
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kuo-Chin Hung | + 2120 word(s) | 2120 | 2021-08-18 09:52:02 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 2120 | 2021-08-26 03:58:24 | | |
Video Upload Options
Extracellular uric acid (UA) exhibits antioxidant properties by effectively scavenging free radicals in human plasma, but this benefit might be disturbed by the hydrophobic lipid layer of the cell membrane. In contrast, intracellular free oxygen radicals are produced during UA degradation, and superoxide is further enhanced by interacting with NADPH oxidase. This intracellular oxidative stress, together with inflammatory cytokines induced by UA, stimulates osteoclast bone resorption and inhibits osteoblast bone formation. UA also inhibits vitamin D production and thereby results in hyper-parathyroidism, which causes less UA excretion in the intestines and renal proximal tubules by inhibiting the urate transporter ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2 (ABCG2).
1. Introduction
2. The Clearance of Uric Acid (UA) in Humans
3. Osteoporosis
3.1. Normal Bone Remodeling
3.2. Coupling of Bone Stimulators and Turnover Inhibitors
3.3. The Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis
- (a) Increased inflammatory cytokine-associated osteolysis. It leads to excessive activity of osteoclasts and leads to more bone resorption than bone formation. This phenomenon can be seen in gouty arthritis, inflammation, and vitamin D deficiency [26].
- (b) Incoordination of the RANK/RANKL system. Increased RANK/RANKL signal in OC strengthens the performance of osteoclasts and brings about more bone resorption. There are many clinical scenarios such as in hyperparathyroidism and some autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and estrogen deprivation (postmenopausal women) [26][27].
- (c) Excessive Wnt signaling inhibitors in osteoblasts. Dickkopf-1, sclerostin, and secreted frizzled related proteins lead to diminished functioning of osteoblasts via a decrease in Wnt signaling activity, then reduced bone formation. This has been proven in chronic kidney disease, glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, and vascular calcification-related bone loss [28].
4. The Uric Acid Oxidant and Antioxidant Paradox
4.1. Antioxidant Properties of Uric Acid in Human Plasma
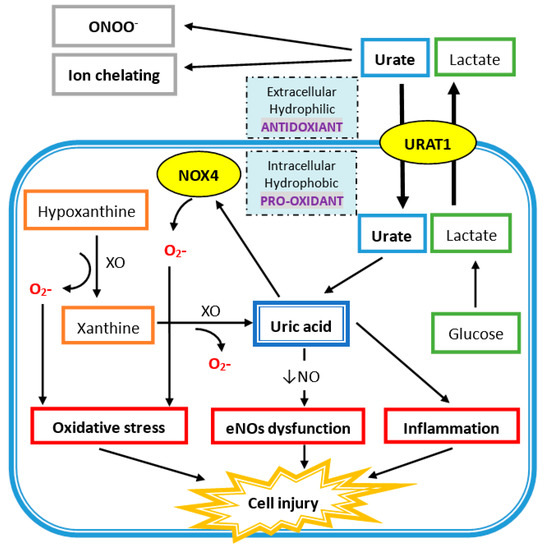
4.2. Intracellular Uric Acid Acts as a Pro-Oxidant to Damage Tissue
References
- Anton, F.M.; Garcia Puig, J.; Ramos, T.; Gonzalez, P.; Ordas, J. Sex differences in uric acid metabolism in adults: Evidence for a lack of influence of estradiol-17 beta (e2) on the renal handling of urate. Metab. Clin. Exp. 1986, 35, 343–348.
- Williamson, M.A.; Snyder, L.M.; Wallach, J.B. Wallach’s Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests, 9th ed.; Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; p. xvi. 1143p.
- Zhu, Y.; Pandya, B.J.; Choi, H.K. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the us general population: The national health and nutrition examination survey 2007–2008. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3136–3141.
- Campion, E.W.; Glynn, R.J.; DeLabry, L.O. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia. Risks and consequences in the normative aging study. Am. J. Med. 1987, 82, 421–426.
- Hall, A.P.; Barry, P.E.; Dawber, T.R.; McNamara, P.M. Epidemiology of gout and hyperuricemia. A long-term population study. Am. J. Med. 1967, 42, 27–37.
- Viggiano, D.; Gigliotti, G.; Vallone, G.; Giammarino, A.; Nigro, M.; Capasso, G. Urate-lowering agents in asymptomatic hyperuricemia: Role of urine sediment analysis and musculoskeletal ultrasound. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2018, 43, 606–615.
