Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Evangelia Tsiani | + 2595 word(s) | 2595 | 2021-07-13 11:54:29 | | | |
| 2 | Vivi Li | Meta information modification | 2595 | 2021-07-14 04:14:55 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Tsiani, E. Antidiabetic Properties of Naringenin. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/12059 (accessed on 12 January 2026).
Tsiani E. Antidiabetic Properties of Naringenin. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/12059. Accessed January 12, 2026.
Tsiani, Evangelia. "Antidiabetic Properties of Naringenin" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/12059 (accessed January 12, 2026).
Tsiani, E. (2021, July 14). Antidiabetic Properties of Naringenin. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/12059
Tsiani, Evangelia. "Antidiabetic Properties of Naringenin." Encyclopedia. Web. 14 July, 2021.
Copy Citation
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by insulin resistance and hyperglycemia and is associated with personal health and global economic burdens. Current strategies/approaches of insulin resistance and T2DM prevention and treatment are lacking in efficacy resulting in the need for new preventative and targeted therapies. In recent years, epidemiological studies have suggested that diets rich in vegetables and fruits are associated with health benefits including protection against insulin resistance and T2DM. Naringenin, a citrus flavanone, has been reported to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, nephroprotective, immunomodulatory and antidiabetic properties.
insulin resistance
diabetes
naringenin
naringin
skeletal muscle
adipose
liver
pancreas
1. Introduction
1.1. Glucose Homeostasis: Role of Insulin
Insulin is a protein hormone primarily involved in glucose and nutrient homeostasis. Insulin is produced by the β-cells of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans [1][2][3]. In response to elevated blood glucose levels, following a meal, the β-cells release insulin into the circulation to be transported to its target tissues, including skeletal muscle, adipocytes, and hepatocytes [1][2][3]. Insulin increases glucose uptake by skeletal muscle and adipose tissue, while it suppresses the endogenous production of glucose by the liver resulting in a reduction/restoration of blood glucose back to normal levels [1][2][3].
Insulin initiates its mechanism of action through binding to its receptor located on the plasma membrane of its target cells. Insulin binding to its receptor leads to increased receptor tyrosine kinase activity, phosphorylation of the insulin receptor substrate (IRS), and downstream activation of the lipid kinase phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3-K) and the serine/threonine kinase Akt/PKB [2][3][4]. In adipose and muscle cells, this leads to downstream glucose transporter (GLUT4) translocation from an intracellular compartment to plasma membrane and entry of glucose, while in liver cells, the result is suppression of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis and reduced endogenous glucose production [3]. Impairments in insulin signaling leads to insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) [2][3][4].
Insulin resistance is a condition characterized by reduced responsiveness of target tissues to normal circulating levels of insulin [2][4][5]. Insulin resistance/T2DM is associated with inflammation, obesity, aging and a sedentary lifestyle and results in chronic elevations of plasma glucose levels, known as hyperglycemia, that can lead to long-term complications including macrovascular and microvascular damage, cardiovascular disease, retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy [2][4][5][6][7][8][9]. Obesity is strongly linked to insulin resistance and excess plasma free-fatty acids (FFA) have been established to impair the ability of insulin to suppress hepatic glucose output and to stimulate glucose uptake by skeletal muscle [7][9]. Furthermore, strong evidence have established that chronic inflammation contributes to insulin resistance. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), reduce the insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor and IRS-1, impairing insulin action and inducing insulin resistance [10]. T2DM accounts for 90%–95% of all diabetes cases [2]. The global burden of diabetes continues to rise and resulted in 5 million deaths in 2017, in the 20+ age demographic, compared to 665,000 deaths in 1990 [11]. Additionally, it is estimated that approximately 451 million people, aged 18+ are living with diabetes worldwide [11]. Diabetic complications such as diabetic foot and diabetic neuropathy significantly increased by 47.1% and 62.6%, respectively, from 2001 to 2014 [12], and overall the rise of diabetes cases exerts a significant economic burden on the health care systems globally [13][14]. For example, an incidence predictive study on the cost of diabetes in Canada over 10 years has estimated 2.16 million new cases of diabetes occurring during this timeframe, which is accompanied by a health care costs of $15.36 billion due to acute hospitalizations and prescription medications [15].
