
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chang-Hun Huh | + 2328 word(s) | 2328 | 2021-05-31 07:39:02 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 2328 | 2021-08-01 05:38:22 | | |
Video Upload Options
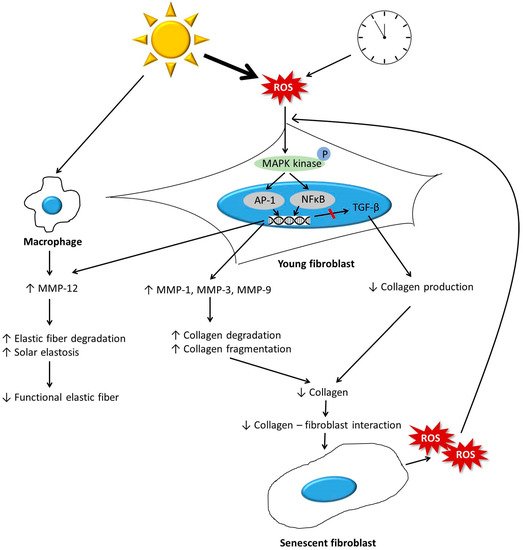
The dermis is primarily composed of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and fibroblasts. During the aging process, the dermis undergoes significant changes. Collagen, which is a major component of ECM, becomes fragmented and coarsely distributed, and its total amount decreases. This is mainly due to increased activity of matrix metalloproteinases, and impaired transforming growth factor-β signaling induced by reactive oxygen species generated during aging. The reduction in the amount of collagen hinders the mechanical interaction between fibroblasts and the ECM, and consequently leads to the deterioration of fibroblast function and further decrease in the amount of dermal collagen. Other ECM components, including elastic fibers, glycosaminglycans (GAGs), and proteoglycans (PGs), also change during aging, ultimately leading to a reduction in the amount of functional components. Elastic fibers decrease in intrinsically aged skin, but accumulate abnormally in photoaged skin. A reduction in the levels of functional dermal components results in the emergence of clinical aging features, such as wrinkles and reduced elasticity. Various antiaging approaches, including topicals, energy-based procedures, and dermal fillers, can restore the molecular features of dermal aging with clinical efficacy.
1. Introduction
2. Composition of the Dermis
3. Changes in Dermal Components with Aging
3.1. Collagen
3.2. Changes to other ECM Components
3.2.1. Elastic Fiber Remodeling
3.2.2. Changes in Glycosaminoglycans
3.2.3. Changes to Proteoglycans
3.2.4. Summary
|
Photoaging |
Components |
Intrinsic Aging |
|---|---|---|
|
Decreased and fragmented |
Collagen |
Decreased and fragmented |
|
Abnormally accumulated (SE) |
Elastic fiber |
Decreased |
|
Increased in SE region |
Hyaluronic acid |
Not changed |
|
Increased |
Total sulfated GAGs |
Decreased |
|
Increased in SE region |
Versican |
Not changed? |
|
Not changed |
Biglycan |
Decreased |
|
Decreased in SE region |
Decorin |
Not changed? |
GAG = glycosaminoglycan, SE = solar elastosis.
