
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amanuel Gebisa Aga | + 2187 word(s) | 2187 | 2021-11-08 07:50:35 | | | |
| 2 | Nora Tang | Meta information modification | 2187 | 2021-11-08 09:46:21 | | | | |
| 3 | Nora Tang | Meta information modification | 2187 | 2021-11-12 06:55:32 | | |
Video Upload Options
Standard driving cycles (DCs) and real driving emissions (RDE) legislation developed by the European Commission contains significant gaps with regard to quantifying local area vehicle emission levels and fuel consumption (FC). The aim of this paper was to review local DCs for estimating emission levels and FC under laboratory and real-world conditions. This review article has three sections.
1. Introduction
Exhaust emissions from vehicles present a serious risk in urban areas, affecting air quality and human health [1]. Vehicle emissions are influenced by numerous issues such as driving style, traffic congestion, emission control devices, vehicle performance, fuel quality, and ambient operating conditions [2].
The DC has been defined by various authors as “a series of data points representing speed versus time, and gear selection as a function of time, speed versus distance in a specific region, or a part of a road segment” [3] and “a speed-time profile for a study area within which a vehicle can be idling, accelerating, decelerating, or cruising” [4]. The most important functions of vehicle driving cycles are to determine emission levels and FC [4][5], evaluate vehicle performance [6], estimate driving style [7], and simulate driving circumstances on a laboratory chassis dynamometer (CD) [8], which provides the basis for vehicle design [9]. For electric vehicles, the driving range calculation and state of charge estimation are generally performed on the basis of the standard driving cycle [9].
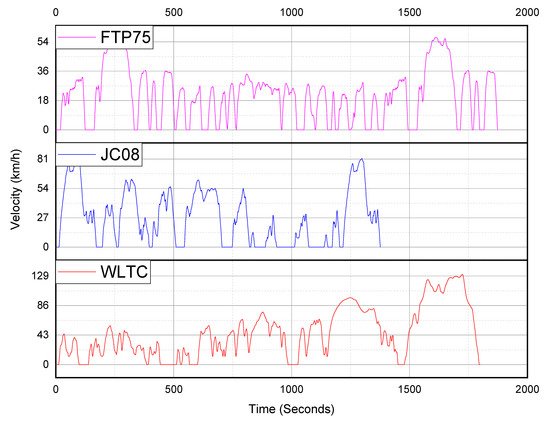
The Japanese driving cycle JC08 shown in Figure 1 has been used for emission certification of PCs and light-duty trucks since 2011 [10]. JC08 is highly transient with a minimum cruising time and long idling period, with a cold start weighted at 25% and a hot start at 75% [11].
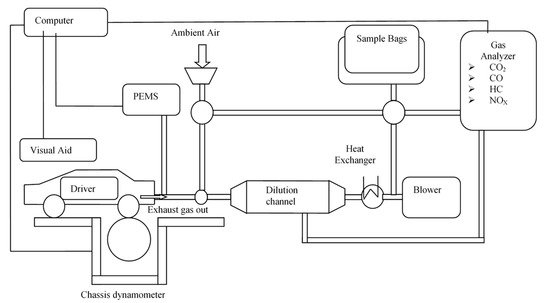
The CD and emission model software is used most to determine vehicle emission factors. However, in recent years, researchers have found a significant gap in emissions reported using the above two methods. Measuring vehicular emissions on a CD involves driving a vehicle through a predetermined DC [6][13] by a human driver, with a device known as a driver’s aid informing the driver how to drive the vehicle, including speed tolerances around the target speed trace [14]. During this test, the exhaust flow rate is continuously monitored, and the exhaust gas is collected in sample bags for subsequent analysis of content and concentration after dilution with ambient air. A constant volume sampler (CVS) system based on a CD is displayed in Figure 2 [2].
2. Driving Cycle Development Process
For the accurate development of DCs, a large sample of representative driving data is required [15]. Among the current technologies, GPS and an on-board diagnostics (OBD) interface are the most common instruments for the collection of driving data.
GPS: provides data on a vehicle’s velocity, time, date, latitude, longitude, and altitude. Galgamuwa et al. (2016) used the on-board measurement method with five GPS devices for data collection in the study area, collecting data on 78 trips at one-second intervals [16]. GPS-based data collection has the advantages of being small and easy to carry on vehicles, device installation and operation not affecting the operation of a vehicle, good signal reception, bulk data storage, and being a high-frequency data acquisition system [17]. A similar approach was taken by [18][19][20][21][22] for data collection using GPS.
