
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Julio Galvez | + 2810 word(s) | 2810 | 2021-07-09 05:23:09 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 2810 | 2021-07-13 08:33:42 | | |
Video Upload Options
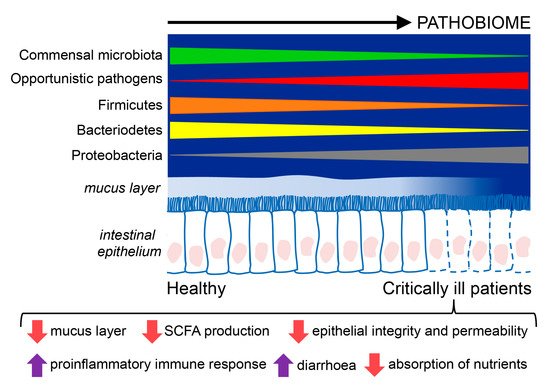
Critically ill patients have an alteration in the microbiome in which it becomes a disease-promoting pathobiome. It is characterized by lower bacterial diversity, loss of commensal phyla, like Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, and a domination of pathogens belonging to the Proteobacteria phylum. Critically ill patients also have a hyperpermeable gut barrier and dysregulation of the inflammatory response that favor the development of the pathobiome, translocation of pathogens, and facilitate the emergence of sepsis.
1. Introduction
2. The Gut Microbiome
3. The Gut Microbiome in Critically Ill Patients
3.1. Changes in the Gut Microbiota in Critically Ill Patients
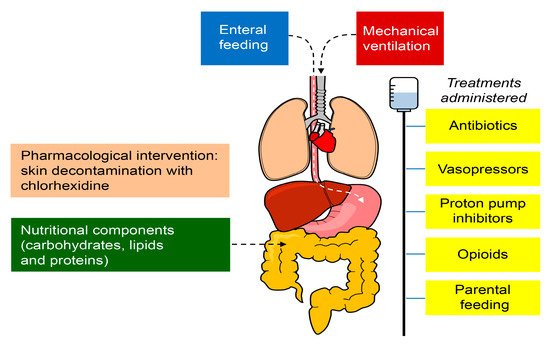
3.2. Modulators of the Microbiome in Critical Illness
3.3. Epithelial Alterations and Intestinal Hyperpermeability in Critically Ill Patients
3.4. Relevance of the Gut Microbiome in Critical Illness
4. Nutrition of the Critically Ill Patient
|
Enteral Nutrition in Special Conditions |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Early EN should be implemented |
Low dose EN should be administered |
EN should be delayed |
|
Patients receiving ECMO |
Patients with therapeutic hypothermia |
Patients with uncontrolled shock (when hemodynamic and tissue perfusion goals are not reached) |
|
Patients with traumatic brain injury |
Patients with intra-abdominal hypertension without abdominal compartment syndrome |
Patients in uncontrolled life-threatening hypoxemia, hypercapnia or acidosis |
|
Patients with stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) |
Patients with acute liver failure |
Patients suffering from active upper gastrointestinal bleeding |
|
Patients with spinal cord injury |
Patients with overt bowel ischemia |
|
|
Patients with severe acute pancreatitis |
Patients with high-output intestinal fistula |
|
|
Patients after gastrointestinal surgery |
Patients with abdominal compartment syndrome |
|
|
Patients after abdominal aortic surgery |
Patients with gastric aspirate volume above 500 mL/6 h. |
|
|
Patients with abdominal trauma while the continuity of the gastrointestinal tract is restored |
||
|
Patients delivery neuromuscular blocking agents |
||
|
Patients managed in prone position |
||
|
Patients with an open abdomen |
||
Note: Recommendations published by the European Society of Intensive Medicine (ESCIM) for the initiation of early enteral nutrition (within 48 h of Intensive Care Unit admission) and recommendations favoring delaying it [53]. EN (enteral nutrition), ECMO (ExtraCorporeal Membrane Oxygenation).
References
- Robertson, L.C.; Al-Haddad, M. Recognizing the critically ill patient. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 14, 11–14.
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The human intestinal microbiome in health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379.
