
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Guendalina Zuccari | + 2814 word(s) | 2814 | 2020-05-26 12:47:50 | | | |
| 2 | Catherine Yang | -1361 word(s) | 1453 | 2020-05-29 05:14:31 | | | | |
| 3 | Catherine Yang | -66 word(s) | 1387 | 2020-10-28 04:45:39 | | |
Video Upload Options
Ellagic acid, a polyphenolic compound present in fruit and berries, has recently been the object of extensive research for its antioxidant activity, which might be useful for the prevention and treatment of cancer, cardiovascular pathologies, and neurodegenerative disorders. Its protective role justifies numerous attempts to include it in functional food preparations and in dietary supplements, and not only to limit the unpleasant collateral effects of chemotherapy. However, ellagic acid use as a chemopreventive agent has been debated because of its poor bioavailability associated with low solubility, limited permeability, first pass effect, and interindividual variability in gut microbial transformations. To overcome these drawbacks, various strategies for oral administration including solid dispersions, micro and nanoparticles, inclusion complexes, self-emulsifying systems, and polymorphs were proposed. Here, we listed an updated description of pursued micro and nanotechnological approaches focusing on the fabrication processes and the features of the obtained products, as well as on the positive results yielded by in vitro and in vivo studies in comparison to the raw material. The micro and nanosized formulations here described might be exploited for pharmaceutical delivery of this active, as well as for the production of nutritional supplements or for the enrichment of novel foods.
Introduction
Pomegranate, Punica granatum, is well-known as a traditional medicinal fruit mentioned in the Old Testament of the Bible, the Qur’an, the Jewish Torah, and the Babylonian Talmud as a sacred fruit harbinger of fertility, abundance, and luck. Historically and currently, pomegranate has been used for various purposes [1]. The bioactive compound mainly responsible for the health effects of pomegranate is ellagic acid (EA), as it represents one of the most potent dietary antioxidants.
EA is a polyphenol compound which derives from ellagitannins (ET), a family of molecules in which hexahydroxydyphenic acid residues are esterified with glucose or quinic acid. Following a hydrolytic process, the hexahydroxydyphenic acid group is released, dehydrates and spontaneously lactonizes, forming EA. Punicalagin isomers are the most representative of total tannins extracted from pomegranate (Figure 1).
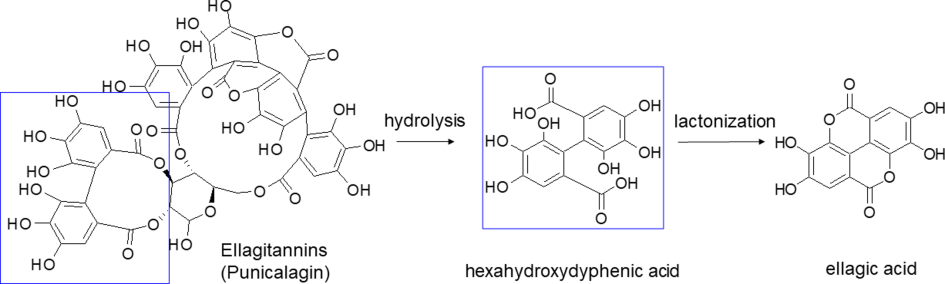
Figure 1. Hydrolysis of punicalagin (a pomegranate ellagitannin) to produce ellagic acid.
