
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tamara Ius | + 5676 word(s) | 5676 | 2021-06-02 10:23:29 | | | |
| 2 | Conner Chen | Meta information modification | 5676 | 2021-06-06 13:26:20 | | |
Video Upload Options
The most frequent intracranial neoplasm is meningioma. About 30% of these are represented by skull base meningiomas (SBMs). Patients with SBMs can be treated with a multimodal approach based on surgery, medical treatment and radiation-based therapy; however, the gold standard treatment for the majority of symptomatic meningiomas is still surgery. Surgical intervention is performed with the goal of maximum safe resection. This, however, poses technical challenges because of the proximity of these tumors with deep critical neurovascular structures, tumoral texture and consistency. A multimodal treatment, in combination with stereotactic radiosurgery and radiation therapy, is thus of utmost importance to achieve a satisfactory functional outcome and tumor control.
1. Background
Meningioma account for 16–36% of all intracranial tumors in adults [1]. According to the World Health Organization, these lesions are currently classified into fifteen histotypes and three grades of malignancy, of which 90% are of Grade I [2]. The most significant prognostic factors for these tumors include the histological grade according to the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria [2] and the extent of surgical resection according to the Simpson scale [3]. About 30% of intracranial meningiomas are represented by skull base meningiomas (SBMs) [4][5][6][7]. The surgical goal of radical resection is frequently hindered by the proximity of SBMs with deep critical neurovascular structures, complex vascularity, tumoral texture and consistency. In the past, the skull base was considered an inaccessible surgical location. Recent advances including the introduction of microsurgical techniques, improvements in imaging, virtual surgical simulation, and technological refinement of surgical instruments, along with the widespread use of minimally invasive approaches have radically changed SBM surgical management.
The goal of SBM surgery is the complete resection of the tumor, surrounding dura and infiltrated bone (if present), traditionally recognized as Simpson grade I resection [8]. Despite recent advances in microsurgical techniques and treatment strategies, this goal is often challenging to achieve, mainly because of the involvement of neurovascular structures and/or limited instrument maneuverability along narrow surgical corridors [9][10]. Bone infiltration or venous sinuses involvement can further limit the radical resection rate. Multimodal treatment, in combination with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and/or fractionated radiation therapy (fSRT), is thus increasingly considered to achieve a satisfactory functional outcome and long-term tumor control.
2. Modern Surgical Planning
2.1. The Role of Computer-Aided Approaches
SBM surgery is demanding due to both the size and involvement of deep neurovascular structures such as perforating arteries, veins and cranial nerves, which are often encased or displaced by the tumor. Considering the above, a detailed surgical strategy is crucial for obtaining a maximum-allowed resection with minimal risks of permanent morbidity. The so-called “4D rule” (de-vascularization, detachment, de-bulking, dissection) is essential in SBM surgery.
Nowadays, virtual surgical planning gives the opportunity to perform highly accurate surgical approach rehearsal, greatly enhancing the preoperative workflow. Virtual planning starts with appropriate image acquisition, often requiring multiple modalities [11]: Tel et al. [12] described a multimodal image fusion algorithm based on automatic registration of CT and MRI images. For computer-reconstruction of intracranial vessels, MRI angiography is essential to analyze the three-dimensional spatial relationship between the tumor and the vessels [13][14]. Segmentation, defined as the process of automatic or semi-automatic detection of boundaries for regions of interest within DICOM images, allows anatomical and pathological structures to be identified, which are rebuilt in the three-dimensional space across all slices of the radiological image [15]. Segmentation can be performed using a combination of semi-automatic algorithms, including thresholding and region growing, and manual refinements, yielding tessellated geometrical representations named “mesh”. Geometrical models can undergo CAD (computer-assisted design) operations, including the simulation of osteotomies, removal of bone segments, tumor excision, showing a virtual representation of planned surgical maneuvers in relation to critical anatomical structures [12]. Three-dimensional geometry files, named STL (Standard Tessellation Language), can be imported in navigation systems to allow navigation of the entire virtual plan and not just raw DICOM images.
Virtual surgical planning plays a prominent role in simulating surgical accesses. Combined maxillofacial and neurosurgical procedures may be selected for huge SBM developing within the clival region or anterior skull base with ethmoido-orbital invasion [16]. In this setting, virtual surgical planning allows the shape and trajectory to be defined for osteotomies and the simulation of facial skeleton dismantling, paving the way for skull base fossae in a relatively compact space, dense in essential anatomical structures (Figure 1).
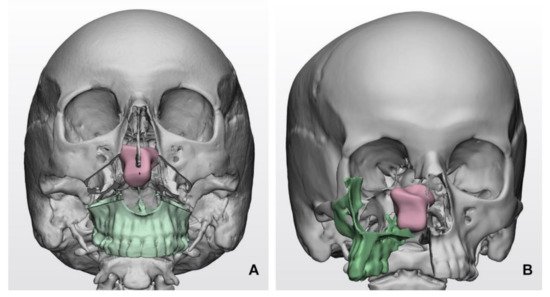
Figure 1. Simulated transfacial accesses using virtual models in clival meningiomas: (A) Le Fort I transmaxillary access; (B) transfacial maxillary-split approach. The bone flap is represented in green color, while the tumor mass is represented in pink color.
Virtual planning plays a crucial role in the reconstructive phases as well, as it provides a foreseeable geometrical configuration of the final anatomical geometries, allowing devices to be personalized, such as reconstructing plates and prostheses.
2.2. The Role of Tractography
Diffusion MRI and tractography currently represent the only way to reconstruct white matter in humans in vivo, providing a non-invasive and feasible method for evaluating the subcortical pathways changes, especially in glioma surgery [17][18][19]. In recent years, its use has been gradually spread for preoperative cranial nerve reconstruction in SBM surgery [20][21][22]. In the latter clinical setting, probabilistic tractography currently appears to be an emerging and promising tool to predict the position of displaced cranial nerves around skull base lesions [20][21].
Applying tractography to cranial nerves demands, however, advanced anatomical, radiological, and computational skills to achieve correct fiber tracking and to avoid spurious tracts. In addition, the main challenging limitations in cranial nerves tacking are represented by their small size, intricate anatomical environment sensitive to susceptibility artifacts, and a limited MRI spatial and angular resolution. Nevertheless, recent studies have demonstrated effective tracking for large cranial nerves such as optic nerve, trigeminal nerve, or acoustic-facial bundle, highlighting the potential role of tractography both in a surgical setting and intraoperative strategy [21][22].
In order to validate tractography’s effectiveness in SBM surgery, further prospective investigations are required with the aim of assessing the tracking reproducibility and the impact on patients in terms of operative time, clinical follow-up and quality of life.
3. The Role of Surgery
Surgical access to SBMs is one of the most challenging procedures due to the narrow surgical corridors and the proximity of these tumors to critical neurovascular structures.
Approach selection is a key-point in SBM surgery in order to manage the lesion without harming the neurovascular surrounding structures and, in the last 20 years, many different approaches have been described. Table 1 shows the main surgical approaches subclassified in three main categories (anterior, middle and posterior fossa meningioma) according to meningioma locations.
Table 1. Literature review of surgical approaches according to SBMs location. Surgical approach is selected by interdisciplinary consultation according to the site of disease.
