
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | yoshiyasu takefuji | + 3722 word(s) | 3722 | 2021-05-26 04:36:07 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 3722 | 2021-05-31 10:14:27 | | | | |
| 3 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 3722 | 2021-06-23 08:55:09 | | |
Video Upload Options
Molecular hydrogen (H2) has the potential to be a radioprotective agent because it can selectively scavenge •OH, a reactive oxygen species with strong oxidizing power. Animal experiments and clinical trials have reported that H2 exhibits a highly safe radioprotective effect.
1. Introduction
2. Biological Effects of Radiation
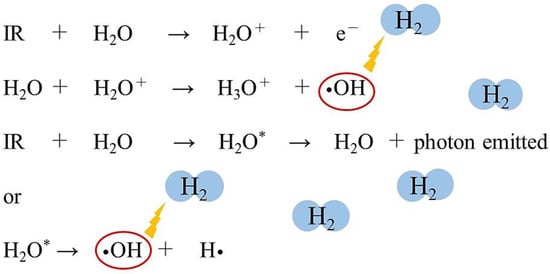
3. Radioprotective Effects of H2 in Animal Models
|
Damages/Damage Models |
Species/Cells |
Effects of H2 |
Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cell-free system |
•OH is produced by the Fenton reaction and water radiolysis, and it was reduced by H2. |
[48] |
|
|
Cognitive impairment |
Rats |
Radiation-induced cognitive dysfunction was protected by H2-rich water. |
[36] |
|
Immune dysfunction |
AHH-1 cells |
Pretreatment with H2-rich PBS prior to radiation reduced the levels of MDA and 8-OHdG. |
[37] |
|
AHH-1 cells |
Pretreatment with H2-rich saline increased the viability of AHH-1 cells and inhibited apoptosis. |
[38] |
|
|
AHH-1 cells |
Pretreatment with H2-rich medium reduced •OH induced by radiation. |
[39] |
|
|
Mice |
H2-rich saline protected immunocytes from radiation-induced apoptosis. |
[39] |
|
|
Mice |
H2-rich saline protected against radiation-induced immune dysfunction. |
[40] |
|
|
Lung damage |
A549 cells |
H2-rich PBS suppressed ROS production, and improved oxidative stress and apoptosis markers. |
[41] |
|
Mice |
H2 gas inhibited not only acute lung damage, but also chronic lung damage. |
[41] |
|
|
Myocardial damage |
Mice |
H2-rich water protected against radiation-induced myocardium damage. |
[42] |
|
Rats |
H2-rich water protected against radiation-induced myocardium damage. |
[43] |
|
|
Gastrointestinal damage |
HIEC |
H2-rich PBS inhibited apoptosis and increased the cell viability of HIEC. |
[37] |
|
Mice |
H2-rich saline protected against radiation-induced gastrointestinal disorders. |
[38] |
|
|
Mice |
H2 water ameliorated radiation-induced gastrointestinal toxicity. |
[44] |
|
|
IEC-6 cells |
H2-rich medium improved survival and inhibited ROS production. |
[45] |
|
|
Mice |
H2-rich saline improved mouse survival and intestinal mucosal damage and function. |
[45] |
|
|
Hematopoietic cell injury |
Mice |
H2-rich water ameliorated radiation-induced hematopoietic stem cell injury. |
[46] |
|
Spermatogenesis and hematopoiesis disorders |
Mice |
H2-rich saline protected spermatogenesis and hematopoietic functions of irradiated mice. |
[47] |
|
Testicular damage |
Rats |
H2-rich saline protected against radiation-induced testicular damage. |
[49] |
|
Skin damage |
HaCaT cells |
H2-rich medium protected HaCaT cells from radiation injury by improving the survival rate. |
[50] |
|
Rats |
H2-rich saline reduced the severity of dermatitis, accelerated tissue recovery, and inhibited weight loss. |
[50] |
|
|
Rats |
Prior inhalation of H2 gas mitigated radiation-induced skin damage. |
[51] |
|
|
Rats |
H2-rich water promoted wound healing in radiation-induced skin lesions. |
[52] |
|
|
Cartilage damage |