- Prevention and management of osteoporosis. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2003, 921, 1–164.
- Griffith, J.F. Bone marrow changes in osteoporosis. In Osteoporosis and Bone Densitometry Measurements; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 69–85.
- Yeung, D.K.; Griffith, J.F.; Antonio, G.E.; Lee, F.K.; Woo, J.; Leung, P.C. Osteoporosis is associated with increased marrow fat content and decreased marrow fat unsaturation: A proton mr spectroscopy study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2005, 22, 279–285.
- Di Pietro, G.; Capuani, S.; Manenti, G.; Vinicola, V.; Fusco, A.; Baldi, J.; Scimeca, M.; Hagberg, G.; Bozzali, M.; Simonetti, G.; et al. Bone marrow lipid profiles from peripheral skeleton as potential biomarkers for osteoporosis: A 1h-mr spectroscopy study. Acad. Radiol. 2016, 23, 273–283.
- Guido, G.; Scaglione, M.; Fabbri, L.; Ceglia, M.J. The “osteoporosis disease”. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2009, 6, 114–116.
- Charles, J.F.; Aliprantis, A.O. Osteoclasts: More than ‘bone eaters’. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 449–459.
- Huls, M.; Brown, C.D.; Windass, A.S.; Sayer, R.; van den Heuvel, J.J.; Heemskerk, S.; Russel, F.G.; Masereeuw, R. The breast cancer resistance protein transporter abcg2 is expressed in the human kidney proximal tubule apical membrane. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 220–225.
- Maiuolo, J.; Oppedisano, F.; Gratteri, S.; Muscoli, C.; Mollace, V. Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 213, 8–14.
- Woodward, O.M.; Kottgen, A.; Coresh, J.; Boerwinkle, E.; Guggino, W.B.; Kottgen, M. Identification of a urate transporter, abcg2, with a common functional polymorphism causing gout. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10338–10342.
- Matsuo, H.; Takada, T.; Nakayama, A.; Shimizu, T.; Sakiyama, M.; Shimizu, S.; Chiba, T.; Nakashima, H.; Nakamura, T.; Takada, Y.; et al. Abcg2 dysfunction increases the risk of renal overload hyperuricemia. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2014, 33, 266–274.
- Matsuo, H.; Nakayama, A.; Sakiyama, M.; Chiba, T.; Shimizu, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Nakashima, H.; Nakamura, T.; Takada, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; et al. Abcg2 dysfunction causes hyperuricemia due to both renal urate underexcretion and renal urate overload. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3755.
- Ichida, K.; Matsuo, H.; Takada, T.; Nakayama, A.; Murakami, K.; Shimizu, T.; Yamanashi, Y.; Kasuga, H.; Nakashima, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Decreased extra-renal urate excretion is a common cause of hyperuricemia. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 764.
- Wallace, M.C.; Roberts, R.L.; Nanavati, P.; Miner, J.N.; Dalbeth, N.; Topless, R.; Merriman, T.R.; Stamp, L.K. Association between abcg2 rs2231142 and poor response to allopurinol: Replication and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 656–660.
- Cheng, S.T.; Wu, S.; Su, C.W.; Teng, M.S.; Hsu, L.A.; Ko, Y.L. Association of abcg2 rs2231142-a allele and serum uric acid levels in male and obese individuals in a han taiwanese population. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2017, 116, 18–23.
- Kini, U.; Nandeesh, B.N. Physiology of bone formation, remodeling, and metabolism. In Radionuclide and Hybrid Bone Imaging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012.
- Raisz, L.G. Physiology and pathophysiology of bone remodeling. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 1353–1358.
- Suda, T.; Takahashi, F.; Takahashi, N. Bone effects of vitamin d—Discrepancies between in vivo and in vitro studies. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 523, 22–29.
- Edwards, C.M.; Mundy, G.R. Eph receptors and ephrin signaling pathways: A role in bone homeostasis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 5, 263–272.
- Matsuo, K.; Otaki, N. Bone cell interactions through eph/ephrin: Bone modeling, remodeling and associated diseases. Cell Adh. Migr. 2012, 6, 148–156.
- Hou, Y.C.; Wu, C.C.; Liao, M.T.; Shyu, J.F.; Hung, C.F.; Yen, T.H.; Lu, C.L.; Lu, K.C. Role of nutritional vitamin d in osteoporosis treatment. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 484, 179–191.
