
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Md Jamal Uddin | + 2201 word(s) | 2201 | 2021-08-31 07:48:10 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 2201 | 2021-09-01 04:17:04 | | |
Video Upload Options
The prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is increasing worldwide, and a close association between acute kidney injury (AKI) and CKD has recently been identified. Black cumin (Nigella sativa) has been shown to be effective in treating various kidney diseases. Accumulating evidence shows that black cumin and its vital compound, thymoquinone (TQ), can protect against kidney injury caused by various xenobiotics, namely chemotherapeutic agents, heavy metals, pesticides, and other environmental chemicals. Black cumin can also protect the kidneys from ischemic shock. The mechanisms underlying the kidney protective potential of black cumin and TQ include antioxidation, anti-inflammation, anti-apoptosis, and antifibrosis which are manifested in their regulatory role in the antioxidant defense system, NF-κB signaling, caspase pathways, and TGF-β signaling.
1. Introduction
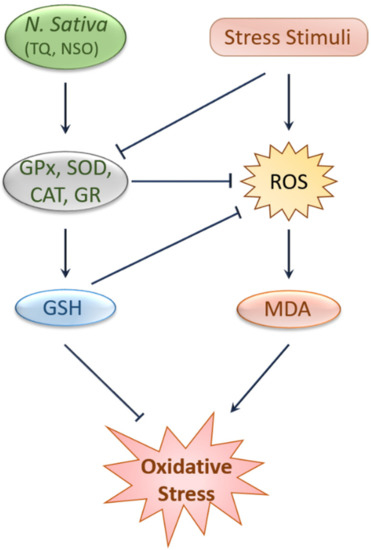
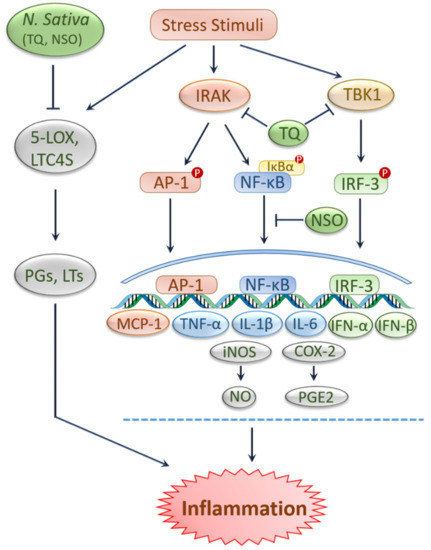
2. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Black Cumin and TQ
3. Protective Effects of Black Cumin and TQ against Kidney Injury
|
Experimental Models |
Treatment with Doses |
Pathophysiological Alterations |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Acetylsalicylic acid-induced nephrotoxicity in rats |
Ethanolic NSE (250 mg/kg) |
Improved paired kidney weight, body weight, relative tissue body weight index, and normalized serum urea and creatinine |
[18] |
|
Aspirin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats |
Ethanolic NSE (250 mg/kg) |
Significant improvement in histological parameters, including disrupted brush border, epithelial necrosis, intraluminal protein casts, and basement membrane integrity |
[17] |
|
Calcium oxalate-induced urolithiasis in rats |
NSO (5 mL/kg BW/dose/ day for 28 days) |
↓Urinary and serum rates of calcium phosphate and oxalate; ↑volume of urine excreted |
[58] |
|
CCl4-induced kidney injury in rats |
Combined fish oil/ NSO (300 mg oil emulsions /kg BW, for 20 days) |
↑Unsaturated fatty acids; ↓oxidative stress and inflammation |
[59] |
|
CP-induced AKI in rats |
NSO (2 mL/kg BW orally) |
↓Serum creatinine, BUN and ↑BBM enzyme activities in kidney cortical and medullary homogenates and BBMV; carbohydrate metabolism enzyme activities, and in the enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant parameters toward normalcy |
[15] |
|
CP-induced kidney toxicity in rats |
NSP (3 g/kg/day), extract (0.5g/kg/ day) and NSO (2 g/kg/day) for 60 days |
↓Serum levels of urea, creatinine, and K+; ↑Na+, Na+/K+ ratio, vitamin D, nutritional markers, and antioxidant enzymes |
[60] |
|
Diazinon-induced nephrotoxicity in rats |
NSO (2 mg/kg/daily) |
↓AST, ALT, ALP, BIL, creatinine and urea |
[22] |
|
Haloperidol (HAL)-induced nephrotoxicity in rats |
NSO (Pre-, co- and post-treatment: 150 mg/kg BW for 7 days) |
↓K+, Na+, MDA contents and aldose-reductase activity, and AMP hydrolysis; ↑ATP in the plasma cell membranes of rat kidney; ↓inner kidney cortex and outer medulla |
[61] |
|
IRI-induced kidney injury in rats |
Single dose of NSP (400 mg/kg orally) |
↓Stain-positive cells in kidney tissue; ↓tissue MDA levels; ↑GPx and CAT |
[12] |
|
Methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in mice |
NSO (0.125 mL/daily) |
↓MDA; ↑GSH levels in kidney homogenate |
[14] |
|
Paracetamol-induced nephrotoxicity in rats |
Ethanolic NSE (250, 500 and 1000 mg/kg) |