Duran and Earleywine (2018) applied seven logic-based filters for the filtration process to remove duplicated records and negative differential time steps, replace outlying high/low-speed values, remove zero-speed signal drift when the vehicle stopped, replace false zero-speed records, amend gaps in data, repair outlying acceleration or deceleration values, and denoise and smooth final signals using the Savitzky–Golay filter technique [23].
Huertas et al. (2018) disregarded trip data that were missing typical values with less than 90% of available data. Rather than fixing missing values, they ignored the data [24].
3. Comparison of RDE Tests with Laboratory-Based and Real-World Emissions
Conducting emission tests on a chassis dynamometer (CD) is standard practice for comparing the vehicle’s emissions and verifying whether they remain under the emission limit, as per standards. However, CD tests suffer from shortcomings associated with their non-representativeness of actual on-road driving conditions. Comparison of RDE with laboratory-based cycles (WLTC, FTP75, and CADC) is presented in Table 1.
| DC | Year | Methods Applied or Source of Sample Data | Country/City of RDE Data | Vehicle Category | Laboratory-Based Emissions Level (g/km) | On-Road Emissions Level (g/km) | Difference | FC | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WLTC | 2020 | WLTP and RDE | Gothenburg, Sweden | Diesel and gasoline vehicles | 143 for CO2 136 for CO2 |
148 for CO2 151 for CO2 |
↑3%CO2 for CI vehicles ↑11% CO2 for SI vehicles |
[25] | |
| WLTC | 2020 | WLTP and RDE | NM | Euro 6b diesel | - | - | - | ↑18.03% | [26] |
| WLTC | 2020 | Real-world data from the consumer website (Spritmonitor.de) | German | WLTP type approved vehicle (2018) | NM | NM | ↑14% CO2 | ↑14% | [27] |
| FTP75, HWFET | 2020 | FTP, HWFET, and US06, and Canadian 5-mode on-road driving cycle | Canada | Gasoline and Diesel LDVs | <0.0435 FTP limit of NOX | 0.061–0.326 for NOX | 1.4–7.5 times FTP NOX limit | ↑22% | [25] |
| WLTC | 2019 | WLTP and RDE | Lombardy | Euro 6d-temp diesel (DOC + DPF + SCR) | 146.31 for CO2 | 165.33 for CO2 0.282 for NOX 0.0197 for CO |
↑13% CO2 | [28] | |
| WLTC | 2019 | WLTP and on-road testing | Thessaloniki, Greece | Euro 6b diesel (DOC + DPF + EGR) | CO2 close enough to the RDE CO2 levels | NOX are 3 times higher than WLTP level | ↓50–100% CO2 and ↑300 for NOx | [29] | |
| Standard road speed | 2019 | On-road and CD tests | Warsaw | Ford focus PV | 229 for CO2 6.9 for CO 1.23 for NOX 1.04 for HC |
242 for CO2 7.9 for CO 1.17 for NOX 0.68 for HC |
↑5.4% CO2 ↑12.6% CO ↓5.12% NOX ↓50.72% HC |
[30] | |
| CADC | 2019 | CADC and on-road testing | Thessaloniki, Greece | Euro 6b diesel (DOC + DPF + EGR) | NOX levels are close to the levels of the RDE test | NOx levels are close to the levels of the RDE test | [29] | ||
| MIDC | 2018 | MIDC and the average real-world emissions of the three routes | Dehradun city, India | Gasoline (TWC) | 216.83 for CO2 0.977 for CO 0.008 for THC 0.011 for NOX |
263.35 for CO2 2.03 for CO 0.021 for THC 0.025 for NOX |
↑1.12–1.39 times for CO2 ↑1.35–2.39 times for CO, ↑2.17–5.0 times for THC ↑2.04–2.32 times for NOx, and |
↑18.4% | [31] |
| WLTC | 2018 | WLTP and pre-recorded RDE cycle under lab-RDE cycle | Italy | Euro 6 gasoline (TWC) and diesel (DOC + DPF + NS) | NC | NC | ↑10% CO2 ↑15%NOx |
[32] | |
| WLTC | 2018 | Powertrain Road Performance Simulator (PRoPS) within the Matlab-Simulink | Lombardy | Euro 5 diesel | 180 for CO2 ≈0.31 for NOX 1.21 for CO 0.05 for HC 0.013 for PM10 |
400 for CO2 ≈0.84 for NOX 1.82 for CO 0.28 for HC 0.015 for PM10 |