BMSC |
H2-rich medium increased cell viability and differentiation potential. |
[53] |
|
Rats |
H2-rich saline protected against the osteonecrosis of jaw cartilage induced by radiation. |
[53] |
|
|
Thymic lymphoma |
Mice |
H2-rich saline protected against radiation-induced thymic lymphoma. |
[54] |
|
Impaired QOL |
Humans |
H2-rich water improved side effects of poor QOL by radiation therapy. |
[23] |
|
Bone marrow damage |
Humans |
H2 gas inhalation protected bone marrow damage in cancer patients receiving IMRT. |
H2: molecular hydrogen; •OH: hydroxy radical; AHH-1: human lymphocyte cell; MDA: malondialdehyde; 8-OHdG: 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine; ROS: reactive oxygen species; HIEC: human intestinal crypt cell; IEC-6: intestinal crypt epithelial cell; HaCaT: human keratinocyte cell; BMSC: marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell; QOL: quality of life; IMRT: intensity-modulated radiation therapy; Ref.: references.
4. Radioprotective Effects of H2 in Humans
4.1. Improvement of Decreased QOL in Cancer Treatment
4.2. Improvement of Bone Marrow Damage in Cancer Treatment
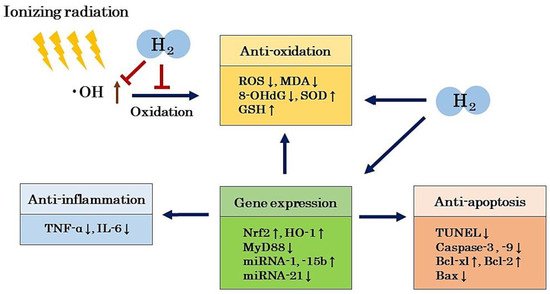
5. Mechanism of the Radioprotective Effects of H2
5.1. Antioxidant Effects
5.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
5.3. Anti-Apoptotic Effects
5.4. Regulation of Gene Expression
References
- Fischer-Valuck, B.W.; Rao, Y.J.; Michalski, J.M. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2018, 7, 297–307.
- Shao, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, D. Hematopoietic stem cell injury induced by ionizing radiation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1447–1462.
- Ward, J.F. DNA damage produced by ionizing radiation in mammalian cells: Identities, mechanisms of formation, and reparability. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1988, 35, 95–125.
- Caer, S.L. Water radiolysis: Influence of oxide surfaces on H2 production under ionizing radiation. Water 2011, 3, 235–253.
- Nickoloff, J.A.; Sharma, N.; Taylor, L. Clustered DNA double-strand breaks: Biological effects and relevance to cancer radiotherapy. Gene 2020, 11, 99.
- Dole, M.; Wilson, F.R.; Fife, W.P. Hyperbaric hydrogen therapy: A possible treatment for cancer. Science 1975, 190, 152–154.
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.I.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694.
- Yanagihara, T.; Arai, K.; Miyamae, K.; Sato, B.; Shudo, T.; Yamada, M.; Aoyama, M. Electrolyzed hydrogen-saturated water for drinking use elicits an antioxidative effect; a feeding test with rats. Biosci. Biotrechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 1985–1987.
- Hirano, S.I.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kurokawa, R.; Takefuji, Y.; Satoh, F. A “philosophical molecule,” hydrogen may overcome senescence and intractable diseases. Med. Gas Res. 2020, 10, 47–49.
- Hirano, S.i.; Ichikawa, Y.; Sato, B.; Satoh, F.; Takefuji, Y. Hydrogen is promising for medical applications. Clean. Technol. 2020, 2, 33.
- Sato, T.; Kinoshita, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Ito, M.; Nishida, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Saitoh, D.; Seki, S.; Mukai, Y. Treatment of irradiated mice with high-dose ascorbic acid reduced lethality. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117020.