↓Serum urea and creatinine; ↑SOD and GSH; ↓MDA levels in the kidneys; reversed kidney pathological damage |
[16] |
|
Penconazole-induced nephrotoxicity in rats |
NSO (orally 0.2ml black cumin oil /100 g BW three days/ week for four weeks) |
↓Subcapsular space and hypercellularity of the glomerular cells; attachment of podocytes and their processes; ↑Bcl-2 immune marker; ↓intercalated cells of cortical; ↓α-SMA and collagen fibers; ↓MDA level; ↑SOD and CAT |
[21] |
|
Sodium nitrite-induced nephrotoxicity in rats |
NSO (2.5, 5, and 10 mL/kg for 12 weeks) |
↓Serum urea and creatinine; ↑normal appearance of kidney tissue; ↓glycogen levels; ↓fibrosis markers, partially; ↓caspase-3 and pJNK/JNK |
[62] |
|
Unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced kidney damage in rats |
NSE (200 and 400 mg/kg, 2 doses for 18 days) |
↓Kidney angiotensin II and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression, MDA and TNF-α levels, and the number of apoptotic cells; ↑kidney total thiol content and the activity of antioxidant enzymes |
[63] |
|
Arsenic-induced kidney toxicity in female rats |
TQ (10 mg/kg) and ebselen (5 mg/kg) |
↓Oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, As accumulation in the kidney tissue; ↓histological kidney damage |
[19] |
|
Cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity in rats |
TQ (50 mg/kg BW) |
↓Toxicity of Cd and preserved histological architecture of the kidney tissue; ↓Overexpression of NF-κB in kidney tissue; ↓apoptotic cells; subdued lipid peroxidation; ↓SOD, GPx, and CAT activities in kidney tissue |
[20] |
|
IRI-induced kidney injury in rats |
TQ (10 mg/kg/day) |
Reduction of IRI-related alteration in kidney functions: ↑left RBF and GFR; ↑left kidney FENa; ↓gene expressions of KIM-1, NGAL, TNF-α, TGF-β1 and PAI-1 |
[13] |
|
Sodium nitrite-induced kidney toxicity in rats |
TQ (25 and 50 mg/kg, p.o., daily) |
↓Oxidative stress, restoration of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and protection of kidney tissue from apoptosis |
[24] |
|
CP-induced nephrotoxicity in rats |
NSO (2 mL/kg BW, orally) and TQ (1.5 mg/kg BW, orally) |
Improve kidney function, restored serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels; ↑BBM marker enzymes (ALP, GGTase and LAP) in BBMVs, homogenates of kidney cortex and medulla; ↓kidney metabolic and redox status |
[64] |
AKI, Acute kidney injury; ALP, Alkaline phosphatase; ALT, Alanine aminotransferase; AMP, Activated protein kinase; AST, Aspartate aminotransferase; ATP, Adenosine triphosphate, As, Arsenic; BBM, Brush border membrane; BBMV, Brush border membrane vesicle; BIL, Bilirubin; BUN, Blood urea nitrogen; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; CAT, Catalase; CCl4, Carbon tetrachloride; CKD, Chronic kidney disease; CP, Cisplatin; Cd, Cadmium; FENa, Fractional excretion of sodium; GFR, Growth factor receptor; GGTase, Geranylgeranyltransferase; GPx, Glutathione peroxidase; GSH, Glutathione; IRI–Ischemia-reperfusion injury; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases; KIM-1, Kidney injury molecule-1; LAP, latency-associated peptide; MDA, Malondialdehyde; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa B; NGAL, Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; NSO, N. sativa oil; NSP, N. sativa seed powder; NSE, N. sativa seed extract; pJNK, Phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinase; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; RBF, Renal blood flow; SOD, Superoxide dismutase; TGF-β1, Transforming growth factor beta 1; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor alpha; TQ, Thymoquinone; α-SMA, Smooth muscle alpha-actin.