4. Antiaging Approaches
|
Modalities |
Mechanisms of Action |
Clinical Efficacies |
|---|---|---|
|
Topicals |
||
|
Retinoid acid (RA) |
Acts through RARs and RXRs [47] Increases type I, III, and VII collagens [48] Reorganizes elastic fiber [50] Normalizes GAG deposition [51] |
Application of 0.05% RA for 6 months improved fine and coarse wrinkles, roughness, and skin laxity [52]. Application of 0.025% RA for 3 months improved rough and fine wrinkles, skin firmness, and roughness (Ho ET) |
|
Ascorbic acid |
Reduces ROS [53] Acts as a cofactor in the biosynthesis of procollagen and elastin [54] Induces collagen synthesis in human skin fibroblasts and increase dermal thickness [55][56] |
Application of 5% ascorbic acid for 6 months led to a clinical improvement of the photodamaged skin [57]. |
|
Glycolic acid |
Stimulates the production of GAGs and collagen in the dermis [58] Improves histologic quality of elastic fibers [58] |
Application of 25% glycolic acid for 6 months increased skin thickness [58]. |
|
Peptides |
Regulate fibroblasts and control the production of ECM [59][60]. |
Application of Pal-KTTKS for 3 months reduced wrinkles [61]. Application of copper–GHK reduced the depth and length of wrinkles and made skin smoother [62]. |
|
Energy-based devices |
||
|
Fractional lasers (FL) |
Heat the dermis and stimulate matrix remodeling by deeply penetrating columns of laser energy [63] Induce biosynthesis of type I and III protocollagens [63][64] |
Two or three treatments with CO2 fractional laser improved skin texture, laxity, and overall cosmetic outcome [65]. Two treatments with 2790 nm Er:YSGG laser improved wrinkle and skin texture [66]. Three treatments of fractional 1550 nm erbium-doped fiber laser improved wrinkles [67]. |
|
Ablative FL |
||
|
Nonablative FL |
||
|
Radiofrequency (RF) |
Causes direct collagen contraction and immediate skin tightening [68][69] Reorganizes collagen bundles [70] Induces increase in types I and III collagens [71] Improves the quality of elastic fibers and solar elastosis [71] |
Three treatments with fractional bipolar RF improved wrinkles and skin texture [72]. Six treatments with monopolar RF improved laxity, texture, and wrinkles [73]. |
|
High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) |
Creates precision microwounds in the dermis [74] Induces the higher level of neocollagenesis and neoelastogenesis in the deep reticular dermis [75] |
Single treatment with HIFU improved skin laxity of lower face and neck [76]. Single treatment with HIFU improved skin laxity of face and upper neck [77]. |
|
Fillers |
||
|
Restore the contractile properties and elongation of aged fibroblasts [78][79] Induce type I collagen synthesis [78] |
Further investigation is needed. |
ECM = extracellular matrix, ER:YSGG = erbium:yttrium scandium gallium garnet, GAG = glycosaminoglycan, GHK = glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysyl, MMP = matrix metalloproteinase, pal-KTTKS = palmitoyl pentapeptide palmitoyl-lysine-threonine-threonine-lysine-serine, RAR = retinoic acid receptor, RXR = retinoid X receptors.
References
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors in skin ageing: A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2008, 30, 87–95.
- Zeng, J.P.; Bi, B.; Chen, L.; Yang, P.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Liu, T.Y. Repeated exposure of mouse dermal fibroblasts at a sub-cytotoxic dose of uvb leads to premature senescence: A robust model of cellular photoaging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 73, 49–56.
- Varani, J.; Dame, M.K.; Rittie, L.; Fligiel, S.E.; Kang, S.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Decreased collagen production in chronologically aged skin: Roles of age-dependent alteration in fibroblast function and defective mechanical stimulation. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1861–1868.
- Purohit, T.; He, T.; Qin, Z.; Li, T.; Fisher, G.J.; Yan, Y.; Voorhees, J.J.; Quan, T. Smad3-dependent regulation of type i collagen in human dermal fibroblasts: Impact on human skin connective tissue aging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2016, 83, 80–83.
- Xia, W.; Quan, T.; Hammerberg, C.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. A mouse model of skin aging: Fragmentation of dermal collagen fibrils and reduced fibroblast spreading due to expression of human matrix metalloproteinase-1. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 78, 79–82.
- Griffiths, C.E. The clinical identification and quantification of photodamage. Br. J. Dermatol. 1992, 127 (Suppl. 41), 37–42.
- Lapiere, C.M. The ageing dermis: The main cause for the appearance of ‘old’ skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 1990, 122 (Suppl. 35), 5–11.
- Kohl, E.; Steinbauer, J.; Landthaler, M.; Szeimies, R.M. Skin ageing. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 873–884.
- Quan, T.; Qin, Z.; Xia, W.; Shao, Y.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Matrix-degrading metalloproteinases in photoaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 20–24.
