51–59.
- Priori, S.G.; Schwartz, P.J.; Napolitano, C.; Bloise, R.; Ronchetti, E.; Grillo, M.; Vicentini, A.; Spazzolini, C.; Nastoli, J.; Bottelli, G.; et al. Risk Stratification in the Long-QT Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1866–1874.
- Mazzanti, A.; Maragna, R.; Vacanti, G.; Monteforte, N.; Bloise, R.; Marino, M.; Braghieri, L.; Gambelli, P.; Memmi, M.; Pagan, E.; et al. Interplay Between Genetic Substrate, QTc Duration, and Arrhythmia Risk in Patients With Long QT Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1663–1671.
- Vink, A.S.; Clur, S.A.B.; Geskus, R.B.; Blank, A.C.; De Kezel, C.C.A.; Yoshinaga, M.; Hofman, N.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Blom, N.A. Effect of Age and Sex on the QTc Interval in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 and 2 Long-QT Syndrome. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2017, 10.
- Jons, C.; Moss, A.J.; Goldenberg, I.; Liu, J.; McNitt, S.; Zareba, W.; Qi, M.; Robinson, J.L. Risk of Fatal Arrhythmic Events in Long QT Syndrome Patients After Syncope. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 783–788.
- Sharma, N.; Cortez, D.; Disori, K.; Imundo, J.R.; Beck, M. A Review of Long QT Syndrome: Everything a Hospitalist Should Know. Hosp. Pediatr. 2020, 10, 369–375.
- Moore, J.P.; Gallotti, R.G.; Shannon, K.M.; Bos, J.M.; Sadeghi, E.; Strasburger, J.F.; Wakai, R.T.; Horigome, H.; Clur, S.A.; Hill, A.C.; et al. Genotype Predicts Outcomes in Fetuses and Neonates With Severe Congenital Long QT Syndrome. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 1561–1570.
- Seth, R.; Moss, A.J.; McNitt, S.; Zareba, W.; Andrews, M.L.; Qi, M.; Robinson, J.L.; Goldenberg, I.; Ackerman, M.J.; Benhorin, J.; et al. Long QT Syndrome and Pregnancy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1092–1098.
- Shimizu, W.; Makimoto, H.; Yamagata, K.; Kamakura, T.; Wada, M.; Miyamoto, K.; Inoue-Yamada, Y.; Okamura, H.; Ishibashi, K.; Noda, T.; et al. Association of Genetic and Clinical Aspects of Congenital Long QT Syndrome with Life-Threatening Arrhythmias in Japanese Patients. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 246–254.
- Amin, A.S.; Herfst, L.J.; Delisle, B.P.; Klemens, C.A.; Rook, M.B.; Bezzina, C.R.; Underkofler, H.A.S.; Holzem, K.M.; Ruijter, J.M.; Tan, H.L.; et al. Fever-induced QTc prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias in individuals with type 2 congenital long QT syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2552–2561.
- Giudicessi, J.R.; Ackerman, M.J. Determinants of incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity in heritable cardiac arrhythmia syndromes. Transl. Res. 2013, 161, 1–14.
- Crotti, L.; Spazzolini, C.; Schwartz, P.J.; Shimizu, W.; Denjoy, I.; Schulze-Bahr, E.; Zaklyazminskaya, E.V.; Swan, H.; Ackerman, M.J.; Moss, A.J.; et al. The common long-QT syndrome mutation KCNQ1/A341V causes unusually severe clinical manifestations in patients with different ethnic backgrounds: Toward a mutation-specific risk stratification. Circulation 2007, 116, 2366–2375.
- Priest, J.R.; Gawad, C.; Kahlig, K.M.; Yuf, J.K.; O’Hara, T.; Boyle, P.M.; Rajamani, S.; Clark, M.J.; Garcia, S.T.K.; Ceresnak, S.; et al. Early somatic mosaicism is a rare cause of long-QT syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11555–11560.
- Napolitano, C.; Novelli, V.; Francis, M.D.; Priori, S.G. Genetic modulators of the phenotype in the long QT syndrome: State of the art and clinical impact. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2015, 33, 17–24.
- Riuró, H.; Campuzano, O.; Berne, P.; Arbelo, E.; Iglesias, A.; Pérez-Serra, A.; Coll-Vidal, M.; Partemi, S.; Mademont-Soler, I.; Picó, F.; et al. Genetic analysis, in silico prediction, and family segregation in long QT syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 79–85.
- Marín, P.N.; Jiménez-Jáimez, J.; Tinaquero, D.; Alfayate, S.; Utrilla, R.G.; Del Rey, M.D.M.R.V.; Perin, F.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Monserrat, L.; Brugada, J.; et al. Digenic Heterozigosity in SCN5A and CACNA1C Explains the Variable Expressivity of the Long QT Phenotype in a Spanish Family. Rev. Española Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 72, 324–332.
