
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ksenia Serebrennikova | + 3620 word(s) | 3620 | 2021-12-23 08:43:30 | | | |
| 2 | Conner Chen | Meta information modification | 3620 | 2022-01-07 02:01:20 | | |
Video Upload Options
The effect of Raman scattering is a result of inelastic light scattering processes, which lead to the emission of scattered light with a different frequency associated with molecular vibrations of the identified molecule. Spontaneous Raman scattering is usually weak, resulting in complexities with the separation of weak inelastically scattered light and intense Rayleigh scattering. These limitations have led to the development of various techniques for enhancing Raman scattering, including resonance Raman spectroscopy (RRS) and nonlinear Raman spectroscopy (coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy and stimulated Raman spectroscopy). Furthermore, the discovery of the phenomenon of enhanced Raman scattering near metallic nanostructures gave impetus to the development of the surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) as well as its combination with resonance Raman spectroscopy and nonlinear Raman spectroscopic techniques. The combination of nonlinear and resonant optical effects with metal substrates or nanoparticles can be used to increase speed, spatial resolution, and signal amplification in Raman spectroscopy, making these techniques promising for the analysis and characterization of biological samples.
1. Recent Advances of Raman Spectroscopy in Biosensing
| Analyte | SERS Substrate/Receptor Molecule | Assay | SERS Nanotag | LOD | Sample | Features | Year, Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gp51 antigen of bovine leukemia virus | Magnetic gold nanoparticles (AuNPs)/the native (anti-gp51) and fragmented anti-gp51 antibody (Ab) | Homogenous SERS-based sandwich immunoassay | Gold nanorods modified with 5-thio-nitrobenzoic acid (DTNB) and specific anti-gp51 Ab | 0.95 μg/mL | Milk | Oriented and random Ab immobilization, application of two kinds of nanoparticles | 2013, [13] |
| Escherichia coli (E. coli) | Gold-coated magnetic spherical nanoparticles/polyclonal antibody (pAb) | Homogenous SERS-based sandwich immunoassay | Rod shaped AuNPs modified with DTNB, avidin, and biotin-labeled Ab | 8 cfu/mL | Real water samples | Two kinds of AuNPs | 2011, [14] |
| E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) | Magnetic beads (400 nm)/anti-E. coli2, anti-S. aureus2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) | Homogenous SERS-based sandwich immunoassay | Poly-l-lysine-coated triple-bond-coded AuNPs modified with 4-cyanobenzenethiol (MBN) | 10 and 25 cfu/mL | Bottled water and milk | Simultaneous detection with “hot spot” effect resulting in a significant enhancement of the Raman signal at 2105 and 2227 cm−1 | 2020, [15] |
| Human immunoglobulin (hIgG) | 100 nm thick gold film evaporated on microscope slide or silicon wafer/goat anti-human IgG Ab | SERS immunoassay of human immunoglobulin | 60 nm gold nanoparticles modified with 4-nitrobenzenethiol (4-NBT) and anti-human IgG Ab | 3 pM on silicon and 28 pM on gold | Standard solution | Comparison of Si wafer and tradition gold surface | 2020, [16] |
| Human IgG, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) | 2D arrays of Au (42 nm-core)@Ag (4.5 nm-shell) NPs on ITO substrate/polyclonal anti H-IgG, PSA mAb | Heterogenous SERS-based sandwich immunoassay | SH-PEG-COOH-coated AuNPs modified with 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (MBA) and anti H-IgG or PSA mAb | 0.3 pg/mL (10 fM) for PSA and 0.05 pg/mL (0.3 fM) for H-IgG | Standard solution | Comparison of the size of AuNPs in SERS nanotag (26, 53, 110 nm) | 2017, [17] |
| Escherichia coli (E. coli) | Spherical gold coated magnetic nanoparticles/pAb | Homogenous SERS-based sandwich immunoassay | Gold nanorods labeled with alkaline phosphatase (ALP) enzyme and also modified with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate (BCIP) and E. coli Ab |