- Rothschild, D.; Weissbrod, O.; Barkan, E.; Kurilshikov, A.; Korem, T.; Zeevi, D.; Costea, P.I.; Godneva, A.; Kalka, I.N.; Bar, N.; et al. Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 2018, 555, 210–215.
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227.
- Wolff, N.S.; Hugenholtz, F.; Wiersinga, W.J. The emerging role of the microbiota in the ICU. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 1–7.
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Solvsten Burgdorf, K.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65.
- Bäckhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-Bacterial Mutualism in the Human Intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920.
- Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; de Vos, W.M. The first 1000 cultured species of the human gastrointestinal microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 996–1047.
- Browne, H.P.; Forster, S.C.; Anonye, B.O.; Kumar, N.; Neville, B.A.; Stares, M.D.; Goulding, D.; Lawley, T.D. Culturing of “unculturable” human microbiota reveals novel taxa and extensive sporulation. Nature 2016, 533, 543–546.
- Blaut, M.; Clavel, T. Metabolic Diversity of the Intestinal Microbiota: Implications for Health and Disease. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 751S–755S.
- Guarner, F. Enteric flora in health and disease. Digestion 2006, 73, 5–12.
- Alverdy, J.C.; Krezalek, M.A. Collapse of the microbiome, emergence of the pathobiome, and the immunopathology of sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 337–347.
- Lankelma, J.M.; van Vught, L.A.; Belzer, C.; Schultz, M.J.; van der Poll, T.; de Vos, W.M.; Wiersinga, W.J. Critically ill patients demonstrate large interpersonal variation in intestinal microbiota dysregulation: A pilot study. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 59–68.
- McDonald, D.; Ackermann, G.; Khailova, L.; Baird, C.; Heyland, D.; Kozar, R.; Lemieux, M.; Derenski, K.; King, J.; Vis-Kampen, C.; et al. Extreme Dysbiosis of the Microbiome in Critical Illness. mSphere 2016, 1, e00199-16.
- Wischmeyer, P.E.; McDonald, D.; Knight, R. Role of the microbiome, probiotics, and “dysbiosis therapy” in critical illness. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2016, 22, 347–353.
- Ojima, M.; Motooka, D.; Shimizu, K.; Gotoh, K.; Shintani, A.; Yoshiya, K.; Nakamura, S.; Ogura, H.; Iida, T.; Shimazu, T. Metagenomic Analysis Reveals Dynamic Changes of Whole Gut Microbiota in the Acute Phase of Intensive Care Unit Patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1628–1634.
- Defazio, J.; Fleming, I.D.; Shakhsheer, B.; Zaborina, O.; Alverdy, J.C. The opposing forces of the intestinal microbiome and the emerging pathobiome. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 94, 1151–1161.
- Yeh, A.; Rogers, M.B.; Firek, B.; Neal, M.D.; Zuckerbraun, B.S.; Morowitz, M.J. Dysbiosis Across Multiple Body Sites in Critically Ill Adult Surgical Patients. Shock 2016, 46, 649–654.
- Zaborin, A.; Smith, D.; Garfield, K.; Quensen, J.; Shakhsheer, B.; Kade, M.; Tirrell, M.; Tiedje, J.; Gilbert, J.A.; Zaborina, O.; et al. Membership and behavior of ultra-low-diversity pathogen communities present in the gut of humans during prolonged critical illness. mBio 2014, 5, e01361-14.
- Taur, Y.; Jenq, R.R.; Perales, M.-A.; Littmann, E.R.; Morjaria, S.; Ling, L.; No, D.; Gobourne, A.; Viale, A.; Dahi, P.B.; et al. The effects of intestinal tract bacterial diversity on mortality following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2014, 124, 1174–1182.
- Shimizu, K.; Ogura, H.; Hamasaki, T.; Goto, M.; Tasaki, O.; Asahara, T.; Nomoto, K.; Morotomi, M.; Matsushima, A.; Kuwagata, Y.; et al. Altered Gut Flora Are Associated with Septic Complications and Death in Critically Ill Patients with Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 1171–1177.
- Jung, E.; Byun, S.; Lee, H.; Moon, S.Y.; Lee, H. Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus colonization in the intensive care unit: Clinical outcomes and attributable costs of hospitalization. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 1062–1066.
