Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Biology
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the leading cause of cancer death in men, and its treatment is commonly associated with severe adverse effects. Thus, new treatment modalities are required. In this context, natural compounds have been widely explored for their anti-PCa properties. Aquatic organisms contain numerous potential medications. Anticancer peptides are less toxic to normal cells and provide an efficacious treatment approach via multiple mechanisms, including altered cell viability, apoptosis, cell migration/invasion, suppression of angiogenesis and microtubule balance disturbances.
- marine peptides
- apoptosis
- antimetastatic
- antimitotic
1. Introduction
Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the most often diagnosed cancers worldwide. It is the second leading source of cancer-related mortality in males, trailing behind only lung cancer, based on GLOBOCAN 2020 estimates [1]. Radiation and surgical procedures are used to treat this disease when it first appears and is localized. Despite a considerable increase in disease-free life following first surgical or radiation therapy, the illness recurs in more than 30% of patients. Androgen deprivation treatment (ADT) is the most often alternative for PCa treatment, because of the tumor’s requirement for male hormones for progression. This treatment is focused on pharmacological castration achieved via GnRH agonists alone or in conjunction with anti-androgens. However, despite an excellent initial response, most patients relapse within 2–3 years, and the tumor advances. Chemotherapeutic drugs, such as docetaxel, cabazitaxel, doxorubicin, abiraterone and enzalutamide, provide a few months of progression-free survival with highly toxic effects. Therefore, the development and refinement of unique anticancer drugs with minimal adverse side effects are required [2,3].
Natural products provide benefits over synthetic compounds because of their broader variety of targets, larger structural diversity and low toxicity against PCa [4,5]. Many bioactive substances found in the marine ecosystem have potential applications in the treatment of human diseases including cancer. A large number of novel sea-based biological compounds have been derived from corals, sponges, tunicates, bacteria, fungi, micro- and macroalgae, and other marine micro- and macro-organisms. Treatments have been impacted by marine-based medicines, with anticancer treatments made available with several marine chemical compounds. Indeed, clinical approval has been granted for several such treatments, including belantamabmafodotin, cytarabine, enfortumabvedotin, brentuximab vedotin, eribulin mesylate, lurbinectedin, fludarabine phosphate (prodrug of ara-A), nelarabine (prodrug of ara-G), polatuzumabvedotin, trabectedin, vidarabine, and plitidepsin [6,7,8,9]. Improvement in the physiological state of cancer patients depends on the introduction of natural strategies for clinical treatment. Due to their small size, ease of synthesis, capacity to cross cell membranes, low drug–drug interactions, precision targeting, and reduced side responses, marine peptides have also spurred attention in the development of anticancer medicines. The downsides of anticancer peptides include their short half-life, low bioavailability, poor pharmacokinetics, and protease sensitivity [10,11,12]. A schematic representation of the pathophysiology of prostate cancer is shown in Figure 1.
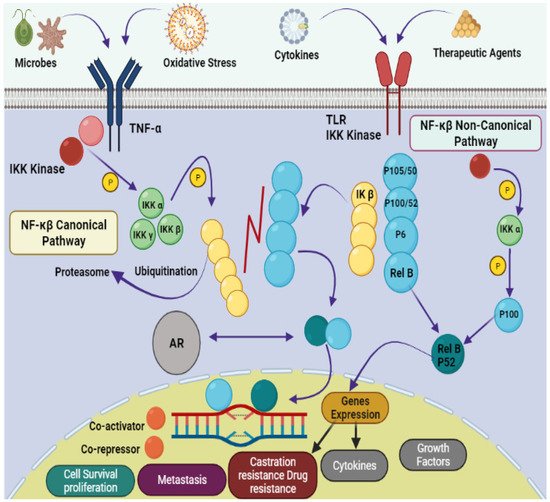
Figure 1. Pathophysiology of prostate cancer via NF-κB canonical and non-canonical pathways. The leading dimers of NF-κB are P50-P65, which activate the transcription process in canonical pathways. Different subunits like Toll-like receptor (TLR); tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNF-R); Inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB); IκB kinase; NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK); mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP); androgen receptor (AR); bone marrow-derived cell (BMDC) and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) are also involved in the pathology of prostate cancer.
Presently, more than 60% of clinically accessible anticancer medications have been derived from natural sources. Peptides are categorized depending on their ability to induce antioxidative mechanisms, cytotoxicity, apoptosis, inhibit cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis, microtubule-destabilization, or undiscovered mechanisms in diverse malignant cell lines, relating to clinical research for cancer treatment evaluation [12,13]. Anticancer peptides from algae, ascidians, bacteria, fungi, cyanobacteria, mollusks, sponges, and protein hydrolysates from clam, coral and fish, have been isolated. Linear and cyclic peptides are the two types of marine peptides. A straight-chain of amino acids linked together by amide bonds forms a linear peptide (Figure 2) [7]. HTI-286 [14], SHP [15], SIO [16] (tripeptides); Microsporin A [17], SCH-P9 and SCH-P10 [18] (tetrapeptides); dolastatin 10 [19], ILYMP [20] (pentapeptides); AAP-H (oligopeptide) [21] are reported from mollusk, sponges, fish, clam, sea anemone and marine derived fungus. Cyclic tetra, penta, hepta, octa, dodecapeptides and depsipetides are claimed to have anti-PCa effects. Cyclic depsipeptides have more complex structures, where successive ester linkages replace more amide bonds due to the presence of hydroxy acids in the peptide structure [7]. Aurilide B [22], lagunamide C [23], cryptophycin-52 [24] and coibamide A [25] are obtained from cyanobacteria. Geodiamolides D–F [26], homophymines A–E [27], jaspamide [28,29] and neamphamides B–D [30] from sponges are cyclic depsipeptides with anti- cancer effects. Kahalalide F from (mollusk) [31]; tamandarins A,B (ascidia) [32,33] sansalvamide A (fungus) [34] are other reported anticancer cyclic depsipeptides. Furthermore, microsporin A (cyclic tetrapeptide) [17], zygosporamide (cyclic pentadepsipeptide) [35] rolloamide A [36] and trunkamide A (a cyclic heptapeptide) [12,37], patellamides B and F (cyclic octapeptides) [38] and laxaphycin B (a cyclic dodecapeptide) [39] have been isolated from ascidia, cyanobacteria, sponge and marine derived fungus. Protein hydrolysates, the complex mixtures of oligopeptides and free amino acids have antioxidant, antiproliferative, antihypertensive, and antibacterial properties [40,41,42]. Protein hydrolysates obtain from mollusk [43], fish [15,16,44,45] and clam [18,20] have anti-PCa properties.
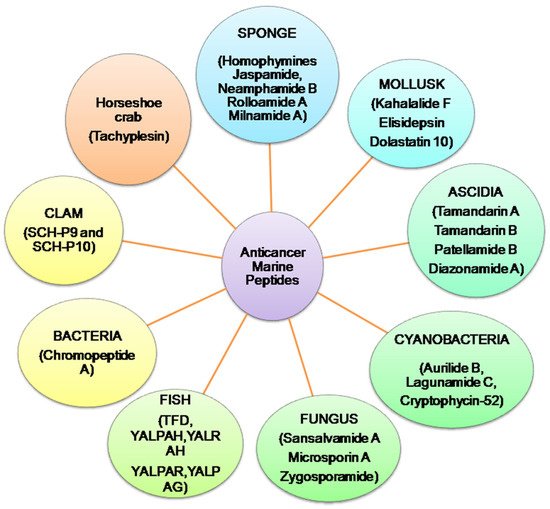
Figure 2. Summary of anticancer marine peptides isolated from different marine sources.