↑≈ 122%CO2, ↑≈ 1.71 times for NOX, ↑≈ 350.4% CO, ↑≈ 4.6 times for HC, and ↑≈ 14.5% PM10 |
[33] | |
| CADC | 2018 | PRoPS within the Matlab-Simulink | Lombardy | Euro 5 diesel | 380 for CO2 ≈0.08 for NOX 0.095 for CO 0.045 for HC 0.0065 for PM10 |
400 for CO2 ≈0.84 for NOX 1.82 for CO 0.28 for HC 0.015 for PM10 |
↑ 5.26%CO2, ↑≈ 9.5% times for NOX, ↑≈ 18 times for CO, ↑≈ 5.2 times for HC and ↑≈ 13.77 times for PM10 |
||
| WLTC | 2017 | WLTP and simulation of real-world driving conditions | NC | Euro 5 gasoline and diesel | 143.9 for CO2 | 162.6 for CO2 | ↑13% CO2 | [34] | |
| WLTC | 2017 | Real-world data from the consumer website Spritmonitor.de | German | Gasoline and diesel | NM | NM | ↑37% CO2 (gasoline) ↑41% CO2 (diesel) |
[35] | |
| WLTC | 2017 | WLTP and RDE | Beijing and Xiamen | Euro 5 gasoline LDV (TWC) | 182 for CO2 0.62 for CO 0.028 for NOX |
175 for CO2 0.248 for CO 0.0185 for NOX |
↓4% CO2, ↓60% CO, and ↓34% NOX |
[36] | |
| WLTC | 2016 | WLTC simulated on IVE model and on-road testing | Deharsun, India | Euro 4 gasoline LDV (TWC) | 111.23 for CO2 0.953 for CO 0.08 for HC 0.086 for NOX |
145.7 for CO2 1.4 for CO 0.1304 for HC 0.141 for NOX |
↑31%CO2, ↑46.9%CO, ↑63%HC, and ↑64% NOX |
[37] | |
| WLTC | 2016 | WLTP and on road data | NM | Euro 5 vehicles | 130.25 for CO2 0.409 for NOX |
143.687 for CO2 0.498 for NOX |
↑10.% for CO2 ↑21.83% NOX | ↑10.55% | [38] |
In urban areas, a cold start can significantly contribute to vehicles’ overall emissions and FC due to short trips and frequent starts [39]. Reduction in atmospheric temperature from 25 °C to 8 °C during a cold start (in the considered period of 300 s) resulted in a 16% rise in CO 2 (FC), a 195% rise in CO, a 280% rise in PN, and an 11% decrease in NO X [40]. The EU RD exclusions of a cold start and idling decrease the emission of CO 2 in the urban drive mode by 8% and leading to a decrease in CO emission by 18% [36]. For diesel vehicles in a RDE test, trips between 5 and 10 °C have up to 30% differences in NO X emissions, but for gasoline vehicles, the difference is not as significant [41]. CO 2 emissions are highest during a cold start, by a factor of 1.6 and 1.3, at temperatures of −7 and +23 °C, respectively, when compared with the warm start at +23 °C for a gasoline direct-injection vehicle equipped with a particulate filter, where the PN emission at −7 °C was 2.6 times higher than the 23 °C at ambient temperature [42].
3. Effect of route selection on RDE
In many metropolitan cities, traffic conditions are becoming more congested, and most passenger vehicles in developing countries are operated more in congested traffic conditions and signalized intersections. In the EU’s RDE legislation, the share of urban roads, rural roads, and motorways is nearly the same, but they contribute to different emission levels and FC.
Williams et al. (2018) conducted RDE performance tests on three different test routes. Route 1 had the largest share of urban driving section and, therefore, a lack of a motorway section; route 2 was equivalent to driving mainly on rural roads. Route 3 was consistent with the EU’s RDE legislation. They found that the emission of CO increased in proportion to the duration of the test, regardless of the type of test route used. They obtained higher CO and HC in those tests than within the EU RDE test. Such a situation occurs when these tests are shorter and the urban and rural part makes up a larger share in the whole test conducted. The authors confirmed that it is possible to shorten the test distance by about 20% without a significant change in the results of specific distance exhaust emissions [43].