Present also in a large variety of tropical fruit, nuts, berries (strawberries, raspberries, blackberries, cranberries, goji berries) and in a type of edible mushroom (Fistulina epatica), EA has recently attracted deep interest, since many research studies showed the role of oxidative stress in different pathologic conditions such as cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and autoimmune diseases, obesity, and neurodegenerative disorders [2][3][4][5][6][7]. In this regard, EA may be a useful adjunct in Parkinson’s disease treatment, as it proved to protect dopamine from oxidation and, by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, to exert a neuroprotective effect [8]. Besides being able to reduce the pathological levels of NF-kB, EA may play a beneficial role in diseases associated with CNS inflammation, such as multiple sclerosis. EA has also been proposed as antidepressant and anxiolytic drug for its capability to modulate the monoaminergic system and to increase the endogenous levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factors [6]. In the last decade, several studies investigated EA effects on many types of cancer, showing its ability to arrest cell cycle progression, modulate pathways linked to cell viability, and inhibit angiogenesis via inactivating metalloproteinases [9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17][18]. For example, EA resulted in inducing apoptosis and modulating gene expression in different colon cancer cell lines at the concentrations achievable in the intestinal lumen from the diet, suggesting a potential role in cancer chemoprevention [19]. Moreover, EA may counterbalance the dangerous side effects of antitumoral drugs such as cisplatin, doxorubicin, and cyclosporine [20][21][22]. In addition, EA proved to possess antimicrobial properties inhibiting the growth of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella [23]. These properties were explained through the ability of EA of either coupling with proteins of the bacterial wall or inhibiting gyrase activity, which cleaves the DNA strand during bacterial replication. Furthermore, EA seemed to counteract the HIV-1 virus replication, by binding envelope proteins and inhibiting reverse transcriptase [24]. Pomegranate extract has been traditionally used for treating gastrointestinal bleeding and various types of wounds, due to EA’s ability to promote blood coagulation by the activation of the Hageman factor (Factor XII) [25]. Moreover, preliminary results suggest potential anti-inflammatory properties [26][27] and an important role in prevention of cardiovascular diseases [28][29][30]. Finally, EA finds application also in cosmetic and nutraceutical industries, mainly for antiaging and prophylactic purposes respectively [31][32][33]. An overview of EA activities is shown in Figure 2.
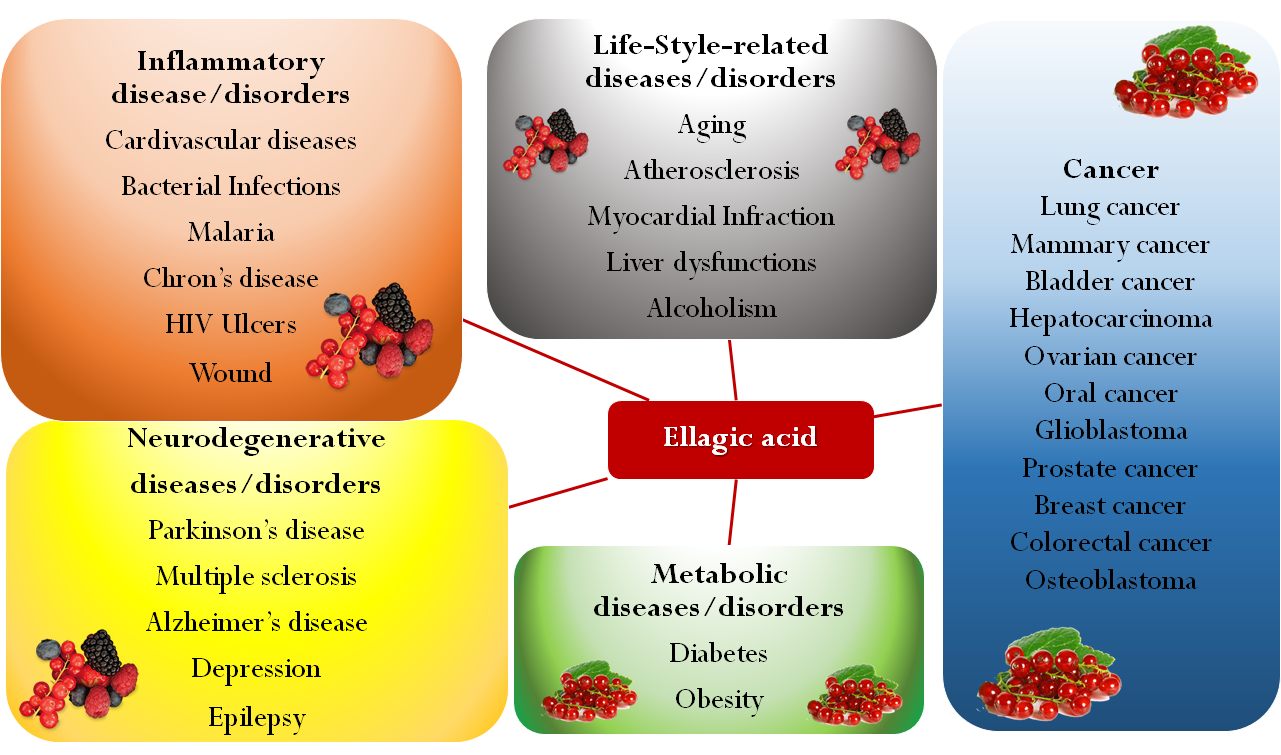
Figure 2. An overview of different ellagic acid’s activities versus human diseases.
