
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ananya Gupta | + 4058 word(s) | 4058 | 2021-12-30 07:22:56 | | | |
| 2 | Vicky Zhou | Meta information modification | 4058 | 2021-12-31 01:52:52 | | |
Video Upload Options
Expression and functions of microRNAs (miRNAs) have been widely investigated in cancer treatment-induced complications and as a response to physical activity, respectively, but few studies focus on the application of miRNAs as biomarkers in exercise-based cancer rehabilitation. Research has shown that certain miRNA expression is altered substantially due to tissue damage caused by cancer treatment and chronic inflammation. MiRNAs are released from the damaged tissue and can be easily detected in blood plasma. Levels of the miRNA present in peripheral circulation can therefore be used to measure the extent of tissue damage. Moreover, damage to tissues such as cardiac and skeletal muscle significantly affects the individual’s health-related fitness, which can be determined using physiologic functional assessments. These physiologic parameters are a measure of tissue health and function and can therefore be correlated with the levels of circulating miRNAs.
1. Introduction to miRNAs
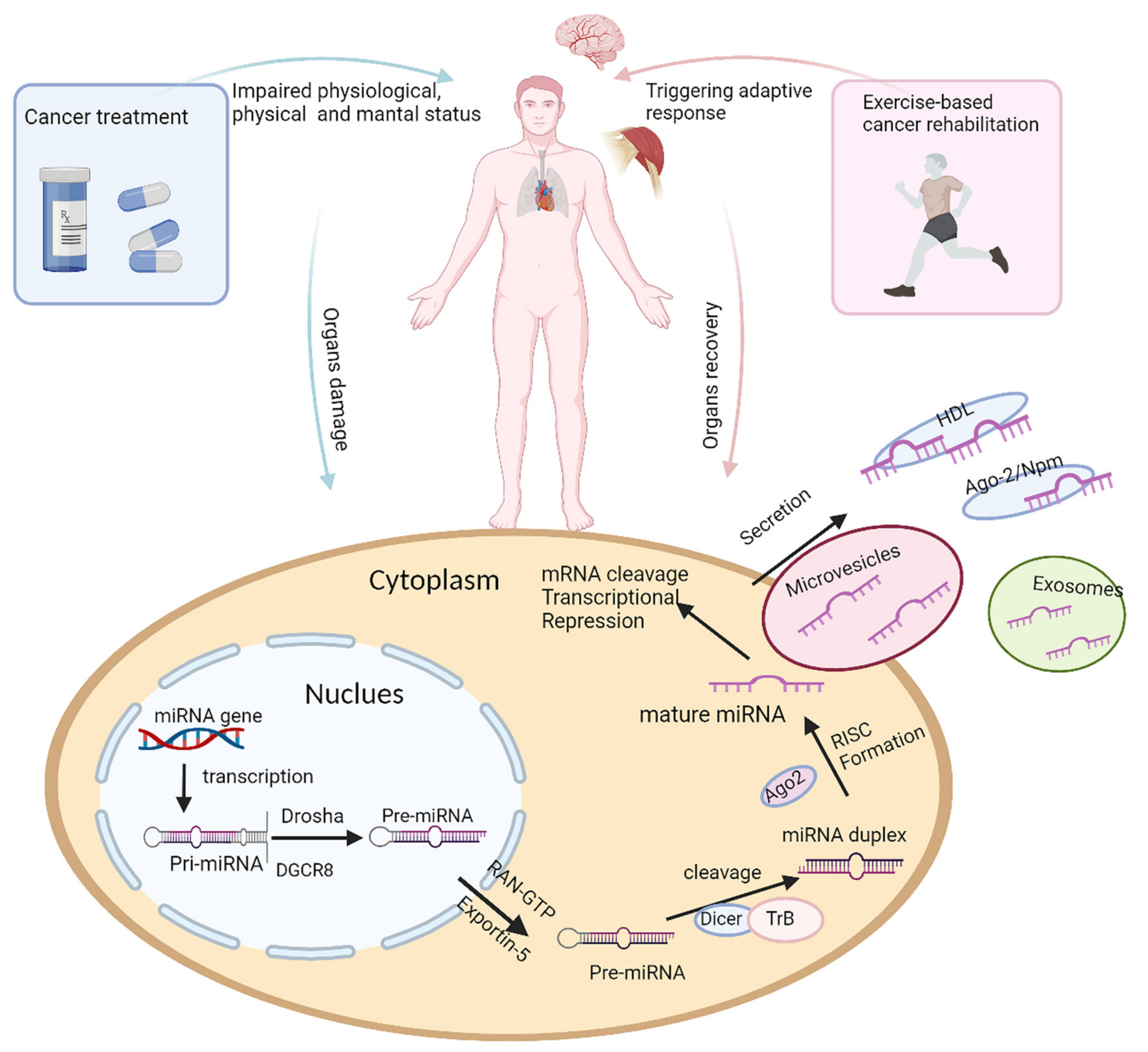
2. Potential miRNAs as Biomarkers in Exercise-Based Cancer Rehabilitation
2.1. Metabolic Syndrome
2.1.1. miR-126 and miR-146a
2.1.2. miR-9 and miR-375
2.1.3. Others
2.2. Cardiorespiratory Capacity
2.2.1. myomiRs
2.2.2. miR-126
2.2.3. miR-21 and miR-146a
2.2.4. miR-222
2.2.5. miR-155
2.2.6. Others
2.3. Cancer Cachexia
2.3.1. miR-21
2.3.2. miR-378
2.3.3. miR-1 and miR-133
2.4. Depression and Anxiety
2.4.1. let-7
2.4.2. miR-132 and miR-182
2.4.3. miR-134
2.4.4. miR-34b/c
2.4.5. Others
3. The Challenge of miRNAs as Biomarkers in Exercise-based Cancer Rehabilitation
References
- Santos, J.M.O.; Da Silva, S.P.; Da Costa, R.M.G.; Medeiros, R. The Emerging Role of MicroRNAs and Other Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer Cachexia. Cancers 2020, 12, 1004.