2. Mechanistic Insights
2.1. Apoptosis
One of the most critical mechanisms of cell death is apoptosis, and its failure is a severe barrier to cancer therapy. Cytochrome-c (cyt c) release leads to caspases activation and ensuing apoptosis [47]. C-phycocyanin from cyanobacteria [48] and AAP-H from sea anemone [21] have shown apoptotic efficacy by initiating cyt c release in DU145 and LNCaP cells. Caspases are the main executors of apoptosis, which are activated after proteolytic cleavage. Initiator caspases that include caspase-8, -9 and -10 initiate a regulated and programmed cell death cascade to trigger downstream caspases-3, -6, and -7 expression [49]. Tachyplesin, a cyclic peptide from horseshoe crab, triggers cyt c release, increasing caspases-3, -6, -7, -8, and -9 expression in TSU cells with IC50 of 75 μg mL−1 [50]. AAP-H from sea anemone has shown apoptotic efficacy by initiating cyt c release, enhancing caspases-3 and -9 activity in DU145 cells [21]. Cryptophycin-52 increases caspases-3 and -7 activities in DU145 and LNCaP cells [24]. The chromopeptide A from Chromobacterium sp. also increases caspase-3 activities and PARP cleavage in PC-3, DU145 and LNCaP cells [51]. Similarly, protein hydrolysates from clam, such as ILYMP, SCH-P9 and SCH-P10 [18,20] and MCH from mollusk have shown efficacy in DU145 and PC-3 [43]. SHP and SIO from fish increase caspase-3 activity in PC-3 and DU145 with IC50s of 15 and 1 mg mL−1, respectively [15,44,45].
Bcl-2 inhibition and BAX induction represents another method for initiating apoptosis [52]. C-phycocyanin induces apoptosis via caspases-3 and -9 activation, increasing BAX and decreasing Bcl2 and Bcl-xL in human prostate carcinoma DU145 and LNCaP cell lines with the IC50s in the range of 1-10 pM [48]. When DU145 cancer cells are treated with AAP-H oligopeptide, Bcl-2 is reduced, an effect related to the increased production of BAX, with IC50 of 2.298 mM [21]. Similarly, Sepia ink peptides SHP and SIO have been shown to induce apoptosis in PC-3 and DU145 by upregulating BAX and reducing Bcl-2 [15,44,45]. ILYMP initiates the phosphorylation of Bcl-2 and increases BAX in DU145 cells with IC50 of 11.25 mM [20]. Similarly, SCH-P9 and SCH-P10 from clam [18] and MCH from mollusk have shown the same behavior in DU145 and PC-3 [43].
PI3K/AKT pathways play a significant role in regulating cell cycle and survival. AKT inhibitors attenuate the degree of BAK, BAX, and BAD phosphorylation, cause cyt c release, and activate casp-9 [53]. Decreased PI3K/AKT and ErbB3 levels are involved in cell cycle arrest as well as BAX and BAK activation [54]. PI3K/AKT and ErbB3 deficiency in PC-3 and DU145 have been noted upon treatment with Kahalalide F [31,55]. Elisidepsin or Irvalec (a Kahalalide F synthetic derivative) have been shown to inhibit PI3K/AKT and deplete ErbB3 in PC-3 and DU145 cells [56,57]. Furthermore, elisidepsin causes cellular swelling, plasma membrane rupture, and loss of intracellular contents, as well as necrotic cell death in PC-3 and 22RV1 at IC50s of 0.6M and 0.3M, respectively [58]. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) are activated by microtubule inhibitors, suggesting this may represent a general stress response to microtubule dysfunction. Cyt c release is induced by JNK and p38 MAPK activation, which, in turn, triggers caspase cascades. Activation of JNK and ERK induces mitochondrial-related apoptosis via JNK signaling and S phase cell cycle arrest via ERK signaling [59,60]. Cryptophycin-52 induces apoptosis in DU145 and LNCaP cells via caspases-3, -7; JNK, p38 MAPK and ERK activation, increasing BAX and decreasing Bcl2 and Bcl-xL expression (Figure 3) [24].
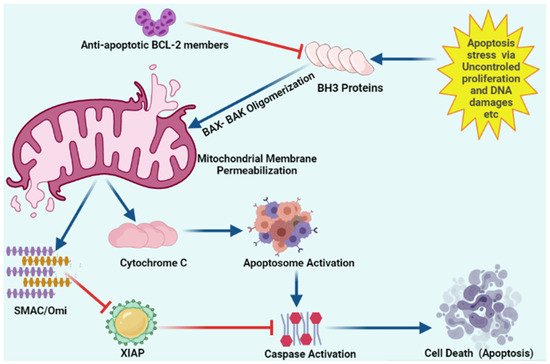
Figure 3. Schematic representation of intracellular apoptosis pathway.
Apoptosis stress involves mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization via uncontrolled BH3 only proteins. BH-3 only proteins lead to oligomerization of BAK/BAX multimers. These BAK/BAX multimers within the outer membrane of the mitochondria form pores that allow cytochrome C release. Released cytochrome C interacts with Apaf-1 and pro-caspase-9 to form the apoptosome. Upon release, mitochondria-derived activator of caspase (SMAC) Cytochrome C and Omi activate apoptosome from procaspase-9 and cytochrome C. Caspases upon activation results in the cleavage of cellular proteins that leads to apoptosis. “Activation” is represented by blue arrows, whereas red T-bars show “inhibition”.
2.2. Antimitotic Effect
Antimitotic drugs function by stabilizing and destabilizing microtubule dynamics, as well as shifting the balance between tubulin polymerization and depolymerization. The majority of these drugs act via G2/M phase arrest [61]. Microtubules provide a variety of critical cellular activities, including chromosomal segregation, cell shape preservation, transport, motility, and organelle distribution. Microtubules, the key components of the mitotic spindle, play an important role in cell division. Microtubular dynamic disruption arrests the cell cycle at the metaphase–anaphase transition leading to cell death [62]. Hemiasterlin and its analogue HTI-286 depolymerize microtubules by disrupting microtubular dynamics in LNCaP, C4-2, PC-3, PC-3dR cell lines with IC50s in the range of 0.65–4.6 nM. The same effect has been noted in PC3-MM2, PC-3 and PC-3dR xenografts at 1–1.5 mg/kg i.v. [26,63]. Dolastatin 10 (IC50:0.5 nM) inhibits microtubule assembly in DU145 cells [19]. Analogous behavior has been observed for Diazonamide A in PC-3 cells with IC50 of 2.3 nM [64]. Cryptophycin-52 (LY355703), a synthetic cryptophycin, inhibits DU145 and LNCaP cell growth during mitosis by depolymerizing spindle microtubules and alters chromosomal organization [24]. By attaching to the microtubules, microtubule-stabilizing drugs promote microtubule polymerization and target the cytoskeleton and spindle apparatus of tumor cells, leading to mitotic interruption [62]. Aurilide B has been shown to cause microtubular destabilization in PC-3 and DU145 carcinoma cell lines with GI50 < 10 nM [22].