- Talwar, H.S.; Griffiths, C.E.; Fisher, G.J.; Hamilton, T.A.; Voorhees, J.J. Reduced type i and type iii procollagens in photodamaged adult human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 105, 285–290.
- Fisher, G.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Datta, S.C.; Varani, J.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1419–1428.
- Quan, T.; Fisher, G.J. Role of age-associated alterations of the dermal extracellular matrix microenvironment in human skin aging: A mini-review. Gerontology 2015, 61, 427–434.
- El-Domyati, M.; Attia, S.; Saleh, F.; Brown, D.; Birk, D.E.; Gasparro, F.; Ahmad, H.; Uitto, J. Intrinsic aging vs. Photoaging: A comparative histopathological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 11, 398–405.
- Yasui, T.; Yonetsu, M.; Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Yamashita, T.; Ogura, Y.; Hirao, T.; Murota, H.; Araki, T. In vivo observation of age-related structural changes of dermal collagen in human facial skin using collagen-sensitive second harmonic generation microscope equipped with 1250-nm mode-locked cr:Forsterite laser. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 31108.
- Fisher, G.J.; Varani, J.; Voorhees, J.J. Looking older: Fibroblast collapse and therapeutic implications. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 666–672.
- Quan, T.; Shao, Y.; He, T.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Reduced expression of connective tissue growth factor (ctgf/ccn2) mediates collagen loss in chronologically aged human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 415–424.
- Varani, J.; Warner, R.L.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Phan, S.H.; Kang, S.; Chung, J.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Datta, S.C.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Vitamin a antagonizes decreased cell growth and elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 480–486.
- Amano, S. Characterization and mechanisms of photoageing-related changes in skin. Damages of basement membrane and dermal structures. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25 (Suppl. 3), 14–19. [Green Version]
- Doubal, S.; Klemera, P. Visco-elastic response of human skin and aging. J. Am. Aging Assoc. 2002, 25, 115–117. [Green Version]
- Naylor, E.C.; Watson, R.E.; Sherratt, M.J. Molecular aspects of skin ageing. Maturitas 2011, 69, 249–256.
- Weihermann, A.C.; Lorencini, M.; Brohem, C.A.; de Carvalho, C.M. Elastin structure and its involvement in skin photoageing. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 241–247.
- Rossetti, D.; Kielmanowicz, M.G.; Vigodman, S.; Hu, Y.P.; Chen, N.; Nkengne, A.; Oddos, T.; Fischer, D.; Seiberg, M.; Lin, C.B. A novel anti-ageing mechanism for retinol: Induction of dermal elastin synthesis and elastin fibre formation. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 33, 62–69.
- Noblesse, E.; Cenizo, V.; Bouez, C.; Borel, A.; Gleyzal, C.; Peyrol, S.; Jacob, M.P.; Sommer, P.; Damour, O. Lysyl oxidase-like and lysyl oxidase are present in the dermis and epidermis of a skin equivalent and in human skin and are associated to elastic fibers. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 621–630.
- Kielty, C.M.; Sherratt, M.J.; Shuttleworth, C.A. Elastic fibres. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 2817–2828.
- Sherratt, M.J. Tissue elasticity and the ageing elastic fibre. Age (Dordr) 2009, 31, 305–325. [Green Version]
- Ramirez, F.; Carta, L.; Lee-Arteaga, S.; Liu, C.; Nistala, H.; Smaldone, S. Fibrillin-rich microfibrils—Structural and instructive determinants of mammalian development and physiology. Connect. Tissue Res. 2008, 49, 1–6.
- Dahlback, K.; Ljungquist, A.; Lofberg, H.; Dahlback, B.; Engvall, E.; Sakai, L.Y. Fibrillin immunoreactive fibers constitute a unique network in the human dermis: Immunohistochemical comparison of the distributions of fibrillin, vitronectin, amyloid p component, and orcein stainable structures in normal skin and elastosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1990, 94, 284–291.
- Yanagisawa, H.; Davis, E.C.; Starcher, B.C.; Ouchi, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; Richardson, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Fibulin-5 is an elastin-binding protein essential for elastic fibre development in vivo. Nature 2002, 415, 168–171.