Table 2. Summary on the protective effects of black cumin against various kidney diseases in patients.
|
Types of Kidney Disease |
Treatment with Doses |
Pathophysiological Alterations |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Randomized, prospective, comparative, and open-labeled clinical trial with Stages 3 and 4 CKD patients |
NSO (2.5 mL, p.o., once daily) along with alpha-keto analog of essential amino acids |
↓Blood urea, serum creatinine, and 24-h total urine protein; ↑24-h total urine volume and glomerular filtration rate; delaying the progression of CKD at stages 3 and 4 |
[27] |
|
Prospective, comparative, and open-label study with patients with CKD (Stage 3 and 4) due to diabetic nephropathy |
NSO (2.5 mL, once daily and orally) |
↓Blood glucose, serum creatinine, blood urea, 24 h total urinary protein levels; ↑glomerular filtration rate, 24 h total urinary volume, and hemoglobin level |
[25] |
|
Randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial in patients with kidney stones |
Seed capsule (500 mg, twice for 10 weeks |
Retreated or decreased the size of kidney stones |
[26] |
CKD, chronic kidney disease; NSO, Nigella sativa oil.
References
- Uchino, S.; Kellum, J.A.; Bellomo, R.; Doig, G.S.; Morimatsu, H.; Morgera, S.; Schetz, M.; Tan, I.; Bouman, C.; Macedo, E.; et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: A multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 2005, 294, 813–818.
- Coca, S.G.; Singanamala, S.; Parikh, C.R. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 442–448.
- Lewington, A.J.; Cerda, J.; Mehta, R.L. Raising awareness of acute kidney injury: A global perspective of a silent killer. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 457–467.
- Doi, K. Role of kidney injury in sepsis. J. Intensive Care 2016, 4, 17.
- Togel, F.; Westenfelder, C. Recent advances in the understanding of acute kidney injury. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 83.
- Radi, Z.A. Kidney pathophysiology, toxicology, and drug-induced injury in drug development. Int. J. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 215–227.
- Dixon, J.; Lane, K.; Macphee, I.; Philips, B. Xenobiotic metabolism: The effect of acute kidney injury on non-renal drug clearance and hepatic drug metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 2538–2553.
- Kinsey, G.R.; Okusa, M.D. Pathogenesis of acute kidney injury: Foundation for clinical practice. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 58, 291–301.
- Kooti, W.; Hasanzadeh-Noohi, Z.; Sharafi-Ahvazi, N.; Asadi-Samani, M.; Ashtary-Larky, D. Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and therapeutic uses of black seed (Nigella sativa). Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 732–745.
- Kanter, M.; Coskun, O.; Uysal, H. The antioxidative and antihistaminic effect of Nigella sativa and its major constituent, thymoquinone on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage. Arch. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 217–224.
- Hannan, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Uddin, M.J.; Dash, R.; Sikder, M.H.; Rahman, M.S.; Timalsina, B.; Munni, Y.A.; Sarker, P.P.; et al. Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.): A Comprehensive Review on Phytochemistry, Health Benefits, Molecular Pharmacology, and Safety. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1784.
- Caskurlu, T.; Kanter, M.; Erboga, M.; Erboga, Z.F.; Ozgul, M.; Atis, G. Protective effect of Nigella Sativa on renal reperfusion injury in rat. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 10, 135–143.