However, though EA has the potential to become an efficacious agent in the prevention and therapy of several diseases, as supported by several papers present in the literature, the working efficacy of EA dietary and therapeutic formulations have been mainly examined at preclinical level. To date, few clinical studies have been performed to evaluate EA beneficial effects in humans, with often a limited number of patients, and most of them concern the administration of pomegranate juice or extract in cancer patient diet or deal with the evaluation of the enhancement of cognitive/functional recovery after stroke [34][35]. It was suggested that EA’S low water solubility and rapid metabolism might hinder the progress towards translational research. In our opinion, further studies focused on the application of micro and nanotechnology could provide more encouraging data, opening the path to new strategies able to overcome EA’s poor biopharmaceutical characteristics. Hence, the goal of this review is to provide to scientists, embarking on the research involving EA, a scenario of all pursued formulation attempts. Therefore, starting from a description of EA bioavailability and solubility, a summary of micro and nanosystem-based strategies suitable for improving orally administered EA efficacy is provided.
EA Chemical Structure and Solubility
EA is a chromene-dione derivative (2,3,7,8-tetrahydroxy-chromeno [5,4,3-cde]chromene-5,10-dione), encompassing both a hydrophilic moiety with 4 hydroxyl groups and 2 lactone groups, and a planar lipophilic moiety with 2 biphenyl rings. This particular structure has both hydrogen bonding acceptor (lactone) and donor (–OH) sites (Figure 1). Due to the weak acidic nature of its four phenolic groups (pKa1 = 5.6 at 37 °C), around neutral pH it is mainly deprotonated on positions 8 and 8′, while above pH 9.6 lactone rings open to give a carboxyl derivative [36]. EA low oral bioavailability is mostly due to its poor water solubility (9.7 µg/mL), which increases with pH, as well as the antioxidant action [37]. However, in basic solutions, phenolic compounds lack stability as these molecules, under ionic form, undergo extensive transformations or are converted to quinones as a result of oxidation. A stability study on pomegranate fruit peel extract demonstrated that EA content significantly decreases in few weeks regardless of the pH of the solution, due to the hydrolysis of the ester group with hexahydroxydiphenic acid formation, suggesting that EA should not be stored in aqueous medium [38]; this aspect reinforces the need to develop novel systems also for EA stabilization.
Prior to facing the route of the development of a new delivery system, the knowledge of solvents, co-solvents and substances in which EA could be consistently soluble and stable represents an indispensable step for designing a good formulation. In this regard, with the aim of providing a useful guidance for further research studies, Table 1 gathers published data concerning EA solubility. Concerning organic solvents, EA is slightly soluble in methanol, soluble in DMSO and shows maximum solubility in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), confirming the effect of basic pH on EA dissolution. An analogous trend is also observable in aqueous solutions, where results implied that the solubility of EA depends on the pH values of the media. While EA is almost insoluble in acidic media and distilled water, its water solubility is significantly improved by basic pH. As highlighted further ahead, one of the mostly exploited vehicles is polyethylene glycol (PEG) 400, as it is endowed with satisfactory biocompatibility and, at the same time, is miscible with both aqueous and organic solvents. EA solubility in oils and surfactants is also provided, helpful for developing emulsifying-based techniques.
| Vehicles | Solubility (mg/mL) | Temperature | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone | 25 | 37 °C | |
| DMSO | 2.5 | 37 °C | |
| Pyridine | 2.0 | 37 °C | |
| Methanol | (671 ± 17) × 10−3 | 37 °C | |
| Ethanol | 1.02 ± 0.04 | 25 °C | |
| PEG 200 | 4.178 | 25 °C | |
| PEG 400 | 11.0 ± 0.5 | 25 °C | |
| Propylene glycol | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 25 °C | |
| Palmester 3575 | 0.030 | 25 °C | |
| Cottonseed oil | 0.005 | 25 °C | |
| Soybean oil | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 25 °C | |
| Castor oil | 1.63 ± 0.07 | 25 °C | |
| Oleic acid | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 25 °C | |
| Ethyl oleate | 2.34 ± 0.06 | 25 °C | |
| Tween 20 | 1.605 | 25 °C | |
| Sucrose esters | 0.115 | 25 °C | |
| Isopropyl myristate | 1.94 ± 0.07 | 25 °C | |
| Cremophor RH40 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 25 °C | |
| Tween 80 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 25 °C | |
| Lecithin | 0.085 ± 0.004 | 25 °C | |
| Poloxamer F68 | 0.036 ± 0.002 | 25 °C | |
| Phosphate buffer pH 7.4 | (33 ± 16) × 10−3 | 37 °C | |
| Phosphate buffer pH 6.8 | (11.1 ± 0.4) × 10−3 | 25 °C | |
| Acetate buffer pH 4.5 | (6.9 ± 0.3) × 10−3 | 25 °C | |
| Distilled water | (8.2 ± 0.4) × 10−3 | 25 °C | |
| HCl 0.1 M in water | (1.03 ± 0.06) × 10−3 | 25 °C |
References
- Miguel, M.G.; Neves, M.A.; Antunes, M.D.; Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.): A medicinal plant with myriad biological properties—A short review. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2836–2847.