| Skull Base Region | Location | Incidence | Surgical Approaches | IONM | Surgical Pitfalls | Complications | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vascular | Nerves | Others | Clinical Manifestations | |||||
| Anterior Fossa 4, 27–36,49,51 |
Olfactory Groove Meningiomas | 8–13% | Subfrontal approach Transbasal Approach Pterional approach Fronto-lateral approach Supraorbital keyhole Endoscopic endonasal approach *Transfacial reconstitutive approach also known as facial translocation, further subdivided into:
|
EEG, MEPs, SSEPs, VEPs (in selected cases) | branches of the OA, ICA, ACoA, A2 Ethmoidal arteries |
CN I, II, III, IV | EOM | Anosmia, CSF leak Visual disturbances (diplopia, anopsia, eye globe injury) Hemorrhage Hemorrhage, epiphora, diplopia and dystopia, soft tissue swelling, ectropion (associated with Weber–Ferguson incision). Poor bone consolidation, misalignment (related to bad osteosynthesis), wound dehiscence (cutaneous and intraoral) |
| Sphenoid wing Meningiomas | 11–20% | Pterional approach Fronto-temporal-orbito-zygomatic approach Lateral, superior, medial orbitotomy |
anterior circulation arteries Ethmoidal artery in medial accesses |
CN II, III, VI supraorbital nerve, facial nerve |
EOM, medial and lateral canthal tendons | |||
| Tuberculum Sellae/Planum Meningiomas | 5–10% | Pterional approach Endoscopic endonasal approach Supraorbital key-hole |
Anterior circulation arteries | CN II, III, IV, V, VI | aesthetic orbital reconstruction | |||
| Cavernous Sinus Meningiomas | 1% | Pterional approach Fronto-temporo-orbito- Zygomatic approach |
Anterior circulation arteries | CN II, III, IV, V, VI | ||||
| Middle Fossa 4,35,44 |
Middle fossa and Sphenoid wing | 1.1–1.4% | Pterional approach (anterolateral approach) Fronto-temporo-orbito- zygomatic |
EEG, MEPs, SSEPs EMG CNs III, IV, VI can be considered |
ICA Vein of Labbè |
CN II, III, IV, V, VI | Temporal lobe | Language deficit, hemiparesis, hemianopsia, hemorrhages, temporal lobe edema, trigeminal anesthesia, |
| Middle fossa and cavernous sinus | ||||||||
| Middle fossa with infratemporal extension | Subtemporal approach (lateral approach) |
|||||||
| Middle fossa and petrous ridge | ||||||||
| Posterior Fossa 4,35,38–43,45,46,51 |
Cerebellopontine Angle | 10% | Anterior Petrosectomy Approach Posterior and Combined Petrosal Approaches Retrolabyrinthine Approach Translabyrinthine Approach Combined Petrosal Approach Retrosigmoid approach |
EEG, MEPs, SSEPs, CB-MEP (CN VII) EMG (CNs VI, VII) BAERs |
Intrapetrous ICA, SCA and AICA encasement | CN V, VI, VII, VIII | Brainstem adhesion | Brain steam and cerebellum edema, CSF leak Venous infarction Cranial nerve injury Vertebral artery injury, Hydrocephalus, CSF leak Infection Hemorrhage, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, soft tissue edema of the oral cavity, infection, wound dehiscence, velopalatine dysfunction, malocclusion, dysphagia, malocclusion when osteotomies are required, oro-nasal fistula, laceration of nasal mucosa, lesion of teeth apices |
| Foramen Magnum | 2.5% | Posterior Suboccipital Approach with C1 laminectomy; Far Lateral Approach Extreme Lateral Approach |
EEG, MEPs, SSEPs, CB-MEP (CN VII, IX, X, XI, XII) EMG (CNs VI, VII, IX, X, XI, XII) BAERs |
VA encasement JV encasement |
CN IX, X, XI, XII | Brainstem adhesion Extradural extension |
||
| Clival Meningiomas | <1% | Retrosigmoid approach Petrosal approach Transoral:
far-lateral approach Endoscopic approach |
Internal maxillary artery Palatine artery |
CN VI, VII, VIII, XI, X, XI, XII | Brainstem adhesion | |||
| Petroclival Meningiomas | 2% of posterior fossa meningiomas | Retrosigmoid approach Combined transpetrosal Retrolabyrinthine Approach Translabyrinthine Approach |
BA BA perforating arteries |
CN V, VI, VII, VIII | Brainstem adhesion | |||
Legend: * alone or in combination with bifrontal craniotomy for selected wide Olfactory Groove meningiomas invading cribriform plate; OA: ophthalmic artery; ICA: internal carotid artery; ACoA: anterior communicating artery; A2: second segment of anterior cerebral artery; ACA: anterior cerebral artery; SCA: superior cerebellar artery, AICA: anterior inferior cerebellar artery, VA: vertebral artery; BA: basilar artery; JV: jugular vein; CN: cranial nerve; EOM: extraocular muscles; IONM: intraoperative nerve monitoring; BAERs: brain stem auditory-evoked responses; CB-MEPs: corticobulbar motor-evoked potentials; CNs: cranial nerves; EEG: electroencephalogram; EMG: electromyography; MEPs: motor-evoked potentials; SSEPs: somatosensory-evoked potentials; VEPs: visual-evoked potentials.
The trans-sphenoidal and the other extended transnasal approaches have revolutionized the management of meningiomas involving areas of the median and paramedian skull base surrounding the sella and cavernous sinuses regions. Selected SBMs, originating from the tuberculum sellae, planum sphenoidale, and olfactory groove, have become amenable to transnasal resection [23][24][25]. The undaunting amelioration of these novel techniques has led to these indications expanding to a wide range of SBMs. At present, “the edge of the envelope” has still not been defined [26] and the surgical possibilities of removing meningiomas of the skull base are widening [27]. In this regard, in selected cases, cooperation with maxillofacial surgeons can be useful to create adjunctive surgical corridors through facial incisions or bone osteotomies [28][29].
In selected cases, the cooperation between neurosurgeons and maxillofacial surgeons in SBM surgery might be twofold, representing an aid to create wider surgical accesses as well as to perform a more radical resection. This latter point should represent the choice for patients presenting with bulky tumors invading the nasal cavity or intraorbital space.
Therefore, bulky disease with infiltration of orbits and ethmoid requires extensive resection for which wider surgical exposure is achieved through transfacial or transoral approaches. In detail, such approaches allow for a wide exposure of the ethmoidal cells and orbital compartment, enabling resection of masses extending downward beyond the cribriform plate or invading the orbit [30][31].
Middle and posterior cranial fossa approaches represent a very flourishing field that have been proposed and intermittently preferred over the years. The approaches so far described go from the standard subtemporal or retrosigmoid approaches [32][33][34][35][36] to more complex and extended ones, and/or also combined with wider skull base bone removal [37][38][39]. Indeed, bony structure removal does not always correlate with a better surgical maneuverability or a reduced parenchymal retraction [40][41]. The best approach needs to be tailored to each patient based upon several peculiar factors (pathological, anatomical, functional and reconstructive). Several studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between the extent of resection and the frequency of recurrence in SBMs, highlighting the central role of surgery in their workflow [42][43][44][45].
There is no general consensus in considering SBMs genetically different from their non-SBM counterparts [8]; continuous refining of operative techniques is thus required to obtain satisfactory long term outcomes Complete surgical resection is the goal of SBM surgery, but can seldom be limited because of the intimate relationships with the brain stem, neurovascular structures and cranial nerves [46][47]. Therefore, the surgical aggressiveness needs to be weighed against risks of morbidity, tumor biology, patients age, functional status and functional expectations [48][49].
The approaches can be extended and combined in relation to the meningioma’s size and surgeon’s choice (Table 1, Figure 2). Appropriate knowledge of surgical anatomy, adequate corridors, release of CSF, comfortable and precise microsurgical instrumentation are the key concepts in SBM surgery, resulting essential for the patient outcomes.
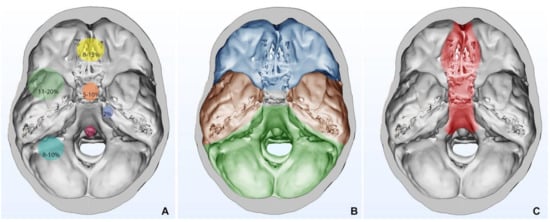
Figure 2. (A) Relative frequencies in SBM locations are stratified and shown with circles of progressively wider diameter; (B) Topological subdivision of skull base: anterior skull base is shown in blue, middle skull base is shown in brown, and posterior skull base is shown in green; (C) Anatomical area for which endoscopic endonasal approach can be used.
3.1. Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring in Skull Base Meningiomas
Nowadays, there is an increasing interest in the role of intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring (IONM) in SBM surgery.
The surgical resection of large meningioma, especially when encasing nerves and/or the main cerebral vascular trunks and/or their perforating vessels skull base, requires extensive maneuvers that can lead to pyramidal tract impairments or cranial nerves palsy [50][51]. Advances in anatomy, microsurgery, neuroimaging, and intraoperative monitoring have gradually reduced the incidence of cranial nerve palsy [51][52]. The IONM strategy during SBM surgery has to be tailored according to tumor location and the vascular and neural structures involved. IONM details are reported in Table 1 [4].
3.2. Preoperative Embolization
Devascularization of the lesion remains an important goal in meningioma surgery, to be achieved before other maneuvers. Differently from meningiomas of the convexity, those arising at the skull base have deep, poorly accessible feeding vessels. Preoperative embolization might ease surgical dissection, inducing a lower risk of intraoperative blood loss, and as a consequence, decreasing the surgical morbidity. Preoperative embolization of SBM is still, however, a controversial and debated issue, also because of the poor effectiveness and the risk of complications related to inadvertent occlusion of off-target arteries [53][54][55].
The preoperative embolization indication depends mainly on the meningioma’s size and location. The most commonly cited indications for pre-operative embolization include size >4 cm, high vascularity, and the convexity site for meningioma being supplied primarily by the external carotid artery. However, in selected cases, embolization may also result as useful for SBM meningiomas in which the arterial supply is deep and not reached until the late phases of tumor debulking [56].
As a general rule, amongst factors that deter preoperative embolization, ease of vascular access intraoperatively, dangerous external carotid artery–internal carotid artery anastomosis, the presence of feeders to cranial nerves, internal carotid artery predominant blood supply (>50% on angiography), and high tortuosity or narrowness of the feeding vessels are included [57]. Until further evidence from clinical trials emerges, the decision to preoperatively embolize a meningioma should be tailored for each patient according to tumor size, location, and estimation of degree of blood loss [56][57].
3.3. Reconstruction of the Surgical Route
Reconstruction of the anterior skull base has the main role of restoring the separation between the intracranial and the extracranial space, in particular to prevent leakage of CSF and related threatened complications, above all meningitis. A variety of techniques have been described [58], accounting for the use of dural substitutes and local flaps, used to restore separation between the brain and extracranial space [59]. In the case of wider defects, free flaps also represent an option [60].
Amongst local flaps, it is worth mentioning the nasoseptal flap, described by Hadad et al., because of its impact on endoscopic surgery, as it provides a minimally invasive and effective method to repair anterior skull base defects [61]. It consists of a vascularized mucoperichondrial/periosteal flap harvested from the nasal septum, which is pedicled on the posterior septal branch of the sphenopalatine artery and can be mobilized and transposed on the defect using an entirely endoscopic approach.
For transfacial accesses requiring the disassembly of facial subunits, reconstruction follows the same principles of fracture treatment using internal rigid fixation with titanium miniplates and miniscrews. Recently, supporting the experience of maxillofacial surgeons, the use of CAD-CAM technology has been introduced in clinical practice to simulate the reconstruction of skull base defects.
Moreover, the widespread distribution of virtual planning software in laboratories embedded in modern hospitals makes such processes more affordable and contributes to shared knowledge on technology. Nowadays, models for pre-operative planning [62] or reconstruction of parts of the skull base or the facial skeleton can be performed “in-house”, using commercially available technology, by 3D printing of molds for PMMA modelling according to the desired plan [63]. Nevertheless, reconstruction of the skull base using a prosthetic device, although customized, is generally difficult, and few examples are documented. If the lesion extends through the lateral skull base into the glenoid fossa of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) causing joint dysfunction, concomitant skull base and TMJ replacement has been described using a customized TMJ prostheses extended to the lateral skull base [64]. As for the anterior fossa, reconstruction across the cribriform plate is usually performed using a soft tissue flap, whereas the orbital roof can be reconstructed using customized alloplastic implants, which offer the maximum accuracy in replicating the original anatomy. Alternatively, a titanium mesh can be prebent over a 3D printed template to provide a customized implant at a considerably lower cost [65][66].