Epidemiological studies have suggested that diets high in fruits and vegetables help regulate body weight and protect against chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes [16][17][18]. However, the role the individual components of these foods play in disease prevention and treatment is difficult to determine. Specific components, known as polyphenols, have increasingly gained attention within the scientific community for their potential health benefits and preventive and therapeutic properties against chronic diseases [13][14][19][20][21][22].
1.2. Naringenin
Naringenin (4,5,7-trihydroxy-flavanone) (Figure 1 [27]) is a polyphenol belonging to flavonoids, the largest class of polyphenols with over 6000 identified sharing the common structure of 2 aromatic rings joined by a linear 3 carbon chain (C6-C3-C6) that forms an oxygenated heterocycle [28]. In naringenin, a flavanone subclass of flavonoids, this heterocycle contains a saturated 3-carbon chain and an oxygen atom at carbon 4 [28]. Naringenin is found mainly in citrus fruits, with considerably high levels found in grapefruit (43.5 mg/100 mL), lower levels found in orange juice (2.13 mg/100 mL), and much lower levels found in lemon juice (0.38 mg/100 mL) [29][30].
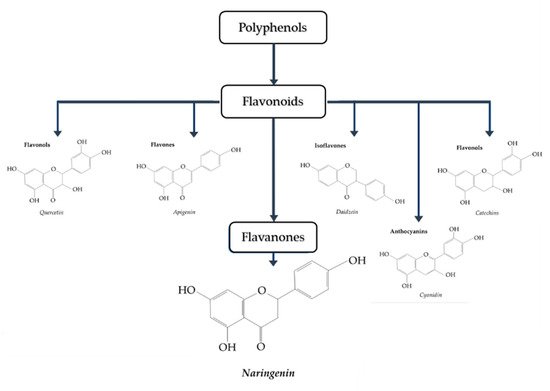
Figure 1. Classification of polyphenols. Naringenin belongs to the class known as flavanones [27].
The formation of flavonoids, including naringenin, in plants/fruits is influenced by numerous factors such as plant genetics, environmental conditions (soil and light), germination, degree of ripeness, processing and storage [31]. Naringenin has been studied for its pharmacological effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, hepatoprotective, nephroprotective, neuroprotective, anti-cancer, anti-atherosclerotic, and anti-diabetic properties [32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40][41][42].
There are limited number of studies examining the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of naringenin. Administration of grapefruit juice (250 mL) containing approximately 200 mg of naringenin in healthy individuals, resulted in peak plasma naringenin concentrations that ranged from 0.7 µM to 14.8 µM [43]. In another study, administration of 135 mg of naringenin resulted in peak plasma naringenin levels of 2009.51 ± 770.82 ng/mL [44]. Given that the molecular weight of naringenin is 272.257 g/mole, the plasma concentration of naringenin of 2 µg/mL corresponds to 7.34 µM. These two studies indicate that micromolar levels of naringenin can be reached in plasma after administration of grapefruit juice [43] or pure naringenin [44]. More studies should be performed to examine plasma naringenin levels and bioavailability in humans. Furthermore, there are no studies examining tissue distribution of naringenin in humans. Administration of 2.5 mg naringenin by gastric gavage in Sprague–Dawley rats resulted in the accumulation of naringenin in plasma, brain, liver, kidney, small intestine, large intestine, and feces. Approximately 42.11% of the initial naringenin was found in the urine, indicating increased clearance by the kidneys [45].
2. Anti-Diabetic Effects of Naringenin
2.1. Effects of Naringenin: In Vitro Skeletal Muscle Cell Studies
Zygmunt, et al. (2010) using L6 muscle cells found an increase in glucose uptake by naringenin (75 µM, 2 h) treatment [46]. In addition, naringenin significantly increased 5′ AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation/activation, and AMPK silencing using small interference RNA abolished the naringenin-stimulated glucose uptake (Table 1) [46].