- Drouet, M.; Mourcin, F.; Grenier, N.; Leroux, V.; Denis, J.; Mayol, J.F.; Thullier, P.; Lataillade, J.J.; Herodin, F. Single administration of stem cell factor, FLT-3 ligand, megakaryocyte growth and development factor, and ineterleukin-3 in combination soon after irradiation prevents nonhuman primates from myelosuppression: Long-term follow-up of hematopoiesis. Blood 2004, 103, 878–885.
- Farese, A.M.; Casey, D.B.; Smith, W.G.; Vigneulle, R.M.; McKearn, J.P.; MacVittie, T. Leridistim, a chimeric dual G-CSF and IL-3 receptor agonist, enhances multilineage hematopoietic recovery in a nonhuman primate model of radiation-induced myelosuppression: Effect of schedule, dose, and route of administration. Stem Cells 2001, 19, 522–533.
- Herodin, F.; Bourin, P.; Mayol, J.F.; Lataillade, J.J.; Drouet, M. Short-term injection of antiapoptotic cytokine combinations soon after lethal gamma-irradiation promotes survival. Blood 2003, 101, 2609–2616.
- MacVittie, T.J.; Farese, A.M.; Smith, W.G.; Baum, C.M.; Burton, E.; McKearn, J.P. Myelopoietin, an engineered chimeric IL-3 and G-CSF receptor agonist, stimulates multilineage hematopoietic recovery in a nonhuman primate model of radiation-induced myelosuppression. Blood 2000, 95, 837–845.
- Nuszkiewicz, J.; Wanzniak, A.; Szewezyk-Golec, K. Inonizing radiation as a source of oxidative stress-The protective role of melatonin and Vitamin D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5804.
- Seed, T.M.; Fry, S.A.; Neta, R.; Weiss, J.W.; Jarrett, D.G.; Thomassen, D. Prevention and treatments: Summary statement. Milit. Med. 2002, 167, 87–93.
- Thorstad, W.I.; Haughey, B.; Chao, K.S.-C. Pilot study of subcutaneous amifostine in patients undergoing postoperative intensity modulated radiation therapy for head and neck cancer: Preliminary data. Semin. Oncol. 2003, 30, 96–100.
- Seed, T.M.; Inal, C.E.; Singh, V.K. Radioprotection of hematopoietic progenitors by low dose amifostine prophylaxis. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2014, 90, 594–604.
- Mishra, K.; Alsbeih, G. Appraised of biochemical classes of radioprotectors: Evidence, current status and guidelines for future development. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 292.
- Huang, B.; He, T.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yao, Y.; Tang, H.; Gong, P. Amifostine suppresses the side effects of radiation on BMSCs by promoting cell proliferation and reducing ROS production. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 8749090.
- Mertsch, K.; Grune, T.; Kunstmann, S.; Wiesner, B.; Ladhoff, A.M.; Siems, W.G.; Haseloff, R.F.; Blasig, I.E. Protective effects of the thiophosphate amifostine (WR2721) and a lazaroid (U83836E) on lipid peroxidation in endothelial cells during hypoxia/reoxygenation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 56, 945–954.
- Kang, K.M.; Kang, Y.N.; Choi, I.B.; Gu, Y.; Kawamura, T.; Toyoda, Y.; Nakao, A. Effects of drinking hydrogen-rich water on the quality of life of patients treated with radiotherapy for liver tumors. Med. Gas Res. 2011, 1, 11.
- Hirano, S.i.; Aoki, Y.; Li, X.K.; Ichimaru, N.; Takahara, S.; Takefuji, Y. Protective Effects of Hydrogen Gas Inhalation on Radiation-Induced Bone Marrow Damage in Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study. 2020. Available online: (accessed on 22 March 2021).