4. Histopathological Features
Several studies have demonstrated that meningiomas at different anatomical sites have diverse histological and genetic features [67][68] (Table 2), which could provide relevant prognostic information and open the perspective to novel target therapies.
Table 2. Genetic alterations in skull based meningiomas.
| Altered Gene | Preferential Tumor Localization | Main Histotype |
|---|---|---|
| NF2 | Posterior and lateral skull base | Fibrous, Transitional, Atypical |
| AKT1, PI3K | Anterior and middle skull base | Meningothelial |
| SMO | Olfactory groove | Meningothelial * |
| TRAF7/KLF4 | Middle skull base | Meningothelial, Secretory for co-occurring TRAF7/KLF4 |
| POL2RA | Tuberculum sellae | Meningothelial |
* SMO mutated meningiomas have significantly higher recurrence risk than AKT1 meningiomas at the same site.
SBMs mainly show the meningothelial histotype, and compared to non-skull based ones, they have a lower incidence of grade II/III histology (8.6–20% vs. 40%) and of NF2 alterations (20% vs. 46%), and a higher incidence of secretory histotype (63% vs. 37%) [58][60][61], a rare grade I variant, characterized by peritumoral edema [69]. Then, SBMs can be further categorized, as those localized at the lateral and posterior skull base mainly feature NF2 impairment [70][71], while those at the anterior and middle skull base are NF2 wild type and may have mutations in other genes, including AKT1, PIK3CA, SMO, TRAF7, KLF4 and POLR2A [67][70][71][72]. In detail, around 15% of skull base meningiomas have alterations in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, consisting of AKT1E17K and PIK3CA mutations, in association with meningothelial histotype or brain invasion [67][72][73]. About 28% of meningioma at the middle anterior skull base, and, specifically, at the olfactory groove, have an impaired hedgehog pathway due to SMO mutations (L412F and W535L), which are mutually exclusive to AKT1 mutations [67][70][71][73][74][75]. These latter tumors mainly have meningothelial histotype and a low mitotic index, but a significantly higher recurrence rate than AKT1-mutated meningiomas at the same site [75]. A proportion of meningiomas at the middle skull base (ranging between 2.1% and 24%, and between 8.6% and 11.8%, respectively) were reported to display TRAF7 and KLF4K409Q mutations [67][73][74], which co-occur in secretory meningiomas, and which may coexist with AKT1 mutations [67][71][73][74]. Finally, there is a distinctive group of skull base meningiomas, originating at the tuberculum sellae and with meningothelial histotype, that are characterized by mutations of POLR2A, which encodes for the catalytic subunit of Polymerase RNA II (DNA directed) polypeptide A [76].
5. Radiation Therapy
5.1. Fractionated Radiotherapy
Postoperative radiation therapy (RT) using doses of 50–55 Gy in 30–33 fractions has been frequently used for benign SBMs, either after incomplete resection or tumor progression. Local control rates from 75 to 90% at 10 years have been reported following conventional RT and 3D conformal RT (Table 3) [77][78][79][80][81][82], equivalent to that observed after complete resection, and better than that achieved with subtotal resection alone [83]. Similar tumor control has been observed for patients receiving postoperative RT or at the time of tumor recurrence/regrowth [79][80][81].
Table 3. Summary of selected published studies on conventionally fractionated radiotherapy for benign SBMs.
| Authors | Patients (N) | Radiation Modality | Median Dose/ Dose per Fraction (Gy) | Median Volume (mL) | Median Follow-Up (Months) | Local Control | Late Toxicity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goldsmith et al., 1994 [77] | 117 | CRT | 54 | NA | 40 | 89 at 5 and 77 at 10 years | 3.6 |
| Maire et al., 1995 [78] | 91 | CRT | 52 | NA | 40 | 94 | 6.5 |
| Nutting et al., 1999 [79] | 82 | CRT | 55–60 | NA | 41 | 92 at 5 and 83 at 10 years | 14 |
| Vendrely et al., 1999 [80] | 156 | 3D-RT | 50 | NA | 40 | 79 at 5 years | 11.5 |
| Mendenhall et al., 2003 [81] | 101 | 3D-RT | 54 | NA | 64 | 95 at 5, 92 at 10 and 15 years | 8 |
| Henzel et al., 2006 [84] | 84 | fSRT | 56 | 11,1 | 30 | 100 | NA |
| Tanzler et al., 2010 [85] | 144 | fSRT | 52.7 | NA | 87 | 97 at 5 and 95 at 10 years | 7 |
| Minniti et al., 2011 [86] | 52 | fSRT | 50 | 35.4 | 42 | 93 at 5 years | 5.5 |
| Slater et al., 2012 [87] | 68 | Protons | 56 | 27.6 | 74 | 99 at 5 years | 9 |
| Weber et al., 2012 [88] | 24 | Protons | 56/1.8–2.0 | 21.5 | 62 | 100 at 5 years | 15.5 |
| Solda et al., 2013 [89] | 222 | fSRT | 50/55 | 12 | 43 | 100 at 5 and 10 years | 4.5 |
| Combs et al., 2013 [90] | 507 | fSRT/IMRT | 57.6/1.8–2.0 | 53.4 | 107 | 95.5 at 5 and 88 at 10 years | 1.8 |
| Fokas et al., 2014 [91] | 253 * | fSRT | 55.8/1.8–2.0 | 16 | 50 | 92.9 at 5 and 87.5 at 10 years | 12 (G2) |
| Han et al., 2014 [92] | 143 | fSRT | 50.4/1.8 | 11.1 | 32 | 95% | 0.7 |
| Kaul et al., 2014 [93] | 136 | fSRT | 57/1.8–2.0 | 24 | 44.9 | 93.8 at 5 and 91.5 at 10 years | G1 only |
| Sanford et al., 2017 [94] | 44 | Protons | 55.8–63 | 39.7/13.2 | 195 | 98 at 10 and 90 at 15 years | 59% (≥G2) |
| Lillie O’steen et al., 2019 [82] | 149 | 3D-RT | 50–52/1.7–1.8 | NA | 144 | 95 at 10 and 92 at 20 years | NA |
CRT, conventional radiation therapy; fSRT, fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy; IMRT, intensity modulated radiation therapy; G, grade; 3D-RT, three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy; * series including skull base and intracranial meningiomas; NA, not assessed.
The reported treatment-related toxicity is relatively low and includes the development of neurological and endocrinological adverse events (Table 3). Radiation-induced optic neuropathy, presenting as decreased visual acuity or visual field defects, occurs in less than 5% of irradiated patients with an SBM. Deficits of cranial nerves passing through the cavernous sinus, which include the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, abducens nerve, and the V1 to V2 branches of the trigeminal nerve have been reported in 1–4% of patients when radiation doses do not exceed 54 Gy in conventional fractionation 1.8–2.0 Gy daily [77][78][79][80][81][82]. Similarly, the risk of radionecrosis remains exceptional for doses less than 60 Gy. Hypopituitarism is reported in up to 20% of patients, with higher risk for large SBMs invading the pituitary sella. Neurocognitive dysfunction has been occasionally reported in irradiated patients with large meningiomas, especially impairment of short-term memory [78][95][96][97].
Postoperative fractionated RT using doses of 59.4 Gy in 13 fractions of 1.8 Gy per fraction is typically recommended after surgical resection of Grade II and Grade III meningiomas [98][99]. Cooperative group studies RTOG 0539 and EORTC 22042 support the role of early postoperative RT in patients with WHO grade II meningiomas after subtotal resection and grade III meningiomas with any resection extent. However, the benefit of RT in terms of survival and local tumor control following complete surgical resection remains a matter of debate. The recently closed ROAM/EORTC randomized trial will clarify the role of adjuvant radiotherapy in reducing the risk of tumor recurrence following complete surgical resection of atypical meningioma [100].
Over the last few decades, RT has seen technological advances through all the steps involved in radiation treatment with improvement in the accuracy of target delineation, treatment planning process and delivery [101]. Modern radiation techniques, including fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (fSRT), intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT), allow for more precise treatments as compared with conformal RT, while reducing radiation exposure to surrounding sensitive brain structures. Table 3 shows a summary selected series using either fSRT or IMRT [77][78][79][80][81][82][84][85][86][89][90][91][102][92][87][88][94]. With a median follow-up of 42–107 months, the reported actuarial median local control ranges from 93 to 100% at 5 years and 91.5 to 100% at 10 years.
A clinical neurological improvement is reported in 14–44% of patients after fSRT [85][86][89][90][91][102][92], with acceptable late significant toxicity. With doses of 50–55 Gy in 1.8.2.0 Gy per fraction, pituitary hormone deficits occur in less than 15% of patients. The development of optic neuropathy or other cranial deficits is reported in less than 3–4% of patients. For patients treated with conventionally fractionated RT, the analysis of prognostic factors showed that tumor size was a predictor of tumor control [77][78][86][90][92][93]. In 54 patients with SBMs who received conventional RT, Connell et al. [93] observed 5-year tumor control rates of 93% for lesions more than 5 cm and 40% for lesions less than 5 cm; similar results have been reported by others [77][78][86][90]. In some, but not all, studies, clinical outcome was similar for patients treated with early postoperative RT or at the time of tumor progression. With regard to the radiation dose, no outcome differences have been reported following doses of 50–54 Gy or >54 Gy.