- Hammad, F.T.; Lubbad, L. The effect of thymoquinone on the renal functions following ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharm. 2016, 8, 152–159.
- Ahmed, J.H.; Abdulmajeed, I.M. Effect of Nigella sativa (black seeds) against methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmcol. 2017, 6, 9–13.
- Farooqui, Z.; Ahmed, F.; Rizwan, S.; Shahid, F.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, F. Protective effect of Nigella sativa oil on cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative damage in rat kidney. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 7–15.
- Canayakin, D.; Bayir, Y.; Kilic Baygutalp, N.; Sezen Karaoglan, E.; Atmaca, H.T.; Kocak Ozgeris, F.B.; Keles, M.S.; Halici, Z. Paracetamol-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats: The protective role of Nigella sativa. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 2082–2091.
- Asif, S.; Mudassir, S.; Toor, R.S. Histological Effects of Nigella sativa on Aspirin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Albino Rats. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2018, 28, 735–738.
- Asif, S.; Malik, L. Protective effects of Nigella sativa on acetylsalicylic acid-induced nephrotoxicity in albino rats. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2017, 27, 536–539.
- Al-Brakati, A.Y.; Kassab, R.B.; Lokman, M.S.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; Amin, H.K.; Abdel Moneim, A.E. Role of thymoquinone and ebselen in the prevention of sodium arsenite–induced nephrotoxicity in female rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 482–493.
- Erboga, M.; Kanter, M.; Aktas, C.; Sener, U.; Fidanol Erboga, Z.; Bozdemir Donmez, Y.; Gurel, A. Thymoquinone Ameliorates Cadmium-Induced Nephrotoxicity, Apoptosis, and Oxidative Stress in Rats is Based on its Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Oxidant Properties. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 170, 165–172.
- Khair, N.S.; Nooreldien, N.M. The protective effect of Nigella sativa oil on Penconazole induced -renal toxicity in adult albino rats: Histological, Immunohistochemical and Biochemical study. Egypt. J. Histol. 2019, 42, 99–120.
- Alhilo, R.M.; Kadhim, H.J.; Abbas, M.T. Effects of nigella sativa oil on biochemical parameters of white male rats exposed to diazinon. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 1286–1290.
- Ebuehi, O.A.T.; Olowojaiye, A.A.; Erukainure, O.L.; Ajagun-Ogunleye, O.M. Nigella sativa (black seed) oil ameliorates CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity and mediates neurotransmitter levels in male Sprague Dawley albino rats. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13108.
- Elsherbiny, N.M.; Maysarah, N.M.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Al-Gayyar, M.M. Renal protective effects of thymoquinone against sodium nitrite-induced chronic toxicity in rats: Impact on inflammation and apoptosis. Life Sci. 2017, 180, 1–8.
- Ansari, Z.M.; Nasiruddin, M.; Khan, R.A.; Haque, S.F. Protective role of Nigella sativa in diabetic nephropathy: A randomized clinical trial. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2017, 28, 9–14.
- Ardakani Movaghati, M.R.; Yousefi, M.; Saghebi, S.A.; Sadeghi Vazin, M.; Iraji, A.; Mosavat, S.H. Efficacy of black seed (Nigella sativa L.) on kidney stone dissolution: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1404–1412.
- Alam, M.A.; Nasiruddin, M.; Haque, S.F.; Khan, R.A. Evaluation of safety and efficacy profile of Nigella sativa oil as an add-on therapy, in addition to alpha-keto analogue of essential amino acids in patients with chronic kidney disease. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2020, 31, 21–31.
- Ahmad, A.; Husain, A.; Mujeeb, M.; Khan, S.A.; Najmi, A.K.; Siddique, N.A.; Damanhouri, Z.A.; Anwar, F. A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: A miracle herb. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 337–352.
- Islam, M.N.; Hossain, K.S.; Sarker, P.P.; Ferdous, J.; Hannan, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Chu, D.T.; Uddin, M.J. Revisiting pharmacological potentials of Nigella sativa seed: A promising option for COVID-19 prevention and cure. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1329–1344.