- Eddy, C.A.; MacCormick, J.M.; Chung, S.K.; Crawford, J.R.; Love, D.R.; Rees, M.I.; Skinner, J.R.; Shelling, A.N. Identification of large gene deletions and duplications in KCNQ1 and KCNH2 in patients with long QT syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2008, 5, 1275–1281.
- Barc, J.; Briec, F.; Schmitt, S.; Kyndt, F.; Le Cunff, M.; Baron, E.; Vieyres, C.; Sacher, F.; Redon, R.; Le Caignec, C.; et al. Screening for copy number variation in genes associated with the long QT syndrome: Clinical relevance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 40–47.
- Stattin, E.L.; Boström, I.M.; Winbo, A.; Cederquist, K.; Jonasson, J.; Jonsson, B.A.; Diamant, U.B.; Jensen, S.M.; Rydberg, A.; Norberg, A. Founder mutations characterise the mutation panorama in 200 Swedish index cases referred for Long QT syndrome genetic testing. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2012, 12, 95.
- Campuzano, O.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Mademont-Soler, I.; Allegue, C.; Cesar, S.; Ferrer-Costa, C.; Coll, M.; Mates, J.; Iglesias, A.; Brugada, J.; et al. Identification of genetic alterations, as causative genetic defects in long QT syndrome, using next generation sequencing technology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114894.
- Mates, J.; Mademont-Soler, I.; Del Olmo, B.; Ferrer-Costa, C.; Coll, M.; Pérez-Serra, A.; Picó, F.; Allegue, C.; Fernandez-Falgueras, A.; Álvarez, P.; et al. Role of copy number variants in sudden cardiac death and related diseases: Genetic analysis and translation into clinical practice. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 26, 1014–1025.
- Earle, N.; Crawford, J.; Smith, W.; Hayes, I.; Shelling, A.; Hood, M.; Stiles, M.; Maxwell, F.; Heaven, D.; Love, D.R.; et al. Community detection of long QT syndrome with a clinical registry: An alternative to ECG screening programs? Heart Rhythm 2013, 10, 233–238.
- Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Cesar, S.; Zambrano, M.D.; Fernandez-Falgueras, A.; Fiol, V.; Iglesias, A.; Torres, F.; Garcia-Algar, O.; Arbelo, E.; Brugada, J.; et al. Electrocardiographic Assessment and Genetic Analysis in Neonates: A Current Topic of Discussion. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2018, 15, 30–37.
- Gomez, A.T.; Prutkin, J.M.; Rao, A.L. Evaluation and Management of Athletes With Long QT Syndrome: An Evolved Paradigm. Sports Health 2016, 8, 527–535.
- Ahluwalia, N.; Raju, H. Assessment of the QT Interval in Athletes: Red Flags and Pitfalls. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 20, 1–12.
- Wilde, A.A.M.; Moss, A.J.; Kaufman, E.S.; Shimizu, W.; Peterson, D.R.; Benhorin, J.; Lopes, C.; Towbin, J.A.; Spazzolini, C.; Crotti, L.; et al. Clinical Aspects of Type 3 Long-QT Syndrome: An International Multicenter Study. Circulation 2016, 134, 872–882.
- Yang, Y.; Ly, T.T.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, P. Sodium channel blockers in the management of long QT syndrome types 3 and 2: A system review and meta-analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 3057–3067.
- Ackerman, M.J.; Priori, S.G.; Dubin, A.M.; Kowey, P.; Linker, N.J.; Slotwiner, D.; Triedman, J.; Van Hare, G.F.; Gold, M.R. Beta-blocker therapy for long QT syndrome and catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: Are all beta-blockers equivalent? Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, e41–e44.
- Waddell-Smith, K.E.; Earle, N.; Skinner, J.R. Must every child with long QT syndrome take a beta blocker? Arch. Dis. Child. 2015, 100, 279–282.
- Niaz, T.; Bos, J.M.; Sorensen, K.B.; Moir, C.; Ackerman, M.J. Left Cardiac Sympathetic Denervation Monotherapy in Patients with Congenital Long QT Syndrome. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008830.
- Schwartz, P.J.; Spazzolini, C.; Priori, S.G.; Crotti, L.; Vicentini, A.; Landolina, M.; Gasparini, M.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Knops, R.E.; Denjoy, I.; et al. Who are the long-QT syndrome patients who receive an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator and what happens to them?: Data from the European Long-QT syndrome implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (LQTS ICD) registry. Circulation 2010, 122, 1272–1282.