- Langton, A.K.; Sherratt, M.J.; Griffiths, C.E.; Watson, R.E. Differential expression of elastic fibre components in intrinsically aged skin. Biogerontology 2012, 13, 37–48.
- Ashworth, J.L.; Murphy, G.; Rock, M.J.; Sherratt, M.J.; Shapiro, S.D.; Shuttleworth, C.A.; Kielty, C.M. Fibrillin degradation by matrix metalloproteinases: Implications for connective tissue remodelling. Biochem. J. 1999, 340, 171–181.
- Chakraborti, S.; Mandal, M.; Das, S.; Mandal, A.; Chakraborti, T. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: An overview. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2003, 253, 269–285.
- Ryu, J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, I.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Nam, T.J. Protective effect of porphyra-334 on uva-induced photoaging in human skin fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 796–803.
- Chung, J.H.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Eun, H.C.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Ultraviolet modulation of human macrophage metalloelastase in human skin in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 507–512.
- Imokawa, G.; Ishida, K. Biological mechanisms underlying the ultraviolet radiation-induced formation of skin wrinkling and sagging i: Reduced skin elasticity, highly associated with enhanced dermal elastase activity, triggers wrinkling and sagging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7753–7775.
- Cenizo, V.; Andre, V.; Reymermier, C.; Sommer, P.; Damour, O.; Perrier, E. Loxl as a target to increase the elastin content in adult skin: A dill extract induces the loxl gene expression. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 15, 574–581.
- Taylor, K.R.; Gallo, R.L. Glycosaminoglycans and their proteoglycans: Host-associated molecular patterns for initiation and modulation of inflammation. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 9–22.
- Oh, J.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Jung, J.Y.; Shin, J.E.; Chung, J.H. Changes in glycosaminoglycans and related proteoglycans in intrinsically aged human skin in vivo. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 454–456. [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Oh, J.H.; Chung, J.H. Glycosaminoglycan and proteoglycan in skin aging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2016, 83, 174–181.
- Anderegg, U.; Simon, J.C.; Averbeck, M. More than just a filler—The role of hyaluronan for skin homeostasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 295–303.
- Humbert, P.G.; Haftek, M.; Creidi, P.; Lapiere, C.; Nusgens, B.; Richard, A.; Schmitt, D.; Rougier, A.; Zahouani, H. Topical ascorbic acid on photoaged skin. Clinical, topographical and ultrastructural evaluation: Double-blind study vs. Placebo. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 12, 237–244.
- Oh, J.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Jung, J.Y.; Shin, J.E.; Kim, K.H.; Cho, K.H.; Eun, H.C.; Chung, J.H. Intrinsic aging- and photoaging-dependent level changes of glycosaminoglycans and their correlation with water content in human skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 62, 192–201.
- Maytin, E.V. Hyaluronan: More than just a wrinkle filler. Glycobiology 2016, 26, 553–559. [Green Version]
- Tobiishi, M.; Sayo, T.; Yoshida, H.; Kusaka, A.; Kawabata, K.; Sugiyama, Y.; Ishikawa, O.; Inoue, S. Changes in epidermal hyaluronan metabolism following uvb irradiation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 64, 31–38.
- Tzellos, T.G.; Klagas, I.; Vahtsevanos, K.; Triaridis, S.; Printza, A.; Kyrgidis, A.; Karakiulakis, G.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Papakonstantinou, E. Extrinsic ageing in the human skin is associated with alterations in the expression of hyaluronic acid and its metabolizing enzymes. Exp. Dermatol. 2009, 18, 1028–1035.
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, W.; Lei, D.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Age-dependent alterations of decorin glycosaminoglycans in human skin. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2422.
- Bernstein, E.F.; Fisher, L.W.; Li, K.; LeBaron, R.G.; Tan, E.M.; Uitto, J. Differential expression of the versican and decorin genes in photoaged and sun-protected skin. Comparison by immunohistochemical and northern analyses. Lab. Investig. 1995, 72, 662–669.