- Uddin, M.J.; Kim, E.H.; Hannan, M.A.; Ha, H. Pharmacotherapy against oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: Promising small molecule natural products targeting nrf2-ho-1 signaling. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 258.
- Pandiri, I.; Moni, A. Ocimum herb species: A potential treatment strategy for diabetic kidney disease. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 1, 88–91.
- Farjana, M.; Moni, A.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Hasan, A.; Hannan, M.A.; Hossain, M.G.; Uddin, M.J. Repositioning vitamin C as a promising option to alleviate complications associated with COVID-19. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 52, 461–477.
- Moni, A.; Iqbal, A.; Uddin, M. Resveratrol attenuates inflammation through tristetraprolin expression in human hepatocytes. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 1, 78–82.
- Hassanien, M.F.; Assiri, A.M.; Alzohairy, A.M.; Oraby, H.F. Health-promoting value and food applications of black cumin essential oil: An overview. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6136–6142.
- Yimer, E.M.; Tuem, K.B.; Karim, A.; Ur-Rehman, N.; Anwar, F. Nigella sativa L. (black cumin): A promising natural remedy for wide range of illnesses. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 1528635.
- Omidi, H.; Khorram, S.; Mesgari, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Tarighat-Esfanjani, A. Effects of separate and concurrent supplementation of Nano-sized clinoptilolite and Nigella sativa on oxidative stress, anti-oxidative parameters and body weight in rats with type 2 diabetes. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 96, 1335–1340.
- Ozdemir, N.; Kantekin-Erdogan, M.N.; Tat, T.; Tekin, A. Effect of black cumin oil on the oxidative stability and sensory characteristics of mayonnaise. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1562–1568.
- Sultan, M.T.; Butt, M.S.; Karim, R.; Ahmed, W.; Kaka, U.; Ahmad, S.; Dewanjee, S.; Jaafar, H.Z.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M. Nigella sativa fixed and essential oil modulates glutathione redox enzymes in potassium bromate induced oxidative stress. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 330.
- Mostafa, R.M.; Moustafa, Y.M.; Mirghani, Z.; AlKusayer, G.M.; Moustafa, K.M. Antioxidant effect of garlic (Allium sativum) and black seeds (Nigella sativa) in healthy postmenopausal women. SAGE Open Med. 2013, 1, 2050312113517501.
- Kazemi, M. Phytochemical composition, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activity of Nigella sativa L. essential oil. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2014, 17, 1002–1011.
- Singh, S.; Das, S.S.; Singh, G.; Schuff, C.; de Lampasona, M.P.; Catalán, C.A.N. Composition, in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of essential oil and oleoresins obtained from black cumin seeds (Nigella sativa L.). BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 918209.
- Imam, A.; Sulaiman, N.; Oyewole, A.; Amin, A.; Shittu, S.; Ajao, M. Pro-neurogenic and antioxidant efficacy of Nigella sativa oil reduced vulnerability to cholinesterase dysfunction and disruption in amygdala-dependent behaviours in chlorpyrifos exposure. J. Krishna Inst. Med. Sci. Univ. 2018, 7, 1–12.
- Mabrouk, A. Protective effect of thymoquinone against lead-induced antioxidant defense system alteration in rat liver. Acta Biol. Hung. 2017, 68, 248–254.
- Cobourne-Duval, M.K.; Taka, E.; Mendonca, P.; Bauer, D.; Soliman, K.F. The Antioxidant Effects of Thymoquinone in Activated BV-2 Murine Microglial Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 3227–3238.
- El-Gindy, Y.; Zeweil, H.; Zahran, S.; El-Rahman, M.A.; Eisa, F. Hematologic, lipid profile, immunity, and antioxidant status of growing rabbits fed black seed as natural antioxidants. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 999–1004.
- Shahid, F.; Farooqui, Z.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, F. Oral Nigella sativa oil and thymoquinone administration ameliorates the effect of long-term cisplatin treatment on the enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism, brush border membrane, and antioxidant defense in rat intestine. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharm. 2018, 391, 145–157.
- Ardiana, M.; Pikir, B.S.; Santoso, A.; Hermawan, H.O.; Al-Farabi, M.J. Effect of Nigella sativa supplementation on oxidative stress and antioxidant parameters: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 2390706.