- Shah, M.J.; Silka, M.J.; Silva, J.N.A.; Balaji, S.; Beach, C.M.; Benjamin, M.N.; Berul, C.I.; Cannon, B.; Cecchin, F.; Cohen, M.I.; et al. 2021 PACES Expert Consensus Statement on the Indications and Management of Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Devices in Pediatric Patients. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 1888–1924.
- Brugada, J.; Campuzano, O.; Arbelo, E.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Brugada, R. Present Status of Brugada Syndrome: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 1046–1059.
- Mizusawa, Y.; Wilde, A.A.M. Brugada syndrome. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2012, 5, 606–616.
- Benito, B.; Sarkozy, A.; Mont, L.; Henkens, S.; Berruezo, A.; Tamborero, D.; Arzamendi, D.; Berne, P.; Brugada, R.; Brugada, P.; et al. Gender Differences in Clinical Manifestations of Brugada Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1567–1573.
- Milman, A.; Andorin, A.; Gourraud, J.B.; Sacher, F.; Mabo, P.; Kim, S.H.; Maeda, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Kamakura, T.; Aiba, T.; et al. Age of First Arrhythmic Event in Brugada Syndrome: Data from the SABRUS (Survey on Arrhythmic Events in Brugada Syndrome) in 678 Patients. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2017, 10, e005222.
- Raharjo, S.B.; Maulana, R.; Maghfirah, I.; Alzahra, F.; Putrinarita, A.D.; Hanafy, D.A.; Yuniadi, Y. SCN5A gene mutations and the risk of ventricular fibrillation and syncope in brugada syndrome patients: A meta-analysis. J. Arrhythm. 2018, 34, 473–477.
- Brugada, P.; Brugada, J. Right bundle branch block, persistent ST segment elevation and sudden cardiac death: A distinct clinical and electrocardiographic syndrome. A multicenter report. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1992, 20, 1391–1396.
- Monasky, M.M.; Micaglio, E.; Ciconte, G.; Pappone, C. Brugada syndrome: Oligogenic or mendelian disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1687.
- Campuzano, O.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Cesar, S.; Arbelo, E.; Brugada, J.; Brugada, R. Update on genetic basis of Brugada syndrome: Monogenic, polygenic or oligogenic? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7155.
- Musunuru, K.; Hershberger, R.E.; Day, S.M.; Klinedinst, N.J.; Landstrom, A.P.; Parikh, V.N.; Prakash, S.; Semsarian, C.; Sturm, A.C. Genetic testing for inherited cardiovascular diseases: A scientific statement from the american heart association. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2020, 13, 373–385.
- Crotti, L.; Marcou, C.A.; Tester, D.J.; Castelletti, S.; Giudicessi, J.R.; Torchio, M.; Medeiros-Domingo, A.; Simone, S.; Will, M.L.; Dagradi, F.; et al. Spectrum and prevalence of mutations involving BrS1-Through BrS12-susceptibility genes in a cohort of unrelated patients referred for brugada syndrome genetic testing: Implications for genetic testing. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1410–1418.
- Abbott, G.W. KCNE4 and KCNE5: K(+) channel regulation and cardiac arrhythmogenesis. Gene 2016, 593, 249–260.
- Ackerman, M.J.; Priori, S.G.; Willems, S.; Berul, C.; Brugada, R.; Calkins, H.; Camm, A.J.; Ellinor, P.T.; Gollob, M.; Hamilton, R.; et al. HRS/EHRA expert consensus statement on the state of genetic testing for the channelopathies and cardiomyopathies: This document was developed as a partnership between the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) and the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA). Europace 2011, 13, 1077–1109.
- Michowitz, Y.; Milman, A.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Andorin, A.; Champagne, J.; Postema, P.G.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Leshem, E.; Juang, J.J.; Giustetto, C.; et al. Fever-related arrhythmic events in the multicenter Survey on Arrhythmic Events in Brugada Syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 1394–1401.
- Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Sun, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, F. Electrocardiogram Characteristics and Arrhythmic Events during Fever in Patients with Fever-Induced Brugada Syndrome. Cardiology 2020, 145, 130–135.
- Coronel, R.; Casini, S.; Koopmann, T.T.; Wilms-Schopman, F.J.G.; Verkerk, A.O.; De Groot, J.R.; Bhuiyan, Z.; Bezzina, C.R.; Veldkamp, M.W.; Linnenbank, A.C.; et al. Right ventricular fibrosis and conduction delay in a patient with clinical signs of Brugada syndrome: A combined electrophysiological, genetic, histopathologic, and computational study. Circulation 2005, 112, 2769–2777.
- Nademanee, K.; Raju, H.; De Noronha, S.V.; Papadakis, M.; Robinson, L.; Rothery, S.; Makita, N.; Kowase, S.; Boonmee, N.; Vitayakritsirikul, V.; et al. Fibrosis, connexin-43, and conduction abnormalities in the Brugada syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1976–1986.
