
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kanika Khanna | + 3093 word(s) | 3093 | 2021-09-10 05:57:06 | | | |
| 2 | Lily Guo | Meta information modification | 3093 | 2021-09-10 09:45:06 | | | | |
| 3 | Lily Guo | Meta information modification | 3093 | 2021-09-10 09:46:37 | | |
Video Upload Options
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is predominantly considered as a gaseous transmitter or signaling molecule in plants.
1. Introduction
Hydrogen sulfide has been known as a crucial player during various plant cellular and physiological processes and has been gaining unprecedented attention from researchers since decades. They regulate growth and plethora of plant developmental processes such as germination, senescence, defense, and maturation in plants. Owing to its gaseous state, they are effectively diffused towards different parts of the cell to counterbalance the antioxidant pools as well as providing sulfur to cells. H2S participates actively during abiotic stresses and enhances plant tolerance towards adverse conditions by regulation of the antioxidative defense system, oxidative stress signaling, metal transport, Na+/K+ homeostasis, etc. They also maintain H2S-Cys-cycle during abiotic stressed conditions followed by post-translational modifications of cysteine residues. Besides their role during abiotic stresses, crosstalk of H2S with other biomolecules such as NO and phytohormones (abscisic acid, salicylic acid, melatonin, ethylene, etc.) have also been explored in plant signaling.
2. H2S-Mediated Mechanism of Action in Plants
2.1. Role of H2S in Post-Translational Modification of Cysteine Residues and Protein Sulfidation
2.1.1. Protein Persulfidation
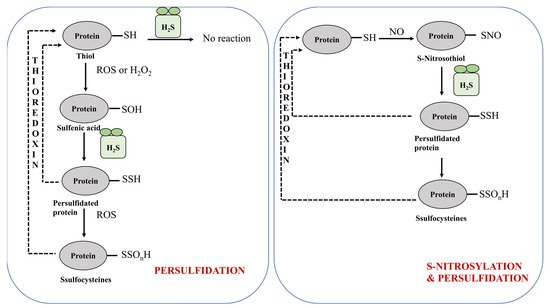
2.1.2. Protein Persulfidation in Plants
3. H2S-Signaling during Abiotic Stresses
3.1. H2S-Signaling during Heavy Metal Stresses
3.2. H2S-Signaling during Salinity Stress
3.3. H2S-Signaling during Drought/Osmotic Stress
3.4. H2S-Signaling during Temperature Stress
3.5. H2S-Signaling during Nutritional Stress
References
- Filipovic, M.R. Persulfidation (S-sulfhydration) and H2S. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 230, 29–59.
- Krishnan, N.; Fu, C.; Pappin, D.J.; Tonks, N.K. H2S—Induced sulfhydration of the phosphatase PTP1B and its role in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Sci. Sign. 2011, 4, ra86.
- Paul, B.D.; Snyder, S.H. H2S: A novel gasotransmitter that signals by sulfhydration. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 687–700.
- Vandiver, M.; Snyder, S. Hydrogen sulfide: A gasotransmitter of clinical relevance. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 255–263.
- Garcia-Mata, C.; Lamattina, L. Hydrogen sulphide, a novel gasotransmitter involved in guard cell signalling. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 977–984.
- Kimura, H. The physiological role of hydrogen sulfide and beyond. Nitric Oxide 2014, 41, 4–10.
- Mustafa, A.K.; Gadalla, M.M.; Sen, N.; Kim, S.; Mu, W.; Gazi, S.K.; Barrow, R.K.; Yang, G.; Wang, R.; Synder, S.H. H2S signals through protein S-sulfhydration. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra72.
- Aroca, A.; Serna, A.; Gotor, C.; Romero, L.C. S-sulfhydration: A cysteine posttranslational modification in plant systems. Plant Physiol. 2015, 168, 334–342.
- Aroca, A.; Gotor, C.; Romero, L.C. Hydrogen sulfidesignaling in plants: Emerging roles of protein persulfidation. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1369.
- Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, H.; Cui, B.; Gotor, C.; Romero, L.C.; Fu, L.; Yang, J.; Foyer, C.H.; et al. Persulfidation-based modification of cysteine desulfhydrase and the NADPH Oxidase RBOHD controls guard cell abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 1000–1017.