10 cfu mL−1 | Standard solution | ALP activity; BCIP was hydrolyzed to SERS-active product; 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indole (BCI) | 2018, [3] |
| IgM and IgG to SARS-CoV-2 | No SERS substrate/mouse anti-human IgM and IgG capture Abs | SERS-based LFIA | Gap-enhanced Raman nanotags (GERTs) with 4-nitrobenzenethiol (4-NBT) between core and shell, modified with COVID-19 recombinant antigens (CN97) | 1 ng/mL (IgM), 0.1 ng/mL (IgG) | Standard solution | Simultaneous determination of IgM and IgG | 2021, [18] |
| IgM and IgG to SARS-CoV-2 | No SERS substrate/anti-human IgM and anti-human IgG Abs | SERS-based LFIA | Ag shell on SiO2 core (SiO2@Ag) 5,5-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) modified with dual layers of DTNB and SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein | 1.28 × 107-fold dilution by the IUPAC standard method, which is 800 times lower than that of the visualization results | Clinical serum samples (n = 68) | Simultaneous determination of IgM and IgG | 2021, [19] |
| Ferritin (FER) | Hydrophilic AgNPs onto the specific area of the hydrophobic polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)–hydrophilic/hydrophobic Ag/PDMS/anti-FER Ab | SERS-based LFIA | Raspberry-like AuNPs modified with 4-MBA and anti-FER Ab | 0.41 pg/mL | Standard solution | Combination of SERS substrate and SERS nanotag in LFIA format | 2020, [20] |
| Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) | Hydrophilic AgNPs with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)/anti-CEA Ab | SERS-based LFIA | Flower-shaped Ag nanoplates modified with crystal violet and anti-CEA Ab | 4.92 pg/mL | Standard solution | Combination of SERS substrate and SERS nanotag in LFIA format | 2021, [21] |
| α-Fetoprotein (AFP) | Few layers of MoS2 nanosheets exfoliated by NaK alloys/capture mAb | SERS-based sandwich immunoassay | Au@AgNCs and R6G–mAb complex | 0.03 pg/mL | Human blood serum samples | The sandwich immunocomplex “capture probe/target/SERS tag” was deposited on a silicon wafer and decorated with silver-coated gold nanocubes to increase the density of “hot spots” on the surface of the immunosensor | 2021, [22] |
| Human immunoglobulin (hIgG) | AuNP array (AuA)-coated solid substrate/rabbit anti-human IgG Ab | SERS-based sandwich immunoassay | AuNPs modified with 4-aminothiophenol (4-ATP) and rabbit anti-human IgG Ab | 0.1 μg mL−1 | Human serum samples | The combination of a SERS substrate based on AuNP array with SERS nanotag resulted in sensitive detection | 2021, [23] |
| Pancreatic cancer marker MUC4 | Immobilization of gold nanoflowers onto thiol-functionalized silicon wafer/Anti-MUC4 Ab | SERS-based sandwich immunoassay | Gold nanoflowers modified with 4-mercaptobenzoic acid and anti-MUC4 Ab | 0.1 ng mL−1 | Standard solution | Raman mapping was applied for a large substrate area to decrease a “spot-to-spot” variation of SERS signal | 2020, [24] |
| IgG/PSA | No SERS substrate/anti-rabbit IgG/anti-PSA Ab | Homogeneous enzyme-amplified SERS immunoassay | AuNP-assembled silica NPs (SiO2@Au-RLC@Ag) with Ag shell modified with 4-aminothiophenol (4-ATP) Polyclonal alkaline phosphatase (AP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG or AP-streptavidin-biotin-conjugated anti-PSA Ab were used as a tracer Ab to produce ascorbic acid for reduction of Ag+ to Ag |
0.09 ng/mL for IgG and 0.006 ng/mL for PSA | Human serum samples | Enzyme-induced Ag growth on the surface of SERS nanotag to produce the amplification of the SERS signal | 2020, [25] |
| Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) | Silver shell magnetic nanoparticles Fe3O4@Ag MNPs/anti-CEA monoclonal antibody | SERRS-based sandwich immunoassay | Silver-coated gold nanorods (Au@AgNRs) modified with diethylthiatricarbocyanineiodide (DTTC), coated with mPEG-SH and conjugated with anti-CEA antibodies | 4.75 fg/mL | Human serum samples | Au@AgNRs were in resonance with the resonant Raman dye DTTC at 785 nm excitation laser | 2016, [26] |
| Mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan (ManLAM) | Resonance Raman-enhanced adlayer of cyanine 5 on a smooth gold surface/polyclonal rabbit antibody for Mycobacterium tuberculosis | SERRS-based sandwich immunoassay | AuNPs modified with 5,5′-dithiobis (succinimidyl-2-nitrobenzoate; DSNB) and MAb to ManLAM | 1.1 ng/mL | Human serum samples | Cy5 modified gold substrates were characterized; the SERRS performance was compared with SERS and revealed a ≈9.3 gain in sensitivity of immunoassay | 2019, [27] |
2. Microfluidic SERS-Based Biosensors
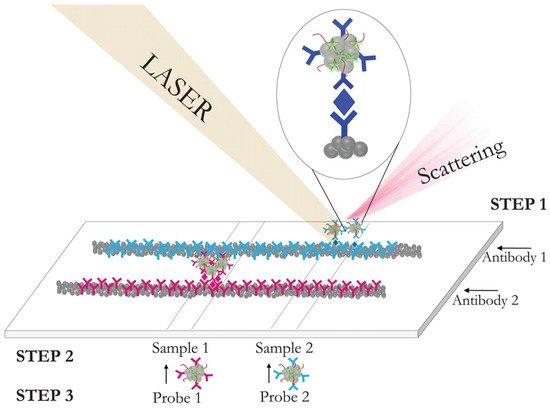
3. Integration of SERS with Different Methods
4. SERS-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay
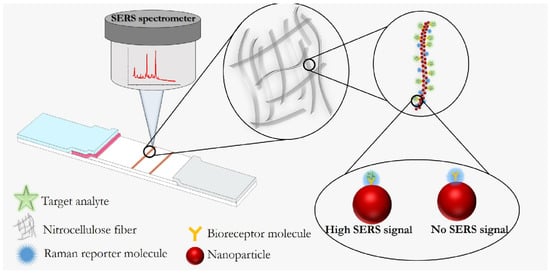
References
- Wang, Z.; Zong, S.; Wu, L.; Zhu, D.; Cui, Y. SERS-activated platforms for immunoassay: Probes, encoding methods, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7910–7963.
- Smolsky, J.; Kaur, S.; Hayashi, C.; Batra, S.K.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.V. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based immunoassay technologies for detection of disease biomarkers. Biosensors 2017, 7, 7.
- Bozkurt, A.G.; Buyukgoz, G.G.; Soforoglu, M.; Tamer, U.; Suludere, Z.; Boyaci, I.H. Alkaline phosphatase labeled SERS active sandwich immunoassay for detection of Escherichia coli. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 194, 8–13.
- Hwang, M.J.; Jang, A.S.; Lim, D.-K. Comparative study of fluorescence and surface-enhanced Raman scattering with magnetic microparticle-based assay for target bacterial DNA detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129134.
- Yu, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, W.; Ruan, W.; Zhao, B.; Cong, Q. A SERS-active enzymatic product used for the quantification of disease-related molecules. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2014, 45, 75–81.
- Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Yan, T.; Qian, W. Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of alkaline phosphatase. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9168–9172.
- Ingram, A.; Moore, B.D.; Graham, D. Simultaneous detection of alkaline phosphatase and beta-galactosidase activity using SERRS. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 1569–1571.
- Su, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Han, H.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Ratiometric surface enhanced raman scattering immunosorbent assay of allergenic proteins via covalent organic framework composite material based nanozyme tag triggered raman signal “turn-on” and amplification. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11687–11695.
- Neng, J.; Li, Y.; Driscoll, A.J.; Wilson, W.C.; Johnson, P.A. Detection of multiple pathogens in serum using silica-encapsulated nanotags in a surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based immunoassay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5707–5712.
- Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, M.; Petti, L.; Jiang, T.; Jia, Z.; Xie, S.; Zhou, J. SERS-based multiplex immunoassay of tumor markers using double SiO2@Ag immune probes and gold-film hemisphere array immune substrate. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 546, 48–58.
- Chen, R.; Liu, B.; Ni, H.; Chang, N.; Luan, C.; Ge, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhao, X. Vertical flow assays based on core–shell SERS nanotags for multiplex prostate cancer biomarker detection. Analyst 2019, 144, 4051–4059.
- Zhang, W.; Tang, S.; Jin, Y.; Yang, C.; He, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Multiplex SERS-based lateral flow immunosensor for the detection of major mycotoxins in maize utilizing dual Raman labels and triple test lines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122348.