Table 1. Effects of naringenin: in vitro skeletal muscle cell studies.
| Cell | Naringenin Concentration/Duration | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| L6 muscle cells | 10–75 µM, 2 h | ↑ Glucose uptake ↑ Phospho-AMPK |
[46] |
| Primary porcine myotubes | Sambucus nigra flower (elderflower); Naringenin 0.1–10 µM, 1 h | ↑ Glucose uptake ↓ ROS levels |
[47] |
| L6 myotubes insulin resistance induced by palmitate (750 µM) | 50 and 75 µM, 16 h | ↑ Glucose uptake ↑ GLUT4 translocation ↑ Phospho-AMPK ↑ SIRT1 ↑ PGC-1α |
[48] |
5′ AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK); reactive oxygen species (ROS); Glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4); Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1); Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α).
Using primary porcine myotubes Bhattacharya et al., (2013) found that exposure to the Sambucus nigra flower (elderflower) and its major polyphenol, naringenin (0.1–10 µM), significantly increased glucose uptake [47]. In addition, exposure of the myotubes to elderflower extract (100–500 µg/mL), containing significant levels of naringenin (representing 23% of total phenolic compounds analyzed), reduced the formation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Table 1) [47]. Increased ROS formation leads to increased oxidative DNA damage, protein modification, and is associated with insulin resistance [49] while antioxidants such as N-acetylcysteine (NAC) counteract insulin resistance [50]. These data [47] indicate that naringenin may act as an antioxidant to increase muscle glucose uptake.
In L6 myotubes rendered insulin resistant by exposure to the free-fatty acid (FFA) palmitate (750 µM) treatment with naringenin (50 µM and 75 µM) for 16 h abrogated the effects of palmitate by significantly restoring the insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and GLUT4 translocation [48]. Additionally, naringenin increased the phosphorylation of AMPK and the levels of SIRT1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) (Table 1) [48].
Overall, these studies (Table 1) indicate that in skeletal muscle cells naringenin has the potential to activate AMPK, increase glucose uptake and counteract the palmitate-induced insulin resistance. Some of these effects of naringenin may be related to its antioxidant properties.
2.2. Effects of Naringenin: In Vitro Adipocyte Studies
Treatment of 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes with naringenin (5–100 µM) for 48 h significantly decreased proliferation in a dose-dependent manner (Table 2) [51]. This was accompanied with a significant increase in lactic acid dehydrogenase (LDH) release without an effect on triglyceride accumulation or adipogenesis gene expression (PPAR-γ and STAT3) during adipocyte differentiation [51].
Table 2. Effects of naringenin: in vitro adipocyte studies.
| Cell | Naringenin Concentration/Duration | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3T3-L1 preadipocytes | 5–100 µM, 48 h | ↓ Adipocyte proliferation ↑ LDH release |
[51] |
| 3T3-L1 adipocytes | 100 µM, 30 min | ↓ TNF-α FFA secretion ↓ IκB-α degradation ↓ Phospho-ERK protein expression ↑ Perilipin mRNA ↑ PDE3B mRNA |
[52] |
| 3T3-L1 adipocytes and mature human adipocytes | 20 µM, 2 min | ↓ Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake ↓ GLUT4 recruitment |
[53] |
| 3T3-L1 adipocytes | 10, 50 and 100 µM, 0.5–3 h | ↓ Inflammation ↓ TLR2 expression ↓ TNF-α ↓ MCP-1 |
[54] |
| 3T3-L1 differentiating and mature adipocytes | 0–50 µM, 0–120 h (Pre-adipocytes) and 0–24 h (Mature) | ↓ Adipogenesis ↓ Lipid accumulation ↓ aP2, PPARγ, STAT5A and adiponectin protein ↓ IRS-1 (Y896) ↓ Adiponectin |
[55] |
| Human white adipocytes | 8 µM, 7 to 14 days | ↑ GLUT4 mRNA ↑ Adiponectin mRNA ↑ UCP1, ATGL, CPT1β, PGC-1α and PGC-1β mRNA ↑ Oxygen consumption rate |
[56] |
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH); Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα); Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (IκBα); Extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK); Phosphodiesterase 3B (PDE3B); Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2); Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1); Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ); Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A (STAT5A); Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1); Uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1); Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL); Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1β (CPT1β).