- Ren, X.; Zou, L.; Zhang, X.; Branco, V.; Wang, J.; Carvalho, C.; Holmgren, A.; Lu, J. Redox signaling mediated by thioredoxin and glutathione systems in the central nervous system. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 989–1010.
- Wedmann, R.; Onderka, C.; Wei, S.; Szijártó, I.A.; Miljkovic, J.L.; Mitrovic, A.; Lange, M.; Savitsky, S.; Yadav, P.K.; Torregrossa, R.; et al. Improved tag-switch method reveals that thioredoxin acts as depersulfidase and controls the intracellular levels of protein persulfidation. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 3414–3426.
- Filipovic, M.R.; Zivanovic, J.; Alvarez, B.; Banerjee, R. Chemical biology of H2S signaling through persulfidation. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1253–1337.
- Feng, J.; Chen, L.; Zuo, J. Protein S-nitrosylation in plants: Current progresses and challenges. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, 1206–1223.
- Stamler, J.S.; Simon, D.I.; Jaraki, O.; Osborne, J.A.; Francis, S.; Mullins, M.; Singel, D.; Loscalzo, J. S-nitrosylation of tissue-type plasminogen activator confers vasodilatory and antiplatelet properties on the enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8087–8091.
- Hess, D.T.; Matsumoto, A.; Kim, S.O.; Marshall, H.E.; Stamler, J.S. Protein S-nitrosylation: Purview and parameters. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 150–166.
- Zhao, D.D.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, M.J.; Zhou, H.; Gotor, C.; Romero, L.C.; Shen, J.; Yuan, X.X.; Xie, Y.J. Current approaches for detection of hydrogen sulfide and persulfidation in biological systems. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 367–373.
- Aroca, A.; Benito, J.M.; Gotor, C.; Romero, L.C. Persulfidation proteome reveals the regulation of protein function by hydrogen sulfide in diverse biological processes in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 4915–4927.
- Li, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Shi, C.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Shi, W.; Guo, J.; Jia, H. Hydrogen sulfide disturbs actin polymerization via S-sulfhydration resulting in stunted root hair growth. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 936–949.
- Mcdowell, J.M.; Huang, S.; Mckinney, E.C.; An, Y.; Meagher, R.B. Structure and evolution of the actin gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 1996, 142, 587–602.
- Jia, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Liesche, J.; Shi, C.; Wang, J.; Ren, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Shi, W.; et al. Ethylene-induced hydrogen sulfide negatively regulates ethylene biosynthesis by persulfidation of ACO in tomato under osmotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1517.
- Gong, Z.; Xiong, L.; Shi, H.; Yang, S.; Herrera-Estrella, L.R.; Xu, G.; Chao, D.Y.; Li, J.; Wang, P.Y.; Qin, F.; et al. Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 635–674.
- Chen, L.; Wu, R.; Feng, J.; Feng, T.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Zhan, N.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Ren, B.; et al. Transnitrosylation mediated by the non-canonical catalase ROG1 regulates nitric oxide signaling in plants. Dev. Cell 2020, 53, 444–457.
- Ali, B.; Gill, R.A.; Yang, S.; Gill, M.B.; Ali, S.; Rafiq, M.T.; Zhou, W. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates cadmium-induced morpho-physiological and ultrastructural changes in Brassica napus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 197–207.
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, K. Sodium hydrosulfide mitigates cadmium toxicity by promoting cadmium retention and inhibiting its translocation from roots to shoots in Brassica napus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 67, 433–440.
- Zhu, C.Q.; Zhang, J.H.; Sun, L.M.; Zhu, L.F.; Abliz, B.; Hu, W.J.; Zhong, C.; Bai, Z.G.; Sajid, H.; Cao, X.C.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity via decreasingapoplast and symplast Al contents in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 294.
- Wang, H.; Ji, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Liang, W. Interactions between hydrogen sulphide and nitric oxide regulate two soybean citrate transporters during the alleviation of aluminium toxicity. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 2340–2356.