- Pieroni, M.; Notarstefano, P.; Oliva, A.; Campuzano, O.; Santangeli, P.; Coll, M.; Nesti, M.; Carnevali, A.; Fraticelli, A.; Iglesias, A.; et al. Electroanatomic and Pathologic Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Abnormalities in Patients With Brugada Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2747–2757.
- Michowitz, Y.; Milman, A.; Andorin, A.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Gonzalez Corcia, M.C.; Gourraud, J.B.; Conte, G.; Sacher, F.; Juang, J.J.M.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Characterization and Management of Arrhythmic Events in Young Patients With Brugada Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1756–1765.
- Gourraud, J.-B.; Barc, J.; Thollet, A.; Le Marec, H.; Probst, V. Brugada syndrome: Diagnosis, risk stratification and management. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 110, 188–195.
- Gonzalez Corcia, M.C.; Sieira, J.; Sarkozy, A.; De Asmundis, C.; Chierchia, G.B.; Hernandez Ojeda, J.; Pappaert, G.; Brugada, P. Brugada syndrome in the young: An assessment of risk factors predicting future events. Europace 2017, 19, 1864–1873.
- Milman, A.; Gourraud, J.B.; Andorin, A.; Postema, P.G.; Sacher, F.; Mabo, P.; Conte, G.; Giustetto, C.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Hochstadt, A.; et al. Gender differences in patients with Brugada syndrome and arrhythmic events: Data from a survey on arrhythmic events in 678 patients. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 1457–1465.
- Priori, S.G.; Gasparini, M.; Napolitano, C.; Della Bella, P.; Ottonelli, A.G.; Sassone, B.; Giordano, U.; Pappone, C.; Mascioli, G.; Rossetti, G.; et al. Risk Stratification in Brugada Syndrome: Results of the PRELUDE (PRogrammed ELectrical stimUlation preDictive valuE) Registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 37–45.
- Probst, V.; Veltmann, C.; Eckardt, L.; Meregalli, P.G.; Gaita, F.; Tan, H.L.; Babuty, D.; Sacher, F.; Giustetto, C.; Schulze-Bahr, E.; et al. Long-term prognosis of patients diagnosed with brugada syndrome: Results from the finger brugada syndrome registry. Circulation 2010, 121, 635–643.
- Morita, H.; Kusano, K.F.; Miura, D.; Nagase, S.; Nakamura, K.; Morita, S.T.; Ohe, T.; Zipes, D.P.; Wu, J. Fragmented QRS as a marker of conduction abnormality and a predictor of prognosis of Brugada syndrome. Circulation 2008, 118, 1697–1704.
- Argenziano, M.; Antzelevitch, C. Recent advances in the treatment of Brugada syndrome. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2018, 16, 387–404.
- Jongman, J.K.; Jepkes-Bruin, N.; Ramdat Misier, A.R.; Beukema, W.P.; Delnoy, P.P.H.M.; Oude Luttikhuis, H.; Dambrink, J.H.E.; Hoorntje, J.C.A.; Elvan, A. Electrical storms in Brugada syndrome successfully treated with isoproterenol infusion and quinidine orally. Neth. Heart J. 2007, 15, 151–154.
- Gonzalez Corcia, M.C.; Sieira, J.; Pappaert, G.; de Asmundis, C.; Chierchia, G.B.; La Meir, M.; Sarkozy, A.; Brugada, P. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators in Children and Adolescents With Brugada Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 148–157.
- Hernandez-Ojeda, J.; Arbelo, E.; Borras, R.; Berne, P.; Tolosana, J.M.; Gomez-Juanatey, A.; Berruezo, A.; Campuzano, O.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Mont, L.; et al. Patients With Brugada Syndrome and Implanted Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Long-Term Follow-Up. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1991–2002.
- Rizzo, A.; de Asmundis, C.; Brugada, P.; La Meir, M.; Chierchia, G.B. Ablation for the treatment of Brugada syndrome: Current status and future prospects. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2020, 17, 123–130.
- Priori, S.G.; Napolitano, C.; Gasparini, M.; Pappone, C.; Della Bella, P.; Brignole, M.; Giordano, U.; Giovannini, T.; Menozzi, C.; Bloise, R.; et al. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity of right bundle branch block and ST-segment elevation syndrome: A prospective evaluation of 52 families. Circulation 2000, 102, 2509–2515.
- Probst, V.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Barc, J.; Sacher, F.; Babuty, D.; Mabo, P.; Mansourati, J.; Le Scouarnec, S.; Kyndt, F.; Le Caignec, C.; et al. SCN5A Mutations and the role of genetic background in the pathophysiology of brugada syndrome. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 552–557.