2.3. Antimetastatic Activity
Non-caspase proteases (elastase, trypsin and chymotrypsin) are critical regulators of PCa progression. The PCa metastatic cascade is characterized by a defined chain of steps, beginning with neoangiogenesis or lymphangiogenesis, culminating in the loss of tumor cell adhesion, local invasion of host stroma, and tumor cell escape into the vasculature or lymphatics, and eventually dissemination, extravasation, and colonization of specific metastatic sites. Proteases secrete angiogenic factors, cell adhesion molecules, breakdown basement membranes, induce epithelial–mesenchymal transition, participate in extravasation, and are necessary for metastatic site colonization. Several proteases are increased in tumor cells, and have specific roles in facilitating various phases of this cascade [65,66]. Trypsin plays a tumorigenic role in PCa and suppressing trypsin/mesotrypsin activity may provide a new PCa therapeutic strategy. PC-3 cells originating from a grade IV prostate cancer bone metastases exhibit an extremely significant overexpression of PRSS3/mesotrypsin [67]. LNCaP human prostate cells have shown upregulation of chymotrypsin-like proteasomal activity, suggesting the involvement of chymotrypsin in PCa [68]. Elastase increases PCa proliferation, migration, invasion and has been used as a therapeutic target [69]. Symplocamide A blocks chymotrypsin and trypsin with IC50s of 0.38 and 80.2 μM, respectively [70]. Kempopeptin A inhibits porcine pancreatic elastase (0.32 μM) and bovine pancreatic α-chymotrypsin (2.6 μM), whereas, Kempopeptin B only inhibits trypsin activity (8.4 μM) [71]. Bouillomides A and B inhibit elastase and chymotrypsin from porcine pancreas [72]. Molassamide, a depsipeptide from the cyanobacteria Dichothrixutahensis, inhibits porcine pancreatic elastase (IC50:0.032 μM) and α-chymotrypsin (IC50: 0.234 μM) from bovine pancreas [73]. Largamides are cyclic peptides isolated from Lyngbyaconfervoides and Oscillatoria sp. Largamides A-C inhibit elastase with IC50 ranges from 0.53 to 1.41 μM [74]. Chymotrypsin is also inhibited by argamides D through G, with IC50 values between 4 and 25 M [75]. Pompanopeptin A inhibits trypsin with IC50 of 2.4 μM [76]. Elastase and chymotrypsin were inhibited by Lyngbyastatin 4, a cyclic depsipeptide from Lyngbya sp., at 0.03 M [77]. With IC50s of 3.2–8.3 nM for elastase and 2.5–2.8 nM for chymotrypsin, ligbystatin 5–7 inhibit both enzymes [78]. Lyngbyastatin 8–10 inhibit elastase with IC50s of 120–210 nM [79]. Tiglicamides A-C and cyclodepsipeptides from the same source have IC50s that range from 2.14 to 7.28 M for inhibiting elastase [80]. The pitipeptolides A and B inhibit elastase activity at 50 μg mL−1 [81]. Somamide B from the same source inhibits elastase (9.5 nM) and chymotrypsin (4.2 µM) [78]. Cathepsins D and E are lysosomal proteases having anti-apoptotic functions and which play an important role in PCa [82,83]. Grassystatins A and B depsipeptides strongly inhibit cathepsins D (IC50:26.5 and 7.27 nM, respectively) and E (IC50:886 and 354 pM), whereas grassystatin C inhibits cathepsins D (IC50:1.62 µM) and E (IC50:42.9 nM) [84].
The cytoskeletal microfilament, actin, is required for cytokinesis, cell migration, and a host of other processes crucial for the stability of cancerous cells. Inhibiting actin polymerization slows the growth of metastatic neoplastic cells by causing the breakdown of microfilaments, which, in turn, reduces cell motility [85]. Jaspamide, a cyclicdepsipeptide from sponge (Jaspis johnstoni), has shown antiproliferative activity against DU145, LNCaP, and PC-3 with IC50s of 0.8, 0.07 and 0.3µM by actin filament disruption. The same peptide has shown anticancer activity in a DU-145 xenograft [85].
Voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSC) are considered to have a role in cancer cell invasion and metastasis. In PCa, VGSC overexpression is crucial for cell movement and invasiveness [86,87,88]. Palmyramide A, a cyclic depsipeptide with an IC50 of 17.2 μM, and hermitamides A and B (lipopeptides) with IC50s of 1 μM have been shown to block sodium channels via VGSC inhibition [89,90].
2.4. Antiangiogenic Effect
Angiogenesis is crucial in the development of cancer [90]. VEGF is produced in cancer cells and is required for angiogenesis. During low oxygen (hypoxia) periods, Mucin 1 (MUC1) increases HIF-1α to stimulate tumor development and angiogenesis. Its overexpression restricts apoptosis via upregulating Bcl-xL and inactivating BAD protein. A decline in VEGF expression level is associated with MUC1 silencing, establishing that MUC1 downregulation has an anti-angiogenic impact [91,92,93]. TFD and SIO peptides from fish inhibit PC-3 and DU145 cell migration by decreasing VEGFR1 and MUC1 protein expression [44,45,94].
2.5. Cell Cycle Arrest
Cell cycle arrest limits cell viability and is related to apoptosis [95]. The two main regulators of G2/M transition/progression are cdc2 and cell division cycle-25C (cdc25C). Multiple signaling pathways influence their regulation in the cell cycle, and are linked to carcinogenesis and tumor formation. cdc2 and cdc25C have been shown to enhance mitotic cell G2/M transition by dephosphorylating cyclin-dependent kinase-1 (CDK1) and activating the cyclin B1/CDK1 complex. Their downregulation causes G2/M cell cycle arrest via p53-mediated signal transduction [96]. cdc2 and cdc25C are highly expressed in PCa [97]. Chromopeptide A promotes G2/M phase arrest in PCa cells by suppressing cdc2 and cdc25C phosphorylation [51]. Similarly, cryptophycin-52 induces G2/M phase arrest in DU145 and LNCaP cells [24].
2.6. p53 Upregulation
The functional tumor protein p53 (p53) protein takes part in apoptosis initiation via BAK, BAX increment and Bcl2, Bcl-xL decrement. Cells also arrest in the G1 and G2/M stages when p53 is activated. Low p53 level has been detected in PCa [98,99,100]. Cryptophycin-52 [24], chromopeptide A [51] and sepia ink peptides [15,44,45] induce p53 upregulation in PC-3, DU145 and LNCaP cells and hence regulate p53-dependent apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.
2.7. Stimulation of Histone Hyperacetylation
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are widely produced and over-activated in PCa. Stimulation of histone hyperacetylation in tumor through cellular HDAC inhibition results in G2/M phase arrest, apoptosis, activates p53, DNA-damage response and inhibition of metastasis and angiogenesis [101]. The chromopeptide A from marine-derived Chromobacterium sp. stimulates histone hyperacetylation by HDAC inhibition in PC-3, DU145, LNCaP cell lines and human PC-3 xenograft mouse model [51].