- José-Luis Ríos; Rm Giner; Marta Marín; M. Recio; A Pharmacological Update of Ellagic Acid. Planta Medica 2018, 84, 1068-1093, 10.1055/a-0633-9492.
- Yuee Cai; Jinming Zhang; Nelson G. Chen; Zhi Shi; Jiange Qiu; Chengwei He; Meiwan Chen; Recent Advances in Anticancer Activities and Drug Delivery Systems of Tannins. Medicinal Research Reviews 2016, 37, 665-701, 10.1002/med.21422.
- Akram Ahangarpour; Majed Sayahi; Miaad Sayahi; The antidiabetic and antioxidant properties of some phenolic phytochemicals: A review study. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews 2019, 13, 854-857, 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.11.051.
- Vafa Baradaran Rahimi; Mobarakeh Ghadiri; Mobina Ramezani; Vahid Reza Askari; Antiinflammatory and anti‐cancer activities of pomegranate and its constituent, ellagic acid: Evidence from cellular, animal, and clinical studies. Phytotherapy Research 2020, 34, 685-720, 10.1002/ptr.6565.
- Alfei, S.; Turrini, F.; Catena, S.; Zunin, P.; Grilli, M.; Pittaluga, A.M.; Boggia, R. Ellagic acid a multi-target bioactive compound for drug discovery in CNS? A narrative review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111724.
- Inhae Kang; Teresa Buckner; Neil F Shay; Liwei Gu; Soonkyu Chung; Improvements in Metabolic Health with Consumption of Ellagic Acid and Subsequent Conversion into Urolithins: Evidence and Mechanisms. Advances in Nutrition: An International Review Journal 2016, 7, 961-72, 10.3945/an.116.012575.
- Alireza Sarkaki; Yaghoob Farbood; Mojtaba Dolatshahi; Seyed Mohammad Taqhi Mansouri; Ali Khodadadi; Neuroprotective Effects of Ellagic Acid in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease.. ACTA MEDICA IRANICA 2016, 54, 494-502.
- Ujjal Das; Sushobhan Biswas; Sreya Chattopadhyay; Anindita Chakraborty; Rakhi Dey Sharma; Asoke Banerji; Sanjit Dey; Radiosensitizing effect of ellagic acid on growth of Hepatocellular carcinoma cells: an in vitro study. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 14043, 10.1038/s41598-017-14211-4.
- Ai N. H. Phan; Jong-Whan Choi; Hyungmin Jeong; Anti-cancer effects of polyphenolic compounds in epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmacognosy Magazine 2017, 13, 595-599, 10.4103/pm.pm_535_16.
- Luca Vanella; C. Di Giacomo; Rosaria Acquaviva; Ignazio Barbagallo; Giovanni Li Volti; Venera Cardile; Nader G. Abraham; Valeria Sorrenti; Effects of Ellagic Acid on Angiogenic Factors in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancers 2013, 5, 726-738, 10.3390/cancers5020726.
- Zhaoli Dai; Vidhya Nair; Maruf Khan; Henry P Ciolino; Pomegranate extract inhibits the proliferation and viability of MMTV-Wnt-1 mouse mammary cancer stem cells in vitro. Oncology Reports 2010, 24, 1087–1091.