In addition, few studies have compared the outcome of SRS and fSRT in SBMs [90][103][104][105]. In a large retrospective study of 927 patients from three German centers treated with either SRS (median dose, 13 Gy) or fSRT (median dose, 54 Gy/30 fractions) for meningiomas, Combs et al. [90] reported local control rates of 92% at 5 years and 86% at 10 years, with no difference between techniques. Among patients treated with fSRT, there was no difference between 54 Gy and 57.6 Gy. Side effects were below 5% after either SRS or fSRT, without any severe treatment-related complications. In another series of 51 treated with fSRT and 77 who had SRS for a SBMs, Torres et al. [103] showed tumor control rates of 97% for patients with a median follow-up of 24 months and 90% for those with a median follow-up of 40 months. Late toxicity was observed in 5% of patients treated with SRS and 5.2% patients who received fSRT.
Some retrospective studies have reported the use hypofractionated SRT for SBMs, as shown in Table 4 [91][92][106][107][108][109]. Using doses of 21–25 Gy delivered in 3–5 fractions, the observed local control in six studies including 337 patients is 93–95% at 5 years, with a reported cranial nerve toxicity of less than 5%. In a large retrospective series of 168 patients receiving CyberKnife-based hypofractionated SRT for SBMs, Marchetti et al. [109] showed a local control rate of 95% at 5 years with a toxicity rate of 3.7%, and similar results have been observed in a few other studies using either CyberKnife or LINAC technologies. In a systematic review on the clinical outcomes of hypofractionated SRT for intracranial meningiomas including 630 patients reported in fourteen studies published between 2004 and 2016, Nguyen et al. [110] reported a crude control of 90–100% with median late toxicity rates of about 10%.
Table 4. Summary of selected published studies on conventionally fractionated radiotherapy for skull base meningiomas.
| Authors | Patients (N) | Technique | Median Dose (Gy)/Fractions | Median Volume (mL) | Median Follow-Up (Months) | Local Control | Late Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colombo et al., 2009 [106] | 150 * | CK | 16–25/2–5 | 7.5 (0.1–64) | 30 | 96 | 3.5 |
| Fokas et al., 2014 [91] | 49 * | LINAC | 25–35/5 | 6.11 (1.9–35.7) | 50 | 92.9 at 5 and 87.5 at 10 years | 12 (G2) |
| Han et al., 2014 [92] | 22 * | LINAC | 25/5 | 4.8 (0.88–20.38) | 32 | 95 | 0.7 |
| Navarria et al., 2015 [107] | 26 | LINAC | 25/5 | 13° | 24.5 | 93% at 2 years | G3, none |
| Marchetti et al., 2016 [108] | 143 | CK | 21–25/2–5 | 8 (0.1–126.3) | 44 | 93 at 5 years | 5.1 |
| Marchetti et al., 2019 [109] | 168 | CK | 25/5 | 7.3 (0.1–76.8) | 51 | 94% at 5 years | 3.7 |
CK, CyberKnife; LINAC, linear accelerator; mean; * including skull base and intracranial meningiomas
Based on several retrospective studies, hypofractionated SRT may represent an alternative to single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of SBMs, especially for those close to the optic apparatus. With regard to the development of radiation-induced optic neuropathy, a similar risk <1% has been observed for maximum point doses to optic apparatus of 12 Gy given in one fraction, 20 Gy in three fractions, and 25 Gy in five fractions [111].
Over the last few decades, proton beam RT has been extensively employed in patients with skull base tumors with the rationale of better covering of the target while sparing surrounding critical structures compared to 3D-conformal RT and IMRT, especially in the case of large and irregularly shaped lesions [83]. Several studies of proton beam therapy for SBMs show 5-year local tumor control rates of 85–100% after either conventionally fractionated and hypofractionated schedules, being consistent with those observed following photon irradiation [87][88][94]. Using doses of 56 Gy, a variable occurrence of long-term side effects of 9 to 59% is reported in three studies including 136 patients (Table 3). In a small prospective study of 44 patients randomized to receive 55.8 Gy and 63.0 Gy (relative biological effectiveness, RBE) given as fractionated combined proton-photon RT, Sanford et al. [94] showed local control rates of 98% at 10 years and 90% at 15 years. With a median follow-up of 17 years, 26 patients (59%) experienced a grade 2 or higher late toxicity, including 9 patients (20%) who experienced a cerebrovascular accident. Currently, the superiority of proton beam therapy over advanced photon techniques in terms of efficacy and toxicity remains to be proven.
In summary, fractionated RT is a safe and effective technique for the treatment of patients with benign SBMs, with long-term local control consistent with those obtained following SRS. The choice of appropriate technique should be based on tumor size and site. In clinical practice, single doses of 8–10 Gy to the optic apparatus should be avoided to limit the risk of radiation-induced optic neuropathy. This means that SRS is usually suitable for patients with relatively small SBMs not in close proximity (less than 2 mm) to the optic apparatus, whereas fractionated schedules using either photons or protons would be preferred for tumors abutting the optic chiasm. Conventionally fractionated RT would be preferred over hypofractionated RT for larger tumors extensively involving the optic apparatus.
5.2. Radiosurgery
5.2.1. Overview
SRS is nowadays widely accepted as a reliable alternative to microsurgery in selected cases [112], especially in the elderly and in tumors in critical locations, lowering mortality, morbidity and recurrences after surgery. The combined approach of subtotal resection and SRS post-operative treatment is of increased use.
Cranial nerve preservation is of utmost importance and in this clinical setting, SBMs represent the milestone of this phenomenon.
In the last decade, an increasing number of SBMs closer to critical brain structures such as the anterior optic pathways, brain stem, etc., have undergone SRS more and more often thanks to the introduction of innovative “volume staging” and “hypo-fractionated” irradiation techniques and modalities [108].
The excellent effectiveness and safety of SRS are thus reported, with a described 5-year actuarial progression-free survival (PFS) and local tumor control rates (LTR) of 86.2–97.9% [113][114][115] with very low sequelae [116][117][118], if appropriate indications are warranted, particularly regarding tumor volume and cytologic grading.
5.2.2. Posterior Fossa
As is well-known, the posterior fossa presents some unique anatomical features resulting in a tiny space for mass effect. Surgical and radiosurgical features’ attitudes are therefore peculiar. In the literature, despite its enormous development, surgery results in mortality and morbidity (ranging in various studies from 40% to 96%), and could lead to recurrence after subtotal removal. Even if resection remains a class-A choice in cases with appreciable mass effect, a multimodality post-surgical approach is strongly recommended. Recent papers have even proposed conservative subtotal resection leading to the relief of mass effect and avoiding neurological injury, with SRS on the remnant [119]. In addition, posterior fossa meningiomas today are found at earlier stages of growth due to MRI availability and spreading. These are frequently asymptomatic or associated with minimal symptoms. Control rates reported following SRS have proved to guarantee a high tumoral control rate both in post-operative recurrences and in newly diagnosed, small non-symptomatic meningiomas [120][121][122] with progression-free survival rates greater than 90% [123][124]. Prognostic factors described in the literature for failures include age greater than 65 years, prior history of radiotherapy, and increasing tumor volume [124][125].
Moreover, predictors of neurological deterioration after radiosurgery could include large tumor volume, clival location or cerebellopontine angle (as opposed to tentorium or foramen magnum), but these last factors show a low statistical relation. On the contrary, tumoral shrinkage after 3 years from radiosurgery and a dose >16 Gy have been demonstrated to be positive prognostic factors [119].
5.2.3. WHO Grade II and III
WHO Grade II meningiomas appear much less effective to SRS. The reported 5- and 10-year LTC rates are much lower (49–77% and 0–24%, respectively) [126][127]. In the past few years, these results caused fractionated RT to be advocated as an adjuvant or salvage treatment of these neoplasms [128].
If we consider the recent literature, however, SRS proved to be safe and effective for biopsy-proven WHO Grade II meningiomas. Adjuvant SRS following STR in small remnants or small surgical beds resulted in equivalent rates of long-term LTC as adjuvant RT.
Finally, higher radiation doses similar to those applied for malignant tumors should be recommended when possible for SRS treatment of atypical MNs [129].
5.2.4. Combined MS–SRS Approach
A “combined Microsurgical-SRS approach” consists of a deliberate subtotal surgical resection, leaving a remnant near critical structures, followed by SRS [130]. A partial resection, due to its close-fitting position to neurovascular structures, results in increasing tumoral recurrence [131]. Therefore, in cases of atypical or anaplastic meningiomas, radiosurgery always has to be taken into account as an option after surgical debulking [132][133]. In cases of cavernous sinus or/and Meckel’s cave involvement in the skull base, a complete surgical resection might not be reliable, or very dangerous [134]. Common surgical strategies include resecting the maximal part of the tumor, followed by SRS on the remnant, especially if critically located. Radiosurgery in an early post-operative stage is nowadays routinely performed in patients with Grade 1 MN after incomplete resection [117][118][119][135][136]. A combined MS–SRS strategy has proved to be particularly worthy in cases of SBMs [136][137] and in some centers, this strategy is decided with the patients before surgery [137]. On the other hand, several studies have reported a progression of an untreated remnant for which a “wait and scan” policy is adopted [135].
Therefore, in cases of a surgical remnant, an early SRS might be planned in Grade 1–Grade 2 MNs, in order to avoid recurrence [138].
5.2.5. Long-Term Follow-Up
In fact, many studies described excellent short to intermediate period results with 5- and 10-year LTR rates ranging from 86% to 100% and from 69% to 97%, respectively [139][140].
Kondziolka et al. [141] published a retrospective study on meningioma patients treated with GK (gamma-Kinife) SRS (70% of them located on the skull base and 97% WHO Grade I or with typical imaging features of a benign MN). The overall LTC rate was 91%. The 10- and 20-year actuarial rates of freedom from tumor progression of the targeted tumor after SRS was 85.3% ± 2.9% at both time points.