Elevated levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α is associated with insulin resistance. Treatment of 3T3-L1 adipocytes with naringenin (100 µM) for 30 min significantly reduced the TNF-α-induced FFA secretion [52]. Treatment with naringenin resulted in increased IκB-α cytosolic levels and decreased p-ERK protein levels. In addition, naringenin treatment significantly increased the antilipolytic gene (perilipin and PDE3B) mRNA levels (Table 2) [52].
A study by Claussnitzer et al., (2011) using 3T3-L1 adipocytes and mature human adipocytes found that treatment with naringenin (20 µM) significantly reduced the insulin-stimulated glucose transport and reduced the insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation (Table 2) [53].
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are involved in the obesity-induced inflammation of adipose tissue and contribute to insulin resistance and T2DM. In 3T3-L1 differentiating adipocytes, TLR2 expression was significantly inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by naringenin (10–100 µM) treatment (Table 2) [54]. This was accompanied by a significant decrease in inflammatory mediators, TNF-α and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 levels. In addition, naringenin suppressed the TNF-α-induced and macrophage co-culture-induced TLR2 adipocyte expression. These effects were associated with the inhibition of the NF-κB and JNK signaling cascades by naringenin [54].
In a study by Richard et al., (2013), 3T3-L1 differentiating and differentiated adipocytes treated with naringenin (25 µM) resulted in impaired mature adipocyte function and inhibition of adipogenesis [55]. Naringenin treatment (0–120 h) of immature 3T3-L1 cells resulted in the inhibition of lipid accumulation and decreased protein expression of aP2, PPARγ, STAT5A and adiponectin, all involved in adipogenesis. In mature differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes naringenin treatment prevented the insulin-induced glucose uptake, reduced tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and reduced adiponectin levels, indicating induction of insulin resistance (Table 2) [55]. These two studies [53][55] show an effect of naringenin to counteract insulin action in adipocytes in vitro, suggesting a potential negative effect on glucose homeostasis in vivo.
On the other hand, in a recent study of human white adipocytes, treatment with naringenin (8 µM) for 7 to 14 days resulted in increased thermogenesis [56]. Basal, adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-linked and maximal and reserve oxygen consumption rate was increased. Naringenin treatment increased mRNA levels of UCP1, ATGL, CPT1β, PGC-1α and PGC-1β, all involved in fat oxidation. In addition, GLUT4, adiponectin and CREBpβ mRNA levels were increased with naringenin treatment [56]. This study indicates that naringenin increased energy expenditure, thermogenesis and insulin sensitivity in human adipocytes (Table 2). From all the above 6 studies, performed using adipocytes in culture, the evidence indicate that treatment with naringenin inhibits adipocyte proliferation [51] indicating a potential to inhibit adipose tissue expansion seen in obesity. The reduction in the levels of the inflammatory mediators TNF-α and MCP-1 [54], the reduced action of TNF-α [52], together with the reduced TLRs levels [54] seen with naringenin treatment point to its anti-inflammatory properties in adipocytes. The increased adipocyte thermogenesis and increased energy expenditure by naringenin treatment [56] is novel and indicates a potential to convert white adipose to brown adipose tissue which is associated with increased insulin sensitivity and anti-diabetic potential [57].
2.3. Effects of Naringenin: In Vitro Hepatocyte Studies
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a structural protein that is an integral component of very-low density lipoprotein (VLDL) and is sequestered in the liver postprandially. However, insulin resistance reduces this sequestering, allowing ApoB to be readily secreted from hepatocytes and drive the formation of VLDLs. HepG2 human hepatoma cells treated with naringenin (10–200 µM) for 24 h had significantly reduced ApoB accumulation and cellular cholesteryl ester mass (Table 3) [58]. In addition, naringenin treatment significantly reduced acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 2 (ACAT2) mRNA levels and microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) levels and activity. Naringenin treatment significantly increased LDL receptor mRNA levels and increased LDL uptake and degradation [58].