2.8. Mitochondrial Dysfunctions and Oxidative Damage
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation induces oxidative stress caused by mitochondrial abnormalities, and malignant cells require high ROS concentrations [102]. The most frequent type of DNA damage is DNA fragmentation, a direct consequence of oxidative stress [103]. Dolastatin 10 induces DNA damage in DU145 [19]. Similarly, Cryptophycin 52 and C-phycocyanin induce DNA damage in DU145 and LNCaP [24,48]. A schematic representation of the anticancer mechanisms of marine peptides is depicted in Figure 4 as under:
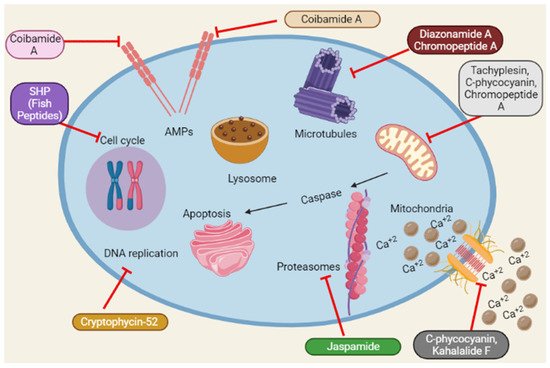
Figure 4. Summary of the schematic representation of the anticancer mechanisms of marine peptides at different cellular pathways. Marine peptides inhibit different pathways such as inhibition of cell cycle, Amps, caspase, Ca+2 influx, DNA replication, protein synthesis and lysosomal pathways.
2.9. Unidentified Mechanisms for Anticancer Activity
Geodiamolides D–F [26], homophymines A–E [27], milnamides A–G [26], neamphamides B–D [30], rolloamide A [36], yaku’amides A and B [104] from sponges; lagunamide C [23], coibamide A [25], laxaphycin B [39] from cyanobacteria exhibit strong cytotoxicity in several PCa cells, although the specific targets are yet unknown. Patellamides B and F, ulithiacyclamide [38], trunkamide A [12,37], tamandarins A-B [32,33] from ascidia also elicit anti-PCa activity via unrevealed process. Microsporin A [17], sansalvamide A [34] and zygosporamide [35] from marine derived fungus; YALPAH from fish [105] possess anti-PCa properties via an unknown mechanism. Some of the anticancer effects of marine peptides are summarized in Table 1:
Table 1. Summary of the sources, active peptides and anticancer mechanisms of action of Marine peptides.
| Peptides | Marine Sources (Species Name) |
Active Derivative | Anticancer Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aurilide B | Cyanobacteria (Lyngbya majuscula) | Cyclic depsipeptide | Microtubule stabilization | [22] |
| Lagunamide C | ↓ cell viability | [23] | ||
| Cryptophycin-52 (LY355703) |
Cyanobacteria (Nostoc sp.) | DNA fragmentation; Bcl2 ↓; Bax ↑; Bcl-xL ↓; caspase 3, 7 ↑; PARP ↑; p53 ↑; G2/M phase arrest; Microtubule depolymerization | [24] | |
| Coibamide A | Cyanobacteria (Leptolyngbya sp.) | ↓ cell viability | [25] | |
| Laxaphycin B | Cyanobacteria (Lyngbya majuscula) | Cyclic dodecapeptide | [39] | |
| C-phycocyanin | Cyanobacteria (Limnothrix sp.) | Peptide | Caspases 3, 9 ↑; cyt c release ↑; DNA fragmentation | [48] |
| Bisebromoamide | Cyanobacteria (Lyngbya sp.) | ↓ cancer cell growth | [106] | |
| Jaspamide | Sponge (Jaspis johnstoni ) |
Cyclic depsipeptide | Actin filament disruption | [28] |
| [29] | ||||
| Homophymines A–E | Sponge (Homophymia sp.) | ↓ cell viability | [27] | |
| Neamphamides B–D | Sponge (Neamphius huxleyi) |
[30] | ||
| Geodiamolides D–F | Sponge (Pipestela candelabra) | [26] | ||
| Milnamides A–G | N-methylated linear peptide | |||
| Rolloamide A | Sponge (Eurypon laughlini) |
Cyclic heptapeptide | [36] | |
| HTI-286 | Sponge (Hemiasterella minor) | Tripeptide | Microtubule depolymerization | [14] |
| [107] | ||||
| Kahalalide F | Mollusk (Elysia rufescens) | Cyclic depsipeptide | PI3K-AKT inhibition; ErbB3 depletion | [31] |
| ↓ cancer cell growth | [108] | |||
| Elisidepsin | PI3K-AKT inhibition; ErbB3 depletion | [56] | ||
| Dolastatin 10 | Mollusk (Dolabella auricularia) |
Pentapeptide | Microtubule depolymerization | [19] |
| MCH | Mollusk (Mytilus coruscus) |
Peptide | Bcl2 ↓; Bax ↑; caspase 3, 9 ↑ | [43] |
| KLH | Mollusk (Megathura crenulata) | ↓ cancer cell growth | [109] | |
| Tamandarin A | Ascidia (Trididemnum solidum) | Cyclic depsipeptide | ↓ cell viability | [32] |
| Tamandarin B | [33] | |||
| Patellamide B | Ascidia (Lissoclinum patella) |
Cyclic octapeptide | [38] | |
| Patellamide F | ||||
| Ulithiacyclamide | Cyclic peptide | |||
| Trunkamide A | Ascidia (Lissoclinum sp.) |
Cyclic heptapeptide | [12,37] | |
| Diazonamide A | Ascidia (Diazona angulata) | Macrocyclic peptide | Microtubule depolymerization | [64] |
| Chromopeptide A | Bacteria (Chromobacterium sp. HS-13-94) | Depsipeptide | caspase 3 ↑; PARP cleavage; HDAC inhibition; G2/M phase arrest; p53 ↑ | [51] |
| Sansalvamide A | Fungus (Fusarium sp.) | Cyclic depsipeptide | ↓ cell viability | [34] |
| Microsporin A | Fungus (Microsporum cf. gypseum) | Cyclic tetrapeptide | [17] | |
| Zygosporamide | Fungus (Zygosporium masonii) | Cyclic pentadepsipeptide | ↓ cancer cell growth | [35] |
| SHP | Fish (Sepia esculenta) |
Tripeptide | Bcl2 ↓; Bax ↑; caspase 3 ↑; p53 ↑ | [15] |
| SIO | Bcl2 ↓; Bax ↑; caspase 3 ↑; p53 ↑; VEGF ↓ | [44,45] | ||
| S and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest | [16] | |||
| TFD | Fish (Gadus sp.) | Peptide | VEGFR1 ↓; MUC1 ↓ | [94] |
| YALPAH | Fish (Setipinna taty) | ↓ cancer cell growth | [105] | |
| YALRAH | ||||
| YALPAR | ||||
| YALPAG | ||||
| ILYMP | Clam (Cyclina sinensis) |
Pentapeptide | Bcl2 ↓; Bax ↑; caspase 3, 9 ↑; cyt c release ↑ |
[20] |
| SCH-P9 and SCH-P10 | Clam (Sinonovacula constricta) |
Tetrapeptide | [18] | |
| AAP-H | Sea anemone (Anthopleura anjunae) | Oligopeptide | [21] | |
| Tachyplesin | Horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus) | Cyclic peptide | caspase 3, 6, 7, 8, 9 ↑; cyt c release ↑ | [50] |
3. Clinical Trial Status
Several marine peptides with potential PCa efficacy are presently undergoing clinical trials. Soblidotin (TZT-1027) has shown efficacy in DU145 cell lines and has entered a phase I clinical trial (Table 2). It was designed to maintain significant anticancer activity while lowering the toxicity of the parent medication, dolastatin 10 [110,111,112]. Tasidotin/synthadotin (ILX651), a dolastatin 15 derivative is in Phase II clinical trial for hormone refractory PCa [113].
Didemnin B displays anti-PCa activity, and has progressed into phase II studies. Due to its high toxicity, low solubility, and short life span, clinical studies were halted favouring second generation dehydrodidemnine B, (aplidin or plitidepsin). Dehydrodidemnine B is in phase III clinical trials [10,32,114].