The long-term risk of severe permanent side effects following the SRS for SKMs is another controversial issue.
Recently, McClelland et al. [142] presented the results of an extensive analysis on the risk of stroke after SRS. On a total of 1431 patients followed up for a median/mean interval ranging from 75 to 144 months, 24 patients suffered a stroke following SRS, providing a stroke rate of 1.7%. This risk proved to be 12 times lower than the risk that occurred after fractionated proton-photon RT, and was comparable to that expected for the general population. Thus, SRS appeared to have the same stroke risk profile as observation.
Recently, Talacchi et al. published a robust retrospective analysis on 170 cavernous sinus meningiomas treated with GK SRS and followed up for at least 10 years. The LTC rate at 15 years after SRS was 89%. Neurological status was stable or improved in 147 patients (86.5%), independently of tumor shrinkage. WHO Grade I vs. Grade II histology (p = 0.019) was proven to be the only independent variable for LTR [136].
Overall, these studies with long-term periods of observation for SBMs treated with SRS led to the conclusion that long-term LTC rates were sustained at intervals of more than 10 years after SRS, as well [142].
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Truitt, G.; Boscia, A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, iv1–iv86.
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820.
- Simpson, D. The Recurrence of Intracranial Meningiomas after Surgical Treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1957, 20, 22–39.
- Flood, L.M. Meningiomas of the Skull Base: Treatment Nuances in Contemporary Neurosurgery; Cappabianca, P., Solari, D., Eds.; Thieme: Stuttgart, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-3-13-241302-3.
- Nanda, A.; Bir, S.C.; Maiti, T.K.; Konar, S.K.; Missios, S.; Guthikonda, B. Relevance of Simpson Grading System and Recurrence-Free Survival after Surgery for World Health Organization Grade I Meningioma. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 201–211.
- Wiemels, J.; Wrensch, M.; Claus, E.B. Epidemiology and Etiology of Meningioma. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 99, 307–314.
- Claus, E.B.; Bondy, M.L.; Schildkraut, J.M.; Wiemels, J.L.; Wrensch, M.; Black, P.M. Epidemiology of Intracranial Meningioma. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, 1088–1095.
- Mansouri, A.; Klironomos, G.; Taslimi, S.; Kilian, A.; Gentili, F.; Khan, O.H.; Aldape, K.; Zadeh, G. Surgically Resected Skull Base Meningiomas Demonstrate a Divergent Postoperative Recurrence Pattern Compared with Non–Skull Base Meningiomas. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 431–440.
- Nakamura, M.; Roser, F.; Dormiani, M.; Vorkapic, P.; Samii, M. Surgical Treatment of Cerebellopontine Angle Meningiomas in Elderly Patients. Acta Neurochir. 2005, 147, 603–610.
- Kolakshyapati, M.; Ikawa, F.; Abiko, M.; Mitsuhara, T.; Kinoshita, Y.; Takeda, M.; Kurisu, K. Alumni Association Group of the Department of Neurosurgery at Hiroshima University Multivariate Risk Factor Analysis and Literature Review of Postoperative Deterioration in Karnofsky Performance Scale Score in Elderly Patients with Skull Base Meningioma. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 44, E14.
- Hu, L.-H.; Zhang, W.-B.; Yu, Y.; Peng, X. Accuracy of Multimodal Image Fusion for Oral and Maxillofacial Tumors: A Revised Evaluation Method and Its Application. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 48, 741–750.
- Tel, A.; Bagatto, D.; Tuniz, F.; Sembronio, S.; Costa, F.; D’Agostini, S.; Robiony, M. The Evolution of Craniofacial Resection: A New Workflow for Virtual Planning in Complex Craniofacial Procedures. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 1475–1483.
- Li, N.; Zhou, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, G. Statistical Modeling and Knowledge-Based Segmentation of Cerebral Artery Based on TOF-MRA and MR-T1. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 186, 105110.
- Segato, A.; Pieri, V.; Favaro, A.; Riva, M.; Falini, A.; De Momi, E.; Castellano, A. Automated Steerable Path Planning for Deep Brain Stimulation Safeguarding Fiber Tracts and Deep Gray Matter Nuclei. Front. Robot. AI 2019, 6, 70.
- Bücking, T.M.; Hill, E.R.; Robertson, J.L.; Maneas, E.; Plumb, A.A.; Nikitichev, D.I. From Medical Imaging Data to 3D Printed Anatomical Models. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178540.
- Soleman, J.; Leiggener, C.; Schlaeppi, A.-J.; Kienzler, J.; Fathi, A.-R.; Fandino, J. The Extended Subfrontal and Fronto-Orbito-Zygomatic Approach in Skull Base Meningioma Surgery: Clinical, Radiologic, and Cosmetic Outcome. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, 433–440.
- Ius, T.; Somma, T.; Baiano, C.; Guarracino, I.; Pauletto, G.; Nilo, A.; Maieron, M.; Palese, F.; Skrap, M.; Tomasino, B. Risk Assessment by Pre-Surgical Tractography in Left Hemisphere Low-Grade Gliomas. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 648432.
- Ius, T.; Turella, L.; Pauletto, G.; Isola, M.; Maieron, M.; Sciacca, G.; Budai, R.; D’Agostini, S.; Eleopra, R.; Skrap, M. Quantitative Diffusion Tensor Imaging Analysis of Low-Grade Gliomas: From Preclinical Application to Patient Care. World Neurosurgery 2017, 97, 333–343.
- Campanella, M.; Ius, T.; Skrap, M.; Fadiga, L. Alterations in Fiber Pathways Reveal Brain Tumor Typology: A Diffusion Tractography Study. PeerJ 2014, 2, e497.
- Jacquesson, T.; Cotton, F.; Attyé, A.; Zaouche, S.; Tringali, S.; Bosc, J.; Robinson, P.; Jouanneau, E.; Frindel, C. Probabilistic Tractography to Predict the Position of Cranial Nerves Displaced by Skull Base Tumors: Value for Surgical Strategy Through a Case Series of 62 Patients. Neurosurgery 2019, 85, E125–E136.
- Jacquesson, T.; Frindel, C.; Kocevar, G.; Berhouma, M.; Jouanneau, E.; Attyé, A.; Cotton, F. Overcoming Challenges of Cranial Nerve Tractography: A Targeted Review. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, 313–325.
- Castellaro, M.; Moretto, M.; Baro, V.; Brigadoi, S.; Zanoletti, E.; Anglani, M.; Denaro, L.; Dell’Acqua, R.; Landi, A.; Causin, F.; et al. Multishell Diffusion MRI-Based Tractography of the Facial Nerve in Vestibular Schwannoma. AJNR. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1480–1486.
- Jho, H.-D.; Carrau, R.L. Endoscopic Endonasal Transsphenoidal Surgery: Experience with 50 Patients. J. Neurosurg. 1997, 87, 44–51.
- Cappabianca, P.; Alfieri, A.; de Divitiis, E. Endoscopic Endonasal Transsphenoidal Approach to the Sella: Towards Functional Endoscopic Pituitary Surgery (Feps)*. MIN-Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 1998, 41, 66–73.
- Kassam, A.B.; Gardner, P.; Snyderman, C.; Mintz, A.; Carrau, R. Expanded Endonasal Approach: Fully Endoscopic, Completely Transnasal Approach to the Middle Third of the Clivus, Petrous Bone, Middle Cranial Fossa, and Infratemporal Fossa. Neurosurg. Focus 2005, 19, E6.
- Zada, G.; Du, R.; Laws, E.R. Defining the “Edge of the Envelope”: Patient Selection in Treating Complex Sellar-Based Neoplasms via Transsphenoidal versus Open Craniotomy: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 286–300.
- De Rosa, A.; Pineda, J.; Cavallo, L.M.; Di Somma, A.; Romano, A.; Topczewski, T.E.; Somma, T.; Solari, D.; Enseñat, J.; Cappabianca, P.; et al. Endoscopic Endo- and Extra-Orbital Corridors for Spheno-Orbital Region: Anatomic Study with Illustrative Case. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 1633–1646.
- Koppe, M.; Gleizal, A.; Orset, E.; Bachelet, J.T.; Jouanneau, E.; Rougeot, A. Superior Eyelid Crease Approach for Transobital Neuroendoscopic Surgery of the Anterior Cranial Fossa. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2013, 24, 1616–1621.
- Abou-Al-Shaar, H.; Krisht, K.M.; Cohen, M.A.; Abunimer, A.M.; Neil, J.A.; Karsy, M.; Alzhrani, G.; Couldwell, W.T. Cranio-Orbital and Orbitocranial Approaches to Orbital and Intracranial Disease: Eye-Opening Approaches for Neurosurgeons. Front. Surg. 2020, 7, 1.
- Janecka, I.P. Classification of Facial Translocation Approach to the Skull Base. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1995, 112, 579–585.
- Skull Base Surgery: Anatomy, Biology, and Technology; Janecka, I.P. (Ed.) Lippincott-Raven: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-397-51716-9.
- Inoue, T.; Rhoton, A.L.; Theele, D.; Barry, M.E. Surgical Approaches to the Cavernous Sinus: A Microsurgical Study. Neurosurgery 1990, 26, 903.
- Jannetta, P.J.; Abbasy, M.; Maroon, J.C.; Ramos, F.M.; Albin, M.S. Etiology and Definitive Microsurgical Treatment of Hemifacial Spasm: Operative Techniques and Results in 47 Patients. J. Neurosurg. 1977, 47, 321–328.
- Parkinson, D. The Posterior Cranial Fossa: Microsurgical Anatomy and Surgical Approaches. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 1196.