Table 3. Effects of naringenin: in vitro hepatocyte studies.
| Cell | Naringenin Concentration/Duration | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2 human hepatoma cells | 10–200 µM, 24 h | ↓ Apo B secretion ↓ ACAT2 mRNA ↓ MTP protein and mRNA ↑ LDL receptor mRNA ↑ LDL uptake ↑ LDL degradation |
[58] |
| HepG2 human hepatoma cells | 200 µM, 6 h | ↓ Apolipoprotein B secretion ↑ SREBP-1 and LDLr expression ↑ PI3K activity |
[59] |
| HepG2 human hepatoma cells | 0–200 µM, 60 min | ↓ Apo B secretion ↑ ERK activity ↓ Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein |
[60] |
| Hepatoma (Fao) cells | 6–100 µM, 6 h | ↓ Glucose production ↓ Cellular ATP levels |
[61] |
| Huh7 hepatocytes and Lewis rat primary hepatocytes | 0–380 µM, 16–24 h | ↓ Triglyceride production ↑ Fatty acid oxidation ↓Trap220/Drip-2 and LBD ↓ LXRα response element ↑ mRNA of CYP4A11, ACOX, UCP1 and ApoAI |
[62] |
| Wistar rat hepatocytes | 300 µM, 30–50 min | ↓ Glucose production ↓ Gluconeogenesis ↓ Pyruvate transport |
[63] |
Apolipoprotein B (Apo B); Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 2 (ACAT2); Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP); Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1); Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K); Cytochrome P450 family 4 A member 11 (CYP4A11); Peroxisomal acyl-CoA oxidase (ACOX).
Treatment of HepG2 cells with naringenin (200 µM) for 7 h resulted in a significant reduction of ApoB secretion [59]. This was accompanied with an increase in HepG2 cell PI3K activity, without an effect on IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation. In addition, naringenin treatment increased sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1) and low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLr) expression in a PI3K-dependent manner (Table 3) [59].
In a follow up study [60] by the same group [59] it was found that the inhibition of ApoB secretion from HepG2 cells by insulin was amplified by naringenin treatment clearly indicating insulin sensitizing effects of naringenin [60]. Importantly, insulin receptor or IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation was not affected, suggesting an effect of naringenin that is independent of the insulin signaling cascade (Table 3) [60].
Exposure of hepatoma (Fao) cells to naringenin for 6 h resulted in dose-dependent suppression of glucose production (Table 3) [61]. Additionally, naringenin did not increase the phosphorylation/activation of Akt (S473) or Akt (T308) indicating that naringenin’s effects are independent of Akt. Naringenin treatment also significantly decreased cellular ATP levels, while not influencing cytotoxicity [61].
Treatment of Huh7 hepatocytes with naringenin (200 µM) for 24 h resulted in reduced triglyceride production [62]. Additionally, naringenin treatment increased fatty acid oxidation, and the mRNA levels of genes involved in fatty acid oxidation (CYP4A11, ACOX, UCP1, ApoAI and PGC1α). Naringenin treatment inhibited the activation of the liver X receptor-α (LXRα) response element in human hepatocytes through the inhibition of the binding of Trap220/Drip-2 co-activator peptide to the LXRα-ligand binding domain (LBD). The interaction of Trap220/Drip-2 to the LXRα-LBD is involved in the transcriptional regulation of genes that control cholesterol efflux and fatty acid biosynthesis. Peroxisome proliferator response element (PPRE) activity was also increased dose-dependently following treatment with naringenin (Table 3) [62].
References
- Sweet, I.R.; Cook, D.L.; DeJulio, E.; Wallen, A.R.; Khalil, G.; Callis, J.; Reems, J. Regulation of ATP/ADP in Pancreatic Islets. Diabetes 2004, 53, 401–409.
- Tripathy, D.; Chavez, A.O. Defects in insulin secretion and action in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2010, 10, 184–191.