- Mates, J.; Mademont-Soler, I.; Fernandez-Falgueras, A.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Cesar, S.; Arbelo, E.; García-Álvarez, A.; Jordà, P.; Toro, R.; Coll, M.; et al. Sudden Cardiac Death and Copy Number Variants: What Do We Know after 10 Years of Genetic Analysis? Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2020, 47, 102281.
- Gonzalez Corcia, M.C.; Brugada, P. Family Screening for Brugada Syndrome in Asymptomatic Young Patients. Is it Better not to Know? Pediatr. Cardiol. 2017, 38, 1313–1314.
- Therasse, D.; Sacher, F.; Petit, B.; Babuty, D.; Mabo, P.; Martins, R.; Jesel, L.; Maury, P.; Pasquie, J.L.; Mansourati, J.; et al. Sodium-channel blocker challenge in the familial screening of Brugada syndrome: Safety and predictors of positivity. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, 1442–1448.
- Rizzo, A.; Borio, G.; Sieira, J.; Van Dooren, S.; Overeinder, I.; Bala, G.; Pappaert, G.; Maj, R.; Osório, T.G.; Terasawa, M.; et al. Ajmaline Testing and the Brugada Syndrome. Am. J. Cardiol. 2020, 135, 91–98.
- Guerrier, K.; Kwiatkowski, D.; Czosek, R.J.; Spar, D.S.; Anderson, J.B.; Knilans, T.K. Short QT Interval Prevalence and Clinical Outcomes in a Pediatric Population. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 1460–1464.
- Bjerregaard, P. Diagnosis and management of short QT syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 1261–1267.
- El-Battrawy, I.; Besler, J.; Liebe, V.; Schimpf, R.; Tülümen, E.; Rudic, B.; Lang, S.; Wolpert, C.; Zhou, X.; Akin, I.; et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with short QT syndrome: Clinical profile and outcome. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e010073.
- Mazzanti, A.; Kanthan, A.; Monteforte, N.; Memmi, M.; Bloise, R.; Novelli, V.; Miceli, C.; O’Rourke, S.; Borio, G.; Zienciuk-Krajka, A.; et al. Novel insight into the natural history of short QT syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1300–1308.
- Hu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pfeiffer, R.; Gollob, M.H.; Healey, J.; Harrell, D.T.; Makita, N.; Abe, H.; Sun, Y.; et al. The Phenotypic Spectrum of a Mutation Hotspot Responsible for the Short QT Syndrome. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 727–743.
- Campuzano, O.; Fernandez-Falgueras, A.; Lemus, X.; Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Cesar, S.; Coll, M.; Mates, J.; Arbelo, E.; Jordà, P.; Perez-Serra, A.; et al. Short QT syndrome: A comprehensive genetic interpretation and clinical translation of rare variants. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1035.
- Harrell, D.T.; Ashihara, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Tominaga, I.; Mazzanti, A.; Takahashi, K.; Oginosawa, Y.; Abe, H.; Maemura, K.; Sumitomo, N.; et al. Genotype-dependent differences in age of manifestation and arrhythmia complications in short QT syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 190, 393–402.
- Dewi, I.P.; Dharmadjati, B.B. Short QT syndrome: The current evidences of diagnosis and management. J. Arrhythm. 2020, 36, 962–966.
- Chinese Expert Consensus Statement on the Diagnosis and Management of Patients with Inherited Primary Arrhythmia Syndromes. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25876716/ (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Hong, K.; Piper, D.R.; Diaz-Valdecantos, A.; Brugada, J.; Oliva, A.; Burashnikov, E.; Santos-De-Soto, J.; Grueso-Montero, J.; Diaz-Enfante, E.; Brugada, P.; et al. De novo KCNQ1 mutation responsible for atrial fibrillation and short QT syndrome in utero. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 68, 433–440.
- Sarquella-Brugada, G.; Campuzano, O.; Iglesias, A.; Grueso, J.; Bradley, D.J.; Kerst, G.; Shmorhun, D.; Brugada, J.; Brugada, R. Short QT and atrial fibrillation: A KCNQ1 mutation-specific disease. Late follow-up in three unrelated children. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2015, 1, 193–197.
- Providência, R.; Karim, N.; Srinivasan, N.; Honarbakhsh, S.; Ferreira, M.J.V.; Gonçalves, L.; Marijon, E.; Lambiase, P.D. Impact of QTc formulae in the prevalence of short corrected QT interval and impact on probability and diagnosis of short QT syndrome. Heart 2018, 104, 502–508.
- Hazeki, D.; Ninomiya, Y.; Ueno, K.; Yoshinaga, M. Tentative screening criteria for short QT interval in children and adolescents. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 2627–2633.
