
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Antoine Balzeau | + 3127 word(s) | 3127 | 2021-10-26 10:10:08 | | | |
| 2 | Catherine Yang | -7 word(s) | 3120 | 2021-11-09 02:04:22 | | |
Video Upload Options
Advances in neuroscience have made it possible to obtain increasing information on the anatomy of the brain, at ever-higher resolutions, with different imaging techniques, on ever-larger samples. At the same time, paleoanthropology has to deal with partial reflections on the shape of the brain, on fragmentary specimens and small samples in an attempt to approach the morphology of the brain of past human species. Paleoanthropology has much to gain from interacting more with the field of neuroimaging. Improving our understanding of the morphology of the endocast necessarily involves studying the external surface of the brain and the link it maintains with the internal surface of the skull. The contribution of neuroimaging will allow us to better define the relationship between brain and endocast. Models of intra- and inter-species variability in brain morphology inferred from large neuroimaging databases will help make the most of the rare endocasts of extinct species. Moreover, exchanges between these two disciplines will also be beneficial to our knowledge of the Homo sapiens brain. Documenting the anatomy among other human species and including the variation over time within our own species are approaches that offer us a new perspective through which to appreciate what really characterizes the brain of humanity today.
1. Does the Endocast Reflects the Brain?
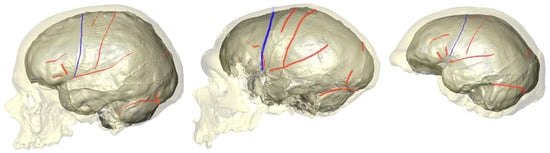
2. What Can Be Deduced about a Species’ Folding Pattern from a Few Samples?
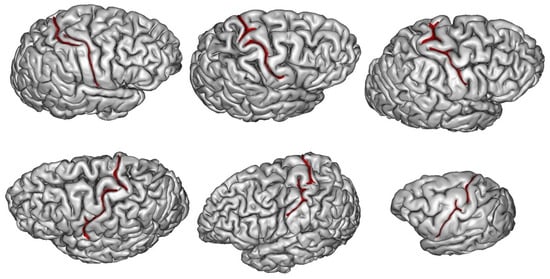
3. How Are Brain Asymmetries Quantified in the Hominin Fossil Record?
4. The Complex Definition of Brain Features and of Their Application to the Fossil Record
5. How to Grow a Hominin Brain?
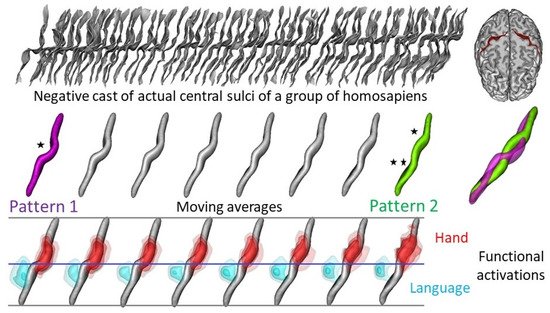
6. Brain Endocast and Function
References
- Jean Dumoncel; Gérard Subsol; Stanley Durrleman; Anne Bertrand; Edwin de Jager; Anna C. Oettlé; Zarina Lockhat; Farhana E. Suleman; Amélie Beaudet; Are endocasts reliable proxies for brains? A 3D quantitative comparison of the extant human brain and endocast. Journal of Anatomy 2020, 238, 480-488, 10.1111/joa.13318.
- Marc Fournier; Benoît Combès; Neil Roberts; José Braga; Sylvain Prima; Mapping the distance between the brain and the inner surface of the skull and their global asymmetries. Medical Imaging 2011: Image Processing 2011, 79620Y, 79620Y-79620Y-7, 10.1117/12.876795.
- Edwin J. De Jager; Albert N. Van Schoor; Jakobus W. Hoffman; Anna C. Oettlé; Caroline Fonta; Muriel Mescam; Laurent Risser; Amélie Beaudet; Sulcal pattern variation in extant human endocasts. Journal of Anatomy 2019, 235, 803-810, 10.1111/joa.13030.