- Valivand, M.; Amooaghaie, R.; Ahadi, A. Interplay between hydrogen sulfide and calcium/calmodulin enhances systemic acquired acclimation and antioxidative defense against nickel toxicity in zucchini. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 158, 40–50.
- Shi, H.; Ye, T.; Chan, Z. Nitric oxide-activated hydrogen sulfide is essential for cadmium stress response in bermudagrass (Cynodondactylon (L). Pers.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 74, 99–107.
- Shivaraj, S.M.; Vats, S.; Bhat, J.A.; Dhakte, P.; Goyal, V.; Khatri, P.; Kumawat, S.; Singh, A.; Prasad, M.; Sonah, H.; et al. Nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide crosstalk during heavy metal stress in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 168, 437–455.
- Fang, H.; Liu, Z.; Long, Y.; Liang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Li, H.; Zhai, J.; Pei, Y. The Ca2+/calmodulin2-binding transcription factor TGA3 elevates LCD expression and H2S production to bolster Cr6+ tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2017, 91, 1038–1050.
- Kaya, C.; Ashraf, M.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Responses of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide in regulating oxidative defence system in wheat plants grown under cadmium stress. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 168, 345–360.
- Liu, Z.; Fang, H.; Pei, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D. WRKY transcription factors down-regulate the expression of H2 S-generating genes, LCD and DES in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 995–1001.
- Jiang, J.L.; Tian, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, M.; Hou, R.P.; Ren, X.M. H2S alleviates salinity stress in cucumber by maintaining the Na+/K+ balance and regulating H2S metabolism and oxidative stress response. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 678.
- Kaya, C.; Higgs, D.; Ashraf, M.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Integrative roles of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide in melatonin-induced tolerance of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants to iron deficiency and salt stress alone or in combination. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 168, 256–277.
- Zulfiqar, F.; Hancock, J.T. Hydrogen sulfide in horticulture: Emerging roles in the era of climate change. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 667–675.
- Christou, A.; Manganaris, G.A.; Papadopoulos, I.; Fotopoulos, V. Hydrogen sulfide induces systemic tolerance to salinity and non-ionic osmotic stress in strawberry plants through modification of reactive species biosynthesis and transcriptional regulation of multiple defence pathways. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1953–1966.
- Kopta, T.; Sekara, A.; Pokluda, R.; Ferby, V.; Caruso, G. Screening of chilli pepper genotypes as a source of capsaicinoids and antioxidants under conditions of simulated drought stress. Plants 2020, 9, 364.
- Corpas, F.J. Hydrogen sulfide: A new warrior against abiotic stress. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 11, 983–988.
- Honda, K.; Yamada, N.; Yoshida, R.; Ihara, H.; Sawa, T.; Akaike, T.; Iwai, S. 8-Mercapto-cyclic GMP mediates hydrogen sulfide-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 1481–1489.
- Chen, J.; Shang, Y.T.; Wang, W.H.; Chen, X.Y.; He, E.M.; Zheng, H.L.; Shangguan, Z. Hydrogen sulfide-mediated polyamines and sugar changes are involved in hydrogen sulfide-induced drought tolerance in Spinacia oleracea seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1173.
- Tang, X.; An, B.; Cao, D.; Xu, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Sun, X. Improving photosynthetic capacity, alleviating photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress under low temperature stress with exogenous hydrogen sulfide in blueberry seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 108.
- Zhang, W.; Cao, J.; Fan, X.; Jiang, W. Applications of nitric oxide and melatonin in improving postharvest fruit quality and the separate and crosstalk biochemical mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 531–541.
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Cao, C.; Liang, S.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Pei, Y. The role of H2S in low temperature-induced cucurbitacin C increases in cucumber. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 99, 535–544.
- Li, S.; Yan, J.P.; Yang, E.; Bai, X.G.; Long, J.; Li, K.Z.; Xu, H.N. Effects of exogenous H2S on the germination of tomato seeds under nitrate stress. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 39–46.
- Kaya, C.; Ashraf, M. The mechanism of hydrogen sulfide mitigation of iron deficiency-induced chlorosis in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) plants. Protoplasma 2019, 256, 371–382.