- Scerrati, A.; Lee, J.-S.; Zhang, J.; Ammirati, M. Microsurgical Anatomy of the Internal Acoustic Meatus as Seen Using the Retrosigmoid Approach. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 568–573.
- Scerrati, A.; Lee, J.-S.; Zhang, J.; Ammirati, M. Exposing the Fundus of the Internal Acoustic Meatus without Entering the Labyrinth Using a Retrosigmoid Approach: Is It Possible? World Neurosurg. 2016, 91, 357–364.
- Hakuba, A.; Nishimura, S.; Jang, B.J. A Combined Retroauricular and Preauricular Transpetrosal-Transtentorial Approach to Clivus Meningiomas. Surg. Neurol. 1988, 30, 108–116.
- King, T.T.; Morrison, A.W. Translabyrinthine and Transtentorial Removal of Acoustic Nerve Tumors: Results in 150 Cases. J. Neurosurg. 1980, 52, 210–216.
- Seoane, E.; Rhoton, A.L. Suprameatal Extension of the Retrosigmoid Approach: Microsurgical Anatomy. Neurosurgery 1999, 44, 553–560.
- Ercan, S.; Scerrati, A.; Wu, P.; Zhang, J.; Ammirati, M. Is Less Always Better? Keyhole and Standard Subtemporal Approaches: Evaluation of Temporal Lobe Retraction and Surgical Volume with and without Zygomatic Osteotomy in a Cadaveric Model. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 157–164.
- Lee, J.-S.; Scerrati, A.; Zhang, J.; Ammirati, M. Quantitative Analysis of Surgical Exposure and Surgical Freedom to the Anterosuperior Pons: Comparison of Pterional Transtentorial, Orbitozygomatic, and Anterior Petrosal Approaches. Neurosurg. Rev. 2016, 39, 599–605.
- Ichinose, T.; Goto, T.; Ishibashi, K.; Takami, T.; Ohata, K. The Role of Radical Microsurgical Resection in Multimodal Treatment for Skull Base Meningioma: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 1072–1078.
- Bassiouni, H.; Ntoukas, V.; Asgari, S.; Sandalcioglu, E.I.; Stolke, D.; Seifert, V. Foramen magnum meningiomas. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, 1177–1187.
- Scheitzach, J.; Schebesch, K.-M.; Brawanski, A.; Proescholdt, M.A. Skull Base Meningiomas: Neurological Outcome after Microsurgical Resection. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 116, 381–386.
- Voß, K.M.; Spille, D.C.; Sauerland, C.; Suero Molina, E.; Brokinkel, C.; Paulus, W.; Stummer, W.; Holling, M.; Jeibmann, A.; Brokinkel, B. The Simpson Grading in Meningioma Surgery: Does the Tumor Location Influence the Prognostic Value? J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 641–651.
- Bassiouni, H.; Asgari, S.; Sandalcioglu, I.E.; Seifert, V.; Stolke, D.; Marquardt, G. Anterior Clinoidal Meningiomas: Functional Outcome after Microsurgical Resection in a Consecutive Series of 106 Patients: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 1078–1090.
- Seifert, V. Clinical Management of Petroclival Meningiomas and the Eternal Quest for Preservation of Quality of Life: Personal Experiences over a Period of 20 Years. Acta Neurochir. 2010, 152, 1099–1116.
- Gousias, K.; Schramm, J.; Simon, M. The Simpson Grading Revisited: Aggressive Surgery and Its Place in Modern Meningioma Management. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 551–560.
- Raheja, A.; Couldwell, W.T. Microsurgical Resection of Skull Base Meningioma—Expanding the Operative Corridor. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 130, 263–267.
- Goto, T.; Muraoka, H.; Kodama, K.; Hara, Y.; Yako, T.; Hongo, K. Intraoperative Monitoring of Motor Evoked Potential for the Facial Nerve Using a Cranial Peg-Screw Electrode and a “Threshold-Level” Stimulation Method. Skull Base 2010, 20, 429–434.
- Cornelius, J.F.; Schipper, J.; Tortora, A.; Krause-Molle, Z.; Smuga, M.; Petridis, A.K.; Steiger, H.-J. Continuous and Dynamic Facial Nerve Mapping during Surgery of Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Clinical Pilot Series. World Neurosurg. 2018, 119, e855–e863.
- Slotty, P.J.; Abdulazim, A.; Kodama, K.; Javadi, M.; Hänggi, D.; Seifert, V.; Szelényi, A. Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring during Resection of Infratentorial Lesions: The Surgeon’s View. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 281–288.
- Ilyas, A.; Przybylowski, C.; Chen, C.-J.; Ding, D.; Foreman, P.M.; Buell, T.J.; Taylor, D.G.; Kalani, M.Y.; Park, M.S. Preoperative Embolization of Skull Base Meningiomas: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 59, 259–264.
- Yoon, N.; Shah, A.; Couldwell, W.T.; Kalani, M.Y.S.; Park, M.S. Preoperative Embolization of Skull Base Meningiomas: Current Indications, Techniques, and Pearls for Complication Avoidance. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 44, E5.
- Di Maio, S.; Ramanathan, D.; Garcia-Lopez, R.; Rocha, M.H.; Guerrero, F.P.; Ferreira, M.; Sekhar, L.N. Evolution and Future of Skull Base Surgery: The Paradigm of Skull Base Meningiomas. World Neurosurg. 2012, 78, 260–275.
- Jumah, F.; AbuRmilah, A.; Raju, B.; Jaber, S.; Adeeb, N.; Narayan, V.; Sun, H.; Cuellar, H.; Gupta, G.; Nanda, A. Does preoperative embolization improve outcomes of meningioma resection? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021.
- Ellis, J.A.; D’Amico, R.; Sisti, M.B.; Bruce, J.N.; McKhann, G.M.; Lavine, S.D.; Meyers, P.M.; Strozyk, D. Pre-operative intracranial meningioma embolization. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 545–556.
- Hanasono, M.M. Reconstruction after Open Surgery for Skull-Base Malignancies. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 150, 469–475.
- Gagliardi, F.; Piloni, M.; Bailo, M.; Gragnaniello, C.; Nocera, G.; Boari, N.; Spina, A.; Caputy, A.J.; Mortini, P. Temporal Myofascial Segmentation for Multilayer Reconstruction of Middle Cranial Fossa Floor after Extradural Subtemporal Approach to the Clival and Paraclival Region. Head Neck 2019, 41, 3631–3638.
- Parkes, W.J.; Krein, H.; Heffelfinger, R.; Curry, J. Use of the Anterolateral Thigh in Cranio-Orbitofacial Reconstruction. Plast. Surg. Int. 2011, 2011, 1–6.
- Hadad, G.; Bassagasteguy, L.; Carrau, R.L.; Mataza, J.C.; Kassam, A.; Snyderman, C.H.; Mintz, A. A Novel Reconstructive Technique After Endoscopic Expanded Endonasal Approaches: Vascular Pedicle Nasoseptal Flap. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 1882–1886.
- Scerrati, A.; Trovalusci, F.; Albanese, A.; Ponticelli, G.S.; Tagliaferri, V.; Sturiale, C.L.; Cavallo, M.A.; Marchese, E. A Workflow to Generate Physical 3D Models of Cerebral Aneurysms Applying Open Source Freeware for CAD Modeling and 3D Printing. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2019, 17, 1–6.
- Tel, A. Computer-Guided in-House Cranioplasty: Establishing a Novel Standard for Cranial Reconstruction and Proposal of an Updated Protocol. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 78, 2297-e1.
- Zheng, J.S.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, X.Z.; Jiang, W.B.; Abdelrehem, A.; Zhang, S.Y.; Chen, M.J.; Yang, C. Customized Skull Base–Temporomandibular Joint Combined Prosthesis with 3D-Printing Fabrication for Craniomaxillofacial Reconstruction: A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 1440–1447.
- Moriwaki, Y.; Tomioka, Y.; Imai, H.; Iida, T.; Yamashita, S.; Kanayama, K.; Iwamoto, N.; Okazaki, M. Treating Pulsatile Exophthalmos in Child with Minimally Invasive Approach and Custom-Made Titanium Mesh Plate. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2070.
- Grob, S.R.; Chen, K.G.; Tao, J.P. Orbital Roof Reconstruction Using Nylon Foil Implants. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 35, 286–289.
- Abedalthagafi, M.; Bi, W.L.; Aizer, A.A.; Merrill, P.H.; Brewster, R.; Agarwalla, P.K.; Listewnik, M.L.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Thorner, A.R.; Van Hummelen, P.; et al. Oncogenic PI3K Mutations Are as Common as AKT1 and SMO Mutations in Meningioma. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 649–655.
- Barresi, V.; Alafaci, C.; Caffo, M.; Barresi, G.; Tuccari, G. Clinicopathological Characteristics, Hormone Receptor Status and Matrix Metallo-Proteinase-9 (MMP-9) Immunohistochemical Expression in Spinal Meningiomas. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2012, 208, 350–355.
- Trivedi, M.M.; Worley, S.; Raghavan, A.; Das, P.; Recinos, P.F.; Barnett, G.H.; Kshettry, V.R. Peritumoral Brain Edema and Surgical Outcome in Secretory Meningiomas: A Matched-Cohort Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2021, 145, e170–e176.
- Brastianos, P.K.; Horowitz, P.M.; Santagata, S.; Jones, R.T.; McKenna, A.; Getz, G.; Ligon, K.L.; Palescandolo, E.; Van Hummelen, P.; Ducar, M.D.; et al. Genomic Sequencing of Meningiomas Identifies Oncogenic SMO and AKT1 Mutations. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 285–289.
- Clark, V.E.; Erson-Omay, E.Z.; Serin, A.; Yin, J.; Cotney, J.; Ozduman, K.; Avsar, T.; Li, J.; Murray, P.B.; Henegariu, O.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Non-Nf2 Meningiomas Reveals Mutations in Traf7, Klf4, Akt1, and Smo. Science 2013, 339, 1077–1080.