- Jaganathan Kowshik; Hemant Giri; Tanagala Kranthi Kiran Kishore; Rushendhiran Kesavan; Raju Naik Vankudavath; Geereddy Bhanuprakash Reddy; Madhulika Dixit; Siddavaram Nagini; Ellagic acid inhibits VEGF/VEGFR2, PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling cascades in the hamster cheek pouch carcinogenesis model. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry 2014, 14, 1249-1260, 10.2174/1871520614666140723114217.
- Claudia Ceci; Lucio Tentori; Maria Grazia Atzori; Pedro Miguel Lacal; Elena Bonanno; Manuel Scimeca; Rosella Cicconi; Maurizio Mattei; Maria Gabriella De Martino; Giuseppe Vespasiani; Roberto Miano; Grazia Graziani; Ellagic Acid Inhibits Bladder Cancer Invasiveness and In Vivo Tumor Growth. Nutrients 2016, 8, 744, 10.3390/nu8110744.
- Liu, H.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Mastriani, E.; Li, Q.H.; Bao, H.X.; Zhou, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; et al.et al. Main components of pomegranate, ellagic acid and luteolin, inhibit metastasis of ovarian cancer by down-regulating MMP2 and MMP9. Cancer Biology & Therapy 2017, 18, 990-999, 10.1080/15384047.2017.1394542.
- Dongliang Wang; Qianxue Chen; Yinqiu Tan; Baohui Liu; Chao Liu; Ellagic acid inhibits human glioblastoma growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncology Reports 2016, 37, 1084-1092, 10.3892/or.2016.5331.
- Wei Xu; Jinjin Xu; Ting Wang; Weibo Liu; Haifeng Wei; Xinghai Yang; Wangjun Yan; Wang Zhou; Jianru Xiao; Ellagic acid and Sennoside B inhibit osteosarcoma cell migration, invasion and growth by repressing the expression of c-Jun. Oncology Letters 2018, 16, 898-904, 10.3892/ol.2018.8712.
- Claudia Ceci; Pedro Miguel Lacal; Lucio Tentori; Maria Gabriella De Martino; Roberto Miano; Grazia Graziani; Experimental Evidence of the Antitumor, Antimetastatic and Antiangiogenic Activity of Ellagic Acid. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1756, 10.3390/nu10111756.
- Syed Umesalma; Ponnuraj Nagendraprabhu; Ganapasam Sudhandiran; Ellagic acid inhibits proliferation and induced apoptosis via the Akt signaling pathway in HCT-15 colon adenocarcinoma cells. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 2014, 399, 303-313, 10.1007/s11010-014-2257-2.
- Yasmeen Goyal; Ashwani Koul; Pavitra Ranawat; Ellagic acid ameliorates cisplatin induced hepatotoxicity in colon carcinogenesis. Environmental Toxicology 2019, 34, 804-813, 10.1002/tox.22747.
- Ming-Cheng Lin; Mei-Chin Yin; Preventive Effects of Ellagic Acid Against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardio-Toxicity in Mice. Cardiovascular Toxicology 2013, 13, 185-193, 10.1007/s12012-013-9197-z.
- Kiran Sonaje; J. L. Italia; G. Sharma; V. Bhardwaj; Kulhushan Tikoo; M. N. V. Ravi Kumar; Development of Biodegradable Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery of Ellagic Acid and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant Efficacy Against Cyclosporine A-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Pharmaceutical Research 2007, 24, 899-908, 10.1007/s11095-006-9207-y.
- Sepúlveda, L.; Ascacio, A.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Aguilera-Carbó, A.; Aguilar, C.N.; Ellagic acid biological properties and biotechnological development. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 4518–4523.
- F Notka; Georg Meier; Ralf Wagner; Concerted inhibitory activities of Phyllanthus amarus on HIV replication in vitro and ex vivo. Antiviral Research 2004, 64, 93-102, 10.1016/s0166-3542(04)00129-9.
- Raghavan Govindarajan; Madhavan Vijayakumar; Chandana Venkateshwara Rao; Annie Shirwaikar; Shanta Mehrotra; Palpu Pushpangadan; Healing potential of Anogeissus latifolia for dermal wounds in rats.. Acta Pharmaceutica 2004, 54, 331–338.
- Juan Antonio Giménez‐Bastida; Mar Larrosa; Antonio González-Sarrías; Francisco Abraham Tomás-Barberán; Juan Carlos Espín; Maria Teresa Garcia-Conesa; Intestinal Ellagitannin Metabolites Ameliorate Cytokine-Induced Inflammation and Associated Molecular Markers in Human Colon Fibroblasts. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2012, 60, 8866-8876, 10.1021/jf300290f.