- Kang, S. The mechanism of action of topical retinoids. Cutis 2005, 75, 10–13; discussion 13.
- Woodley, D.T.; Zelickson, A.S.; Briggaman, R.A.; Hamilton, T.A.; Weiss, J.S.; Ellis, C.N.; Voorhees, J.J. Treatment of photoaged skin with topical tretinoin increases epidermal-dermal anchoring fibrils. A preliminary report. JAMA 1990, 263, 3057–3059.
- Kim, H.J.; Bogdan, N.J.; D’Agostaro, L.J.; Gold, L.I.; Bryce, G.F. Effect of topical retinoic acids on the levels of collagen mrna during the repair of uvb-induced dermal damage in the hairless mouse and the possible role of tgf-beta as a mediator. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 98, 359–363.
- Berardesca, E.; Gabba, P.; Farinelli, N.; Borroni, G.; Rabbiosi, G. In vivo tretinoin-induced changes in skin mechanical properties. Br. J. Dermatol. 1990, 122, 525–529.
- Hubbard, B.A.; Unger, J.G.; Rohrich, R.J. Reversal of skin aging with topical retinoids. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 133, 481e–490e.
- Weinstein, G.D.; Nigra, T.P.; Pochi, P.E.; Savin, R.C.; Allan, A.; Benik, K.; Jeffes, E.; Lufrano, L.; Thorne, E.G. Topical tretinoin for treatment of photodamaged skin. A multicenter study. Arch. Dermatol. 1991, 127, 659–665.
- Masaki, H. Role of antioxidants in the skin: Anti-aging effects. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 58, 85–90.
- Myllyla, R.; Majamaa, K.; Gunzler, V.; Hanauske-Abel, H.M.; Kivirikko, K.I. Ascorbate is consumed stoichiometrically in the uncoupled reactions catalyzed by prolyl 4-hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 5403–5405.
- Yamamoto, I.; Muto, N.; Murakami, K.; Akiyama, J. Collagen synthesis in human skin fibroblasts is stimulated by a stable form of ascorbate, 2-o-alpha-d-glucopyranosyl-l-ascorbic acid. J. Nutr. 1992, 122, 871–877.
- Ohshima, H.; Mizukoshi, K.; Oyobikawa, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Takiwaki, H.; Kanto, H.; Itoh, M. Effects of vitamin c on dark circles of the lower eyelids: Quantitative evaluation using image analysis and echogram. Skin Res. Technol. 2009, 15, 214–217.
- Colven, R.M.; Pinnell, S.R. Topical vitamin c in aging. Clin. Dermatol. 1996, 14, 227–234.
- Ditre, C.M.; Griffin, T.D.; Murphy, G.F.; Sueki, H.; Telegan, B.; Johnson, W.C.; Yu, R.J.; Van Scott, E.J. Effects of alpha-hydroxy acids on photoaged skin: A pilot clinical, histologic, and ultrastructural study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1996, 34, 187–195.
- Katayama, K.; Seyer, J.M.; Raghow, R.; Kang, A.H. Regulation of extracellular matrix production by chemically synthesized subfragments of type i collagen carboxy propeptide. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 7097–7104.
- Langholz, O.; Rockel, D.; Mauch, C.; Kozlowska, E.; Bank, I.; Krieg, T.; Eckes, B. Collagen and collagenase gene expression in three-dimensional collagen lattices are differentially regulated by alpha 1 beta 1 and alpha 2 beta 1 integrins. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 131, 1903–1915. [Green Version]
- Robinson, L.R.; Fitzgerald, N.C.; Doughty, D.G.; Dawes, N.C.; Berge, C.A.; Bissett, D.L. Topical palmitoyl pentapeptide provides improvement in photoaged human facial skin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2005, 27, 155–160.
- Husein El Hadmed, H.; Castillo, R.F. Cosmeceuticals: Peptides, proteins, and growth factors. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 514–519.
- Orringer, J.S.; Sachs, D.L.; Shao, Y.; Hammerberg, C.; Cui, Y.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Direct quantitative comparison of molecular responses in photodamaged human skin to fractionated and fully ablative carbon dioxide laser resurfacing. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 1668–1677.