- Hirano, S.i.; Aoki, Y.; Li, X.K.; Ichimaru, N.; Takahara, S.; Takefuji, Y. Protective effects of hydrogen gas inhalation on radiation-induced bone marrow damage in cancer patients: A retrospective observational study. Med. Gas Res. 2021, 11, in press.
- Qian, L.; Shen, J.; Chuai, Y.; Cai, J. Hydrogen as a new class of radioprotective agent. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 887–894.
- Hu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, W.; Deng, Y.; Shao, A. Molecular hydrogen: A potential radioprotective agent. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110589.
- Kasai, H. Analysis of a form of oxidative DNA damage, 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, as a marker of cellular oxidative stress during carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. 1997, 387, 147–163.
- Floyd, R.A. The role of 8-hydroxyguanine in carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 1990, 11, 1447–1450.
- Pohl, L.R. An immunochemical approach of identifying and characterizing protein targets of toxic reactive metabolites. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1993, 6, 786–793.
- Dubner, D.; Gisone, P.; Jaitovich, I.; Perez, M. Free radicals production and estimation of oxidative stress related to gamma irradiation. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1995, 47, 265–270.
- Verma, S.P.; Sonwalkar, N. Structural changes in plasma membranes prepared from irradiated Chinese hamster V79 cells as revealed by Raman spectroscopy. Radiat. Res. 1991, 126, 27–35.
- Xu, W.L.; Aikeremu, D.; Sun, J.G.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xu, J.B.; Zhou, W.Z.; Zhao, X.B.; Wang, H.; Yuan, H. Effect of intensity-modulated radiation therapy on sciatic nerve injury caused by echinococcosis. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 580–586.
- Tesei, A.; Arienti, C.; Bossi, G.; Santi, S.; Santis, I.D.; Bevilacqua, A.; Zanoni, M.; Pignatta, S.; Cortesi, M.; Zamagni, A.; et al. TP53 drives abscopal effects by secretion of senescence-associated molecular signals in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 89.
- Peng, Q.; Weng, K.; Li, S.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y. A perspective of epigenetic regulation in radiotherapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 624312.
- Liu, M.; Yuan, H.; Yin, J.; Wang, R.; Song, J.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Qin, X. Effect of hydrogen rich water on radiation-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats. Radiat. Res. 2020, 193, 16–23.
- Qian, L.; Li, B.; Cao, F.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Cai, J.; Gao, F. Hydrogen-rich PBS protects cultured human cells from ionizing radiation-induced cellular damage. Nucl. Technol. Radiat. Prot. 2010, 25, 23–29.
- Qian, L.; Cao, F.; Cui, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Cai, J. Radioprotective effect of hydrogen in cultured cells and mice. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 275–282.
- Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, C.; Chuai, Y.; Lei, J.; Gao, F.; Cui, J.; Sun, D.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, C.; et al. Hydrogen-rich saline protects immunocytes from radiation-induced apoptosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2012, 18, BR144–BR148.
- Zhao, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Xuan, Z.; Wu, S.; Yu, S.; Mei, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Cai, J.; et al. Protective effect of hydrogen-rich saline against radiation-induced immune dysfunction. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 938–946.
- Terasaki, Y.; Ohsawa, I.; Terasaki, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kunugi, S.; Dedong, K.; Urushiyama, H.; Anemori, S.; Kaneko-Togashi, M.; Kuwahara, N.; et al. Hydrogen therapy attenuates irradiation-induced lung damage by reducing oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 301, L415–L426.
- Qian, L.; Cao, F.; Cui, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chuai, Y.; Zaho, L.; Jiang, H.; Cai, J. The potential cardioprotective effects of hydrogen in irradiated mice. J. Radiat. Res. 2010, 51, 741–747.
- Kura, B.; Kalocayova, B.; LeBaron, T.W.; Frimmel, K.; Buday, J.; Surovy, J.; Slezak, J. Regulation of microRNAs by molecular hydrogen contributes to the prevention of radiation-induced damage in the rat myocardium. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 457, 61–72.
