Cell membranes, including membrane carrier proteins, membrane channel proteins and ATP drive pumps, are the main transporters. Membrane transporters have wide, but specific tissue distributions. They can impact on multiple endogenous and xenobiotic processes. Transport proteins constitute approximately 10% of most proteomes and play vital roles in the translocation of solutes across the membranes of all organisms. The receptor proteins on the cell membrane are also important structures involved in substrate transport and signal communication. The obstacles of cell transport-related proteins directly lead to the lack or excess of certain substances in cells.
- membrane transporters
- target site recognition
- targeted drug design
- treatment of disease
1. Membrane Transporters
1.1. Carrier Proteins
| Carrier Protein | Typical Positioning | Energy | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+-Glucose Pump | The apical plasma membrane of intestinal and renal cells | Na+ | Glucose active transport | [9] |
| Na+-K+ Pump | The plasma membrane of most animal cells | ATP | Na+ active pumping and K+ active pumping | [10,11] |
| Na +-H + Pump | The plasma membrane of animal cells | ATP | H+ active pumping | [12,13] |
| Na+ dependent neutral amino acid transporter | Absorbent epithelial cells | ATP | Amino acid pumping and downstream signal regulation of amino acid receptors | [14,15] |
| Na+ depends on a centralized carrier | Absorbent epithelial cells | ATP | Active transport of nucleosides | [16] |
| Glucose Carrier | The plasma membrane of most animal cells | — | Passive transport of glucose | [17] |
1.2. Channel Proteins
| Species | Distribution | Somatotype | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquaporins | Brain; membranes; kidneys; testis; liver; nasopharynx; lungs; intestines; eyes; etc. | AQP0; AQP1; AQP2; AQP3; AQP4; AQP5; AQP6; AQP7; AQP8; AQP9; AQP10; AQP11; AQP12 | Formation of various body fluids, reabsorption of water by tissues | [25,26] |
| Channel Protein | Chondriosome | MPTP | Apoptosis and necrosis | [27] |
| Ion Channel Protein | Various organizations | HCN; Slack; KcsA; TRPV; TRPM family; PKD1/2; PIEZO1/2; ENaC; TPCs; VDAC; SLC family; ASICs |
Signal transduction, excitement transfer, substance synthesis, energy metabolism, osmotic pressure balance, nutrition induction, substance transport | [28,29] |
1.3. ATP-Driven Pumps
| Kind | Constitute | Distribution | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P type ion Pump | 2α subunits (transport), 2β subunits (regulatory) |
Plasma membrane; endoplasmic reticulum | Na+, K+, H+ and Ca2+are transported across membranes | [34] |
| Type F ion Pump | Multiple subunits, transmembrane domain F0 and cytoplasmic domain F1 | Mitochondrial inner membrane | ATP synthesis | [35] |
| V type ion Pump | Multiple subunits, transmembrane domain V0 and cytoplasmic domain V1 | Intracellular bodies; lysosomal membranes; osteoclasts | H+ transport | [36] |
| ABC Transporter Superfamily | Two transmembrane domains, two intracellular ATP-binding domains | All kinds of organisms | Amino acids, sugars, lipids, peptides, protein transport, macromolecule transport | [37,38] |
1.4. Functions of Membrane Transporters
1.4.1. Function of Carrier Protein
1.4.2. Function of Channel Proteins
2. Membrane Receptor Proteins
2.1. Types of Membrane Receptor Proteins
2.1.1. Ion Channel-Coupled Receptors
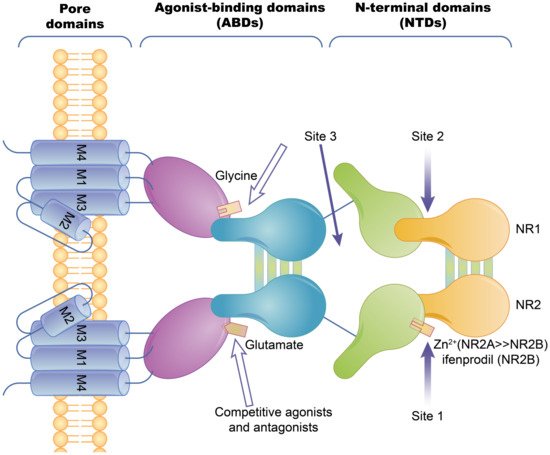
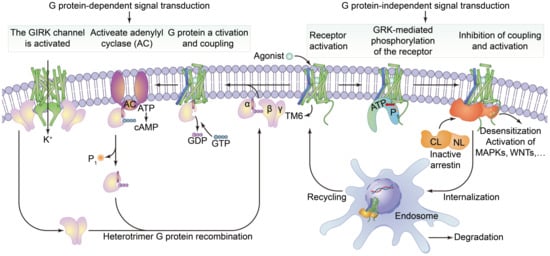
2.1.2. G Protein-Coupled Receptors
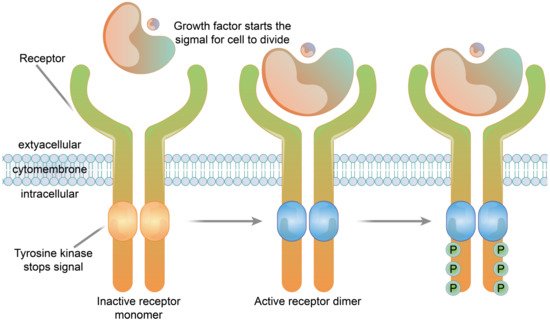
2.1.3. Enzyme-Linked Receptors
2.2. Function of Membrane Receptor Proteins
2.2.1. Ion Channel Receptor Functions
2.2.2. Function of G Protein-Coupled Receptors
2.2.3. Enzyme-Linked Receptor Functions
3. Association between Membrane Proteins and Disease
3.1. Abnormal Ion Channels Induce Cancer
3.2. Substrate Transport Disorders, Induced Metabolic Disorders of the Type of Disease
3.3. Membrane Receptors and Pathogen Invasion
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/membranes11100736