- Kim, J.E.; Won, C.H.; Bak, H.; Kositratna, G.; Manstein, D.; Dotto, G.P.; Chang, S.E. Gene profiling analysis of the early effects of ablative fractional carbon dioxide laser treatment on human skin. Dermatol. Surg. 2013, 39, 1033–1043.
- Tierney, E.P.; Hanke, C.W. Fractionated carbon dioxide laser treatment of photoaging: Prospective study in 45 patients and review of the literature. Dermatol. Surg. 2011, 37, 1279–1290.
- Rhie, J.W.; Shim, J.S.; Choi, W.S. A pilot study of skin resurfacing using the 2,790-nm erbium:Ysgg laser system. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2015, 42, 52–58.
- Wanner, M.; Tanzi, E.L.; Alster, T.S. Fractional photothermolysis: Treatment of facial and nonfacial cutaneous photodamage with a 1,550-nm erbium-doped fiber laser. Dermatol. Surg. 2007, 33, 23–28.
- Zelickson, B.D.; Kist, D.; Bernstein, E.; Brown, D.B.; Ksenzenko, S.; Burns, J.; Kilmer, S.; Mehregan, D.; Pope, K. Histological and ultrastructural evaluation of the effects of a radiofrequency-based nonablative dermal remodeling device: A pilot study. Arch. Dermatol. 2004, 140, 204–209.
- Kist, D.; Burns, A.J.; Sanner, R.; Counters, J.; Zelickson, B. Ultrastructural evaluation of multiple pass low energy versus single pass high energy radio-frequency treatment. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006, 38, 150–154. [Green Version]
- Bogle, M.A.; Ubelhoer, N.; Weiss, R.A.; Mayoral, F.; Kaminer, M.S. Evaluation of the multiple pass, low fluence algorithm for radiofrequency tightening of the lower face. Lasers Surg. Med. 2007, 39, 210–217.
- El-Domyati, M.; El-Ammawi, T.S.; Medhat, W.; Moawad, O.; Brennan, D.; Mahoney, M.G.; Uitto, J. Radiofrequency facial rejuvenation: Evidence-based effect. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 64, 524–535.
- Bloom, B.S.; Emer, J.; Goldberg, D.J. Assessment of safety and efficacy of a bipolar fractionated radiofrequency device in the treatment of photodamaged skin. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2012, 14, 208–211.
- Taub, A.F.; Tucker, R.D.; Palange, A. Facial tightening with an advanced 4-mhz monopolar radiofrequency device. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2012, 11, 1288–1294.
- Ruiz-Esparza, J.; Gomez, J.B. Nonablative radiofrequency for active acne vulgaris: The use of deep dermal heat in the treatment of moderate to severe active acne vulgaris (thermotherapy): A report of 22 patients. Dermatol. Surg. 2003, 29, 333–339; discussion 339.
- Suh, D.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Jeong, K.H.; Song, K.Y.; Shin, M.K. Comparative histometric analysis of the effects of high-intensity focused ultrasound and radiofrequency on skin. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2015, 17, 230–236.
- Oni, G.; Hoxworth, R.; Teotia, S.; Brown, S.; Kenkel, J.M. Evaluation of a microfocused ultrasound system for improving skin laxity and tightening in the lower face. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2014, 34, 1099–1110.
- Fabi, S.G.; Goldman, M.P. Retrospective evaluation of micro-focused ultrasound for lifting and tightening the face and neck. Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40, 569–575.
- Quan, T.; Wang, F.; Shao, Y.; Rittie, L.; Xia, W.; Orringer, J.S.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Enhancing structural support of the dermal microenvironment activates fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and keratinocytes in aged human skin in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 658–667.
- Courderot-Masuyer, C.; Robin, S.; Tauzin, H.; Humbert, P. Evaluation of lifting and antiwrinkle effects of calcium hydroxylapatite filler. In vitro quantification of contractile forces of human wrinkle and normal aged fibroblasts treated with calcium hydroxylapatite. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 260–268.