- Holloway Ralph L., Broadfield Douglas C., Yuan Michael S.. The Human Fossil Record; Holloway Ralph L., Broadfield Douglas C., Yuan Michael S., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: london, 2005; pp. 315.
- Emiliano Bruner; Dominique Grimaud-Hervé; Xiujie Wu; José Manuel de la Cuétara; Ralph Holloway; A paleoneurological survey of Homo erectus endocranial metrics. Quaternary International 2015, 368, 80-87, 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.10.007.
- Simon Neubauer; Jean-Jacques Hublin; Philipp Gunz; The evolution of modern human brain shape. Science Advances 2018, 4, eaao5961, 10.1126/sciadv.aao5961.
- Simon Neubauer; Philipp Gunz; Nadia A. Scott; Jean-Jacques Hublin; Philipp Mitteroecker; Evolution of brain lateralization: A shared hominid pattern of endocranial asymmetry is much more variable in humans than in great apes. Science Advances 2020, 6, eaax9935, 10.1126/sciadv.aax9935.
- Dean Falk; Christoph P.E. Zollikofer; Marcia Ponce De León; Katerina Semendeferi; José Luis Alatorre Warren; William D. Hopkins; Identification of in vivo Sulci on the External Surface of Eight Adult Chimpanzee Brains: Implications for Interpreting Early Hominin Endocasts. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 2018, 91, 45-58, 10.1159/000487248.
- José Luis Alatorre Warren; Marcia S. Ponce de León; William D. Hopkins; Christoph P. E. Zollikofer; Evidence for independent brain and neurocranial reorganization during hominin evolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2019, 116, 22115-22121, 10.1073/pnas.1905071116.
- Dean Efalk; Interpreting sulci on hominin endocasts: old hypotheses and new findings. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 2014, 8, 134, 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00134.
- Jean-François Mangin, Guillaume Auzias, Olivier Coulon, Zhong Sun, Denis Rivière, et al.. Sulci as Landmarks. Toga, Arthur W. Brain Mapping: an Encyclopedic Reference, pp."45 - 52",, 2015
- Jean-François Mangin; Yann Le Guen; Nicole Labra; Antoine Grigis; Vincent Frouin; Miguel Guevara; Clara Fischer; Denis Rivière; William D. Hopkins; Jean Régis; et al.Zhong Yi Sun “Plis de passage” Deserve a Role in Models of the Cortical Folding Process. Brain Topography 2019, 32, 1035-1048, 10.1007/s10548-019-00734-8.
- Cristina Llinares-Benadero; Víctor Borrell; Deconstructing cortical folding: genetic, cellular and mechanical determinants. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2019, 20, 161-176, 10.1038/s41583-018-0112-2.
- Tuomas Tallinen; Jun Young Chung; François Rousseau; Nadine Girard; Julien Lefèvre; Jun Young Chung L. Mahadevan; On the growth and form of cortical convolutions. Nature Physics 2016, 12, 588-593, 10.1038/nphys3632.
- David C. Van Essen; A tension-based theory of morphogenesis and compact wiring in the central nervous system. Nature 1997, 385, 313-318, 10.1038/385313a0.
- J.-F. Mangin; J. Lebenberg; S. Lefranc; N. Labra; G. Auzias; M. Labit; M. Guevara; H. Mohlberg; P. Roca; J. Dubois; et al.F. LeroyG. Dehaene-LambertzA. CachiaT. DickscheidO. CoulonC. PouponD. RivièreK. AmuntsZ.Y. Sun Spatial normalization of brain images and beyond. Medical Image Analysis 2016, 33, 127-133, 10.1016/j.media.2016.06.008.
- Cachia, A.; et al; Towards Deciphering the Fetal Foundation of Normal Cognition and Cognitive Symptoms From Sulcation of the Cortex . Front. Neuroanat. 2021, 15, 68, 10.3389/fnana.2021.712862 .
- Z. Y. Sun; P. Pinel; D. Rivière; A. Moreno; S. Dehaene; J.-F. Mangin; Linking morphological and functional variability in hand movement and silent reading. Brain Structure and Function 2015, 221, 3361-3371, 10.1007/s00429-015-1106-8.