- Pellegrini, L.; Sileno, S.; D’Agostino, M.; Foglio, E.; Florio, M.C.; Guzzanti, V.; Russo, M.A.; Limana, F.; Magenta, A. MicroRNAs in Cancer Treatment-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Cancers 2020, 12, 704.
- Manna, I.; De Benedittis, S.; Quattrone, A.; Maisano, D.; Iaccino, E.; Quattrone, A. Exosomal miRNAs as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 243.
- Kulkarni, B.; Kirave, P.; Gondaliya, P.; Jash, K.; Jain, A.; Tekade, R.K.; Kalia, K. Exosomal miRNA in chemoresistance, immune evasion, metastasis and progression of cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 2058–2067.
- Gomes, J.L.P.; Fernandes, T.; Soci, U.P.R.; Silveira, A.C.; Barretti, D.L.M.; Negrão, C.E.; Oliveira, E.M. Obesity Downregulates MicroRNA-126 Inducing Capillary Rarefaction in Skeletal Muscle: Effects of Aerobic Exercise Training. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–9.
- Ghorbanzadeh, V.; Mohammadi, M.; Dariushnejad, H.; Abhari, A.; Chodari, L.; Mohaddes, G. Cardioprotective Effect of Crocin Combined with Voluntary Exercise in Rat: Role of Mir-126 and Mir-210 in Heart Angiogenesis. Arq. Bras. de Cardiol. 2017, 109, 54–62.
- Zhang, L.; Ouyang, P.; He, G.; Wang, X.; Song, D.; Yang, Y.; He, X. Exosomes from microRNA-126 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis by targeting the PIK3R2-mediated PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 2148–2162.
- Al-Muhtaresh, H.A.; Al-Kafaji, G. Evaluation of Two-Diabetes Related microRNAs Suitability as Earlier Blood Biomarkers for Detecting Prediabetes and type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 12.
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, S.-H.; Zhang, L.; Cai, J.-H. Peripheral blood miRNAs as a biomarker for chronic cardiovascular diseases. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5026.