- Fan, X.; Yang, G.; Kowitx, J.; Duru, F.; Saguner, A.M.; Akin, I.; Zhou, X.; El-Battrawy, I. Preclinical short QT syndrome models: Studying the phenotype and drug-screening. Europace 2021, euab214.
- Suzuki, H.; Horie, M.; Ozawa, J.; Sumitomo, N.; Ohno, S.; Hoshino, K.; Ehara, E.; Takahashi, K.; Maeda, Y.; Yoshinaga, M.; et al. Novel electrocardiographic criteria for short QT syndrome in children and adolescents. Europace 2021, 23, 2029–2038.
- Priori, S.G.; Wilde, A.A.; Horie, M.; Cho, Y.; Behr, E.R.; Berul, C.; Blom, N.; Brugada, J.; Chiang, C.E.; Huikuri, H.; et al. HRS/EHRA/APHRS expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of patients with inherited primary arrhythmia syndromes: Document endorsed by HRS, EHRA, and APHRS in May 2013 and by ACCF, AHA, PACES, and AEPC in June 2013. Heart Rhythm 2013, 10, 1932–1963.
- Roston, T.M.; Yuchi, Z.; Kannankeril, P.J.; Hathaway, J.; Vinocur, J.M.; Etheridge, S.P.; Potts, J.E.; Maginot, K.R.; Salerno, J.C.; Cohen, M.I.; et al. The clinical and genetic spectrum of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: Findings from an international multicentre registry. Europace 2018, 20, 541–547.
- Priori, S.G.; Napolitano, C.; Memmi, M.; Colombi, B.; Drago, F.; Gasparini, M.; DeSimone, L.; Coltorti, F.; Bloise, R.; Keegan, R.; et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of patients with catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation 2002, 106, 69–74.
- Hayashi, M.; Denjoy, I.; Extramiana, F.; Maltret, A.; Buisson, N.R.; Lupoglazoff, J.M.; Klug, D.; Hayashi, M.; Takatsuki, S.; Villain, E.; et al. Incidence and risk factors of arrhythmic events in catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation 2009, 119, 2426–2434.
- Priori, S.G.; Napolitano, C.; Tiso, N.; Memmi, M.; Vignati, G.; Bloise, R.; Sorrentino, V.; Danieli, G.A. Mutataions in the cardiac ryanodine receptor gene (hRyR2) underlie catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation 2001, 103, 196–200.
- Pérez-Riera, A.R.; Barbosa-Barros, R.; de Rezende Barbosa, M.P.C.; Daminello-Raimundo, R.; de Lucca, A.A.; de Abreu, L.C. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, an update. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2018, 23, e12512.
- Gaburjakova, M.; Bal, N.C.; Gaburjakova, J.; Periasamy, M. Functional interaction between calsequestrin and ryanodine receptor in the heart. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2935–2945.
- Webster, G.; Aburawi, E.H.; Chaix, M.A.; Chandler, S.; Foo, R.; Islam, A.K.M.M.; A E Kammeraad, J.; Rioux, J.D.; Al-Gazali, L.; Sayeed, Z.; et al. Life-threatening arrhythmias with autosomal recessive TECRL variants. Europace 2021, 23, 781–788.
- Nyegaard, M.; Overgaard, M.T.; Sondergaard, M.T.; Vranas, M.; Behr, E.R.; Hildebrandt, L.L.; Lund, J.; Hedley, P.L.; Camm, A.J.; Wettrell, G.; et al. Mutations in calmodulin cause ventricular tachycardia and sudden cardiac death. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 703–712.
- Gomez-Hurtado, N.; Boczek, N.J.; Kryshtal, D.O.; Johnson, C.N.; Sun, J.; Nitu, F.R.; Cornea, R.L.; Chazin, W.J.; Calvert, M.L.; Tester, D.J.; et al. Novel CPVT-Associated Calmodulin Mutation in CALM3 (CALM3-A103V) Activates Arrhythmogenic Ca Waves and Sparks. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2016, 9, 9.
- Broendberg, A.K.; Nielsen, J.C.; Bjerre, J.; Pedersen, L.N.; Kristensen, J.; Henriksen, F.L.; Bundgaard, H.; Jensen, H.K. Nationwide experience of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia caused by RyR2 mutations. Heart 2017, 103, 901–909.
- Laitinen, P.J.; Brown, K.M.; Piippo, K.; Swan, H.; Devaney, J.M.; Brahmbhatt, B.; Donarum, E.A.; Marino, M.; Tiso, N.; Viitasalo, M.; et al. Mutations of the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2) gene in familial polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation 2001, 103, 485–490.