- Palmer, A.R.; Strobeck, C. Fluctuating asymmetry analyses revisited. In Developmental Instability: Causes and Consequences; Polak, M., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 279–319.
- Aida Gómez-Robles; William D. Hopkins; Chet C. Sherwood; Increased morphological asymmetry, evolvability and plasticity in human brain evolution. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 2013, 280, 20130575, 10.1098/rspb.2013.0575.
- Timothy D. Weaver; Philipp Gunz; Using geometric morphometric visualizations of directional selection gradients to investigate morphological differentiation. Evolution 2018, 72, 838-850, 10.1111/evo.13460.
- Philipp Mitteroecker; Philipp Gunz; Advances in Geometric Morphometrics. Evolutionary Biology 2009, 36, 235-247, 10.1007/s11692-009-9055-x.
- Richtsmeier, J.T.; Cole, T.M.; Lele, S.R. An invariant approach to the study of fluctuating asymmetry: Developmental instability in a mouse model for Down syndrome. In Modern Morphometrics in Physical Anthropology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 187–212.
- J. T. Kent; Shape, Procrustes tangent projections and bilateral symmetry. Biometrika 2001, 88, 469-485, 10.1093/biomet/88.2.469.
- Christian Peter Klingenberg; Grant S. McIntyre; GEOMETRIC MORPHOMETRICS OF DEVELOPMENTAL INSTABILITY: ANALYZING PATTERNS OF FLUCTUATING ASYMMETRY WITH PROCRUSTES METHODS. Evolution 1998, 52, 1363-1375, 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1998.tb02018.x.
- Christian Peter Klingenberg; Marta Barluenga; Axel Meyer; SHAPE ANALYSIS OF SYMMETRIC STRUCTURES: QUANTIFYING VARIATION AMONG INDIVIDUALS AND ASYMMETRY. Evolution 2002, 56, 1909-1920, 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2002.tb00117.x.
- K. Mardia; Fl Bookstein; Ij Moreton; Statistical assessment of bilateral symmetry of shapes. Biometrika 2000, 87, 285-300, 10.1093/biomet/87.2.285.
- Combès, B.; Hennessy, R.; Waddington, J.L.; Roberts, N.; Prima, S. Automatic symmetry plane estimation of bilateral objects in point clouds. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-CVPR’2008, Anchorage, AK, USA, 24–26 June 200
- Combès, B.; Fournier, M.; Kennedy, D.N.; Braga, J.; Roberts, N.; Prima, S. EM-ICP strategies for joint mean shape and correspondences estimation: Applications to statistical analysis of shape and of asymmetry. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro (ISBI’2011), Chicago, IL, USA, 30 March–2 April 2011; pp. 1257–1263.
- Emam ElHak Abdel Fatah; Natalie R. Shirley; Mohamed R. Mahfouz; Benjamin M. Auerbach; A three-dimensional analysis of bilateral directional asymmetry in the human clavicle. American Journal of Physical Anthropology 2012, 149, 547-559, 10.1002/ajpa.22156.
- Antoine Balzeau; Emmanuel Gilissen; Endocranial shape asymmetries in Pan paniscus, Pan troglodytes and Gorilla gorilla assessed via skull based landmark analysis. Journal of Human Evolution 2010, 59, 54-69, 10.1016/j.jhevol.2010.03.013.
- A. Balzeau; D. Grimaud-Hervé; F. Détroit; R. L. Holloway; B. Combès; S. Prima; First description of the Cro-Magnon 1 endocast and study of brain variation and evolution in anatomically modern Homo sapiens. Bulletins et mémoires de la société d'anthropologie de Paris 2012, 25, 1-18, 10.1007/s13219-012-0069-z.
- Zhong Yi Sun; Stefan Klöppel; Denis Rivière; Matthieu Perrot; Richard Frackowiak; Hartwig Siebner; Jean-François Mangin; The effect of handedness on the shape of the central sulcus. NeuroImage 2011, 60, 332-339, 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.12.050.