- Taur, Y.; Xavier, J.B.; Lipuma, L.; Ubeda, C.; Goldberg, J.; Gobourne, A.; Lee, Y.J.; Dubin, K.A.; Socci, N.D.; Viale, A.; et al. Intestinal Domination and the Risk of Bacteremia in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 905–914.
- Freedberg, D.E.; Zhou, M.J.; Cohen, M.E.; Annavajhala, M.K.; Khan, S.; Moscoso, D.I.; Brooks, C.; Whittier, S.; Chong, D.H.; Uhlemann, A.-C.; et al. Pathogen colonization of the gastrointestinal microbiome at intensive care unit admission and risk for subsequent death or infection. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 44, 1203–1211.
- Pamer, E.G. Resurrecting the intestinal microbiota to combat antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Science 2016, 352, 535–538.
- Schuijt, T.J.; Lankelma, J.M.; Scicluna, B.P.; De Sousa e Melo, F.; Roelofs, J.J.T.H.; De Boer, J.D.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; De Beer, R.; De Vos, A.; Belzer, C.; et al. The gut microbiota plays a protective role in the host defence against pneumococcal pneumonia. Gut 2016, 65, 575–583.
- Dickson, R.P.; Singer, B.H.; Newstead, M.W.; Falkowski, N.R.; Erb-Downward, J.R.; Standiford, T.J.; Huffnagle, G.B. Enrichment of the lung microbiome with gut bacteria in sepsis and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 1–21.
- Meng, J.; Banerjee, S.; Li, D.; Sindberg, G.M.; Wang, F.; Ma, J.; Roy, S. Opioid exacerbation of gram-positive sepsis, induced by gut microbial modulation, is rescued by IL-17A neutralization. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–17.
- Otani, S.; Chihade, D.B.; Coopersmith, C.M. Critical illness and the role of the microbiome. Acute Med. Surg. 2019, 6, 91–94.
- Alverdy, J.C.; Luo, J.N. The influence of host stress on the mechanism of infection: Lost microbiomes, emergent pathobiomes, and the role of interkingdom signaling. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 322.
- Modi, S.R.; Collins, J.J.; Relman, D.A. Antibiotics and the gut microbiota. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4212–4218.
- Davison, J.M.; Wischmeyer, P.E. Probiotic and synbiotic therapy in the critically ill: State of the art. Nutrition 2019, 59, 29–36.
- Banaei, N.; Anikst, V.; Schroeder, L.F. Burden of Clostridium difficile infection in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2368–2369.
- Rello, J.; Quintana, E.; Ausina, V.; Net, A.; Prats, G. A three-year study of severe community-acquired pneumonia with emphasis on outcome. Chest 1993, 103, 232–235.
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108.
- Hildebrandt, M.A.; Hoffmann, C.; Keilbaugh, S.U.E.A.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.O.B.; Ahima, R.S.; Bushman, F.; Wu, G.D. Basic—alimentary tract. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1716–1724.
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563.
- Morowitz, M.J.; Carlisle, E.M.; Alverdy, J.C. Contributions of Intestinal Bacteria to Nutrition and Metabolism in the Critically Ill. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 91, 771–785.
- Rupani, B.; Caputo, F.J.; Watkins, A.C.; Vega, D.; Magnotti, L.J.; Lu, Q.; Xu, D.Z.; Deitch, E.A. Relationship between disruption of the unstirred mucus layer and intestinal restitution in loss of gut barrier function after trauma hemorrhagic shock. Surgery 2007, 141, 481–489.
- Fink, M.P. Intestinal epithelial hyperpermeability: Update on the pathogenesis of gut mucosal barrier dysfunction in critical illness. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2003, 9, 143–151.
- Qin, X.; Caputo, F.J.; Xu, D.Z.; Deitch, E.A. Hydrophobicity of mucosal surface and its relationship to gut barrier function. Shock 2008, 29, 372–376.
- McKenney, P.T.; Pamer, E.G. From Hype to Hope: The Gut Microbiota in Enteric Infectious Disease. Cell 2015, 163, 1326–1332.