- B. Prabha; S. Sini; T. S. Priyadarshini; P. Sasikumar; Greeshma Gopalan; Jayesh P. Joseph; M. M. Jithin; V. V. Sivan; Jaya Murthy; K. V. Radhakrishnan; Anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of action of ellagic acid-3,3',4-trimethoxy-4'-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside isolated from Hopea parviflora in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages.. Natural Product Research 2019, null, 1-5, 10.1080/14786419.2019.1690486.
- Laura Mele; Pedro Mena; Antonio Piemontese; Valentina Marino; Noelia López-Gutiérrez; Franco Bernini; Furio Brighenti; Ilaria Zanotti; Daniele Del Rio; Antiatherogenic effects of ellagic acid and urolithins in vitro. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2016, 599, 42-50, 10.1016/j.abb.2016.02.017.
- Juliana Jordão; Hellen Porto; Flávio Marques Lopes; Aline Carvalho Batista; Matheus Rocha; Protective Effects of Ellagic Acid on Cardiovascular Injuries Caused by Hypertension in Rats. Planta Medica 2017, 83, 830-836, 10.1055/s-0043-103281.
- Federica Turrini; Raffaella Boggia; Dario Donno; Brunella Parodi; Gabriele Beccaro; Sara Baldassari; Maria Grazia Signorello; Silvia Catena; Silvana Alfei; Paola Zunin; From pomegranate marcs to a potential bioactive ingredient: a recycling proposal for pomegranate-squeezed marcs. Zeitschrift für Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und -Forschung 2019, 246, 273-285, 10.1007/s00217-019-03339-4.
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, K.H.; Han, C.S.; Yang, H.C.; Park, S.H.; Jang, H.-I.; Kim, J.-W.; Choi, Y.-S.; Lee, N.H.; Anti-wrinkle activity of Platycarya strobilacea extract and its application as a cosmeceutical ingredient. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 14, 211–223.
- Liu, R.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Huo, T.; Xue, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Effects of ellagic acid-rich extract of pomegranates peel on regulation of cholesterol metabolism and its molecular mechanism in hamsters. Food & Function 2015, 6, 780-787, 10.1039/C4FO00759J.
- Raffaella Boggia; Federica Turrini; Carla Villa; Chiara LaCapra; Paola Zunin; Brunella Parodi; Green Extraction from Pomegranate Marcs for the Production of Functional Foods and Cosmetics. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 63, 10.3390/ph9040063.
- Núñez-Sánchez, M.A.; García-Villalba, R.; Monedero-Saiz, T.; GarcíaTalavera, N.V.; Gómez-Sánchez, M.B.; Sánchez-Álvarez, C.; García-Albert, A.M.; Rodríguez-Gil, F.J.; Ruiz-Marín, M.; Pastor-Quirante, F.A.; et al.et al. Targeted metabolic profiling of pomegranate polyphenols and urolithins in plasma, urine and colon tissues from colorectal cancer patients. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 2014, 58, 1199-1211, 10.1002/mnfr.201300931.
- John A. Bellone; Jeffrey R. Murray; Paolo Jorge; Travis G. Fogel; Mary Kim; Desiree R. Wallace; Richard Hartman; Pomegranate supplementation improves cognitive and functional recovery following ischemic stroke: A randomized trial. Nutritional Neuroscience 2018, 22, 738-743, 10.1080/1028415x.2018.1436413.
- I. Bala; V. Bhardwaj; S. Hariharan; M. N. V. Ravi Kumar; Analytical methods for assay of ellagic acid and its solubility studies. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2006, 40, 206-210, 10.1016/j.jpba.2005.07.006.
- Małgorzata Muzolf-Panek; Henryk Szymusiak; Anna Gliszczyńska-Świgło; Ivonne M. C. M. Rietjens; Bożena Tyrakowska; pH-Dependent Radical Scavenging Capacity of Green Tea Catechins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2008, 56, 816-823, 10.1021/jf0712189.
- Pharkphoom Panichayupakaranant; Atcharaporn Itsuriya; Anusak Sirikatitham; Preparation method and stability of ellagic acid-rich pomegranate fruit peel extract. Pharmaceutical Biology 2009, 48, 201-205, 10.3109/13880200903078503.