- Barresi, V.; Simbolo, M.; Fioravanzo, A.; Piredda, M.; Caffo, M.; Ghimenton, C.; Pinna, G.; Longhi, M.; Nicolato, A.; Scarpa, A. Molecular Profiling of 22 Primary Atypical Meningiomas Shows the Prognostic Significance of 18q Heterozygous Loss and CDKN2A/B Homozygous Deletion on Recurrence-Free Survival. Cancers 2021, 13, 903.
- Yesilöz, Ü.; Kirches, E.; Hartmann, C.; Scholz, J.; Kropf, S.; Sahm, F.; Nakamura, M.; Mawrin, C. Frequent AKT1E17K Mutations in Skull Base Meningiomas Are Associated with MTOR and ERK1/2 Activation and Reduced Time to Tumor Recurrence. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 1088–1096.
- Hao, S.; Huang, G.; Feng, J.; Li, D.; Wang, K.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Wan, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Non-NF2 Mutations Have a Key Effect on Inhibitory Immune Checkpoints and Tumor Pathogenesis in Skull Base Meningiomas. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 144, 11–20.
- Boetto, J.; Bielle, F.; Sanson, M.; Peyre, M.; Kalamarides, M. Smo Mutation Status Defines a Distinct and Frequent Molecular Subgroup in Olfactory Groove Meningiomas. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 276.
- Clark, V.E.; Harmancı, A.S.; Bai, H.; Youngblood, M.W.; Lee, T.I.; Baranoski, J.F.; Ercan-Sencicek, A.G.; Abraham, B.J.; Weintraub, A.S.; Hnisz, D.; et al. Recurrent Somatic Mutations in POLR2A Define a Distinct Subset of Meningiomas. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1253–1259.
- Goldsmith, B.J.; Wara, W.M.; Wilson, C.B.; Larson, D.A. Postoperative Irradiation for Subtotally Resected Meningiomas: A Retrospective Analysis of 140 Patients Treated from 1967 to 1990. J. Neurosurg. 1994, 80, 195–201.
- Maire, J.-P.; Caudry, M.; Guérin, J.; Célérier, D.; San Galli, F.; Causse, N.; Trouette, R.; Dautheribes, M. Fractionated Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Intracranial Meningiomas: Local Control, Functional Efficacy, and Tolerance in 91 Patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1995, 33, 315–321.
- Nutting, C.; Brada, M.; Brazil, L.; Sibtain, A.; Saran, F.; Westbury, C.; Moore, A.; Thomas, D.G.T.; Traish, D.; Ashley, S. Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Benign Meningioma of the Skull Base. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 90, 823–827.
- Vendrely, V.; Maire, J.P.; Darrouzet, V.; Bonichon, N.; San Galli, F.; Célérier, D.; Causse, N.; Demeaux, H.; Trouette, R.; Dahan, O.; et al. Radiothérapie fractionnée des méningiomes intracrâniens: 15 ans d’expérience au centre hospitalier universitaire de Bordeaux. Cancer/Radiothérapie 1999, 3, 311–317.
- Mendenhall, W.M.; Morris, C.G.; Amdur, R.J.; Foote, K.D.; Friedman, W.A. Radiotherapy Alone or after Subtotal Resection for Benign Skull Base Meningiomas. Cancer 2003, 98, 1473–1482.
- O’steen, L.; Amdur, R.J.; Morris, C.G.; Mendenhall, W.M. Challenging the Concept That Late Recurrence and Death from Tumor Are Common after Fractionated Radiotherapy for Benign Meningioma. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 137, 55–60.
- Amichetti, M.; Amelio, D.; Minniti, G. Radiosurgery with Photons or Protons for Benign and Malignant Tumours of the Skull Base: A Review. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 7, 210.
- Henzel, M.; Gross, M.W.; Hamm, K.; Surber, G.; Kleinert, G.; Failing, T.; Strassmann, G.; Engenhart-Cabillic, R. Significant Tumor Volume Reduction of Meningiomas after Stereotactic Radiotherapy. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, 1188–1194.
- Tanzler, E.; Morris, C.G.; Kirwan, J.M.; Amdur, R.J.; Mendenhall, W.M. Outcomes of Who Grade i Meningiomas Receiving Definitive or Postoperative Radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 79, 508–513.
- Minniti, G.; Clarke, E.; Cavallo, L.; Osti, M.F.; Esposito, V.; Cantore, G.; Cappabianca, P.; Enrici, R.M. Fractionated Stereotactic Conformal Radiotherapy for Large Benign Skull Base Meningiomas. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 36.
- Slater, J.D.; Loredo, L.N.; Chung, A.; Bush, D.A.; Patyal, B.; Johnson, W.D.; Hsu, F.P.K.; Slater, J.M. Fractionated Proton Radiotherapy for Benign Cavernous Sinus Meningiomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 83, e633–e637.
- Weber, D.C.; Schneider, R.; Goitein, G.; Koch, T.; Ares, C.; Geismar, J.H.; Schertler, A.; Bolsi, A.; Hug, E.B. Spot Scanning-Based Proton Therapy for Intracranial Meningioma: Long-Term Results from the Paul Scherrer Institute. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 83, 865–871.
- Soldà, F.; Wharram, B.; De Ieso, P.B.; Bonner, J.; Ashley, S.; Brada, M. Long-Term Efficacy of Fractionated Radiotherapy for Benign Meningiomas. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 109, 330–334.
- Combs, S.E.; Farzin, M.; Boehmer, J.; Oehlke, O.; Molls, M.; Debus, J.; Grosu, A.-L. Clinical Outcome after High-Precision Radiotherapy for Skull Base Meningiomas: Pooled Data from Three Large German Centers for Radiation Oncology. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 127, 274–279.
- Fokas, E.; Henzel, M.; Surber, G.; Hamm, K.; Engenhart-Cabillic, R. Stereotactic Radiation Therapy for Benign Meningioma: Long-Term Outcome in 318 Patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 89, 569–575.
- Han, J.; Girvigian, M.R.; Chen, J.C.T.; Miller, M.J.; Lodin, K.; Rahimian, J.; Arellano, A.; Cahan, B.L.; Kaptein, J.S. A Comparative Study of Stereotactic Radiosurgery, Hypofractionated, and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Skull Base Meningioma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 37, 255–260.
- Connell, P.P.; Macdonald, R.L.; Mansur, D.B.; Nicholas, M.K.; Mundt, A.J. Tumor Size Predicts Control of Benign Meningiomas Treated with Radiotherapy. Neurosurgery 1999, 44, 1194–1200.
- Sanford, N.N.; Yeap, B.Y.; Larvie, M.; Daartz, J.; Munzenrider, J.E.; Liebsch, N.J.; Fullerton, B.; Pan, E.; Loeffler, J.S.; Shih, H.A. Prospective, Randomized Study of Radiation Dose Escalation with Combined Proton-Photon Therapy for Benign Meningiomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 99, 787–796.
- Crossen, J.R.; Garwood, D.; Glatstein, E.; Neuwelt, E.A. Neurobehavioral Sequelae of Cranial Irradiation in Adults: A Review of Radiation-Induced Encephalopathy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1994, 12, 627–642.
- Maguire, P.D.; Clough, R.; Friedman, A.H.; Halperin, E.C. Fractionated External-Beam Radiation Therapy for Meningiomas of the Cavernous Sinus. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1999, 44, 75–79.
- Dufour, H.; Muracciole, X.; Métellus, P.; Régis, J.; Chinot, O.; Grisoli, F. Long-Term Tumor Control and Functional Outcome in Patients with Cavernous Sinus Meningiomas Treated by Radiotherapy with or without Previous Surgery: Is There an Alternative to Aggressive Tumor Removal? Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 285–296.
- Rogers, L.; Zhang, P.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Perry, A.; Ashby, L.S.; Modi, J.M.; Alleman, A.M.; Galvin, J.; Brachman, D.; Jenrette, J.M.; et al. Intermediate-Risk Meningioma: Initial Outcomes from NRG Oncology RTOG 0539. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 35–47.
- Rogers, C.L.; Won, M.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Perry, A.; Ashby, L.S.; Modi, J.M.; Alleman, A.M.; Galvin, J.; Fogh, S.E.; Youssef, E.; et al. High-Risk Meningioma: Initial Outcomes From NRG Oncology/RTOG 0539. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 106, 790–799.
- Jenkinson, M.D.; Javadpour, M.; Haylock, B.J.; Young, B.; Gillard, H.; Vinten, J.; Bulbeck, H.; Das, K.; Farrell, M.; Looby, S.; et al. The ROAM/EORTC-1308 Trial: Radiation versus Observation Following Surgical Resection of Atypical Meningioma: Study Protocol for a Randomised Controlled Trial. Trials 2015, 16, 519.
- Scaringi, C.; Agolli, L.; Minniti, G. Technical Advances in Radiation Therapy for Brain Tumors. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6041–6045.
- Kaul, D.; Budach, V.; Misch, M.; Wiener, E.; Exner, S.; Badakhshi, H. Meningioma of the Skull Base: Long-Term Outcome after Image-Guided Stereotactic Radiotherapy. Cancer/Radiothérapie 2014, 18, 730–735.
- Torres, R.C.; Frighetto, L.; De Salles, A.A.F.; Goss, B.; Medin, P.; Solberg, T.; Ford, J.M.; Selch, M. Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Intracranial Meningiomas. Neurosurg. Focus 2003, 14, 1–6.
- Lo, S.S.; Cho, K.H.; Hall, W.A.; Kossow, R.J.; Hernandez, W.L.; McCollow, K.K.; Gerbi, B.J.; Higgins, P.D.; Lee, C.K.; Dusenbery, K.E. Single Dose versus Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Meningiomas. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. J. Can. Sci. Neurol. 2002, 29, 240–248.