- Trisanna Sprung-Much; Nicole Eichert; Erika Nolan; Michael Petrides; Broca’s area and the search for anatomical asymmetry: commentary and perspectives. Brain Structure and Function 2021, 2021, 1-9, 10.1007/s00429-021-02357-x.
- Marjorie Lemay; MORPHOLOGICAL CEREBRAL ASYMMETRIES OF MODERN MAN, FOSSIL MAN, AND NONHUMAN PRIMATE. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1976, 280, 349-366, 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb25499.x.
- Marjorie LeMay; Asymmetries of the skull and handedness: Phrenology revisited. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1977, 32, 243-253, 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90239-8.
- Ralph L. Holloway; Marie Christine De La Costelareymondie; Brain endocast asymmetry in pongids and hominids: Some preliminary findings on the paleontology of cerebral dominance. American Journal of Physical Anthropology 1982, 58, 101-110, 10.1002/ajpa.1330580111.
- William D Hopkins; Lori Marino; Asymmetries in cerebral width in nonhuman primate brains as revealed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Neuropsychologia 2000, 38, 493-499, 10.1016/s0028-3932(99)00090-1.
- Dawn L. Pilcher; Elizabeth A. D. Hammock; William D. Hopkins; Cerebral volumetric asymmetries in non-human primates: A magnetic resonance imaging study. Laterality: Asymmetries of Body, Brain and Cognition 2001, 6, 165-179, 10.1080/713754406.
- William D. Hopkins; Jared P. Taglialatela; Adrien Meguerditchian; Talia Nir; Natalie M. Schenker; Chet C. Sherwood; Gray matter asymmetries in chimpanzees as revealed by voxel-based morphometry. NeuroImage 2008, 42, 491-497, 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.05.014.
- Ralph L. Holloway; Volumetric and asymmetry determinations on recent hominid endocasts: Spy I and II, Djebel Ihroud I, and the salèHomo erectus specimens, with some notes on neandertal brain size. American Journal of Physical Anthropology 1981, 55, 385-393, 10.1002/ajpa.1330550312.
- LeMay, M.; Billig, M.S.; Geschwind, N. Asymmetries of the brains and skulls of nonhuman primates. In Primate Brain Evolution, Methods and Concepts; Falk, D., Armstrong, E., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 263–277.
- Albert M. Galaburda; Marjorie LeMay; Thomas L. Kemper; Norman Geschwind; Right-Left Asymmetries in the Brain. Science 1978, 199, 852-856, 10.1126/science.341314.
- Dean Falk; Charles Hildebolt; James Cheverud; Michael Vannier; R. Criss Helmkamp; Lyle Konigsberg; Cortical asymmetries in frontal lobes of Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Brain Research 1990, 512, 40-45, 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91167-f.
- Antoine Balzeau; Emmanuel Gilissen; Dominique Grimaud-Hervé; Shared Pattern of Endocranial Shape Asymmetries among Great Apes, Anatomically Modern Humans, and Fossil Hominins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29581, 10.1371/journal.pone.0029581.
- LeMay, M. Asymmetries of the brains and skulls of nonhuman primates. In Cerebral Lateralization in Nonhuman Species; Glick, S.D., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 233–245.
- Donald P. Cain; Juhn A. Wada; An Anatomical Asymmetry in the Baboon Brain. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 1979, 16, 222-226, 10.1159/000121838.
- James M. Cheverud; Dean Falk; Charles Hildebolt; Allen J. Moore; R. Criss Helmkamp; Michael Vannier; Heritability and Association of Cortical Petalias in Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta). Brain, Behavior and Evolution 1990, 35, 368-372, 10.1159/000115881.
- Phillip V. Tobias; The brain of Homo habilis: A new level of organization in cerebral evolution. Journal of Human Evolution 1987, 16, 741-761, 10.1016/0047-2484(87)90022-4.