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223.
- Saltiel, A.R. New perspectives into the molecular pathogenesis and treatment of type 2 diabetes. Cell 2001, 104, 517–529.
- Alam, M.A.; Subhan, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, S.J.; Reza, H.M.; Sarker, S.D. Effect of citrus flavonoids, naringin and naringenin, on metabolic syndrome and their mechanisms of action. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 404–417.
- DeFronzo, R.A. Dysfunctional fat cells, lipotoxicity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Clin. Pract. Suppl. 2004, 58, 9–21.
- Lee, C.-H.; Olson, P.; Hevener, A.; Mehl, I.; Chong, L.-W.; Olefsky, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Ham, J.; Kang, H.; Peters, J.M.; et al. PPAR regulates glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3444–3449.
- Defronzo, R.A. Banting Lecture. From the triumvirate to the ominous octet: A new paradigm for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2009, 58, 773–795.
- Frigolet, M.E.; Torres, N.; Tovar, A.R. The renin-angiotensin system in adipose tissue and its metabolic consequences during obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 2003–2015.
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha: A key component of the obesity-diabetes link. Diabetes 1994, 43, 1271–1278.
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281.
- Shrestha, S.S.; Zhang, P.; Hora, I.; Geiss, L.S.; Luman, E.T.; Gregg, E.W. Factors Contributing to Increases in Diabetes-Related Preventable Hospitalization Costs Among U.S. Adults During 2001–2014. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 77–84.
- Baur, J.A.; Sinclair, D.A. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2006, 5, 493–506.
- Park, E.-J.; Pezzuto, J.M. The pharmacology of resveratrol in animals and humans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 1071–1113.
- Anja, B.; Laura, R. The cost of diabetes in Canada over 10 years: Applying attributable health care costs to a diabetes incidence prediction model. Health Promot. Chronic Dis. Prev. Can. 2017, 37, 49–53.
- Vieira, A.R.; Abar, L.; Vingeliene, S.; Chan, D.S.M.; Aune, D.; Navarro-Rosenblatt, D.; Stevens, C.; Greenwood, D.; Norat, T. Fruits, vegetables and lung cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 81–96.
- Kuzma, J.N.; Schmidt, K.A.; Kratz, M. Prevention of metabolic diseases: Fruits (including fruit sugars) vs. vegetables. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 286–293.
- Stefan, N.; Häring, H.-U.; Schulze, M.B. Metabolically healthy obesity: The low-hanging fruit in obesity treatment? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 249–258.
- Serino, A.; Salazar, G. Protective Role of Polyphenols against Vascular Inflammation, Aging and Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2018, 11, 53.
- Moore, J.; Yousef, M.; Tsiani, E. Anticancer Effects of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extract and Rosemary Extract Polyphenols. Nutrients 2016, 8, 731.
- Yousef, M.; Vlachogiannis, I.A.; Tsiani, E. Effects of Resveratrol against Lung Cancer: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1231.
- Naimi, M.; Vlavcheski, F.; Shamshoum, H.; Tsiani, E. Rosemary Extract as a Potential Anti-Hyperglycemic Agent: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Nutrients 2017, 9, 968.
- Dreosti, I.E. Antioxidant polyphenols in tea, cocoa, and wine. Nutrition 2000, 16, 692–694.
- Lagouge, M.; Argmann, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Meziane, H.; Lerin, C.; Daussin, F.; Messadeq, N.; Milne, J.; Lambert, P.; Elliott, P.; et al. Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 2006, 127, 1109–1122.
- Amor, S.; Châlons, P.; Aires, V.; Delmas, D. Polyphenol Extracts from Red Wine and Grapevine: Potential Effects on Cancers. Diseases 2018, 6, 106.
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618.
- D’Archivio, M.; Filesi, C.; Di Benedetto, R.; Gargiulo, R.; Giovannini, C.; Masella, R. Polyphenols, dietary sources and bioavailability. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2007, 43, 348–361.
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and Biological Activities of Flavonoids: An Overview. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 162750.
