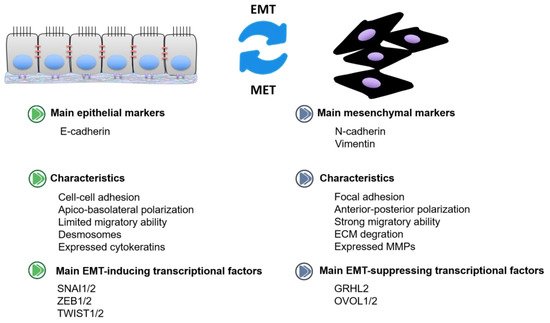
Bioinformatic analysis displayed that miR-1-3p was expressed at a low level in CRC tissues, and real-time PCR results validated the expression in CRC cells. Overexpressed miR-1-3p could inhibit CRC cell proliferation and invasion. Advanced study exerted that miR-1-3p could directly bind to
YWHAZ, resulting in inhibition of the EMT process [
62]. Research suggested that the expression of miR-9-5p was decreased and the expression of
FOXP2 was increased in CRC tissues and cell lines. Moreover,
FOXP2 had oncogenic roles in CRC and miR-9-5p could inhibit cell metastasis and EMT in CRC by targeting
FOXP2. The low miR-9-5p levels and the high
FOXP2 levels were associated with poor prognosis of CRC patients. Therefore, miR-9-5p/
FOXP2 axis is key to diagnose and treat CRC [
63]. Real-time PCR showed that the expression of miR-205 was negatively correlated with
MDM4 in CRC tissues and cells. Luciferase assay displayed a direct binding between miR-205 and
MDM4. Advanced study demonstrated that overexpressed miR-25 inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCT116 cells. Additionally, the decreased N-cadherin, vimentin, MMP2, and MMP9 with the increase of E-cadherin were observed in miR-205-overexpressed cells [
64]. MiR-145-5p were down-regulated in CRC samples and cell lines. Elevated miR-145-5p expression inhibited cell viability, migration, invasion and EMT of LoVo and SW480 cells, while reducing miR-145-5p displayed the opposite effect.
CDCA3 was confirmed as a direct target of miR-145-5p according to the luciferase reporter assay. In addition, rescuing
CDCA3 in SW480 cells could at least partly reverse the influence induced by miR-145-5p [
65]. It was interesting to find that the expression of miR-330 was negatively correlated with HMGA2. The high expression of
HMGA2 and low expression of miR-330 were detected in CRCs with poor long-term patient survival. Evaluated miR-330 expression in HCT116 and SW480 cells suppressed the oncogenic effect of
HMGA2. Further study exerted that miR-330 could inhibit cell migration and viability, the Akt pathway, as well as the essential regulators in the EMT process through the down-regulation of
HMGA2 [
66]. MiR-370-3p played a key role in repressing CRC proliferation and EMT in vitro. The underlying mechanism proved that miR-370-3p could reduce tumor-related inflammatory factors, such as TNF-
α, IL-1 β, and IL-6, thereby inhibiting proteins such as P53, β-catenin, and ki67, which are closely related to tumor growth [
67]. MiR-873-5p overexpression dramatically inhibited CRC cell proliferation and EMT. Mechanistically, miR-873-5p directly targeted
JMJD8 which was significantly up-regulated in CRC tissues and cell lines to impact the proliferation and EMT process. Finally, the research also found that miR-873-5p could suppress the NF-кB pathway in CRC. Taken together, miR-873-5p could inhibit proliferation and EMT in CRC by targeting
JMJD8 and suppressing the NF-кB signaling pathway, which may provide a new antitumor strategy to carcinogenesis [
68]. MiR-3622a-3p was remarkably down-regulated in CRC according to the TCGA database. Functional assays exerted that miR-3622a-3p could inhibit proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, migration, and invasion of CRC cells. The results from dual luciferase assay, RNA immunoprecipitation assay, and pull-down assay showed that
SALL4 was the direct target of miR-3622a-3p. Further studies showed that miR-3622a-3p inhibited stemness and the EMT process of CRC cells through
SALL4 mRNA decrease. Additionally, miR-3622a-3p also manifested the anti-cancer effect in a tumor xenograft model and an in vivo metastasis model [
69].