4. Conclusions
The DC is an important idea in quantifying vehicle emissions and FC, and it is expected to effectively represent real vehicle driving patterns so as to obtain reliable estimates of vehicle emissions. The concern is growing about the gap between actual driving conditions and the standard DCs used for vehicle certifications and regulatory authorities. A review of recent and relevant studies on DCs quantifying vehicle emissions and FC has been undertaken. Local DCs were analysed for their route selection, data collection approach, cycle formation methods, and cycle assessment parameters and were compared with standard DCs. Lastly, the gaps between RDE and laboratory and real-world data were discussed. After performing a comparative analysis of local DCs and standard DCs, the findings of this study are that: A driving cycle that shows the highest coincidence with actual driving data from on-road vehicles is preferable for estimating emission levels and fuel consumption. Therefore, typical or local driving cycles should be developed that reflect local driving patterns or conditions that could be used for type approval tests of new and existing vehicles. Most of the reviewed local DCs do not distinguish between separate phases of urban rods, rural roads, and motorways. Almost all the local DCs reviewed do not identify shifting the strategy followed during the test on CD. Compared with WLTC, the local DCs are capable of producing higher emissions and FC due to a higher acceleration time and greater representativeness of the local DC at a particular place. The main problem associated with most developed local DCs is related to the small sample size collected from a few vehicles within a short period of time. Researchers mostly used micro-trip and Markov chain methods to construct a driving cycle for emission levels and fuel consumption, and recently, a new method called the fuel-based approach has also been introduced.
Future studies on driving cycles should note the importance of route planning, bulk data collection, data filtration, and selection of the most significant characteristic parameters. Furthermore, attention should be given to data collection time including peak times, off-peak times, and weekends.
From the comparison of RDE with laboratory-based emissions measurement and real-world emissions, the conclusions of this study are: RDE measured by PEMS are higher than laboratory-based measurements or CVS. RDE is not reproducible as laboratory-based measurements and results are different within and outside the boundary conditions. Under controlled laboratory conditions, PEMS resulted in higher emissions than CVS with low uncertainty; the major causes of PEMS’ uncertainty are drift of the analyser over time and exhaust flow rate. The gap between RDE and real-world emissions is caused by cold temperatures, road grade, a similar share of types of route, drivers’ dynamic driving conditions, the uncertainty of PEMS, and RDE analysis tools. Driving uphill greatly increases CO 2, FC, and NO X emissions due to higher energy demand on roads with an inclination. Operations in cold temperatures increase CO, PN, and CO 2 emissions compared with warm operation due to a richer air-fuel mixture in cold conditions and the catalytic convertor not reaching an effective operating temperature; however, NO X emissions showed a decreasing trend during cold operation. A more dynamic character than the RDE boundaries resulted in an increase in CO2, NOX, and PN emissions, long-distance driving on a motorway decreased NO X and PN emissions, and shorter trips on urban routes resulted in higher CO and HC emissions than EU RDE.
References
- Chauhan, B.P.; Joshi, G.J.; Parida, P. Development of candidate driving cycles for an urban arterial corridor of Vadodara city. Eur. Transp.-Trasp. Eur. 2020, 4, 1–16.
- Yang, Z.; Deng, B.; Deng, M.; Huang, S. An Overview of Chassis Dynamometer in the Testing of Vehicle Emission. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences; 2018; Volume 175, p. 02015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326124880_An_Overview_of_Chassis_Dynamometer_in_the_Testing_of_Vehicle_Emission (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Galgamuwa, U.; Perera, L.; Bandara, S. Developing a General Methodology for Driving Cycle Construction: Comparison of Various Established Driving Cycles in the World to Propose a General Approach. J. Transp. Technol. 2015, 5, 191–203.
- Amirjamshidi, G. Assessment of Commercial Vehicle Emissions and Vehicle Routing of Fleets Using Simulated Driving Cycles; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2015.
- Kiran, S.; Verma, A. A novel methodology for construction of driving cycles for Indian cities. Transp. Res. Part D 2018, 65, 725–735.
- Mahayadin, A.R.; Shahriman, A.B.; Hashim, M.S.M.; Razlan, Z.M.; Faizi, M.K.; Harun, A.; Kamarrudin, N.S.; Ibrahim, I.; Saad, M.A.M.; Rani, M.F.H.; et al. Efficient methodology of route selection for driving cycle development. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applications and Design in Mechanical Engineering (ICADME 2017), Penang, Malaysia, 21–22 August 2017; Journal of Physics: Conf. Series. IOP Publishing Penang: Penang, Malaysia, 2017; Volume 908, p. 012082.