In phase I study, Kahalalide F was effective against PCa, with a favorable safety profile [115]. It was withdrawn from phase II due to lack of efficacy, short half-life, restricted range of activity, and poor patient response. However, given this compound’s potent cytotoxicity, it has facilitated the development of synthetic analogues to overcome its limitations by increasing its potency and half-life [63,116]. Elisidepsin (Irvalec®), one of PharmaMar’s most powerful Kahalalide F analogues, has progressed to phase II clinical trial due to its superior efficacy and nontoxic profile [117]. The preclinical studies (in vivo, in vitro) are separated according to xenograft’s approach and listed in Table 3.
Table 2. Marine peptides as anticancer agents in clinical trials.
| Cell lines/ (Peptides) | Phase | Clinical Trials.Gov Identifier | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| DU145 (Soblidotin) |
Phase I | NCT00072228 | [22,110,111] |
| Dolastatin 10 | Phase II | NCT00003626 | [23,110] |
| Tasidotin/synthadotin (ILX651) | Phase II | NCT00082134 | [24,113] |
| Dehydrodidemnine B | Phase III | NCT00780975 | [10,25,32] |
| Kahalalide F | Phase I | NCT00106418 | [39,115] |
| Elisidepsin (Irvalec®) | Phase II | NCT00884845 | [48,117] |
Table 3. Marine peptides as anticancer agents in pre-clinical trials.
| In Vitro | In Vivo | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Prostate Cancer Cell Lines | IC50 | Experimental Model | Dose | |
| DU145 and PC-3 Aurilide B | <10 nM | ----- | ----- | [22] |
| PC-3 Lagunamide C | 2.6 nM | ----- | ----- | [23] |
| DU145 and LNCaP Cryptophycin-52 | 1–10 pM | ----- | ----- | [24] |
| DU145 and PC-3 Coibamide A | 300 ng mL−1 | ----- | ----- | [10,25,32] |
| PC-3 Laxaphycin B | 0.58 µM | ----- | ----- | [39] |
| LNCaP C-phycocyanin | 500 µg mL−1 | ----- | ----- | [48] |
| DU145 and PC-3 Bisebromoamide | GI50:40 nM | ----- | ----- | [106] |
| DU145 Jaspamide | 0.8 µM | DU-145 xenograft | 10 mg/kg s.c. | [28] |
| LNCaP Jaspamide | 0.07 µM | ----- | ----- | |
| PC-3 Jaspamide | 0.3 µM | ----- | ----- | |
| TSU-Pr1 Jaspamide | 170 nM | ----- | ----- | [29] |
| PC-3 Homophymines A–E | A:4.2, B:6.2, C:3.0, D:6.3, E:3.9 nM | ----- | ----- | [27] |
| LNCaP Neamphamides B-D | B:230, C:190, D:110 nM | ----- | ----- | [30] |
| PC-3 Geodiamolides D-F | B: 170, C:110, D:130 nM | ----- | ----- | |
| D:33.1, E:118, F:155 nM | ----- | ----- | [26] | |
| DU145 Rolloamide A | 0.85 µM | ----- | ----- | [36] |
| LNCaP Rolloamide A | 0.8 µM | ----- | ----- | |
| PC-3 Rolloamide A | 1.4 µM | ----- | ----- | |
| PC3MM2 Rolloamide A | 4.7 µM | ----- | ----- | |
| LNCaP, C4-2, PC-3, PC-3dR HTI-286 |
0.65–4.6 nM | PC-3 and PC-3dR xenografts | 1.5 mg/kg i.v. | [14] |
| ----- | ----- | PC3-MM2 xenograft | 1.0 mg/kg i.v. | [107] |
| PC-3 Kahalalide F | 0.07 µM | ----- | ----- | [31] |
| DU145 and LNCaP | 0.28 µM | ----- | ----- | |
| ----- | ----- | PC-3 and DU145 xenografts | 123 μg/kg i.v. | [108] |
| PC-3 Elisidepsin | 1.80 µM | ----- | ----- | [56] |
| DU145 | 1.26 µM | ----- | ----- | |
| DU145 Dolastatin 10 | 0.5 nM | DU145 xenograft | 5 µg q4d i.p. | [19] |
| PC-3 MCH | LC50:0.94 mg mL−1 | ----- | ----- | [43] |
| DU145 Tamandarin A | GI50:12.5 μg | ----- | ----- | [109] |
| 1.36 ng mL−1 | ----- | ----- | [32] | |
| PC-3 Tamandarin B | 1.4 µM | ----- | ----- | [33] |
| DU145 and PC-3 Patellamide B Patellamide F |
LC50: 48 µM | ----- | ----- | [38] |
| LC50: 13 µM | ----- | ----- | ||
| LC50: 3 µM | ----- | ----- | ||
| DU145 Trunkamide A |
7.08 nM | ----- | ----- | [12,37] |
| PC-3 Diazonamide A |
2.3 nM | ----- | ----- | [64] |
| 2.43 nmol L−1 | PC-3 xenograft | 1.6 mg/kg i.v. | [51] | |
| DU145 Chromopeptide A |
2.08 nmol L−1 | ----- | ----- | |
| LNCaP Chromopeptide A |
1.75 nmol L−1 | ----- | ----- | |
| PC-3 Sansalvamide A |
27.4 μg mL−1 | ----- | ----- | [34] |
| DU145 and PC-3 Microsporin A Zygosporamide |
2.7 µM | ----- | ----- | [17] |
| GI50:9.1 µM | ----- | ----- | [35] | |
| PC-3 SHP |
15 mg mL−1 | ----- | ----- | [15] |
| DU145 | 1 mg mL−1 | ----- | ----- | [44,45] |
| DU145 and PC-3 SIO |
15 mg mL−1 | ----- | ----- | [16] |
| PC-3 TFD, YALRAH, YALPAH, YALPAG, YALPAR |
3.5 nM | ----- | ----- | [94] |
| GI50:16.9 μM | ----- | ----- | [105] | |
| GI50:11.1 μM | ----- | ----- | ||
| GI50:19.0 μM | ----- | ----- | ||
| GI50:71.2 μM | ----- | ----- | ||
| DU145, ILYMP, SCH-P9 and SCH-P10 | 11.25 mM | ----- | ----- | [20] |
| SCH-P9:1.21, SCH-P10: 1.41 mg mL−1 | ----- | ----- | [18] | |
| PC-3 | SCH-P9:1.09, SCH-P10: 0.91 mg mL−1 | ----- | ----- | |
| DU145, AAP-H | 2.298 mM | ----- | ----- | [21] |
| TSU, Tachyplesin | 75 μg mL−1 | ----- | ----- | [50] |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebello, R.J.; Oing, C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Loeb, S.; Johnson, D.C.; Reiter, R.E.; Gillessen, S.; Van der Kwast, T.; Bristow, R.G. Prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokbel, K.; Wazir, U.; Mokbel, K. Chemoprevention of Prostate Cancer by Natural Agents: Evidence from Molecular and Epidemiological Studies. Anticancer. Res. 2019, 39, 5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, F.; Raimondi, M.; Marzagalli, M.; Di Domizio, A.; Limonta, P. Natural Compounds in Prostate Cancer Prevention and Treatment: Mechanisms of Action and Molecular Targets. Cells 2020, 9, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Diederich, M. Marine Natural Products as Anticancer Agents. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, M.; Spanò, V.; Montalbano, A.; Cueto, M.; Marrero, A.R.D.; Deniz, I.; Erdoğan, A.; Bilela, L.L.; Moulin, C.; Taffin-De-Givenchy, E.; et al. Marine Anticancer Agents: An Overview with a Particular Focus on Their Chemical Classes. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Mirzaei, H.; Aschner, M.; Khan, A.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Khan, H. Marine peptides in breast cancer: Therapeutic and mechanistic understanding. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Hasan, M.M.; Aschner, M.; Mirzaei, H.; Alam, W.; Shah, S.M.M.; Khan, H. Therapeutic potential of marine peptides in glioblastoma: Mechanistic insights. Cell. Signal. 2021, 87, 110142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.K.; Choi, M.-C.; Seo, C.H.; Park, Y. Therapeutic Properties and Biological Benefits of Marine-Derived Anticancer Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiangjong, W.; Chutipongtanate, S.; Hongeng, S. Anticancer peptide: Physicochemical property, functional aspect and trend in clinical application (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 678–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-T.; Liu, Z.-D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, N.; Wang, N.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.-F. Recent Advances in Small Peptides of Marine Origin in Cancer Therapy. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucak, I.; Afreen, M.; Montesano, D.; Carrillo, C.; Tomasevic, I.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Barba, F. Functional and Bioactive Properties of Peptides Derived from Marine Side Streams. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadaschik, B.; Ettinger, S.; Sowery, R.D.; Zoubeidi, A.; Andersen, R.J.; Roberge, M.; Gleave, M.E. Targeting prostate cancer with HTI-286, a synthetic analog of the marine sponge product hemiasterlin. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Jing, Y.; Ding, G.; Yang, Z. Isolation and purification of novel peptides derived from Sepia ink: Effects on apoptosis of prostate cancer cell PC-3. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4222–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Yang, Z.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Ding, G. Sepia ink oligopeptide induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines via caspase-3 activation and elevation of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Cueto, M.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W.; Silverman, R.B. Microsporins A and B: New histone deacetylase inhibitors from the marine-derived fungus Microsporum cf. gypseum and the solid-phase synthesis of microsporin A. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 6535–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Ding, G.; Yang, Z.; Yu, F. Two novel peptides derived from Sinonovacula constricta inhibit the proliferation and induce apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6697–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.; Jackson, W.H.; Pettit, G.R.; Wells, A.; Kraft, A.S. Treatment of human prostate cancer cells with dolastatin 10, a peptide isolated from a marine shell-less mollusc. Prostate 1998, 34, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, L.; Tang, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z. A novel anti-proliferative pentapeptide (ILYMP) isolated from Cyclina sinensis protein hydrolysate induces apoptosis of DU-145 prostate cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 771–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.-Z.; Ding, G.F.; Huang, F.F.; Yang, Z.S.; Yu, F.M.; Tang, Y.P.; Jia, Y.L.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Chen, R. Anticancer Activity of Anthopleura anjunae Oligopeptides in Prostate Cancer DU-145 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Gross, H.; Goeger, D.E.; Mooberry, S.L.; Gerwick, W.H. Aurilides B and C, Cancer Cell Toxins from a Papua New Guinea Collection of the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Puddick, J.; Prinsep, M.R.; Rottmann, M.; Chan, K.P.; Chen, D.Y.K.; Tan, L.T. Lagunamide C, a cytotoxic cyclodepsipeptide from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 2369–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, L.; Fine, R.L.; Do, T.N.; Douglas, G.P.; Petrylak, D.P. The Novel Antimicrotubule Agent Cryptophycin 52 (LY355703) Induces Apoptosis via Multiple Pathways in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 3922. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medina, R.A.; Goeger, D.E.; Hills, P.; Mooberry, S.L.; Huang, N.; Romero, L.I.; Ortega-Barría, E.; Gerwick, W.H.; McPhail, K.L. Coibamide A, a potent antiproliferative cyclic depsipeptide from the Panamanian marine cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6324–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.D.; Pham, N.B.; Fechner, G.A.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Quinn, R.J. Potent cytotoxic peptides from the Australian marine sponge Pipestela candelabra. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3399–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampella, A.; Sepe, V.; Bellotta, F.; Luciano, P.; D’Auria, M.V.; Cresteil, T.; Debitus, C.; Petek, S.; Poupat, C.; Ahond, A. Homophymines B–E and A1–E1, a family of bioactive cyclodepsipeptides from the sponge Homophymia sp. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 4037–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Ara, G.; Sausville, E.A.; Teicher, B. Jasplakinolide: Interaction with radiation and hyperthermia in human prostate carcinoma and Lewis lung carcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1998, 42, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senderowicz, A.M.J.; Pham, N.B.; Fechner, G.; Zencak, D.; Vu, H.T.; Hooper, J.N.; Quinn, R.J. Jasplakinolide’s Inhibition of the Growth of Prostate Carcinoma Cells In Vitro with Disruption of the Actin Cytoskeleton. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.D.; Pham, N.B.; Fechner, G.; Zencak, D.; Vu, H.T.; Hooper, J.N.; Quinn, R.J. Cytotoxic Cyclic Depsipeptides from the Australian Marine Sponge Neamphius huxleyi. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 2200–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, Y.; González, L.; Cuadrado, A.; Berciano, M.; Lafarga, M.; Muñoz, A. Kahalalide F, a new marine-derived compound, induces oncosis in human prostate and breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2003, 2, 863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vervoort, H.; Fenical, W.; Epifanio, R.D.A. Tamandarins A and B: New Cytotoxic Depsipeptides from a Brazilian Ascidian of the Family Didemnidae. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Richard, D.J.; Portonovo, P.S.; Joullie, M.M. Total Syntheses and Biological Investigations of Tamandarins A and B and TamandarinA Analogs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 4469–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Gu, W.; Lo, D.; Ding, X.-Z.; Ujiki, M.; Adrian, T.E.; Soff, G.A.; Silverman, R.B. N-Methylsansalvamide A Peptide Analogues. Potent New Antitumor Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3630–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.-C.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Zygosporamide, a cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide from the marine-derived fungus Zygosporium masonii. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 8625–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Yu, K.; Behrisch, H.W.; Van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Rolloamides A and B, Cytotoxic Cyclic Heptapeptides Isolated from the Caribbean Marine Sponge Eurypon laughlini. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeever, B.; Pattenden, G. Total synthesis of trunkamide A, a novel thiazoline-based prenylated cyclopeptide metabolite from Lissoclinum sp. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 2713–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.A.; Gustafson, K.R.; Ii, J.H.C.; Boyd, M.R. Patellamide F, a New Cytotoxic Cyclic Peptide from the Colonial Ascidian Lissoclinum patella. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnard, I.; Rolland, M.; Salmon, J.-M.; Debiton, E.; Barthomeuf, C.; Banaigs, B. Total Structure and Inhibition of Tumor Cell Proliferation of Laxaphycins. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1266–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei, S.; Rezaei, M.; Asgharzade, S.; Nikoo, M.; Rafieia-Kopai, M. Antioxidant and cytotoxic properties of protein hydrolysates obtained from enzymatic hydrolysis of Klunzinger’s mullet (Liza klunzingeri) muscle. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 55, e18304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha, M.; Alemán, A.; Baccan, G.C.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Gómez-Guillén, C.; Montero, P.; Prentice, C. Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Effects of Underutilized Fish Protein Hydrolysate. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2018, 27, 592–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, M.I.; Sarbon, N.M. A review on purification and characterization of anti-proliferative peptides derived from fish protein hydrolysate. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 38, 1389–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun-Kyung, K.; Joung, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, J.W.; Ahn, C.B.; Jeon, Y.J.; Moon, S.H.; Park, P.J. Purification of a Novel Anticancer Peptide from Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Mytilus coruscus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, G.-F.; Huang, F.F.; Yang, Z.-S.; Yu, D.; Yang, Y.F. Anticancer Activity of an Oligopeptide Isolated from Hydrolysates of Sepia Ink. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2011, 9, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Y.; Yang, Z.; Huang, F. Mechanism of Sepia ink polypeptide-induced apoptosis in DU-145 prostate cancer cells. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; Elias, N.; Farag, M.A.; Chen, L.; Saeed, A.; Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Moustafa, M.S.; El-Wahed, A.A.; Al-Mousawi, S.M.; Musharraf, S.G.; et al. Marine natural products: A source of novel anticancer drugs. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, C.M.; Singh, A.T. Apoptosis: A target for anticancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantar, M.; Dhandayuthapani, S.; Rathinavelu, A. Phycocyanin Induces Apoptosis and Enhances the Effect of Topotecan on Prostate Cell Line LNCaP. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, A.B.; Freel, C.D.; Kornbluth, S. Cellular mechanisms controlling caspase activation and function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Hong, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, N.; Underhill, C.B.; Creswell, K.; Zhang, L. RGD-Tachyplesin Inhibits Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2434. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.-Y.; Wang, J.-D.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.-C.; Zhang, M.-M.; Liu, Y.