- Metellus, P.; Regis, J.; Muracciole, X.; Fuentes, S.; Dufour, H.; Nanni, I.; Chinot, O.; Martin, P.-M.; Grisoli, F. Evaluation of Fractionated Radiotherapy and Gamma Knife Radiosurgery in Cavernous Sinus Meningiomas: Treatment Strategy. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, 873–886.
- Colombo, F.; Casentini, L.; Cavedon, C.; Scalchi, P.; Cora, S.; Francescon, P. Cyberknife Radiosurgery for Benign Meningiomas. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, A7–A13.
- Navarria, P.; Pessina, F.; Cozzi, L.; Clerici, E.; Villa, E.; Ascolese, A.M.; De Rose, F.; Comito, T.; Franzese, C.; D’Agostino, G.; et al. Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiation Therapy in Skull Base Meningiomas. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 124, 283–289.
- Marchetti, M.; Bianchi, S.; Pinzi, V.; Tramacere, I.; Fumagalli, M.L.; Milanesi, I.M.; Ferroli, P.; Franzini, A.; Saini, M.; DiMeco, F.; et al. Multisession Radiosurgery for Sellar and Parasellar Benign Meningiomas: Long-Term Tumor Growth Control and Visual Outcome. Neurosurgery 2016, 78, 638–646.
- Marchetti, M.; Conti, A.; Beltramo, G.; Pinzi, V.; Pontoriero, A.; Tramacere, I.; Senger, C.; Pergolizzi, S.; Fariselli, L. Multisession Radiosurgery for Perioptic Meningiomas: Medium-to-Long Term Results from a CyberKnife Cooperative Study. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 143, 597–604.
- Nguyen, E.K.; Nguyen, T.K.; Boldt, G.; Louie, A.V.; Bauman, G.S. Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Intracranial Meningioma: A Systematic Review. Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2019, 6, 346–353.
- Milano, M.T.; Sharma, M.; Soltys, S.G.; Sahgal, A.; Usuki, K.Y.; Saenz, J.-M.; Grimm, J.; El Naqa, I. Radiation-Induced Edema after Single-Fraction or Multifraction Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Meningioma: A Critical Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 101, 344–357.
- Leksell, L. A Note on the Treatment of Acoustic Tumours. Acta Chir. Scand. 1971, 137, 763–765.
- Team, E.W. Leksell Gamma Knife—50 Years of Iconic Brain Care; Elekta: Stockholm, Sweden, 2018.
- Pollock, B.E.; Stafford, S.L.; Utter, A.; Giannini, C.; Schreiner, S.A. Stereotactic Radiosurgery Provides Equivalent Tumor Control to Simpson Grade 1 Resection for Patients with Small- to Medium-Size Meningiomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2003, 55, 1000–1005.
- Adler, J.R.; Murphy, M.J.; Chang, S.D.; Hancock, S.L. Image-Guided Robotic Radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 1999, 44, 1299–1306.
- Lee, J.Y.K.; Niranjan, A.; McInerney, J.; Kondziolka, D.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D. Stereotactic Radiosurgery Providing Long-Term Tumor Control of Cavernous Sinus Meningiomas. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 65–72.
- Kreil, W. Long Term Experience of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Benign Skull Base Meningiomas. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1425–1430.
- Kondziolka, D.; Nathoo, N.; Flickinger, J.C.; Niranjan, A.; Maitz, A.H.; Lunsford, L.D. Long-Term Results after Radiosurgery for Benign Intracranial Tumors. Neurosurgery 2003, 53, 815–822.
- Patibandla, M.R.; Lee, C.; Tata, A.; Addagada, G.C.; Sheehan, J.P. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for WHO Grade I Posterior Fossa Meningiomas: Long-Term Outcomes with Volumetric Evaluation. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 1249–1259.
- Flannery, T.J.; Kano, H.; Lunsford, L.D.; Sirin, S.; Tormenti, M.; Niranjan, A.; Flickinger, J.C.; Kondziolka, D. Long-Term Control of Petroclival Meningiomas through Radiosurgery: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 957–964.
- Debus, J.; Wuendrich, M.; Pirzkall, A.; Hoess, A.; Schlegel, W.; Zuna, I.; Engenhart-Cabillic, R.; Wannenmacher, M. High Efficacy of Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy of Large Base-of-Skull Meningiomas: Long-Term Results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 3547–3553.
- Aichholzer, M.; Bertalanffy, A.; Dietrich, W.; Roessler, K.; Pfisterer, W.; Ungersboeck, K.; Heimberger, K.; Kitz, K. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery of Skull Base Meningiomas. Acta Neurochir. 2000, 142, 647–653.
- Sheehan, J.P.; Starke, R.M.; Kano, H.; Barnett, G.H.; Mathieu, D.; Chiang, V.; Yu, J.B.; Hess, J.; McBride, H.L.; Honea, N.; et al. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Posterior Fossa Meningiomas: A Multicenter Study. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 1479–1489.
- Starke, R.M.; Nguyen, J.H.; Rainey, J.; Williams, B.J.; Sherman, J.H.; Savage, J.; Yen, C.P.; Sheehan, J.P. Gamma Knife Surgery of Meningiomas Located in the Posterior Fossa: Factors Predictive of Outcome and Remission: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 1399–1409.
- Sheehan, J.; Starke, R.; Nguyen, J.; Reames, D.; Rainey, J. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery of Meningiomas Involving the Foramen Magnum. J. Craniovertebral Junction Spine 2010, 1, 23.
- Malik, I.; Rowe, J.; Walton, L.; Radatz, M.; Kemeny, A. The Use of Stereotactic Radiosurgery in the Management of Meningiomas. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 19, 13–20.
- Stieber, V.W. Radiation Therapy for Visual Pathway Tumors. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2008, 28, 222–230.
- Goldbrunner, R.; Minniti, G.; Preusser, M.; Jenkinson, M.D.; Sallabanda, K.; Houdart, E.; von Deimling, A.; Stavrinou, P.; Lefranc, F.; Lund-Johansen, M.; et al. EANO Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Meningiomas. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e383–e391.
- Aboukais, R.; Zairi, F.; Lejeune, J.-P.; Le Rhun, E.; Vermandel, M.; Blond, S.; Devos, P.; Reyns, N. Grade 2 Meningioma and Radiosurgery. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 1157–1162.
- Aboukais, R.; Zairi, F.; Reyns, N.; Le Rhun, E.; Touzet, G.; Blond, S.; Lejeune, J.-P. Surgery Followed by Radiosurgery: A Deliberate Valuable Strategy in the Treatment of Intracranial Meningioma. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2014, 124, 123–126.
- Hasseleid, B.F.; Meling, T.R.; Rønning, P.; Scheie, D.; Helseth, E. Surgery for Convexity Meningioma: Simpson Grade I Resection as the Goal: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117, 999–1006.
- Aboukais, R.; Baroncini, M.; Zairi, F.; Reyns, N.; Lejeune, J.-P. Early Postoperative Radiotherapy Improves Progression Free Survival in Patients with Grade 2 Meningioma. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 1385–1390.
- Adeberg, S.; Hartmann, C.; Welzel, T.; Rieken, S.; Habermehl, D.; von Deimling, A.; Debus, J.; Combs, S.E. Long-Term Outcome after Radiotherapy in Patients with Atypical and Malignant Meningiomas—Clinical Results in 85 Patients Treated in a Single Institution Leading to Optimized Guidelines for Early Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 83, 859–864.
- Goto, T.; Ohata, K. Surgical Resectability of Skull Base Meningiomas. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2016, 56, 372–378.
- Cohen-Inbar, O.; Lee, C.; Schlesinger, D.; Xu, Z.; Sheehan, J.P. Long-Term Results of Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Skull Base Meningiomas. Neurosurgery 2016, 79, 58–68.
- Talacchi, A.; Hasanbelliu, A.; D’Amico, A.; Regge Gianas, N.; Locatelli, F.; Pasqualin, A.; Longhi, M.; Nicolato, A. Long-Term Follow-up after Surgical Removal of Meningioma of the Inner Third of the Sphenoidal Wing: Outcome Determinants and Different Strategies. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020, 43, 109–117.
- Hardesty, D.A.; Wolf, A.B.; Brachman, D.G.; McBride, H.L.; Youssef, E.; Nakaji, P.; Porter, R.W.; Smith, K.A.; Spetzler, R.F.; Sanai, N. The Impact of Adjuvant Stereotactic Radiosurgery on Atypical Meningioma Recurrence Following Aggressive Microsurgical Resection: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 475–481.
- Frostell, A.; Hakim, R.; Dodoo, E.; Sinclair, G.; Ohlsson, M.; Förander, P.; Milovac, B.; Brundin, L.; Svensson, M. Adjuvant Stereotactic Radiosurgery Reduces Need for Retreatments in Patients with Meningioma Residuals. World Neurosurg. 2016, 88, 475–482.
- Iwai, Y.; Yamanaka, K.; Ikeda, H. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Skull Base Meningioma: Long-Term Results of Low-Dose Treatment: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 109, 804–810.
- Kondziolka, D.; Mathieu, D.; Lunsford, L.D.; Martin, J.J.; Madhok, R.; Niranjan, A.; Flickinger, J.C. Radiosurgery as Definitive Management of Intracranial Meningiomas. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 53–60.
- Kondziolka, D.; Patel, A.D.; Kano, H.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D. Long-Term Outcomes after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Meningiomas. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 453–457.
- McClelland, S.; Ciporen, J.N.; Mitin, T.; Jaboin, J.J. Long-Term Stroke Risk of Single-Fraction Photon-Based Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Meningioma. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 173, 169–172.