- Sentoff, K.M.; Aultman-hall, L.; Holmén, B.A. Implications of driving style and road grade for accurate vehicle activity data and emissions estimates. Transp. Res. Part D 2015, 35, 175–188.
- Al-samari, A. Real-World Driving cycle: Case Study of Baqubah, Iraq. Diyala J. Eng. Sci. 2017, 10, 39–47.
- Zhao, X.; Yu, Q.; Ma, J.; Wu, Y.; Yu, M.; Ye, Y. Development of a representative EV urban driving cycle based on a k-Means and SVM hybrid clustering algorithm. J. Adv. Transp. 2018, 22–25.
- Kühlwein, J.; German, J.; Bandivadekar, A. Development of Test Cycle Conversion Factors among Worldwide Light-Duty Vehicle CO2 Emission Standards. 2014. Available online: www.theicct.org (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Giakoumis, E.G. Driving and Engine Cycles; Springer: Athens, Greece, 2017.
- Diesel Net. Available online: https://dieselnet.com/standards/cycles/ (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- Grüner, J.; Marker, S. A Tool for Generating Individual Driving Cycles-IDCB. SAE Int. J. Commer. Veh. 2016, 9, 417–428.
- Chappell, E. Improving the Precision of Vehicle Fuel Economy Testing on a Chassis Dynamometer; University of Bath: Somerset, UK, 2015.
- Lipar, P.; Strnad, I.; Česnik, M.; Maher, T. Development of Urban Driving Cycle with GPS Data Post Processing. Promet-Traffic Transp. 2016, 28, 353–364.
- Galgamuwa, U.; Perera, L.; Bandara, S. Development of a driving cycle for Colombo, Sri Lanka: An economical approach for developing countries. Adv. Transp. 2016, 50, 1520–1530.
- Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Hou, C.; Ouyang, M. A GPS-based Research on Driving Range and Patterns of Private Passenger Vehicle in Beijing. In Proceedings of the International Battery, Hybrid and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Symposium EVS27, Barcelona, Spain, 17–20 November 2013; pp. 1–7.
- Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Hu, H.; Zhang, T.; Cai, X.; Chen, S. Development and emissions performance analysis of local driving cycle for small-sized passenger cars in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1514–1523.
- Anida, I.N.; Latiff, N.A.A.; Salisa, A.R. Driving Cycle Analysis for Fuel rate and Emissions in Kuala Terengganu City during Go-to-Work Time. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2019, 14, 3143–3157.
- Trobradović, M.; Pikula, B.; Blažević, A.; Bibić, D. Investigation of Vehicle Driving Cycles in Urban Traffic condition. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference of New Technologies, Development and Application, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 25–27 June 2020; pp. 1–6.
- Nguyen, Y.T.; Nghiem, T.; Le, A.; Bui, N. Development of the typical driving cycle for buses in Hanoi, Vietnam. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 423–437.
- Yugendar, P.; Rao, K.R.; Tiwari, G. Driving Cycle Estimation and Validation for Ludhiana City, India. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2020, 2, 229–235.
- Duran, A.; Earleywine, M. GPS Data Filtration Method for Drive Cycle Analysis Applications. SAE Int. 2018.
- Huertas, J.I.; Giraldo, M.; Quirama, L.F.; Díaz, J. Driving cycles based on fuel consumption. Energies 2018, 11, 3064.
- Rosenblatt, D.; Winther, K.; Rosenblatt, D. Real Driving Emissions and Fuel Consumption: A Report from the Advanced Motor Fuels Technology Collaboration Programme. 2020. Available online: https://www.iea-amf.org (accessed on 18 August 2021).
- Pavlovic, J.; Fontaras, G.; Ktistakis, M.; Anagnostopoulos, K.; Komnos, D.; Ciuffo, B.; Clairotte, M.; Valverde, V. Understanding the origins and variability of the fuel consumption gap: Lessons learned from laboratory tests and a real-driving campaign. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 1–16.
- Dornoff, J.; Tietge, U.; Mock, P. On The Way to “Real-World” CO2 Values: The European Passenger Car Market in Its First Year after Introducing The WLTP; ICCT—International Council on Clean Transportation Europe: Berlin, Germany, 2020; Available online: https://theicct.org/publications/way-real-world-co2-values-european-passenger-car-market-its-first-year-after (accessed on 27 August 2021).