-C.; Zhang, C.-H.; Su, Y.; Shen, Y.-Y.; Guo, Y.-W.; et al. Marine-derived chromopeptide A, a novel class I HDAC inhibitor, suppresses human prostate cancer cell proliferation and migration. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.J.; Tait, S.W. Targeting BCL-2 regulated apoptosis in cancer. Open Biol. 2018, 8, 180002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.-J.; Dasgupta, A.; Jung, K.-J.; Um, J.-H.; Burke, A.; Park, H.U.; Brady, J.N. PI3K/AKT inhibition induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in HTLV-1-transformed cells. Virology 2008, 370, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Chin, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, D. ERBB3 knockdown induces cell cycle arrest and activation of Bak and Bax-dependent apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5138–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janmaat, M.L.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Jimeno, J.; Kruyt, F.A.E.; Giaccone, G. Kahalalide F Induces Necrosis-Like Cell Death that Involves Depletion of ErbB3 and Inhibition of Akt Signaling. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 68, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serova, M.; de Gramont, A.; Bieche, I.; Riveiro, M.E.; Galmarini, C.M.; Aracil, M.; Jimeno, J.; Faivre, S.; Raymond, E. Predictive factors of sensitivity to elisidepsin, a novel Kahalalide F-derived marine compound. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 944–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Sorolla, M.A.; Krishnan, P.D.G.; Sorolla, A. From Seabed to Bedside: A Review on Promising Marine Anticancer Compounds. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Guijarro, J.M.; Macías, Á.; García, C.; Muñoz, E.; García-Fernandez, L.F.; David, M.; Núñez, L.; Martínez-Leal, J.F.; Moneo, V.; Cuevas, C.; et al. Irvalec inserts into the plasma membrane causing rapid loss of integrity and necrotic cell death in tumor cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; López, J.M. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canovas, B.; Nebreda, A.R. Diversity and versatility of p38 kinase signalling in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vuuren, R.J.; Visagie, M.H.; Theron, A.E.; Joubert, A.M. Antimitotic drugs in the treatment of cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 76, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanale, D.; Bronte, G.; Passiglia, F.; Calò, V.; Castiglia, C.; Di Piazza, F.; Barraco, N.; Cangemi, A.; Catarella, M.T.; Insalaco, L.; et al. Stabilizing versus destabilizing the microtubules: A double-edge sword for an effective cancer treatment option? Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2015, 2015, 690916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Pinteus, S.; Gaspar, H.; Alpoim, M.C.; Botana, L.M.; Pedrosa, R. From Marine Origin to Therapeutics: The Antitumor Potential of Marine Algae-Derived Compounds. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Vervoort, H.C.; Bai, R.; Newman, D.J.; Howell, S.B.; Los, G.; Mullaney, J.T.; Williams, M.D.; Pettit, G.R.; Fenical, W.; et al. Diazonamide A and a Synthetic Structural Analog: Disruptive Effects on Mitosis and Cellular Microtubules and Analysis of Their Interactions with Tubulin. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, D.R.; Hurst, D.R. Defining the Hallmarks of Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.W.; Pattabiraman, D.R.; Weinberg, R.A. Emerging Biological Principles of Metastasis. Cell 2017, 168, 670–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockla, A.; Miller, E.; Salameh, M.D.A.; Copland, J.A.; Radisky, D.C.; Radisky, E.S. PRSS3/mesotrypsin is a therapeutic target for metastatic prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zeng, W.; Xie, K.; Diao, P.; Tang, P. Potential use of chymotrypsin-like proteasomal activity as a biomarker for prostate cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5149–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, I. Neutrophil Elastase and SERPINB1 Are Critical Regulators of Prostate Cancer Progression; University of Rochester: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2018; p. 159. [Google Scholar]
- Linington, R.G.; Edwards, D.J.; Shuman, C.F.; McPhail, K.L.; Matainaho, T.; Gerwick, W.H. Symplocamide A, a potent cytotoxin and chymotrypsin inhibitor from the marine Cyanobacterium Symploca sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taori, K.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Kempopeptins A and B, Serine Protease Inhibitors with Different Selectivity Profiles from a Marine Cyanobacterium, Lyngbya sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, B.K.; Parrish, S.M.; Yoshida, W.; Schupp, P.J.; Schils, T.; Williams, P.G. Depsipeptides from a Guamanian marine cyanobacterium, Lyngbyabouillonii, with selective inhibition of serine proteases. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 6718–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Miller, M.W.; Kwan, J.C.; Luesch, H.; Paul, V.J. Molassamide, a Depsipeptide Serine Protease Inhibitor from the Marine Cyanobacterium Dichothrixutahensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthew, S.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Largamides A-C, tiglic acid-containing cyclodepsipeptides with elastase-inhibitory activity from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya confervoides. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza, A.; Bewley, C.A. Largamides A−H, Unusual Cyclic Peptides from the Marine Cyanobacterium Oscillatoria sp. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 6898–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, S.; Ross, C.; Rocca, J.R.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Pompanopeptins A and B, new cyclic peptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbyaconfervoides. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 4081–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, S.; Ross, C.; Rocca, J.R.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Lyngbyastatin 4, a Dolastatin 13 Analogue with Elastase and Chymotrypsin Inhibitory Activity from the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbyaconfervoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taori, K.; Matthew, S.; Rocca, J.R.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Lyngbyastatins 5–7, Potent Elastase Inhibitors from Floridian Marine Cyanobacteria, Lyngbya sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, J.C.; Taori, K.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Lyngbyastatins 8-10, elastase inhibitors with cyclic depsipeptide scaffolds isolated from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbyasemiplena. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, S.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Tiglicamides A–C, cyclodepsipeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbyaconfervoides. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 2058–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luesch, H.; Pangilinan, R.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Moore, R.E.; Paul, V.J. Pitipeptolides A and B, New Cyclodepsipeptides from the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, F.L.; He, Y.; Franco, O.E.; Jiang, M.; Cates, J.; Hayward, S.W. Cathepsin D acts as an essential mediator to promote malignancy of benign prostatic epithelium. Prostate 2013, 73, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatemadi, A.; Aiyelabegan, H.T.; Negahdari, B.; Mazlomi, M.A.; Daraee, H.; Daraee, N.; Eatemadi, R.; Sadroddiny, E. Role of protease and protease inhibitors in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, J.C.; Eksioglu, E.A.; Liu, C.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Grassystatins A−C from Marine Cyanobacteria, Potent Cathepsin E Inhibitors That Reduce Antigen Presentation. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5732–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Qin, Y.; Kun, L.; Zhou, Y. The Significant Role of the Microfilament System in Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 620390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, S.; Altun, S.; Gumushan, H.; Patel, A.; Djamgoz, M.B. Voltage-gated sodium channel activity promotes prostate cancer metastasis in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2012, 323, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, M.; Ruben, P. Voltage gated sodium channels in cancer and their potential mechanisms of action. Channels 2019, 13, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Zhang, J.; Körner, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ying, S. The Emerging Role of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels in Tumor Biology. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, E.O.; Graf, K.M.; Patel, M.K.; Baheti, A.; Kong, H.-S.; MacArthur, L.H.; Dakshanamurthy, S.; Wang, K.; Brown, M.L.; Paige, M. Synthesis and evaluation of hermitamides A and B as human voltage-gated sodium channel blockers. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4322–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Nunnery, J.K.; Engene, N.; Esquenazi, E.; Byrum, T.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Gerwick, W.H. Palmyramide A, a Cyclic Depsipeptide from a Palmyra Atoll Collection of the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Its Receptor (VEGFR) Signaling in Angiogenesis: A Crucial Target for Anti- and Pro-Angiogenic Therapies. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceci, C.; Atzori, M.G.; Lacal, P.M.; Graziani, G. Role of VEGFs/VEGFR-1 Signaling and its Inhibition in Modulating Tumor Invasion: Experimental Evidence in Different Metastatic Cancer Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodabakhsh, F.; Merikhian, P.; Eisavand, M.R.; Farahmand, L. Crosstalk between MUC1 and VEGF in angiogenesis and metastasis: A review highlighting roles of the MUC1 with an emphasis on metastatic and angiogenic signaling. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, P.; Kaptan, E.; Bandyopadhyaya, G.; Kaczanowska, S.; Davila, E.; Thompson, K.; Martin, S.S.; Kalvakolanu, D.V.; Vasta, G.R.; Ahmed, H. Cod glycopeptide with picomolar affinity to galectin-3 suppresses T-cell apoptosis and prostate cancer metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110, 5052–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visconti, R.; Della Monica, R.; Grieco, D. Cell cycle checkpoint in cancer: A therapeutically targetable double-edged sword. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2016, 35, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zheng, M.; Lu, R.; Du, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. The role of CDC25C in cell cycle regulation and clinical cancer therapy: A systematic review. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozen, M.; Ittmann, M. Increased Expression and Activity of CDC25C Phosphatase and an Alternatively Spliced Variant in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J. Expression of p53 and its mechanism in prostate cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, E.C.; Sykes, S.M.; McMahon, S.B.; Murphy, M.E. The p53 family and programmed cell death. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6507–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. The Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, W.-G. The Roles of Histone Deacetylases and Their Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 576946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.; Tuli, H.S.; Varol, A.; Thakral, F.; Yerer, M.B.; Sak, K.; Varol, M.; Jain, A.; Khan, M.A.; Sethi, G. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cancer Progression: Molecular Mechanisms and Recent Advancements. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poetsch, A.R. The genomics of oxidative DNA damage, repair, and resulting mutagenesis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueoka, R.; Ise, Y.; Ohtsuka, S.; Okada, S.; Yamori, T.; Matsunaga, S. Yaku’amides A and B, Cytotoxic Linear Peptides Rich in Dehydroamino Acids from the Marine Sponge Ceratopsions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17692–17694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, R.; Wei, R.B.; Luo, H.Y.; Yang, Z.S. Isolation and identification of an antiproliferative peptide derived from heated products of peptic hydrolysates of half-fin anchovy (Setipinnataty). J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teruya, T.; Sasaki, H.; Fukazawa, H.; Suenaga, K. Bisebromoamide, a Potent Cytotoxic Peptide from the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp.: Isolation, Stereostructure, and Biological Activity. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5062–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loganzo, F.; Discafani, C.M.; Annable, T.; Beyer, C.; Musto, S.; Hari, M.; Tan, X.; Hardy, C.; Hernandez, R.; Baxter, M.; et al. HTI-286, a synthetic analogue of the tripeptide hemiasterlin, is a potent antimicrotubule agent that circumvents P-glycoprotein-mediated resistance in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Faircloth, G.; Marchante, M.d.C.C. Kahalalide F and ES285: Potent anticancer agents from marine molluscs. In Molluscs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 363–379. [Google Scholar]
- Riggs, D.R.; Jackson, B.; Vona-Davis, L.; McFadden, D. In vitro anticancer effects of a novel immunostimulant: Keyhole limpet hemocyanin. J. Surg. Res. 2002, 108, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishampayan, U.; Glode, M.; Du, W.; Kraft, A.; Hudes, G.; Wright, J.; Hussain, M. Phase II study of dolastatin-10 in patients with hormone-refractory metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 4205–4208. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, M.; Natsume, T.; Watanabe, J.-I.; Fujio, N.; Mikami, T.; Miyasaka, K.; Tsukagoshi, S. Activity of a novel antitumor agent, TZT-1027. Nihon yakurigakuzasshi. Folia Pharmacol. Jpn. 1999, 114, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greystoke, A.; Blagden, S.; Thomas, A.L.; Scott, E.; Attard, G.; Molife, R.; Vidal, L.; Pacey, S.C.; Sarkar, D.; Jenner, A.; et al. A phase I study of intravenous TZT-1027 administered on day 1 and day 8 of a three-weekly cycle in combination with carboplatin given on day 1 alone in patients with advanced solid tumours. Ann. Oncol. 2006, 17, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogineni, V.; Hamann, M.T. Marine natural product peptides with therapeutic potential: Chemistry, biosynthesis, and pharmacology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 81–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Currano, J.N.; Carroll, P.J.; Joullié, M.M. Didemnins, tamandarins and related natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 404–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rademaker-Lakhai, J.M.; Horenblas, S.; Meinhardt, W.; Stokvis, E.; de Reijke, T.M.; Jimeno, J.M.; Lopez-Lazaro, L.; Martin, J.A.L.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of kahalalide F in patients with advanced androgen refractory prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghareeb, M.A.; Tammam, M.A.; El-Demerdash, A.; Atanasov, A.G. Insights about clinically approved and Preclinically investigated marine natural products. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2020, 2, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Torres, V.; Encinar, J.A.; Herranz-López, M.; Pérez-Sánchez, A.; Galiano, V.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Micol, V. An Updated Review on Marine Anticancer Compounds: The Use of Virtual Screening for the Discovery of Small-Molecule Cancer Drugs. Molecules 2017, 22, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimuthu, S.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.-K. Marine derived bioactive compounds for breast and prostate cancer treatment: A review. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2014, 10, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craik, D.J.; Kan, M.-W. How can we improve peptide drug discovery? Learning from the past. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 1399–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttenthaler, M.; King, G.F.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.-L.; Harris, J.L.; Khanna, K.K.; Hong, J.-H. A Comprehensive Review on Current Advances in Peptide Drug Development and Design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/md20080466
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