- Pivonka, P.; Zimak, J.; Smith, D.W.; Gardiner, B.S.; Dunstan, C.R.; Sims, N.A.; Martin, T.J.; Mundy, G.R. Theoretical investigation of the role of the rank-rankl-opg system in bone remodeling. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 262, 306–316.
- Khosla, S.; Hofbauer, L.C. Osteoporosis treatment: Recent developments and ongoing challenges. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 898–907.
- Robinson, K.M.; Morre, J.T.; Beckman, J.S. Triuret: A novel product of peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation of urate. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 423, 213–217.
- Gersch, C.; Palii, S.P.; Imaram, W.; Kim, K.M.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Angerhofer, A.; Johnson, R.J.; Henderson, G.N. Reactions of peroxynitrite with uric acid: Formation of reactive intermediates, alkylated products and triuret, and in vivo production of triuret under conditions of oxidative stress. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2009, 28, 118–149.
- Kuzkaya, N.; Weissmann, N.; Harrison, D.G.; Dikalov, S. Interactions of peroxynitrite with uric acid in the presence of ascorbate and thiols: Implications for uncoupling endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 343–354.
- Hayden, M.R.; Tyagi, S.C. Uric acid: A new look at an old risk marker for cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: The urate redox shuttle. Nutr. Metab. 2004, 1, 10.
- Hooper, D.C.; Spitsin, S.; Kean, R.B.; Champion, J.M.; Dickson, G.M.; Chaudhry, I.; Koprowski, H. Uric acid, a natural scavenger of peroxynitrite, in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 675–680.
- Chen, C.; Lu, J.M.; Yao, Q. Hyperuricemia-related diseases and xanthine oxidoreductase (xor) inhibitors: An overview. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 2501–2512.
- Fatima, T.; McKinney, C.; Major, T.J.; Stamp, L.K.; Dalbeth, N.; Iverson, C.; Merriman, T.R.; Miner, J.N. The relationship between ferritin and urate levels and risk of gout. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 179.
- Ghio, A.J.; Ford, E.S.; Kennedy, T.P.; Hoidal, J.R. The association between serum ferritin and uric acid in humans. Free Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 337–342.
- Ames, B.N.; Cathcart, R.; Schwiers, E.; Hochstein, P. Uric acid provides an antioxidant defense in humans against oxidant- and radical-caused aging and cancer: A hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6858–6862.
- Yu, Z.F.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Goodman, Y.; Mattson, M.P. Uric acid protects neurons against excitotoxic and metabolic insults in cell culture, and against focal ischemic brain injury in vivo. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 53, 613–625.
- Tsukada, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Tsutsumi, S.; Katoh, H.; Kuwano, H.; Miyazaki, T.; Yamamoto, Y. Effect of uric acid on liver injury during hemorrhagic shock. Surgery 2000, 127, 439–446.
- Becker, B.; Reinholz, N.; Ozcelik, T.; Leipert, B.; Gerlach, E. Uric acid as radical scavenger and antioxidant in the heart. Pflugers Arch. 1989, 415, 127–135.
- Sharaf El Din, U.A.A.; Salem, M.M.; Abdulazim, D.O. Uric acid in the pathogenesis of metabolic, renal, and cardiovascular diseases: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 537–548.
- Fisher, A.B. Redox signaling across cell membranes. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 1349–1356.
- Maples, K.; Mason, R. Free radical metabolite of uric acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 1709–1712.
- Santos, C.X.; Anjos, E.I.; Augusto, O. Uric acid oxidation by peroxynitrite: Multiple reactions, free radical formation, and amplification of lipid oxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 372, 285–294.
- Sautin, Y.Y.; Johnson, R.J. Uric acid: The oxidant-antioxidant paradox. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2008, 27, 608–619.
- Bagnati, M.; Perugini, C.; Cau, C.; Bordone, R.; Albano, E.; Bellomo, G. When and why a water-soluble antioxidant becomes pro-oxidant during copper-induced low-density lipoprotein oxidation: A study using uric acid. Biochem. J. 1999, 340, 143–152.
- Atashi, F.; Modarressi, A.; Pepper, M.S. The role of reactive oxygen species in mesenchymal stem cell adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation: A review. Stem Cells Dev 2015, 24, 1150–1163.
- Mancini, L.; Moradi-Bidhendi, N.; Brandi, M.L.; MacIntyre, I. Nitric oxide superoxide and peroxynitrite modulate osteoclast activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 243, 785–790.
- Airton Castro da Rocha, F.; Fernandes, A. Evidence that peroxynitrite affects human osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2002, 17, 434–442.