- Suarez-bertoa, R.; Valverde, V.; Clairotte, M.; Pavlovic, J.; Giechaskiel, B.; Franco, V.; Kregar, Z.; Astorga, C. On-road emissions of passenger cars beyond the boundary conditions of the real-driving emissions test. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108572.
- Triantafyllopoulos, G.; Dimaratos, A.; Ntziachristos, L.; Bernard, Y.; Dornoff, J.; Samaras, Z. A study on the CO2 and NOx emissions performance of Euro 6 diesel vehicles under various chassis dynamometer and on-road conditions including latest regulatory provisions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 337–346.
- Wiśniowski, P.; Ślęzak, M.; Niewczas, A. Simulation of Road Traffic Conditions on a Chassis. Arch. Automot. Eng. 2019, 84, 171–178.
- Lairenlakpam, R.; Jain, A.K.; Gupta, P.; Kamei, W.; Badola, R. Effect of Real World Driving and Different Drive Modes on Vehicle Emissions and Fuel Consumption. SAE Tech. Pap. 2018, 1, 1–10.
- Varella, R.A.; Giechaskiel, B. Comparison of Portable Emissions Measurement Systems (PEMS) with Laboratory Grade Equipment. MDPI Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1633.
- Chindamo, D.; Gadola, M. What is the Most Representative Standard Driving Cycle to Estimate Diesel Emissions of a Light Commercial Vehicle? IFAC-Papers OnLine 2018, 51, 73–78.
- Tsiakmakis, S.; Marotta, A.; Pavlovic, J.; Anagnostopoulos, K. The Difference Between Reported and Real-world CO2 Emissions: How Much Improvement can be Expected by WLTP Introduction? Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 25, 3937–3947.
- Tietge, U.; Díaz, S.; Mock, P.; Bandivadekar, A.; Icct, J.D.; Tno, N.L. From Laboratory to Road a 2018 Update of Official and “Real-World” Fuel Consumption and CO2 Values for Passenger Cars in Europe; ICCT—International Council on Clean Transportation Europe: Berlin, Germany, 2019.
- Thomas, D.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Song, B.; Ge, Y.; Yu, W.; Ropkins, K. A Comparison of Tailpipe Gaseous Emissions for RDE and WLTC Using SI Passenger Cars. SAE Int. 2017, 1–14.
- Kumar, S.; Sood, V.; Singh, Y.; Channiwala, S.A. Real world vehicle emissions: Their correlation with driving parameters. Transp. Res. Part D 2016, 44, 157–176.
- Duarte, G.O.; Gonçalves, G.A.; Farias, T.L. Analysis of fuel consumption and pollutant emissions of regulated and alternative driving cycles based on real-world measurements. Transp. Res. Part D 2016, 44, 43–54.
- Weiss, M.; Paffumi, E.; Clairotte, M.; Drossinos, Y.; Vlachos, T. Including Cold-Start Emissions in the Real-Driving Emissions (RDE) Test Procedure Effects. 2017. Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC105595 (accessed on 27 August 2021).
- Pielecha, J.; Skobiej, K.; Kurtyka, K. Testing and Evaluation of Cold-Start Emissions From a Gasoline Engine in RDE Test at Two Different Ambient Temperatures. Open Eng. 2021, 11, 425–434.
- Varella, R.A.; Duarte, G.; Patricia, B.; Villafuerte, P.M.; Sousa, L. Analysis of the Influence of Outdoor Temperature in Vehicle Cold-Start Operation Following EU Real Driving Emission Test Procedure. SAE Int. 2017, 10, 596–607.
- Nakamura, K.; Dardiotis, C.; Kandlhofer, C.; Arndt, M. Challenges Related to the Measurement of Particle Emissions of Gasoline Direct Injection Engines Under Cold-Start and Low-Temperature Conditions. Int. J. Automot. Eng. 2019, 10, 332–339.
- Williams, R.; Hamje, H.; Andersson, J.; Ziman, P. Comparison of real driving emissions and chassis dynamometer tests on emissions of two fuels in three Euro 6 diesel cars. In Proceedings of the 7th Transport Research Arena TRA, Vienna, Austria, 16–19 April 2018; pp. 1–11.