- Neubauer, J.; Lecca, M.R.; Russo, G.; Bartsch, C.; Medeiros-Domingo, A.; Berger, W.; Haas, C. Exome analysis in 34 sudden unexplained death (SUD) victims mainly identified variants in channelopathy-associated genes. Int. J. Legal Med. 2018, 132, 1057–1065.
- Van Der Werf, C.; Nederend, I.; Hofman, N.; Van Geloven, N.; Ebink, C.; Frohn-Mulder, I.M.E.; Alings, A.M.W.; Bosker, H.A.; Bracke, F.A.; Van Dan Heuvel, F.; et al. Familial evaluation in catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia disease penetrance and expression in cardiac ryanodine receptor mutation-carrying relatives. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2012, 5, 748–756.
- Kallas, D.; Roston, T.M.; Franciosi, S.; Brett, L.; Lieve, K.V.; Kwok, S.-Y.; Kannankeril, P.J.; Krahn, A.D.; LaPage, M.J.; Etheridge, S.; et al. Evaluation of age at symptom onset, proband status, and sex as predictors of disease severity in pediatric catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 1825–1832.
- Roston, T.M.; Vinocur, J.M.; Maginot, K.R.; Mohammed, S.; Salerno, J.C.; Etheridge, S.P.; Cohen, M.; Hamilton, R.M.; Pflaumer, A.; Kanter, R.J.; et al. Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia in Children: Analysis of Therapeutic Strategies and Outcomes from an International Multicenter Registry. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 633–642.
- McNamara, C.; Cullen, P.; Rackauskas, M.; Kelly, R.; O’Sullivan, K.E.; Galvin, J.; Eaton, D. Left cardiac sympathetic denervation: Case series and technical report. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 186, 607–613.
- Roston, T.M.; Jones, K.; Hawkins, N.M.; Bos, J.M.; Schwartz, P.J.; Perry, F.; Ackerman, M.J.; Laksman, Z.W.; Kaul, P.; Lieve, K.V.; et al. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator use in catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: A systematic review. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 1791–1799.
- Postma, A.V.; Denjoy, I.; Kamblock, J.; Alders, M.; Lupoglazoff, J.M.; Vaksmann, G.; Dubosq-Bidot, L.; Sebillon, P.; Mannens, M.M.A.M.; Guicheney, P.; et al. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: RYR2 mutations, bradycardia, and follow up of the patients. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, 863–870.
- Campbell, M.; Czosek, R.J.; Hinton, R.B.; Miller, E.M. Exon 3 deletion of ryanodine receptor causes left ventricular noncompaction, worsening catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, and sudden cardiac arrest. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2015, 167, 2197–2200.
- Bhuiyan, Z.A.; Van Den Berg, M.P.; Van Tintelen, J.P.; Bink-Boelkens, M.T.E.; Wiesfeld, A.C.P.; Alders, M.; Postma, A.V.; Van Langen, I.; Mannens, M.M.A.M.; Wilde, A.A.M. Expanding spectrum of human RYR2-related disease: New electrocardiographic, structural, and genetic features. Circulation 2007, 116, 1569–1576.
- Persampieri, S.; Pilato, C.A.; Sommariva, E.; Maione, A.S.; Stadiotti, I.; Ranalletta, A.; Torchio, M.; Dello Russo, A.; Basso, C.; Pompilio, G.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Data Define a Diagnosis of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy in a Carrier of a Brugada-Syndrome-Associated PKP2 Mutation. Genes (Basel) 2020, 11, 571.
- Laurent, G.; Saal, S.; Amarouch, M.Y.; Béziau, D.M.; Marsman, R.F.; Faivre, L.; Barc, J.; Dina, C.; Bertaux, G.; Barthez, O.; et al. Multifocal Ectopic Purkinje-Related Premature Contractions: A New SCN5A-Related Cardiac Channelopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 144–156.
- Amin, A.S. SCN5a overlap syndromes-This episode: Long QT syndrome type 3 meets multifocal ectopic Purkinje-related premature contractions. Heart Rhythm 2020, 17, 1777–1778.
- Swan, H.; Amarouch, M.Y.; Leinonen, J.; Marjamaa, A.; Kucera, J.P.; Laitinen-Forsblom, P.J.; Lahtinen, A.M.; Palotie, A.; Kontula, K.; Toivonen, L.; et al. Gain-of-function mutation of the SCN5A gene causes exercise-induced polymorphic ventricular arrhythmias. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 771–781.
- Ghovanloo, M.R.; Atallah, J.; Escudero, C.A.; Ruben, P.C. Biophysical Characterization of a Novel SCN5A Mutation Associated with an Atypical Phenotype of Atrial and Ventricular Arrhythmias and Sudden Death. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 11.