- Rigaud, V.; Ferreira, L.R.; Ayub-Ferreira, S.M.; Ávila, M.S.; Brandão, S.M.; Cruz, F.D.; Santos, M.; Cruz, C.B.; Alves, M.S.; Issa, V.S.; et al. Circulating miR-1 as a potential biomarker of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 6994–7002.
- Fathi, M.; Gharakhanlou, R.; Rezaei, R. The Changes of Heart miR-1 and miR-133 Expressions following Physiological Hypertrophy Due to Endurance Training. Cell J. 2020, 22 (Suppl. 1), 133–140.
- Mooren, F.C.; Viereck, J.; Krüger, K.; Thum, T. Circulating micrornas as potential biomarkers of aerobic exercise capacity. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2014, 306, H557–H563.
- Nielsen, S.; Scheele, C.; Yfanti, C.; Åkerström, T.; Nielsen, A.R.; Pedersen, B.K.; Laye, M. Muscle specific microRNAs are regulated by endurance exercise in human skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 4029–4037.
- Wardle, S.L.; Bailey, M.E.S.; Kilikevicius, A.; Malkova, D.; Wilson, R.H.; Venckunas, T.; Moran, C.N. Plasma MicroRNA Levels Differ between Endurance and Strength Athletes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122107.
- Tony, H.; Yu, K.; Qiutang, Z. MicroRNA-208a Silencing Attenuates Doxorubicin Induced Myocyte Apoptosis and Cardiac Dysfunction. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 1–6.
- Song, W.; Liang, Q.; Cai, M.; Tian, Z. HIF-1α-induced up-regulation of microRNA-126 contributes to the effectiveness of exercise training on myocardial angiogenesis in myocardial infarction rats. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12970–12979.
- Riedel, S.; Radzanowski, S.; Bowen, T.S.; Werner, S.; Erbs, S.; Schuler, G.; Adams, V. Exercise training improves high-density lipoprotein-mediated transcription of proangiogenic microRNA in endothelial cells. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2015, 22, 899–903.
- Dai, B.; Li, H.; Fan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, Z.; Nie, X.; Wang, D.W.; Chen, C. MiR-21 protected against diabetic cardiomyopathy induced diastolic dysfunction by targeting gelsolin. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 123.
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, M.; Wang, J.; Cui, X.; Song, Y.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ge, J. Qiliqiangxin Prescription Promotes Angiogenesis of Hypoxic Primary Rat Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells via Regulating miR-21 Signaling. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 2966–2974.
- He, J.; Lu, Y.; Song, X.; Gong, X.; Li, Y. Inhibition of microRNA-146a attenuated heart failure in myocardial infarction rats. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20191732.
- Li, Y.; Yao, M.; Zhou, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Che, L.; Xu, J.; Xiao, J.; Shen, Z.; Bei, Y. Dynamic Regulation of Circulating microRNAs During Acute Exercise and Long-Term Exercise Training in Basketball Athletes. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 282.
- Baggish, A.L.; Hale, A.; Weiner, R.B.; Lewis, G.D.; Systrom, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, T.; Chan, S.Y. Dynamic regulation of circulating microRNA during acute exhaustive exercise and sustained aerobic exercise training. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 3983–3994.
- Bye, A.; Røsjø, H.; Aspenes, S.T.; Condorelli, G.; Omland, T.; Wisløff, U. Circulating MicroRNAs and Aerobic Fitness—The HUNT-Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57496.
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, L.; Xu, S.; Lin, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, F.; et al. Serum miR-222-3p as a Double-Edged Sword in Predicting Efficacy and Trastuzumab-Induced Cardiotoxicity for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Target Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 631.
- Schmitz, B.; Rolfes, F.; Schelleckes, K.; Mewes, M.; Thorwesten, L.; Krüger, M.; Klose, A.; Brand, S.-M. Longer Work/Rest Intervals During High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) Lead to Elevated Levels of miR-222 and miR-29c. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 395.