- Erlund, I. Review of the flavonoids quercetin, hesperetin, and naringenin. Dietary sources, bioactivities, bioavailability, and epidemiology. Nutr. Res. 2004, 24, 851–874.
- Gattuso, G.; Barreca, D.; Gargiulli, C.; Leuzzi, U.; Caristi, C. Flavonoid Composition of Citrus Juices. Molecules 2007, 12, 1641–1673.
- Aherne, S.A.; O’Brien, N.M. Dietary flavonols: Chemistry, food content, and metabolism. Nutrition 2002, 18, 75–81.
- Zaidun, N.H.; Thent, Z.C.; Latiff, A.A. Combating oxidative stress disorders with citrus flavonoid: Naringenin. Life Sci. 2018, 208, 111–122.
- Sharma, M.; Akhtar, N.; Sambhav, K.; Shete, G.; Bansal, A.K.; Sharma, S.S. Emerging potential of citrus flavanones as an antioxidant in diabetes and its complications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 187–195.
- Coelho, R.C.L.A.; Hermsdorff, H.H.M.; Bressan, J. Anti-inflammatory properties of orange juice: Possible favorable molecular and metabolic effects. Plant. Foods Hum. Nutr. 2013, 68, 1–10.
- Rani, N.; Bharti, S.; Krishnamurthy, B.; Bhatia, J.; Sharma, C.; Kamal, M.A.; Ojha, S.; Arya, D.S. Pharmacological Properties and Therapeutic Potential of Naringenin: A Citrus Flavonoid of Pharmaceutical Promise. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 4341–4359.
- Zeng, W.; Jin, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Liang, W. Naringenin as a potential immunomodulator in therapeutics. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 135, 122–126.
- Hernández-Aquino, E.; Muriel, P. Beneficial effects of naringenin in liver diseases: Molecular mechanisms. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1679–1707.
- Mulvihill, E.E.; Assini, J.M.; Sutherland, B.G.; DiMattia, A.S.; Khami, M.; Koppes, J.B.; Sawyez, C.G.; Whitman, S.C.; Huff, M.W. Naringenin decreases progression of atherosclerosis by improving dyslipidemia in high-fat-fed low-density lipoprotein receptor-null mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 742–748.
- Orhan, I.E.; Nabavi, S.F.; Daglia, M.; Tenore, G.C.; Mansouri, K.; Nabavi, S.M. Naringenin and atherosclerosis: A review of literature. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 245–251.
- Mulvihill, E.E.; Burke, A.C.; Huff, M.W. Citrus Flavonoids as Regulators of Lipoprotein Metabolism and Atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 275–299.
- Testai, L.; Calderone, V. Nutraceutical Value of Citrus Flavanones and Their Implications in Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 502.
- Assini, J.M.; Mulvihill, E.E.; Huff, M.W. Citrus flavonoids and lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2013, 24, 34–40.
- Kannappan, S.; Anuradha, C.V. Naringenin enhances insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation and improves the cellular actions of insulin in a dietary model of metabolic syndrome. Eur. J. Nutr. 2010, 49, 101–109.
- Kanaze, F.I.; Bounartzi, M.I.; Georgarakis, M.; Niopas, I. Pharmacokinetics of the citrus flavanone aglycones hesperetin and naringenin after single oral administration in human subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 472–477.
- El Mohsen, M.A.; Marks, J.; Kuhnle, G.; Rice-Evans, C.; Moore, K.; Gibson, G.; Debnam, E.; Srai, S.K. The differential tissue distribution of the citrus flavanone naringenin following gastric instillation. Free Radic. Res. 2004, 38, 1329–1340.
- Zygmunt, K.; Faubert, B.; MacNeil, J.; Tsiani, E. Naringenin, a citrus flavonoid, increases muscle cell glucose uptake via AMPK. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 178–183.
- Bhattacharya, S.; Christensen, K.B.; Olsen, L.C.B.; Christensen, L.P.; Grevsen, K.; Færgeman, N.J.; Kristiansen, K.; Young, J.F.; Oksbjerg, N. Bioactive components from flowers of Sambucus nigra L. increase glucose uptake in primary porcine myotube cultures and reduce fat accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11033–11040.