- William D. Hopkins; Kimberley Phillips; Amanda Bania; Sarah E. Calcutt; Molly Gardner; Jamie Russell; Jennifer Schaeffer; Elizabeth V. Lonsdorf; Stephen R. Ross; Steven J. Schapiro; et al. Hand preferences for coordinated bimanual actions in 777 great apes: Implications for the evolution of handedness in Hominins. Journal of Human Evolution 2011, 60, 605-611, 10.1016/j.jhevol.2010.12.008.
- Stephanie L. Bogart; Jean-François Mangin; Steven J. Schapiro; Lisa Reamer; Allyson J. Bennett; Peter J. Pierre; William D. Hopkins; Cortical sulci asymmetries in chimpanzees and macaques: A new look at an old idea. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 533-541, 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.082.
- Michael C. Corballis; Gjurgjica Badzakova-Trajkov; Isabelle S. Häberling; Right hand, left brain: genetic and evolutionary bases of cerebral asymmetries for language and manual action. WIREs Cognitive Science 2011, 3, 1-17, 10.1002/wcs.158.
- Li Xiang; Timothy Crow; Neil Roberts; Cerebral torque is human specific and unrelated to brain size. Brain Structure and Function 2019, 224, 1141-1150, 10.1007/s00429-018-01818-0.
- Antoine Balzeau; Emmanuel Gilissen; Ralph L. Holloway; Sylvain Prima; Dominique Grimaud-Hervé; Variations in size, shape and asymmetries of the third frontal convolution in hominids: Paleoneurological implications for hominin evolution and the origin of language. Journal of Human Evolution 2014, 76, 116-128, 10.1016/j.jhevol.2014.06.006.
- Simon S. Keller; Timothy Crow; Anne Foundas; Katrin Amunts; Neil Roberts; Broca’s area: Nomenclature, anatomy, typology and asymmetry. Brain and Language 2009, 109, 29-48, 10.1016/j.bandl.2008.11.005.
- Antoine Balzeau; Dominique Grimaud-Hervé; Teuku Jacob; Internal cranial features of the Mojokerto child fossil (East Java, Indonesia). Journal of Human Evolution 2005, 48, 535-553, 10.1016/j.jhevol.2005.01.002.
- Philipp Gunz; Simon Neubauer; Lubov Golovanova; Vladimir Doronichev; Bruno Maureille; Jean-Jacques Hublin; A uniquely modern human pattern of endocranial development. Insights from a new cranial reconstruction of the Neandertal newborn from Mezmaiskaya. Journal of Human Evolution 2012, 62, 300-313, 10.1016/j.jhevol.2011.11.013.
- Philipp Gunz; Simon Neubauer; Bruno Maureille; Jean-Jacques Hublin; Brain development after birth differs between Neanderthals and modern humans. Current Biology 2010, 20, R921-R922, 10.1016/j.cub.2010.10.018.
- Simon Neubauer; Philipp Gunz; Jean-Jacques Hublin; Endocranial shape changes during growth in chimpanzees and humans: A morphometric analysis of unique and shared aspects. Journal of Human Evolution 2010, 59, 555-566, 10.1016/j.jhevol.2010.06.011.
- Marcia S. Ponce de León; Thibaut Bienvenu; Takeru Akazawa; Christoph P.E. Zollikofer; Brain development is similar in Neanderthals and modern humans. Current Biology 2016, 26, R665-R666, 10.1016/j.cub.2016.06.022.
- Antoine Balzeau; Ralph L. Holloway; Dominique Grimaud-Hervé; Variations and asymmetries in regional brain surface in the genus Homo. Journal of Human Evolution 2012, 62, 696-706, 10.1016/j.jhevol.2012.03.007.
- Coulon, O.; Sein, J.; Auzias, G.; Nazarian, B.; Anton, J.L.; Rousseau, F.; Velly, L.; Girard, N. High temporal resolution longitudinal observation of fetal brain development. A baboon pilot study. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping, Montreal, QC, Canada, 23 June–3 July 2020.
- Eiluned Pearce; Chris Stringer; R. I. M. Dunbar; New insights into differences in brain organization between Neanderthals and anatomically modern humans. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 2013, 280, 20130168, 10.1098/rspb.2013.0168.