- Baniukevic, J.; Boyaci, I.H.; Bozkurt, A.G.; Tamer, U.; Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. Magnetic gold nanoparticles in SERS-based sandwich immunoassay for antigen detection by well oriented antibodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 281–288.
- Guven, B.; Basaran-Akgul, N.; Temur, E.; Tamer, U.; Boyacı, İ.H. SERS-based sandwich immunoassay using antibody coated magnetic nanoparticles for Escherichia coli enumeration. Analyst 2011, 136, 740–748.
- Bai, X.; Shen, A.; Hu, J. A sensitive SERS-based sandwich immunoassay platform for simultaneous multiple detection of foodborne pathogens without interference. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 4885–4891.
- Kunushpayeva, Z.; Rapikov, A.; Akhmetova, A.; Sultangaziyev, A.; Dossym, D.; Bukasov, R. Sandwich SERS immunoassay of human immunoglobulin on silicon wafer compared to traditional SERS substrate, gold film. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 29, 100355.
- Karn-orachai, K.; Sakamoto, K.; Laocharoensuk, R.; Bamrungsap, S.; Dharakul, T.; Miki, K. SERS-based immunoassay on 2D-arrays of core–shell nanoparticles: Influence of the sizes of the SERS probe and sandwich immunocomplex on the sensitivity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14099–14106.
- Chen, S.; Meng, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Ali, S.; Chen, X.; Yu, M.; Yi, M.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; et al. SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive and simultaneous detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG antibodies by using gap-enhanced Raman nanotags. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130706.
- Liu, H.; Dai, E.; Xiao, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bai, Z.; Shao, Y.; Qi, K.; Tu, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Development of a SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay for rapid and ultra-sensitive detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in clinical samples. Sens Actuators B Chem 2021, 329, 129196.
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Gu, C.; Wei, G.; Jiang, T. Improved lateral flow strip based on hydrophilic–hydrophobic SERS substrate for ultra−sensitive and quantitative immunoassay. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 147121.
- Tang, S.; Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Chen, D.; Gu, C.; Wei, G.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, J. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow immunoassay mediated by hydrophilic-hydrophobic Ag-modified PMMA substrate. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 262, 120092.
- Er, E.; Sánchez-Iglesias, A.; Silvestri, A.; Arnaiz, B.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Prato, M.; Criado, A. Metal nanoparticles/MoS2 surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based sandwich immunoassay for α-fetoprotein detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 8823–8831.
- Qu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zeng, C.; Wang, M.; Qi, W.; He, Z. AuNP array coated substrate for sensitive and homogeneous SERS-immunoassay detection of human immunoglobulin G. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 22744–22750.
- Beyene, A.B.; Hwang, B.J.; Tegegne, W.A.; Wang, J.-S.; Tsai, H.-C.; Su, W.-N. Reliable and sensitive detection of pancreatic cancer marker by gold nanoflower-based SERS mapping immunoassay. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105099.
- Pham, X.-H.; Hahm, E.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, H.-M.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.C.; Kang, H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Jeong, D.H.; Choi, H.S.; et al. Enzyme-amplified SERS immunoassay with Ag-Au bimetallic SERS hot spots. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 3338–3346.
- Rong, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Magnetic immunoassay for cancer biomarker detection based on surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering from coupled plasmonic nanostructures. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 84, 15–21.
- Owens, N.A.; Pinter, A.; Porter, M.D. Surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering for the sensitive detection of a tuberculosis biomarker in human serum. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2019, 50, 15–25.
- Chen, Y.-T.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lai, Y.-H.; Lim, J.-C.; Huang, N.-T.; Lin, C.-T.; Huang, J.-J. Review of integrated optical biosensors for point-of-care applications. Biosensors 2020, 10, 209.
- Gao, R.; Lv, Z.; Mao, Y.; Yu, L.; Bi, X.; Xu, S.; Cui, J.; Wu, Y. SERS-Based Pump-Free Microfluidic Chip for Highly Sensitive Immunoassay of Prostate-Specific Antigen Biomarkers. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 938–943.
- Zhang, W.-S.; Wang, Y.-N.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.-R. Highly reproducible and fast detection of 6-thioguanine in human serum using a droplet-based microfluidic SERS system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 532–537.
- Kant, K.; Abalde-Cela, S. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy and microfluidics: Towards ultrasensitive label-free sensing. Biosensors 2018, 8, 62.