- Mutlur Krishnamoorthy, R.; Carani Venkatraman, A. Polyphenols activate energy sensing network in insulin resistant models. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 275, 95–107.
- Di Meo, S.; Iossa, S.; Venditti, P. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance: Role of mitochondria and other ROS sources. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 233, R15–R42.
- Haber, C.; Lam, T.; Yu, Z.; Gupta, N.; Goh, T.; Bogdanovic, E.; Giacca, A.; Fantus, I. N-acetylcysteine and taurine prevent hyperglycemia-induced insulin resistance in vivo: Possible role of oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, 744–753.
- Harmon, A.W.; Harp, J.B. Differential effects of flavonoids on 3T3-L1 adipogenesis and lipolysis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, C807–C813.
- Yoshida, H.; Takamura, N.; Shuto, T.; Ogata, K.; Tokunaga, J.; Kawai, K.; Kai, H. The citrus flavonoids hesperetin and naringenin block the lipolytic actions of TNF-alpha in mouse adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 728–732.
- Claussnitzer, M.; Skurk, T.; Hauner, H.; Daniel, H.; Rist, M.J. Effect of flavonoids on basal and insulin-stimulated 2-deoxyglucose uptake in adipocytes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55 (Suppl. 1), S26–S34.
- Yoshida, H.; Watanabe, W.; Oomagari, H.; Tsuruta, E.; Shida, M.; Kurokawa, M. Citrus flavonoid naringenin inhibits TLR2 expression in adipocytes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1276–1284.
- Richard, A.J.; Amini-Vaughan, Z.; Ribnicky, D.M.; Stephens, J.M. Naringenin inhibits adipogenesis and reduces insulin sensitivity and adiponectin expression in adipocytes. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 549750.
- Rebello, C.J.; Greenway, F.L.; Lau, F.H.; Lin, Y.; Stephens, J.M.; Johnson, W.D.; Coulter, A.A. Naringenin Promotes Thermogenic Gene Expression in Human White Adipose Tissue. Obesity 2019, 27, 103–111.
- Kaisanlahti, A.; Glumoff, T. Browning of white fat: Agents and implications for beige adipose tissue to type 2 diabetes. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 75, 1–10.
- Wilcox, L.J.; Borradaile, N.M.; de Dreu, L.E.; Huff, M.W. Secretion of hepatocyte apoB is inhibited by the flavonoids, naringenin and hesperetin, via reduced activity and expression of ACAT2 and MTP. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 725–734.
- Borradaile, N.M.; de Dreu, L.E.; Huff, M.W. Inhibition of net HepG2 cell apolipoprotein B secretion by the citrus flavonoid naringenin involves activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, independent of insulin receptor substrate-1 phosphorylation. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2554–2561.
- Allister, E.M.; Mulvihill, E.E.; Barrett, P.H.R.; Edwards, J.Y.; Carter, L.P.; Huff, M.W. Inhibition of apoB secretion from HepG2 cells by insulin is amplified by naringenin, independent of the insulin receptor. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 2218–2229.
- Purushotham, A.; Tian, M.; Belury, M.A. The citrus fruit flavonoid naringenin suppresses hepatic glucose production from Fao hepatoma cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 300–307.
- Goldwasser, J.; Cohen, P.Y.; Yang, E.; Balaguer, P.; Yarmush, M.L.; Nahmias, Y. Transcriptional regulation of human and rat hepatic lipid metabolism by the grapefruit flavonoid naringenin: Role of PPARalpha, PPARgamma and LXRalpha. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12399.
- Constantin, R.P.; Constantin, R.P.; Bracht, A.; Yamamoto, N.S.; Ishii-Iwamoto, E.L.; Constantin, J. Molecular mechanisms of citrus flavanones on hepatic gluconeogenesis. Fitoterapia 2014, 92, 148–162.
More
Information
Subjects:
Medicine, General & Internal
Contributor
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.2K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
14 Jul 2021
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