- Yamada, T.; Shimizu, K.; Ogura, H.; Asahara, T.; Nomoto, K.; Yamakawa, K.; Hamasaki, T.; Nakahori, Y.; Ohnishi, M.; Kuwagata, Y.; et al. Rapid and Sustained Long-Term Decrease of Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Critically Ill Patients With Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 569–577.
- Mathewson, N.D.; Jenq, R.; Mathew, A.V.; Koenigsknecht, M.; Hanash, A.; Toubai, T.; Oravecz-Wilson, K.; Wu, S.-R.; Sun, Y.; Rossi, C.; et al. Gut microbiome–derived metabolites modulate intestinal epithelial cell damage and mitigate graft-versus-host disease. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 505–513.
- Hand, T.W. The Role of the Microbiota in Shaping Infectious Immunity. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 647–658.
- Hill, D.A.; Hoffmann, C.; Abt, M.C.; Du, Y.; Kobuley, D.; Kirn, T.J.; Bushman, F.D.; Artis, D. Metagenomic analyses reveal antibiotic-induced temporal and spatial changes in intestinal microbiota with associated alterations in immune cell homeostasis. Mucosal Immunol. 2010, 3, 148–158.
- Ferreyra, J.A.; Ng, K.M.; Sonnenburg, J.L. The enteric two-step: Nutritional strategies of bacterial pathogens within the gut. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 993–1003.
- Deshmukh, H.S.; Liu, Y.; Menkiti, O.R.; Mei, J.; Dai, N.; O’Leary, C.E.; Oliver, P.M.; Kolls, J.K.; Weiser, J.N.; Worthen, G.S. The microbiota regulates neutrophil homeostasis and host resistance to Escherichia coli K1 sepsis in neonatal mice. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 524–530.
- Lankelma, J.M.; Birnie, E.; Weehuizen, T.A.F.; Scicluna, B.P.; Belzer, C.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Roelofs, J.J.T.H.; de Vos, A.F.; van der Poll, T.; Budding, A.E.; et al. The gut microbiota as a modulator of innate immunity during melioidosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, 1–18.
- Singer, P.; Blaser, A.R.; Berger, M.M.; Alhazzani, W.; Calder, P.C.; Casaer, M.P.; Hiesmayr, M.; Mayer, K.; Montejo, J.C.; Pichard, C.; et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in the intensive care unit. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 48–79.
- Briassoulis, G.; Briassoulis, P.; Ilia, S. Nutrition Is More Than the Sum of Its Parts. Pediatric Crit. Care Med. 2018, 19, 1087–1089.
- Kenneth, B.C.M. Nutritional metabolomics in critical illness. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2018, 21, 121–125.
- Wernerman, J.; Christopher, K.B.; Annane, D.; Casaer, M.P.; Coopersmith, C.M.; Deane, A.M.; De Waele, E.; Elke, G.; Ichai, C.; Karvellas, C.J.; et al. Metabolic support in the critically ill: A consensus of 19. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 318.
- Briassoulis, G.; Briassoulis, P.; Ilia, S. If You Get Good Nutrition, You Will Become Happy; If You Get a Bad One, You Will Become an ICU Philosopher. Pediatric Crit. Care Med. 2019, 20, 89–90.
- Levesque, C.L.; Turner, J.; Li, J.; Wizzard, P.; St Pierre, B.; Lim, D.; Wales, P. In a Neonatal Piglet Model of Intestinal Failure, Administration of Antibiotics and Lack of Enteral Nutrition Have a Greater Impact on Intestinal Microflora Than Surgical Resection Alone. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 938–945.
- Ralls, M.W.; Demehri, F.R.; Feng, Y.; Woods Ignatoski, K.M.; Teitelbaum, D.H. Enteral nutrient deprivation in patients leads to a loss of intestinal epithelial barrier function. Surgery 2015, 157, 732–742.
- Schörghuber, M.; Fruhwald, S. Effects of enteral nutrition on gastrointestinal function in patients who are critically ill. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 281–287.
- Reintam Blaser, A.; Starkopf, J.; Alhazzani, W.; Berger, M.M.; Casaer, M.P.; Deane, A.M.; Fruhwald, S.; Hiesmayr, M.; Ichai, C.; Jakob, S.M.; et al. Early enteral nutrition in critically ill patients: ESICM clinical practice guidelines. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 380–398.