- Ackermann, K.R.; Henkel, T.; Popp, J. Quantitative online detection of low-concentrated drugs via a SERS microfluidic system. Chemphyschem 2007, 8, 2665–2670.
- Lee, D.; Lee, S.; Seong, G.H.; Choo, J.; Lee, E.K.; Gweon, D.G.; Lee, S. Quantitative analysis of methyl parathion pesticides in a polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic channel using confocal surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2006, 60, 373–377.
- Yazdi, S.H.; White, I.M. Multiplexed detection of aquaculture fungicides using a pump-free optofluidic SERS microsystem. Analyst 2013, 138, 100–103.
- Ahi, E.E.; Torul, H.; Zengin, A.; Sucularlı, F.; Yıldırım, E.; Selbes, Y.; Suludere, Z.; Tamer, U. A capillary driven microfluidic chip for SERS based hCG detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 195, 113660.
- Wang, L.; Zhou, G.; Guan, X.-l.; Zhao, L. Rapid preparation of surface-enhanced Raman substrate in microfluidic channel for trace detection of amoxicillin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 235, 118262.
- Chen, R.; Du, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ge, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhao, X. Vertical Flow Assay for Inflammatory Biomarkers Based on Nanofluidic Channel Array and SERS Nanotags. Small 2020, 16, 2002801.
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, L.; Li, L.; Zong, S.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Y. Simultaneous and highly sensitive detection of multiple breast cancer biomarkers in real samples using a SERS microfluidic chip. Talanta 2018, 188, 507–515.
- Gao, R.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, G.; Choo, J. Simultaneous immunoassays of dual prostate cancer markers using a SERS-based microdroplet channel. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 119, 126–133.
- Nie, Y.; Jin, C.; Zhang, J.X.J. Microfluidic In situ patterning of silver nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic sensing of biomolecules. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2584–2592.
- Wang, C.; Madiyar, F.; Yu, C.; Li, J. Detection of extremely low concentration waterborne pathogen using a multiplexing self-referencing SERS microfluidic biosensor. J. Biol. Eng. 2017, 11, 9.
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, J.; He, L. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) combined techniques for high-performance detection and characterization. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 1–13.
- Castaño-Guerrero, Y.; Moreira, F.T.; Sousa-Castillo, A.; Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Sales, M.G.F. SERS and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy immunoassay for carcinoembryonic antigen. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 366, 137377.
- Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Ji, X.; Wang, P.; Ding, C. SERS and fluorescence detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) with specific capture-release mode based on multifunctional gold nanomaterials and dual-selective recognition. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1141, 206–213.
- Lee, H.G.; Choi, W.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, S.-G.; Lee, M.-Y.; Jung, H.S. PCR-coupled paper-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) sensor for rapid and sensitive detection of respiratory bacterial DNA. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128802.
- Xu, Y.; Hassan, M.M.; Zhu, A.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Dual-Mode of Magnetic Assisted Ag SERS Tags and Cationic Conjugated UCNPs for qualitative and quantitative analysis of multiple foodborne pathogens. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130305.
- Kim, K.; Kashefi-Kheyrabadi, L.; Joung, Y.; Kim, K.; Dang, H.; Chavan, S.G.; Lee, M.-H.; Choo, J. Recent advances in sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow assay platforms for point-of-care diagnostics of infectious diseases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129214.
- Khlebtsov, B.; Khlebtsov, N. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral-flow immunoassay. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2228.
- Sánchez-Purrà, M.; Roig-Solvas, B.; Versiani, A.; Rodriguez-Quijada, C.; de Puig, H.; Bosch, I.; Gehrke, L.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Design of SERS nanotags for multiplexed lateral flow immunoassays. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2017, 2, 401–409.
- Lin, L.-K.; Stanciu, L. Bisphenol A detection using gold nanostars in a SERS improved lateral flow immunochromatographic assay. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 276, 222–229.
- Maneeprakorn, W.; Bamrungsap, S.; Apiwat, C.; Wiriyachaiporn, N. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering based lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for sensitive influenza detection. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 112079–112085.
- Khlebtsov, B.N.; Bratashov, D.N.; Byzova, N.A.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Khlebtsov, N.G. SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay of troponin I by using gap-enhanced Raman tags. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 413–420.