- Xiao, H.W.; Li, Y.; Dan, L.; Dong, J.L.; Zhou, L.X.; Zhao, S.Y.; Zheng, Q.S.; Wang, H.C.; Cui, M.; Fan, S.J. Hydrogen water ameliorates radiation-induced gastrointestinal toxicity via MyD88′s effects on the gut microbiota. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, e433.
- Qiu, X.; Dong, K.; Guan, J.; He, J. Hydrogen attenuates radiation-induced intestinal damage by reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106517.
- Zhang, J.; Xue, X.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Li, D.; Fan, S. Hydrogen-rich water ameliorates total body irradiation-induced hematopoietic stem cell injury by reducing hydroxyl radical. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 3, 8241678.
- Cauai, Y.; Shen, J.; Qian, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Gao, F.; Cui, J.; Ni, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, S.; et al. Hydrogen-rich saline protects spermatogenesis and hematopoiesis in irradiated BALB/c mice. Med. Sci. Monit. 2012, 18, BR89–BR94.
- Chuai, Y.; Gao, F.; Li, B.; Zhao, L.; Qian, L.; Cao, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Cui, J. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates radiation-induced male germ cell loss in mice through reducing hydroxyl radicals. Biochem. J. 2012, 442, 49–56.
- Jiang, Z.; Xu, B.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, D. Protection by hydrogen against gamma ray-induced testicular damage in rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 112, 186–191.
- Mei, K.; Zhao, S.; Qian, L.; Li, B.; Ni, J.; Cai, J. Hydrogen protects rats from dermatitis caused by local radiation. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2014, 25, 182–188.
- Watanabe, S.; Fujita, M.; Ishihara, M.; Tachibana, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kaji, T.; Kawauchi, T.; Kanatani, Y. Protective effect of inhalation of hydrogen gas on radiation-induced dermatitis and skin injury in rats. J. Radiat. Res. 2014, 55, 1107–1113.
- Zhou, P.; Lin, B.; Wang, P.; Pan, T.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Cheng, S.; Liu, S. The healing effect of hydrogen-rich water on acute radiation-induced skin injury in rats. J. Radiat. Res. 2019, 60, 17–22.
- Chen, Y.; Zong, C.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, B.; Tian, L. A study on the protective effect of molecular hydrogen on osteoradionecrosis of the jaw in rats. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 49, 1648–1654.
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, J.; Gao, F.; Li, B.; Chuai, Y.; Liu, C.; Cai, J. Hydrogen protects mice from radiation induced thymic lymphoma in BALB/c mice. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 297–300.
- NERL Data. Radiation Chemistry Data Center, Notre Dame Radiation Laboratory (n.d.). 2011. Available online: (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Yahyapour, R.; Amini, R.; Rezapour, S.; Cheki, M.; Rezaeyan, A.; Farhood, B.; Shabeeb, D.; Musa, A.E.; Faiiah, H.; Najafi, M. Radiation-induced inflammation and autoimmune disease. Millit. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 9.
- Hirano, S.i.; Ichikawa, Y.; Sato, B.; Yamamoto, H.; Takefuji, Y.; Satoh, F. Potential therapeutic application of hydrogen in chronic inflammatory diseases: Possible inhibiting role on mitochondrial stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2549.
- Li, S.W.; Takahara, T.; Que, W.; Fujino, M.; Guo, W.Z.; Hirano, S.I.; Ye, L.P.; Li, X.K. Hydrogen-rich water protects liver injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through HO-1 enhancement via IL-10 and Sirt 1 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G450–G463.
- Xie, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, H. Hydrogen attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by NRF2 mediated NLRP3 pathway inactivation. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 69, 697–710.
- Xie, K.; Wang, Y.; Yin, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Mao, X.; Wang, G. Hydrogen gas alleviates sepsis-induced brain injury by improving mitochondrial biogenesis through the activation of PGC-α in mice. Shock 2021, 55, 100–109.