- Wilde, A.A.; Amin, A.S. Clinical Spectrum of SCN5A Mutations: Long QT Syndrome, Brugada Syndrome, and Cardiomyopathy. JACC. Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 4, 569–579.
- Hayashi, H.; Sumiyoshi, M.; Nakazato, Y.; Daida, H. Brugada syndrome and sinus node dysfunction. J. Arrhythm. 2018, 34, 216–221.
- Shan, L.; Makita, N.; Xing, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Futatani, T.; Ye, F.; Saito, K.; Ibuki, K.; Watanabe, K.; Hirono, K.; et al. SCN5A variants in Japanese patients with left ventricular noncompaction and arrhythmia. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2008, 93, 468–474.
- Veltmann, C.; Barajas-Martinez, H.; Wolpert, C.; Borggrefe, M.; Schimpf, R.; Pfeiffer, R.; Cáceres, G.; Burashnikov, E.; Antzelevitch, C.; Hu, D. Further Insights in the Most Common SCN5A Mutation Causing Overlapping Phenotype of Long QT Syndrome, Brugada Syndrome, and Conduction Defect. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, 5.
- Sandhu, A.; Borne, R.T.; Mam, C.; Bunch, T.J.; Aleong, R.G. Double jeopardy: Long QT3 and Brugada syndromes. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 1315–1319.
- Bekke, R.M.; Isaacs, A.; Barysenka, A.; Hoos, M.B.; Jongbloed, J.D.; Hoorntje, J.C.; Patelski, A.S.; Enden, A.T.H.-V.D.; Wijngaard, A.V.D.; Stoll, M.; et al. Heritability in a SCN5A-mutation founder population with increased female susceptibility to non-nocturnal ventricular tachyarrhythmia and sudden cardiac death. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, 1873–1881.
- Bezzina, C.; Veldkamp, M.W.; Van Den Berg, M.P.; Postma, A.V.; Rook, M.B.; Viersma, J.W.; Van Langen, I.M.; Tan-Sindhunata, G.; Bink-Boelkens, M.T.E.; Van Der Hout, A.H.; et al. A single Na+ channel mutation causing both long-QT and Brugada syndromes. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 1206–1213.
- Coll, M.; Striano, P.; Ferrer-Costa, C.; Campuzano, O.; Matés, J.; Del Olmo, B.; Iglesias, A.; Pérez-Serra, A.; Mademont, I.; Picó, F.; et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing provides novel clues for associated epilepsy and cardiac conduction disorder/SUDEP. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189618.
- Coll, M.; Oliva, A.; Grassi, S.; Brugada, R.; Campuzano, O. Update on the Genetic Basis of Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1979.
- Chahal, C.A.A.; Salloum, M.N.; Alahdab, F.; Gottwald, J.A.; Tester, D.J.; Anwer, L.A.; So, E.L.; Murad, M.H.; Louis, E.K.S.; Ackerman, M.J.; et al. Systematic Review of the Genetics of Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy: Potential Overlap With Sudden Cardiac Death and Arrhythmia-Related Genes. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e012264.
- Kim, S.H.; Nam, G.B.; Yun, S.C.; Choi, H.O.; Choi, K.J.; Joung, B.; Pak, H.N.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, S.S.; Park, S.J.; et al. Variants of Brugada Syndrome and Early Repolarization Syndrome: An Expanded Concept of J-Wave Syndrome. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 40, 162–174.
- Scheirlynck, E.; Chivulescu, M.; Lie, Ø.H.; Scheirlynck, E.; Chivulescu, M.; Øyvind, L.; Motoc, A.; Koulalis, J.; de Asmundis, C.; Sieira, J.; et al. Worse Prognosis in Brugada Syndrome Patients with Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy Features. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 1353–1363.
- Rabah, H.; Rabah, A. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia and Brugada Syndrome Overlap. Cureus 2021, 13, 13.
- Peters, S.; Trümmel, M.; Denecke, S.; Koehler, B. Results of ajmaline testing in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia-cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2004, 95, 207–210.
- Frustaci, A.; Priori, S.G.; Pieroni, M.; Chimenti, C.; Napolitano, C.; Rivolta, I.; Sanna, T.; Bellocci, F.; Russo, M.A. Cardiac histological substrate in patients with clinical phenotype of Brugada syndrome. Circulation 2005, 112, 3680–3687.
- Hoogendijk, M.G. Diagnostic Dilemmas: Overlapping Features of Brugada Syndrome and Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 144.
- Priori, S.G.; Napolitano, C.; Schwartz, P.J.; Bloise, R.; Crotti, L.; Ronchetti, E. The elusive link between LQT3 and brugada syndrome: The role of flecainide challenge. Circulation 2000, 102, 945–947.