- Liu, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, H.; Wei, X.; Platt, C.; Damilano, F.; Xiao, C.; Bezzerides, V.; Boström, P.; Che, L.; et al. miR-222 Is Necessary for Exercise-Induced Cardiac Growth and Protects against Pathological Cardiac Remodeling. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 584–595.
- Le Sage, C.; Nagel, R.; Egan, D.A.; Schrier, M.; Mesman, E.; Mangiola, A.; Anile, C.; Maira, G.; Mercatelli, N.; Ciafrè, S.A.; et al. Regulation of the p27Kip1 tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3699–3708.
- Eissa, M.G.; Artlett, C.M. The MicroRNA miR-155 Is Essential in Fibrosis. Non-Coding RNA 2019, 5, 23.
- Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Yan, Z.; Liang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Bai, C.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, P.-K. MiRNA-155–5p inhibits epithelium-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by targeting GSK-3β during radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 697, 108699.
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Hasoo, M.K.; Welsh, D.J.; Stewart, L.; McIntyre, D.; Morton, B.E.; Johnstone, S.; Miller, A.M.; Asquith, D.L.; Millar, N.L.; et al. The role of microRNA-155/liver X receptor pathway in experimental and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1946–1956.
- Paula, S.M.; Fernandes, T.; Couto, G.K.; Jordão, M.T.; Oliveira, E.M.; Michelini, L.C.; Rossoni, L.V. Molecular Pathways Involved in Aerobic Exercise Training Enhance Vascular Relaxation. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 2117–2126.
- Barber, J.L.; Zellars, K.N.; Barringhaus, K.G.; Bouchard, C.; Spinale, F.G.; Sarzynski, M.A. The Effects of Regular Exercise on Circulating Cardiovascular-related MicroRNAs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7527.
- Pereira, J.D.; Tosatti, J.A.G.; Simões, R.; Luizon, M.; Gomes, K.B.; Alves, M.T. microRNAs associated to anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and pathway analysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110709.
- Fu, J.; Peng, C.; Wang, W.; Jin, H.; Tang, Q.; Wei, X. Let-7g is involved in doxorubicin induced myocardial injury. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 33, 312–317.
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, B.; Zheng, T.; Wei, M.; Sun, Y. MicroRNA-20a participates in the aerobic exercise-based prevention of coronary artery disease by targeting PTEN. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 756–763.
- Soares, R.J.R.; Cagnin, S.; Chemello, F.; Silvestrin, M.; Musaro, A.; De Pitta, C.; Lanfranchi, G.; Sandri, M. Involvement of MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Muscle Wasting during Catabolic Conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 21909–21925.
- He, W.A.; Calore, F.; Londhe, P.; Canella, A.; Guttridge, D.C.; Croce, C.M. Microvesicles containing miRNAs promote muscle cell death in cancer cachexia via TLR7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4525–4529.
- Okugawa, Y.; Yao, L.; Toiyama, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Shigemori, T.; Yin, C.; Omura, Y.; Ide, S.; Kitajima, T.; Shimura, T.; et al. Prognostic impact of sarcopenia and its correlation with circulating miR-21 in colorectal cancer patients. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1555–1564.
- Borja-Gonzalez, M.; Casas-Martinez, J.C.; McDonagh, B.; Goljanek-Whysall, K. Inflamma-miR-21 Negatively Regulates Myogenesis during Ageing. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 345.
- Davidsen, P.K.; Gallagher, I.; Hartman, J.W.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Dela, F.; Helge, J.; Timmons, J.A.; Phillips, S. High responders to resistance exercise training demonstrate differential regulation of skeletal muscle microRNA expression. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 110, 309–317.
- Kulyté, A.; Lorente-Cebrián, S.; Gao, H.; Mejhert, N.; Agustsson, T.; Arner, P.; Rydén, M.; Dahlman, I. MicroRNA profiling links miR-378 to enhanced adipocyte lipolysis in human cancer cachexia. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2014, 306, 267–274.