- Namazi, N.; Mahdavi, R.; Alizadeh, M.; Farajnia, S. Oxidative Stress Responses to Nigella sativa Oil Concurrent with a Low-Calorie Diet in Obese Women: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Clinical Trial. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1722–1728.
- Dwita, L.P.; Yati, K.; Gantini, S.N. The anti-inflammatory activity of Nigella sativa balm sticks. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 3.
- Koshak, A.; Koshak, E.; Heinrich, M. Medicinal benefits of Nigella sativa in bronchial asthma: A literature review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25.
- Hossen, M.J.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, D.; Aravinthan, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, J.Y. Thymoquinone: An IRAK1 inhibitor with in vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42995.
- Houghton, P.J.; Zarka, R.; de las Heras, B.; Hoult, J.R. Fixed oil of Nigella sativa and derived thymoquinone inhibit eicosanoid generation in leukocytes and membrane lipid peroxidation. Planta Med. 1995, 61, 33–36.
- Mansour, M.; Tornhamre, S. Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase and leukotriene C4 synthase in human blood cells by thymoquinone. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2004, 19, 431–436.
- Aziz, N.; Son, Y.J.; Cho, J.Y. Thymoquinone suppresses IRF-3-mediated expression of type I interferons via suppression of TBK1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1355.
- Abbas, A.T.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Zalata, K.R.; Abd Al-Galel Tel, D. Effect of dexamethasone and Nigella sativa on peripheral blood eosinophil count, IgG1 and IgG2a, cytokine profiles and lung inflammation in murine model of allergic asthma. Egypt J. Immunol. 2005, 12, 95–102.
- Attia, H.N.; Ibrahim, F.M.; Maklad, Y.A.; Ahmed, K.A.; Ramadan, M.F. Characterization of antiradical and anti-inflammatory activities of some cold pressed oils in carrageenan-induced rat model of acute inflammation. Der. Pharma Chem. 2016, 8, 148–158.
- Bordoni, L.; Fedeli, D.; Nasuti, C.; Maggi, F.; Papa, F.; Wabitsch, M.; De Caterina, R.; Gabbianelli, R. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of Nigella sativa oil in human pre-adipocytes. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 51.
- Benhelima, A.; Kaid-Omar, Z.; Hemida, H.; Benmahdi, T.; Addou, A. Nephroprotective and diuretic effect of Nigella sativa L seeds oil on lithiasic wistar rats. Afr. J. Trad. Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 13, 204–214.
- Al-Okbi, S.Y.; Mohamed, D.A.; Hamed, T.E.; Edris, A.E.; Fouda, K. Hepatic regeneration and reno-protection by fish oil, Nigella sativa oil and combined fish oil/Nigella sativa volatiles in CCL4 treated rats. J. Oleo Sci. 2018, 67, 345–353.
- Alsuhaibani, A.M.A. Effect of Nigella sativa against cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2018, 7, 105–109.
- Akintunde, J.K.; Abubakar, O.K. Novel therapeutic approaches of natural oil from black seeds and its underlying mechanisms against kidney dysfunctions in haloperidol-induced male rats. Drug Metab. Pers. Ther. 2017, 32, 97–107.
- Al-Gayyar, M.M.H.; Hassan, H.M.; Alyoussef, A.; Abbas, A.; Darweish, M.M.; El-Hawwary, A.A. Nigella sativa oil attenuates chronic nephrotoxicity induced by oral sodium nitrite: Effects on tissue fibrosis and apoptosis. Redox Rep. 2016, 21, 50–60.
- Hosseinian, S.; Ebrahimzadeh Bideskan, A.; Shafei, M.N.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Soukhtanloo, M.; Shahraki, S.; Samadi Noshahr, Z.; Khajavi Rad, A. Nigella sativa extract is a potent therapeutic agent for renal inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in a rat model of unilateral ureteral obstruction. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2290–2298.
- Farooqui, Z.; Shahid, F.; Abidi, S.; Parwez, I.; Khan, F. Oral thymoquinone administration ameliorates: The effect of cisplatin on brush border membrane enzymes, energy metabolism, and redox status in rat kidney. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2017, 390, 1271–1284.