- Chen, J.-F.; Mandel, E.M.; Thomson, J.M.; Wu, Q.; E Callis, T.; Hammond, S.M.; Conlon, F.L.; Wang, D.-Z. The Role of MicroRNA-1 and MicroRNA-133 in Skeletal Muscle Proliferation and Differentiation. Nat. Genet. 2005, 38, 228–233.
- Huang, M.; Xu, H.; Xie, S.-J.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Is Regulated by microRNA-133 during Skeletal Myogenesis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29173.
- Drummond, M.J.; McCarthy, J.J.; Fry, C.S.; Esser, K.A.; Rasmussen, B.B. Aging differentially affects human skeletal muscle microRNA expression at rest and after an anabolic stimulus of resistance exercise and essential amino acids. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E1333–E1340.
- Nie, Y.; Sato, Y.; Wang, C.; Yue, F.; Kuang, S.; Gavin, T.P. Impaired exercise tolerance, mitochondrial biogenesis, and muscle fiber maintenance in miR-133a–deficient mice. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 3745–3758.
- Bocchio-Chiavetto, L.; Maffioletti, E.; Bettinsoli, P.; Giovannini, C.; Bignotti, S.; Tardito, D.; Corrada, D.; Milanesi, L.; Gennarelli, M. Blood microRNA changes in depressed patients during antidepressant treatment. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 602–611.
- Wei, Y.B.; Liu, J.J.; Villaescusa, J.C.; Åberg, E.; Brené, S.; Wegener, G.; A Mathé, A.; Lavebratt, C. Elevation of Il6 is associated with disturbed let-7 biogenesis in a genetic model of depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e869.
- Gururajan, A.; Naughton, M.E.; Scott, K.A.; O’Connor, R.M.; Moloney, G.; Clarke, G.; Dowling, J.; Walsh, A.; Ismail, F.; Shorten, G.; et al. MicroRNAs as biomarkers for major depression: A role for let-7b and let-7c. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e862.
- Hung, Y.-Y.; Wu, M.-K.; Tsai, M.-C.; Huang, Y.-L.; Kang, H.-Y. Aberrant Expression of Intracellular let-7e, miR-146a, and miR-155 Correlates with Severity of Depression in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder and Is Ameliorated after Antidepressant Treatment. Cells 2019, 8, 647.
- Li, Y.-J.; Xu, M.; Gao, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Yue, Z.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Li, X.-X.; Zhang, C.; Xie, S.-Y.; Wang, P.-Y. Alterations of Serum Levels of BDNF-Related miRNAs in Patients with Depression. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63648.
- Tong, L.; Li, M.-D.; Nie, P.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.-L.; Ji, L.-L. miR-132 downregulation alleviates behavioral impairment of rats exposed to single prolonged stress, reduces the level of apoptosis in PFC, and upregulates the expression of MeCP2 and BDNF. Neurobiol. Stress 2021, 14, 100311.
- Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Qu, C.; Xu, L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J. The enriched environment ameliorates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors and cognitive impairment by activating the SIRT1/miR-134 signaling pathway in hippocampus. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 248, 81–90.
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Tian, J.; Meng, Z.; Ju, M.; Wu, G.; Tian, Z. miR-34b attenuates trauma-induced anxiety-like behavior by targeting CRHR1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 90–100.
- Sun, N.; Yang, C.; He, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, R.; Zhang, K. Impact of Expression and Genetic Variation of microRNA-34b/c on Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1543–1554.
- Liu, W.; Xue, X.; Xia, J.; Liu, J.; Qi, Z. Swimming exercise reverses CUMS-induced changes in depression-like behaviors and hippocampal plasticity-related proteins. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 227, 126–135.
- Ramzan, F.; D’Souza, R.F.; Durainayagam, B.R.; Milan, A.M.; Markworth, J.F.; Miranda-Soberanis, V.; Sequeira, I.R.; Roy, N.C.; Poppitt, S.D.; Mitchell, C.J.; et al. Circulatory miRNA biomarkers of metabolic syndrome. Acta Diabetol. 2020, 57, 203–214.




